Mixed Cropping of Coffee, Banana and Onions for Increased Production, Food Security and Household Income [乌干达]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Babirye Irene
- 编辑者: Kamugisha Rick Nelson
- 审查者: Nicole Harari, Udo Höggel
Okulima emwanyi, matooke n'obutugulu
technologies_3378 - 乌干达
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
土地使用者:
Wogudunya Wilson
+256702390798
Duwabana Farmer's Association
Kikameli Village, Kibando town, Bulambuli District
乌干达
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Scaling-up SLM practices by smallholder farmers (IFAD)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
National Agricultural Research Organisation (NARO) - 乌干达1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
19/10/2017
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Mixed Cropping of coffee (Coffea Canephora) , banana (Musa) and onions (Allium cepa) is a sustainable traditional land management practice that involves the growing of two or more crops (coffee, banana and onions) at the same time on the same field by smallholder farmers for increased production, food security and household income.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
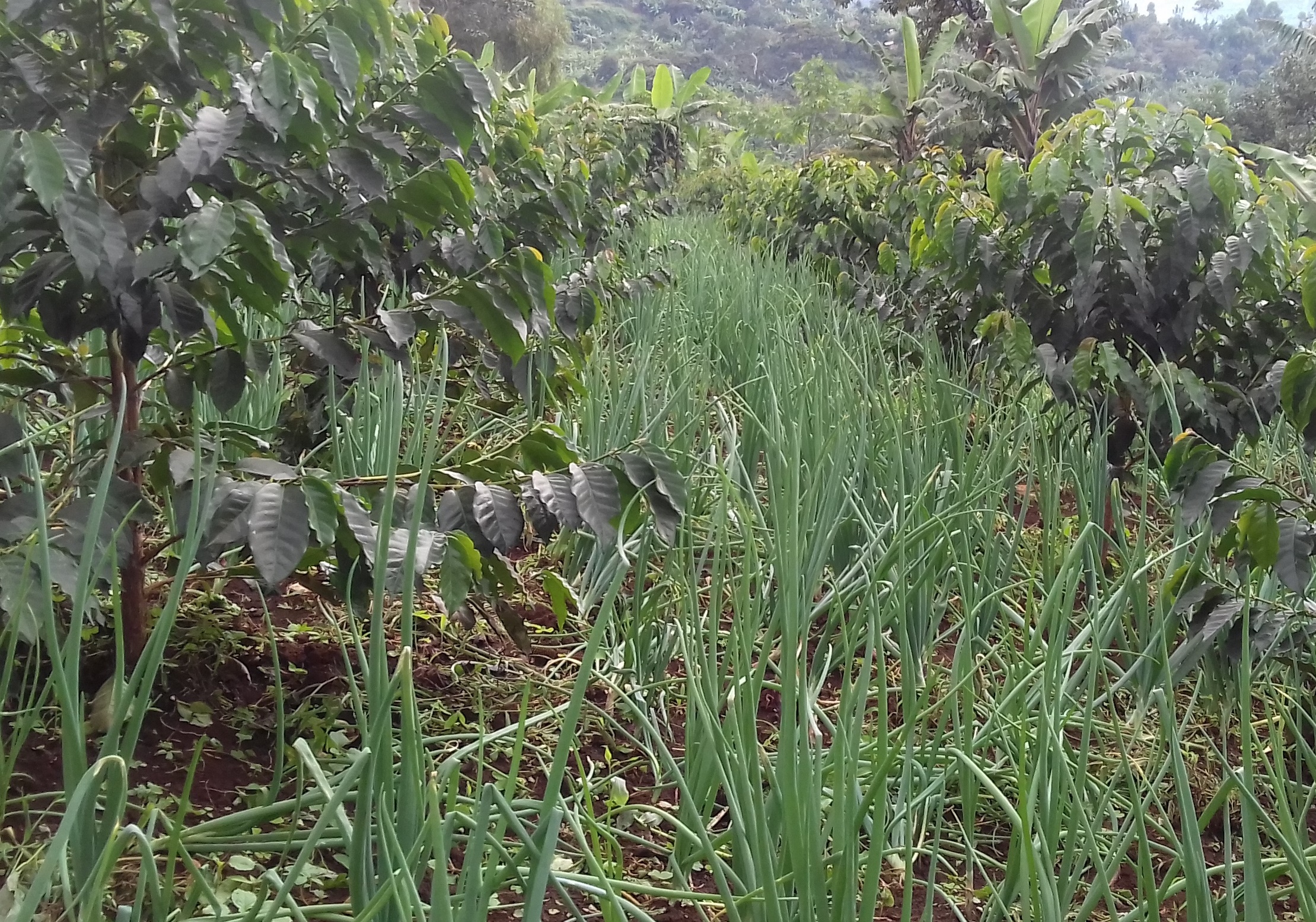
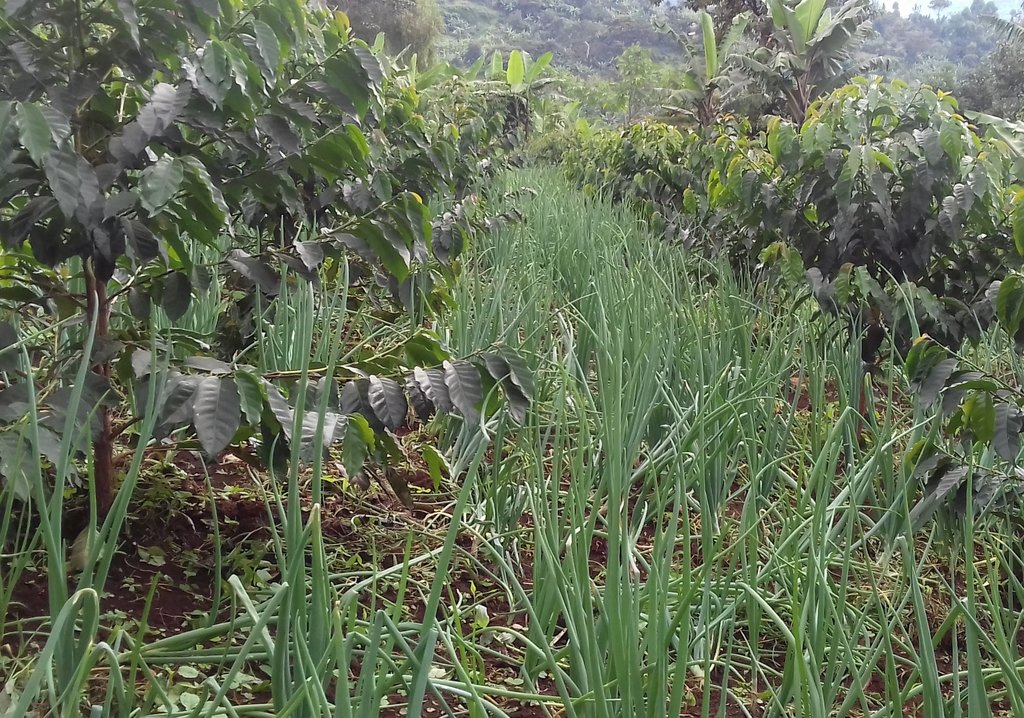
Coffee, banana and onions mixed cropping; is a traditional practice promoted by smallholder farmers in Uganda established in Bulambuli district, Kibande Sub-county, Kimameli village. The area experiences two growing seasons per year; April up to July and September up to December with rainfall ranging from 1, 0001 mm-1,500 mm on 3.4 ha of land located on a gentle sloping area. The aim of this technology is increasing food production, household income , soil fertility improvement , maximizing crop production in a context of population pressure and declining arable land size.
Banana (Musa) and coffee (Coffea Canephora) plantations were established in 2016 followed by onions (Allium cepa) later in August 2017 with Coffee (Coffea robusta) planted at a spacing of 10 feet apart from Coffee to avoid competition for soil nutrients. Using hoes, pangas, coffee and onion seedlings, banana suckers were inter cropped at the ratio of 1 banana to 4 coffee trees on a 3.4 ha. Coffee trees were pruned initially to create room for the banana plants during their establishment. When coffee and banana were planted simultaneously in the field, onions were grown in between them for one year to provide some income before the banana and coffee were ready for harvesting. To establish such a technology the farmer accomplished the following activities: 1.preparing the garden (labor time: four days with three people), 2.Manure application where compost manure was mixed with soil (labor time: one day by three people), 3. Planting (three days by three people for all the crops), 4.Pruning where relevant adjustments were done regularly to the system (e.g. mature coffee trees are pruned to create space for onions to grow is done every three days by one person), and 5. Weeding since inter cropping requires weeding which should be done manually and not with a hoe because it may accidentally damage the roots of the coffee plant.
What is liked about this technology is that its very good according to the farmer’s experience. It is applied on a small piece of land and it incorporates many crops which helps to improve soil fertility, increase crop yield which generates more income and food for consumption. There is also good utilization of labor as a farmer will work on all the crops simultaneously. The farmer testified that bananas provide shade, mulch, nutrients and moisture to young coffee trees. These beneficial effects may particularly be relevant to increase the resilience of the coffee production systems when temperature increases and rainfall becomes more erratic due to climate change. On the other hand coffee being a perennial crop, it requires high levels of initial investment (i.e. labor and capital) with a 10 - 15 years time horizon. The extended time period before realization of economic benefits usually discourages land users from adopting coffee inter cropping with other crops. Also, coffee creates shade which does not favor the growth of maize, beans and tomatoes in the same land, hence there’s competition between the crops for nutrients.
2.3 技术照片
2.4 技术视频
注释、简短说明:
The video showing coffee and banana inter-cropped with onions
日期:
18/10/2017
位置:
Kikameli village, Bulambuli District.
摄影师的名字:
Irene Babirye
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
乌干达
区域/州/省:
Eastern Region
有关地点的进一步说明:
Kikameli village, Kibande sub-county, Bulambuli District
Map
×2.6 实施日期
注明实施年份:
2017
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过土地使用者的创新
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
Land user knew about the technology but he was motivated through projects
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 保护生态系统
- 适应气候变化/极端天气及其影响
- 创造有益的经济影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
- 多年一作(非木材)
主要农作物(经济作物及粮食作物):
Coffee, Banana and Onions
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
每年的生长季节数:
- 2
具体说明:
March to May and September to December
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 土壤肥力综合管理
- 病虫害综合管理(包括有机农业)
- 家庭花园
3.5 技术传播
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果该技术均匀地分布在一个区域上,请注明覆盖的大致区域。:
- < 0.1 平方千米(10 公顷)
注释:
The technology is practiced on 3.5 hectares.
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A1:植被和土壤覆盖层
- A2:有机质/土壤肥力

管理措施
- M4:活动时间安排的重大变化
- M6:废物管理(回收、再利用或减少)
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀

土壤风蚀
- Et:表土流失

生物性退化
- Bq:数量/生物量减少
- Bp:害虫/疾病增加,捕食者减少
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 减少土地退化
注释:
The technology prevents and reduces land degradation through reduced soil erosion and soil exposure and increase soil cover.
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
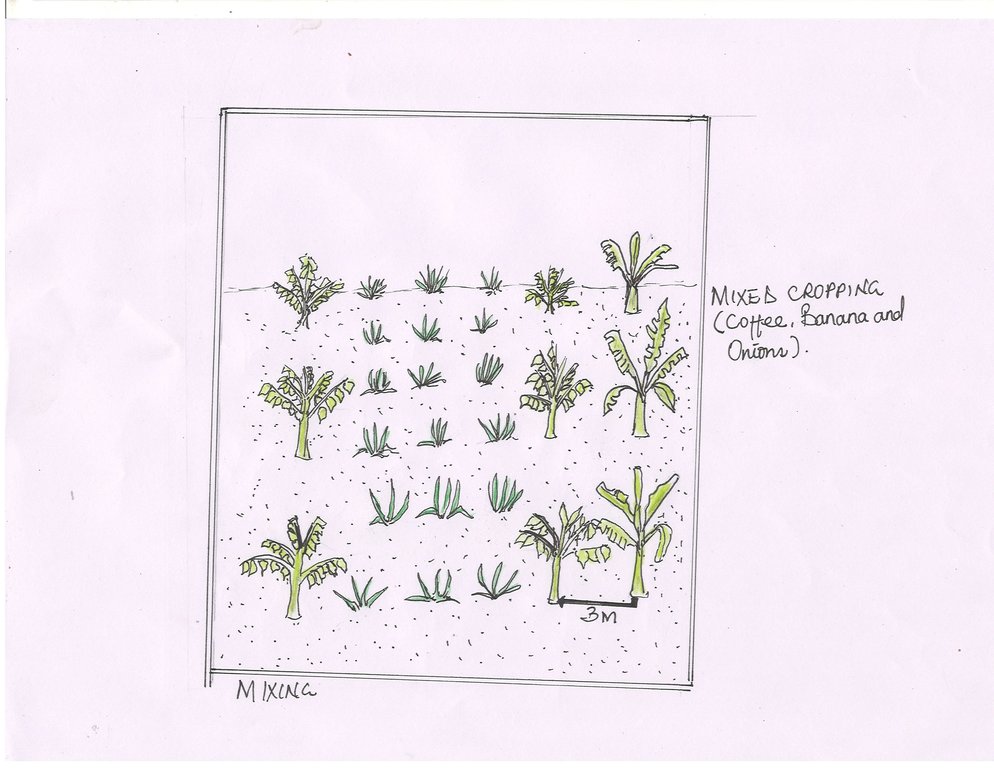
Banana and coffee plantations were established in 2016 and onions added later in August 2017. This practice is carried out on 3.4 ha.
Coffee is the major crop planted with spacing of 3m x 3m, then banana was intercropped at the ratio of 1 banana to 4 coffee trees.
The coffee trees were pruned initially to create room for the banana plants during their establishment. When coffee and banana were planted simultaneously in the field, onions were grown in between them for one year to provide some income before the banana and coffee were ready for harvesting.
The activities and labor demands include:
Digging holes and preparing the garden (labour time: 4 days by 3 people).
Manure application where compost manure was mixed with soil (labour time: 1 day by 3 people).
Planting (3 days by 3 people for all the crops).
Pruning where relevant adjustments are done regularly to the system (e.g. mature coffee trees are pruned to create space for onions to grow is done every three days by one person).
Labor costs are 5000 Uganda shillings per person a day.
Coffee takes three years for the first harvest to happen, onions take four months to grow - here harvesting is continuous.
4.3 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术区域
注明尺寸和面积单位:
3.4 hectares
具体说明成本计算所用货币:
- 美元
注明美元与当地货币的汇率(如相关):1美元=:
3600.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
1.39
4.4 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Digging/ Garden preparation | 农业学的 | 1 week before the rains |
| 2. | Fertilizer Application | 农业学的 | 2 days |
| 3. | Planting | 农业学的 | Before onset of rains |
| 4. | Spraying | 农业学的 | Every after two weeks |
| 5. | Prunning | 农业学的 | monthly |
| 6. | Harvesting | 农业学的 | Seasonal |
注释:
Harvesting onions is done every after three months.
4.5 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Digging/Garden preparations | man days | 4.0 | 1.39 | 5.56 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Planting | man days | 4.0 | 1.39 | 5.56 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Spraying | man days | 1.0 | 1.39 | 1.39 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Pruning | man days | 1.0 | 1.39 | 1.39 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Hoes | Piece | 4.0 | 2.78 | 11.12 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Pangas | Piece | 2.0 | 2.78 | 5.56 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Wheelbarrow | Piece | 1.0 | 33.4 | 33.4 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Sprayer pump | Piece | 1.0 | 13.9 | 13.9 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Onions Seeds | kilograms | 2.0 | 1.94 | 3.88 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Coffee seedlings | pieces | 2000.0 | 0.83 | 1660.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Banana suckers | pieces | 2000.0 | 0.83 | 1660.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Animal Manure | Trip | 1.0 | 22.3 | 22.3 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | NPK Mineral fertiliser | Kilograms | 5.0 | 0.84 | 4.2 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Herbicides | litres | 2.0 | 3.34 | 6.68 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Pesticides | litres | 2.0 | 4.17 | 8.34 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 3443.28 | |||||
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
The land user incurred all the costs
注释:
The farmer got a loan from the village saving loan group to establish the technology
4.6 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Weeding | 管理 | weekly |
| 2. | Spraying | 管理 | weekly |
| 3. | Pruning | 管理 | monthly |
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Weeding | Man Days | 2.0 | 2.8 | 5.6 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Spraying | Man Days | 1.0 | 2.8 | 2.8 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Spray Pump | piece | 1.0 | 1.39 | 1.39 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Hoes | pieces | 2.0 | 2.78 | 5.56 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | NPK Fertiliser | Kilograms | 8.0 | 1.39 | 11.12 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Dudu cyper (pesticide) | litres | 2.0 | 1.39 | 2.78 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Dythene (herbicide) | kilograms | 2.0 | 6.95 | 13.9 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 43.15 | |||||
注释:
The land user incurs all the costs.
4.8 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Fertilizers are very expensive to be applied monthly
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
1600.00
有关降雨的规范/注释:
The zone receives a bi-model pattern of rainfall
注明所考虑的参考气象站名称:
Buginyanya zonal Agricultural Research and Development Institute
农业气候带
- 潮湿的
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 不相关
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
表面上
地表水的可用性:
中等
水质(未处理):
良好饮用水
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
否
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 低
栖息地多样性:
- 低
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
性别:
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 老年人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
The farmer's main source of income is agriculture.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 中等规模的
注释:
The farmer owns 2 hectares which is considered medium compared to other land owners who own more than 5 hectares.
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
用水权:
- 自由进入(无组织)
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
作物质量
SLM之前的数量:
1
SLM之后的数量:
3
木材生产
注释/具体说明:
The pruned trees or brunches are used as wood for firewood at home.
生产故障风险
注释/具体说明:
There is no total crop failure as the farmer gains at least from one crop.
土地管理
注释/具体说明:
The land user grows many crops on the same land hence the available space is utilized.
水资源可用性和质量
饮用水的可用性
SLM之前的数量:
2
SLM之后的数量:
2
注释/具体说明:
There is a nearby water source
收入和成本
农业投入费用
SLM之前的数量:
3
SLM之后的数量:
2
收入来源的多样性
SLM之前的数量:
1
SLM之后的数量:
3
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
注释/具体说明:
There is increased food production as the farmer grows more than one crop
SLM/土地退化知识
注释/具体说明:
The land user improved land management skills.
生态影响
水循环/径流
蒸发
注释/具体说明:
Through inter-cropping less soil is exposed to the sun hence reduced soil moisture loss.
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
对邻近农田的破坏
注释/具体说明:
The land user has trenches which prevent water and soil damage on the neighbor's fields
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 气候变化/极端天气的类型 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年降雨量 | 减少 | 适度 | |
| 季雨量 | 湿季/雨季 | 减少 | 适度 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 适度 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
非常积极
6.5 技术采用
- 1-10%
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
Three farmers in the area.
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发地采用该技术,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 90-100%
注释:
All the farmers who adopted the technology used their personal investments.
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
是
若是,说明它适应了哪些变化的条件:
- 不断变化的市场
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| The technology suppresses weed growth |
| The technology reduces soil erosion. |
| Yield and income advantage as the farmer gains from more than one crop from the same plot. Income recived is invested in buying tree seedlings |
| Reduced crop failure as there is no total crop failure |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| The technology helps the farmer to grow many crops on a small piece of land. |
| Technology can be promoted by other farmers with same pieces of land or more. |
| It increases crop yield which generates more income and food for consumption. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| The technology has too much shade, so other crops cannot grow for example maize and beans. | The farmer should continue to grow onions instead of maize and beans |
| The technology is expensive to establish because high investments need to be made. | The land user should find financial assistance like savings co-operatives. |
| The technology is a long term investment since it involves coffee and banana. | The farmer should buy or rent some other land to be in position to grow other crops. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Competition between the crops for nutrients and sunlight. | Proper selection of crops to inter-crop for example inter-crop deep rooted with shallow rooted crops. |
| The soil is highly depleted of its nutrients as more than one crop is planted. | Inter cropping with some nutrient fixing crops and addition of manure. |
| There is also more work required at the start of the cultivation and harvesting. | Proper selection of crops to inter-crop and the right spacing. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
2
- 与土地使用者的访谈
1
7.3 链接到网络上可用的相关信息
标题/说明:
Annual Weather in Bulambuli District
URL:
https://weatherspark.com/y/98128/Average-Weather-in-Bulambuli-Uganda-Year-Round
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块