Thermo insulation of walls with use of foil to decrease burden on firewood use [塔吉克斯坦]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Askarsho Zevarshoev
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Yacime Khadraoui, Maximilian Knoll, Alexandra Gavilano
Гарминигохдории хонахо ба максади кам гардинаи истифодабарии хезум барои гарм кардани хона
technologies_3465 - 塔吉克斯坦
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
1.5 参考关于SLM方法(使用WOCAT记录的SLM方法)的调查问卷

Access to thermal insulation through micro loans [塔吉克斯坦]
Provision of small scale loans for private households to ensure access to thermal insulation (in the frame of CACILM).
- 编制者: Roziya Kirgizbekova
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
This technology is designed for the high altitude mountains areas, where biomass and growing trees are limited, first because of the harsh climatic conditions and secondly because of the limited arable lands for growing biomass and forests. Thermo insulation is applied in order to keep warmth inside and save using wood and biomass.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
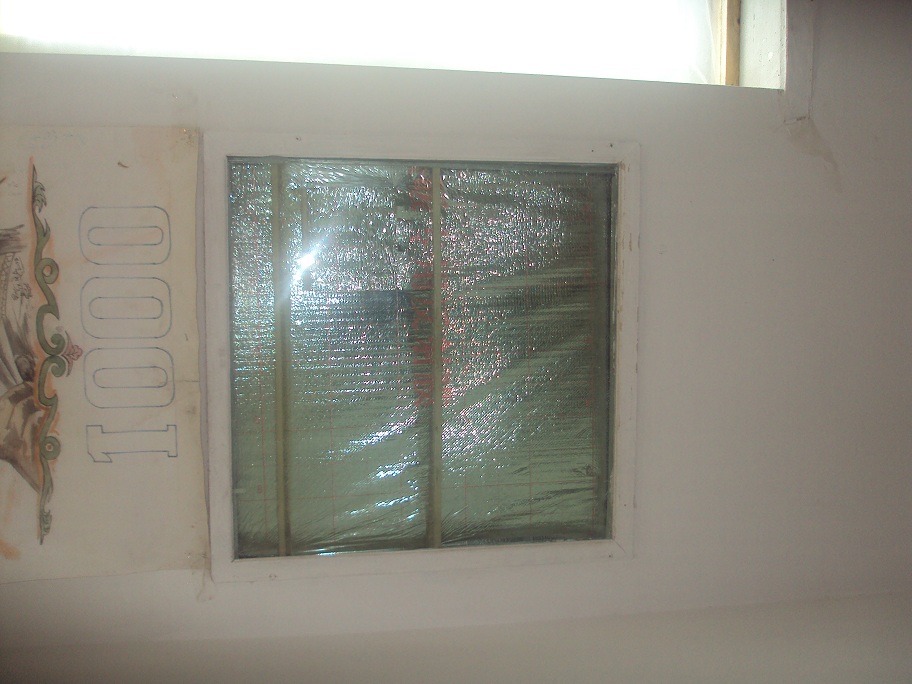
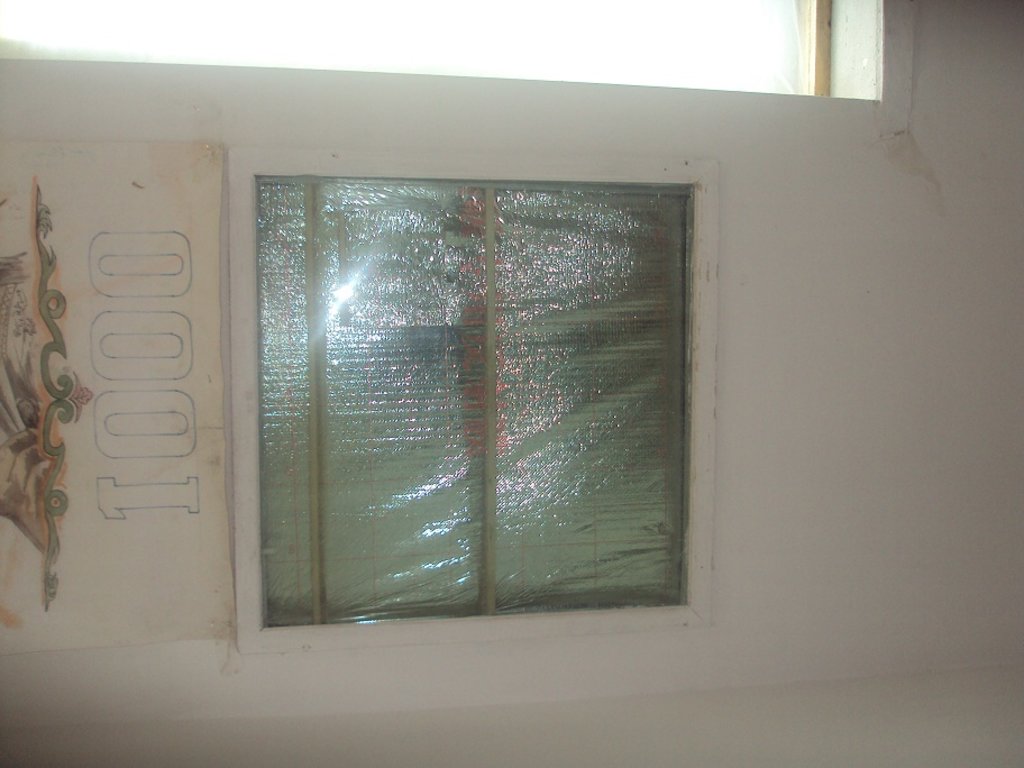
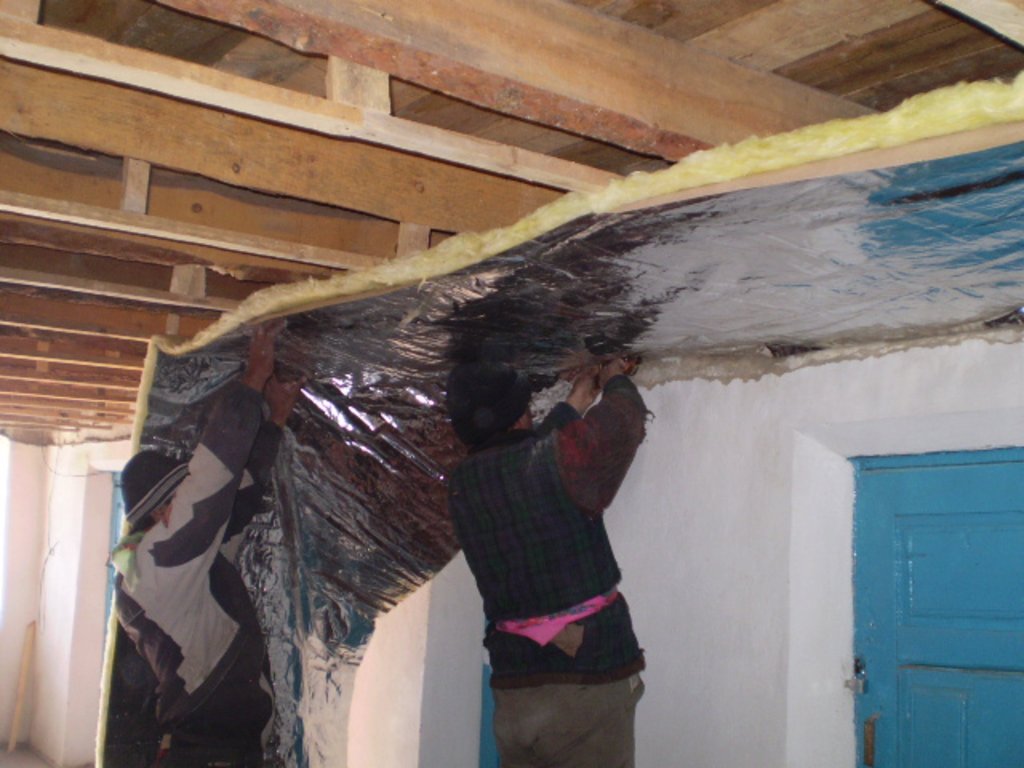
The technology is applied in the mountainous rural areas of Tajikistan, in Rasht, Khatlon and GBAO. In this mountain regions wood and biomass are usually limited because of the harsh climate, risky agricultural zone and limited arable land. In the first decade of the transition period after the collapse of the Soviet Union problems with electricity and therfore the demand for fuel and wood increased. This caused a lot of forest degradation, because people were cutting trees from government owned and community areas for their fuel needs and used animal manure for heating their houses and cooking food. The technology is specifically designed to use low cost materials so that rural households can afford it. The technology consists of material like foil and wood to build frames for some layers to keep in the heat. Depending on the altitude, which is linked to the climate condition, the number of layers is increased where the climate is cold. The layer in between contains air, which prevents outside and inside air to move out/in. The technology was intended for saving up to 30% fuel. The technology includes support of entrepreneurs to make foil available in the market and provides training for local masters and labourers in designing and constructing of the technology. The main benefit is to contribute to biomass savings and forest preservation through reduced use of wood for heating and cooking. Land users are in favour because through this technology they are using less wood and save forest. They also burn less manure and can use it as fertilizers for their land. The technology brings comfort for longer periods of time by keeping heat inside the room. In addition it contribute also to hygine and sanitation, as less fire making prevents smoke emission and therefore keeps the rooms clean. On first sight the technology seems expensive, becasue of the material costs but in the long run when the cost effectiveness is explained land users accepted it.
2.3 技术照片
关于照片的一般说明:
This technology is applied both on wall, floor and ceiling, where all parts is given more effect, then doing only on part of it.
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
塔吉克斯坦
区域/州/省:
GBAO
有关地点的进一步说明:
Khorog city
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 适用于特定场所/集中在较小区域
注释:
The technology is applied in buildings but have direct effect on preserving woodlands and crop lands.
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 在实验/研究期间
- 通过项目/外部干预
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 保护生态系统
- 保持/提高生物多样性
- 降低灾害风险
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

森林/林地
- (半天然)天然森林/林地
- 植树造林
(半天然)天然森林/林地:具体说明管理类型:
- 选伐
植树造林:说明树种的起源和组成:
- 混交品种
产品和服务:
- 薪材

定居点、基础设施
- 定居点、建筑物
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
注释:
As a result of applying the technology in big numbers it is contributing to forest preservation and improving crop land conditions.
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 混合雨水灌溉
注释:
both forest, which are mainly growing along the river flowing from the mountians and the open space irrigation is used in this case. In addition an agroforestry system is traditionally common in the technology area, where both tree are grown and the land is cultivated.
Number of growing seasons per year:
1
Specify:
there is only one season for growing, as the winter is very long and the vegetative period is only 5-6 months. traditonally an agro-foresty system is practiced in this area, where both tree are grown and crop land is cultivated.
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 天然和半天然森林管理
- 森林种植管理
- 农业林学
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

结构措施
- S10:节能措施

管理措施
- M1:改变土地使用类型
- M2:改变管理/强度级别
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤风蚀
- Et:表土流失

物理性土壤退化
- Pc:压实
注释:
when the technology is widely applied, this will prevents tree cutting and forest rehabilitation, which also prevent soil from overgrazing and compaction.
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
注释:
once the technology is widely introduced it will prevents tree cutting, which also prevents soil degradation.
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
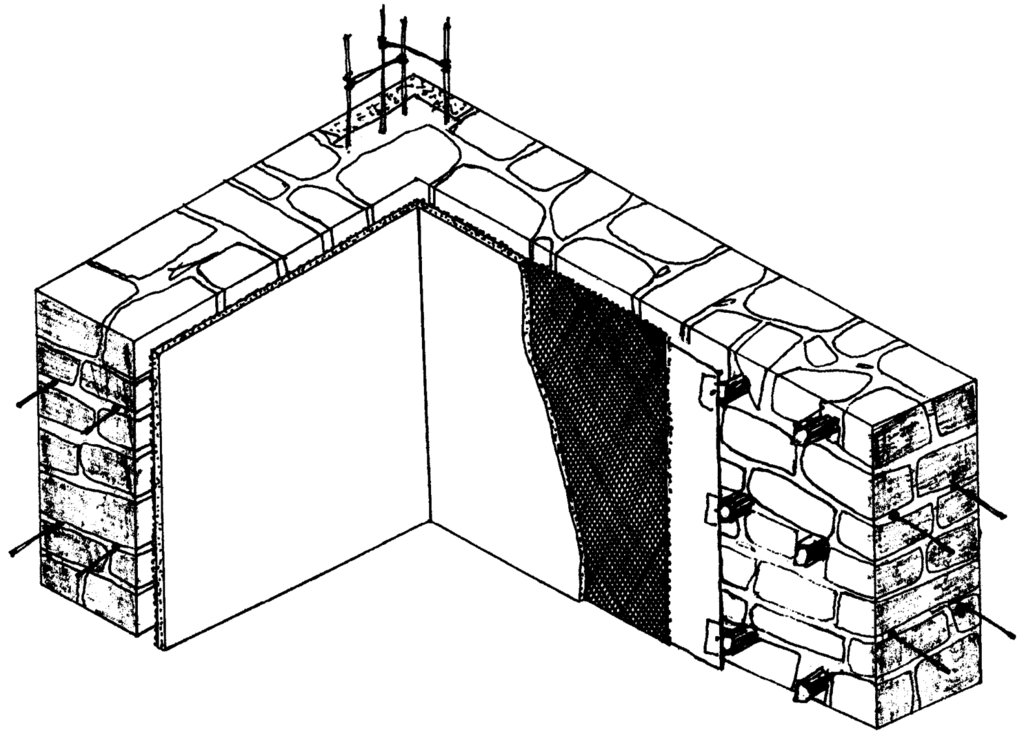
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
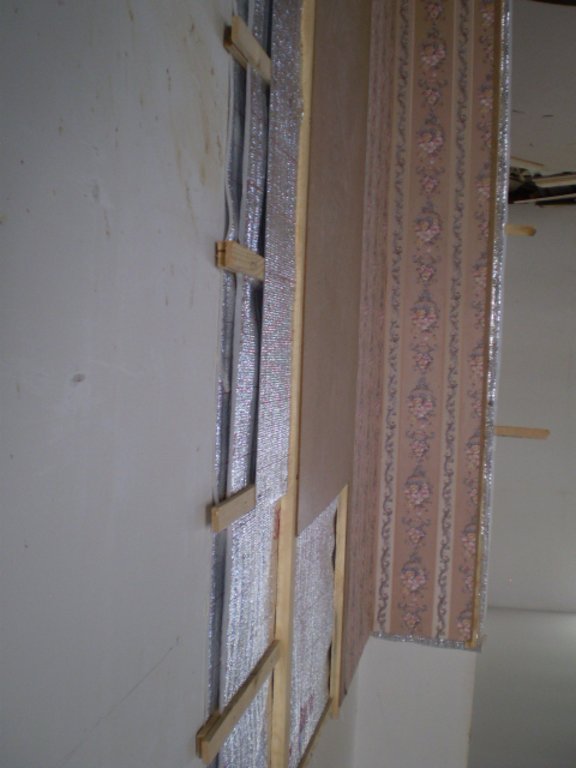
A wooden frames is installed on the wall to cover the whole area. Foil will be stretched and will be fixed on the wooden frame on the wall. Based on the need number of layers is selected, which depend on the min/max outside temperature. If required according to the climate and wether of the area and based on altitude another frame from wood will be constructed on the foil and then again another layer of foil will be fixed. The scheme show the frame on the wall with thermo-insulation materials attached to it. The distance between two part of the foil should be an average 2-3sm.
作者:
Khujamyor Khumorikov
日期:
23/03/2011
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术区域
注明尺寸和面积单位:
1 square meter cost 75
具体说明成本计算所用货币:
- 美元
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
per sequare meter around 2.5 USD
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Installing of the wood frame | 1 day |
| 2. | attaching/fixing the foil with nail on the wooden frame (add frame and foil layer per need) | 1 day |
| 3. | Cover the structure with clay (mixture of soil and water) as construction material | 2-4 days |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Local master | person | 1.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 30.0 |
| 施工材料 | wood | pe sq meter | 0.5 | 100.0 | 50.0 | |
| 施工材料 | nail | piece | 20.0 | 0.1 | 2.0 | |
| 施工材料 | foil | squire meter | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 55.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 55.0 | |||||
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
for the demonstration sites 100% of the cost is covered by the project implemented by MSDSP
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
the cost for the constuction materials in the beginning, because as new technology was introduced foil, as the main product for the technology was difficult to find in the market, which is now commonly sold
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
有关降雨的规范/注释:
The technology is applied in high mountain regions of Tajikistan, which are arid and semi-arid zones where some area have less than 100 mm rainfall and in some could be 200-300
注明所考虑的参考气象站名称:
Regional meteorological station GBAO
农业气候带
- 半干旱
- 干旱
the whole area of Tajikistan, where the technology is applied is classified as arid or semi-arid agro-climatic zone
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 不相关
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
表土有机质:
- 高(>3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
the area is mountain specified as risky agro-climatic zone for agriculture.
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
过量
水质(未处理):
良好饮用水
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
是
规律性:
偶然
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
very rare case, but becoming more frequently in the last years, when there is heavy rainy season are becoming more common.
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 高
栖息地多样性:
- 中等
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 半游牧的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 生计(自给)
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 贫瘠
个人或集体:
- 团体/社区
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 中年人
- 老年人
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 州
土地使用权:
- 个人
用水权:
- 自由进入(无组织)
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
收入和成本
收入来源的多样性
注释/具体说明:
After applying the technology it contributed to 30% of firewood saving, which cost money for the households and community before.
工作量
注释/具体说明:
less workload applied, one the house is kept for longer time heated and additional effort is not required to make fire
生态影响
土壤
土壤覆盖层
注释/具体说明:
in case the technology is used widely, which prevents extensive forest use to provide soil cover with vegetation
生物多样性:植被、动物
栖息地多样性
注释/具体说明:
contributes to saving local trees, which are very few growing in the arid areas
减少气候和灾害风险
滑坡/泥石流
注释/具体说明:
after not cutting the trees and reforestation of degraded area, especially in the slope area contributed to land slide prevention
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
对公共/私人基础设施的破坏
注释/具体说明:
one contributing to disaster prevention, like landslide and mudflow also prevents damage to houses and public infrastructure
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 季节性温度 | 冬季 | 减少 | 适度 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
轻度消极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
稍微积极
长期回报:
中性/平衡
6.5 技术采用
- 11-50%
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 11-50%
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
否
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| One time investment contributes to long term effects in saving forest and biodiversity, provides comfort without additional cost using for collection/buying firewood. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| The technology contributes to habitat improvement at all, besides conservation of natural resources it also has social effects in terms of reduced smoke emissions as a result of less firewood making, comfortable condition during harsh winter weather. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| In the short term a big investment is required. | Funding mechanisms should be improved to provide access for farmers/rural population to invest in such technology. Some of the incentive mechanisms should be worked out for replicating the mechanism. |
| Specialized master skills are required to implement the technology. | More capacity building for existing local farmers should be organized at the local level for long term sustainability. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| By implementing one or two demonstrations at the household level the effect for the purpose of replication and dissemination is very low. | Demonstrations should be applied in public places like school or hospitals so everybody can have access and see the impact. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 与SLM专业人员/专家的访谈
2
- 根据报告和其他现有文档进行编译
1
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
31/08/2015
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Wall Insulation Techniques for Buildings in High Mountain Areas
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
from SLM specialist, free of cost
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Access to thermal insulation through micro loans [塔吉克斯坦]
Provision of small scale loans for private households to ensure access to thermal insulation (in the frame of CACILM).
- 编制者: Roziya Kirgizbekova
模块
无模块