Trenches in a Cocoa Plantation for Soil and Water Conservation [乌干达]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Sarah Babirye
- 编辑者: Kamugisha Rick Nelson
- 审查者: Nicole Harari, Luigi Piemontese, Udo Höggel
COCOA
technologies_3309 - 乌干达
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
土地使用者:
Mugume Isaac
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Scaling-up SLM practices by smallholder farmers (IFAD)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
National Agricultural Research Organisation (NARO) - 乌干达1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
14/10/2017
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
注释:
If the technology is well practiced, it promotes soil and water conservation in a cocoa plantation.
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
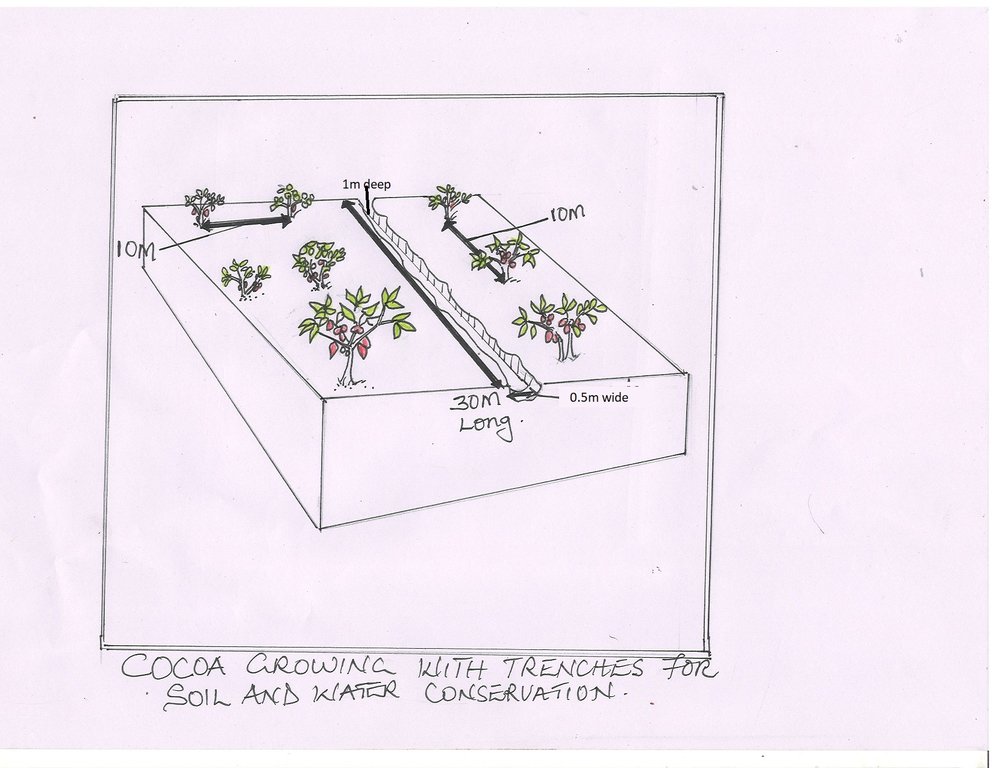
Trenches commonly referred to as contour trenches and running perpendicular to a slope increase water infiltration and reduce soil erosion as a way of conserving soil.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
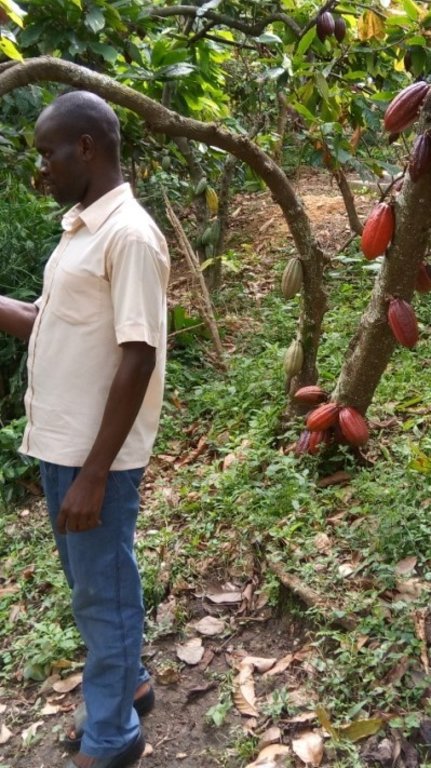
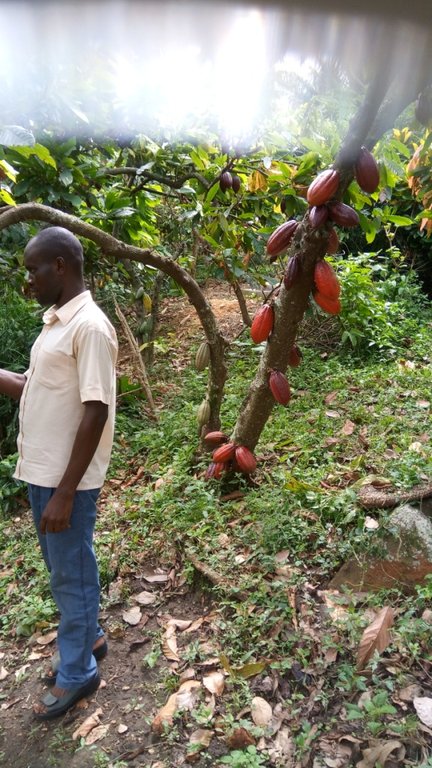
Farmers today face a lot of problems in practicing agriculture and one of them is soil erosion. In hilly areas like Bundibugyo, soil and water runoff is reported to be of paramount importance to farmers growing cocoa on steep slopes. To counteract the problems associated with such cultivation farmers have come up with a strategy of constructing contour trenches. Contour trenches are dug structures, perpendicular to the slopeline, of a certain depth and width in a field of any kind. In this way runoff soil, together with run-off water is caught in such structures and thereby, kept on the field.
In this plantation, the technology reduces water runoff, increases water infiltration and also improves soil fertility. As reported by a cocoa farmer, trenches should be dug in dry season. The numbers of trenches in the plantation depends on the size and the slope of the land. Normally in an acre, 10-15 trenches can be constructed. On establishment of these trenches in hilly area, they are 1m deep, 0.5m wide and 30m long on average along horizontal contour lines. Necessary materials to construct these trenches include a measuring tape, ropes, spades, and hoes.
The soils can be stabilized such that they are not washed into the trenches again. Some grasses are therefore planted on the sides of the trenches. After allocating suitable places for trenches, labour is locally available. However, some farmers who grow cocoa don’t want to dig trenches because it is laborious and requires larger land sizes.
Management is relatively cheaper as it only involves, emptying the trenches periodically.
2.3 技术照片
2.4 技术视频
日期:
17/10/2017
摄影师的名字:
Sarah Babirye
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
乌干达
区域/州/省:
Western Region
有关地点的进一步说明:
Bundibujo District
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 50多年前(传统)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 作为传统系统的一部分(> 50 年)
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 降低灾害风险
- 适应气候变化/极端天气及其影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 多年一作(非木材)
主要农作物(经济作物及粮食作物):
Cocoa
注释:
In hilly areas, trenches are dug to reduce the speed of running water. This is a way of maintaining soil fertility by keeping water and soil in the field.
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
注释:
The area receives much rainfall of over 1500mm-2500mm. Being a hilly area, there is a lot of soil erosion.
每年的生长季节数:
- 2
具体说明:
March and August
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 改良的地面/植被覆盖
- 土壤肥力综合管理
- 集水
3.5 技术传播
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果该技术均匀地分布在一个区域上,请注明覆盖的大致区域。:
- 0.1-1 平方千米
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A1:植被和土壤覆盖层
- A2:有机质/土壤肥力

结构措施
- S2:堤、岸
- S7:集水/供水/灌溉设备
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wg:冲沟侵蚀/沟蚀
- Wo:场外劣化效应

生物性退化
- Bc:植被覆盖的减少
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 减少土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
Trenches are normally established during the dry season on small pieces of land usually an 1 acre.
Slopes range from 16 -30 % in areas with high rainfall. The dimension of the trenches are 1m deep, 0.5m wide and 30m long.
4.3 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术区域
注明尺寸和面积单位:
0.5-1 acre
注明美元与当地货币的汇率(如相关):1美元=:
3600.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
10000/=
4.4 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Identify areas which are prone to soil erosion | 其它措施 | During dry seosons and after strong rains |
| 2. | Get tools and labour | 其它措施 | During dry seseons |
| 3. | Define the size of the trench | 管理 | In dry seseons |
| 4. | Dig standard trenches (30m) long | 结构性的 | In dry seseon |
| 5. | Remove soil that has been washed into the trenches | 管理 | After strong rains |
注释:
Establishment activities are mostly done by family labour or hired labour.
4.5 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Digging trenches | persons | 15.0 | 10000.0 | 150000.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Hiring a hoe | piece | 1.0 | 1000.0 | 1000.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Hiring a slasher | piece | 1.0 | 1000.0 | 1000.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Hiring a spade | piece | 1.0 | 1000.0 | 1000.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Hiring a wheel barrow | piece | 1.0 | 10000.0 | 10000.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 163000.0 | |||||
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
All costs are covered by the land user.
注释:
The initial costs are cost-efficient compared to returns. Planting materials like elephant grass planted on the downslope sides of the trenches can be obtained freely.
Total costs for establishing trenches are slightly expensive. However, maintenance costs are comparatively low.
4.6 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Clearing trenches after long rains | 管理 | Every after heavy rains |
注释:
Most of these management activities are done after strong rains.
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Clearing trenches after rains | Man day | 15.0 | 10000.0 | 150000.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 150000.0 | |||||
注释:
This cost is estimated but could even be less. This makes the technology easily adopted by all cocoa farmers in hilly areas.
4.8 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Labour as some farmers cannot meet all costs.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
1500.00
农业气候带
- 潮湿的
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 高(>3%)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
中等
水质(未处理):
不良饮用水(需要处理)
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
否
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 高
栖息地多样性:
- 高
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 商业/市场
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 贫瘠
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
性别:
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 中年人
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,未命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
用水权:
- 个人
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
注释/具体说明:
Cocoa plantations with trenches increased the quantity in production as moisture is retained.
土地管理
注释/具体说明:
Soil degradation can be significantly reduced.
收入和成本
收入来源的多样性
注释/具体说明:
Besides other activities, farmers earn a lot from cocoa growing
生态影响
水循环/径流
地表径流
注释/具体说明:
Water surface run off is reduced
减少气候和灾害风险
洪水影响
注释/具体说明:
Trenches reduce the run off of water thereby reducing on-site and off-site erosion impact.
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
下游洪水
注释/具体说明:
Water runoff is reduced by trenches.
下游淤积
注释/具体说明:
Water runoff is reduced by trenches.
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 山洪暴发 | 非常好 |
生物灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 流行病 | 适度 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
注释:
Maintenance costs of the trenches are comparatively low.
6.5 技术采用
- 大于 50%
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发地采用该技术,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 90-100%
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
是
若是,说明它适应了哪些变化的条件:
- 气候变化/极端气候
具体说明技术的适应性(设计、材料/品种等):
Making more trenches in the cocoa growing areas.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Improve on production in areas where technology is applied |
| Restore land degraded |
| Improves on soil fertility |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Restores degraded land at a lower costs |
| Improves livelihood among farmers |
| With trenches, the soils are always moist providing suitable conditions for the growth of the crop |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Establishing trenches is expensive | Involve group work |
| Sometimes making trenches is tiresome hence it may be difficult for ladies to do | Involving hired labour |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Requires much labor for making trenches | Involve hired labour |
| Trenches alone cannot solve soil degradation | Apply grasses along the trenches like calliandra and elephant grass among others |
| Trenches are always filled up with soil during water run off hence making it expensive to clear all the time | Always make deeper and wider trenches that can accomodate big volumes of sediments and water |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
4
- 与土地使用者的访谈
1
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Environmental impacts of Cocoa production and processing in Ghana :Life cycle assessment approach by Augustine Ntiamoah,2008
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
http://www.cocoaconnect.org/sites/default/files/publication/Environmental%20impact%20of%20cocoa%20life%20cycle%20assessment.pdf
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块