Planting Eucalyptus on rice bunds to lower saline groundwater [泰国]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Areerat Wangkaew
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Samran Sombatpanit, Pitayakon Limtong, William Critchley
Planting perennial salt-tolerant trees in salt-affected areas of the Northeast of Thailand.
technologies_4099 - 泰国
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
土地使用者:
Chuenchai Sayan
+66-99-0254108
Ban Muang Pia, Muang Pia Sub-district, Ban Phai District, Khon Kaen 40110
泰国
SLM专业人员:
Sritumboon Supranee
ssritumboon@yahoo.com
Land Development Department
2003, 61 Phaholyothin Road, Ladyao, Chatuchak, Bangkok 10900
泰国
SLM专业人员:
Pothinam Pornpana
laosuwan18@hotmail.com
Land Development Department
2003, 61 Phaholyothin Road, Ladyao, Chatuchak, Bangkok 10900
泰国
SLM专业人员:
Rophandung Weera
weerop@hotmail.com
Land Development Department
2003, 61 Phaholyothin Road, Ladyao, Chatuchak, Bangkok 10900
泰国
SLM专业人员:
Srihaban Pranee
pranee.782@gmail.com
Land Development Department
2003, 61 Phaholyothin Road, Ladyao, Chatuchak, Bangkok 10900
泰国
SLM专业人员:
Jakkarach Usa
usa.kl@hotmail.com
Land Development Department
2003, 61 Phaholyothin Road, Ladyao, Chatuchak, Bangkok 10900
泰国
SLM专业人员:
Janplang Chettaruj
joeshua9@hotmail.com
Land Development Department
2003, 61 Phaholyothin Road, Ladyao, Chatuchak, Bangkok 10900
泰国
National consultant:
Arunin Somsri
ssarunin@gmail.com
Land Development Department
2003, 61 Phaholyothin Road, Ladyao, Chatuchak, Bangkok 10900
泰国
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Decision Support for Mainstreaming and Scaling out Sustainable Land Management (GEF-FAO / DS-SLM)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Land Development Department LDD (Land Development Department LDD) - 泰国1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
01/10/2018
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
注释:
The technology is environmentally suited and very well accepted by the land users.
1.5 请参阅有关SLM方法的问卷

Advisory system for planting Eucalyptus camaldulensis on rice … [泰国]
The Thai government promotes planting of Eucalyptus camaldulensis on rice bunds to lower the saline groundwater level and prevent the spread of salt in soils - through cooperation of farmers, land owners, Siam Forestry Co., Ltd., Subdistrict Administration Organization, Land Development Department, and with specialists/ technical advisors.
- 编制者: Areerat Wangkaew
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
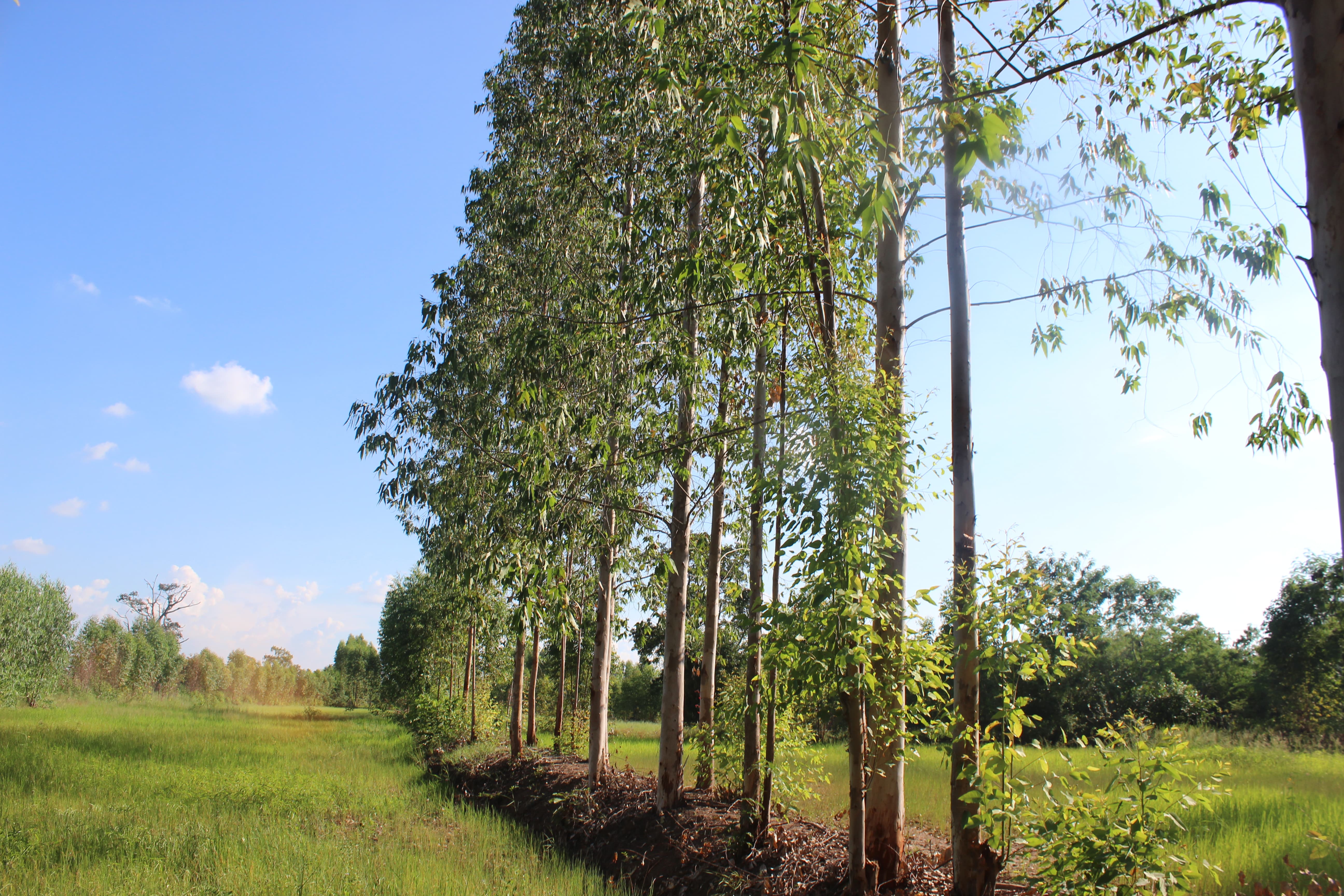
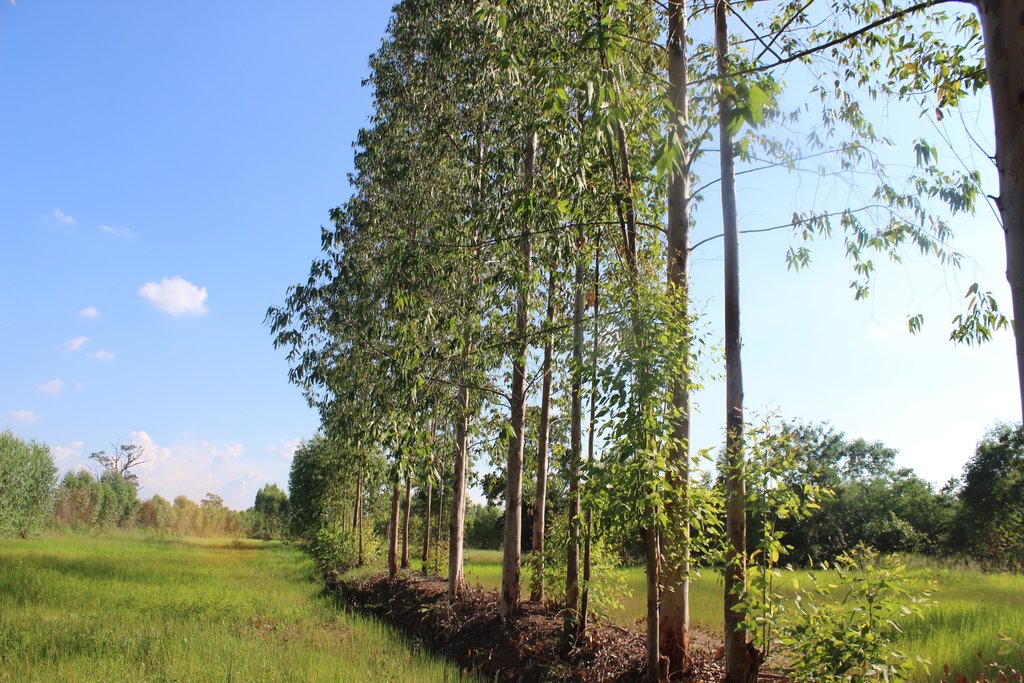
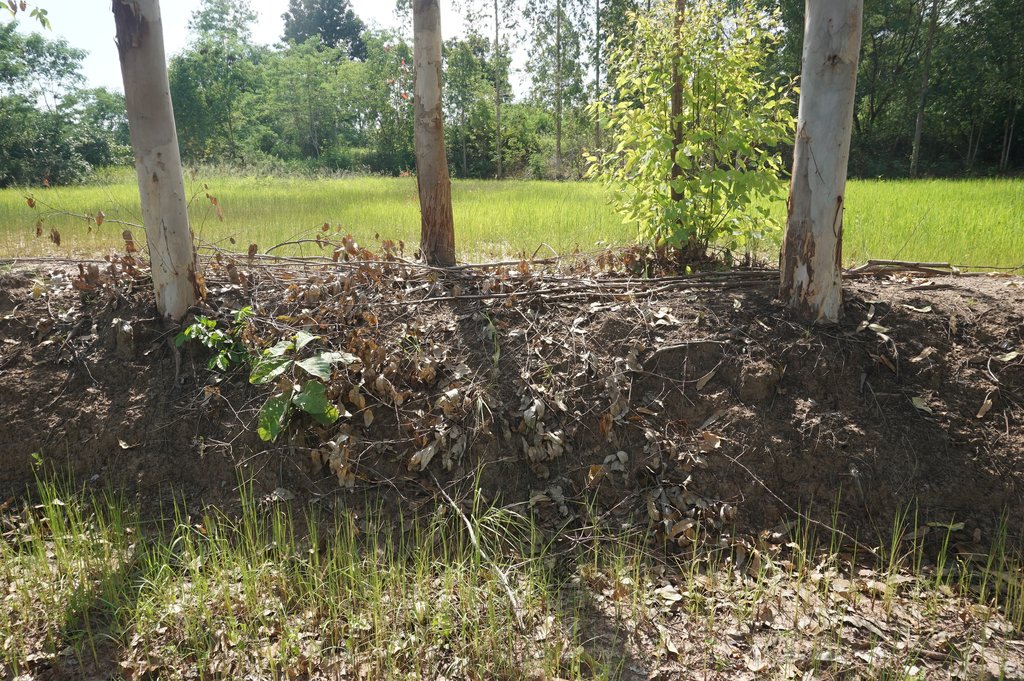
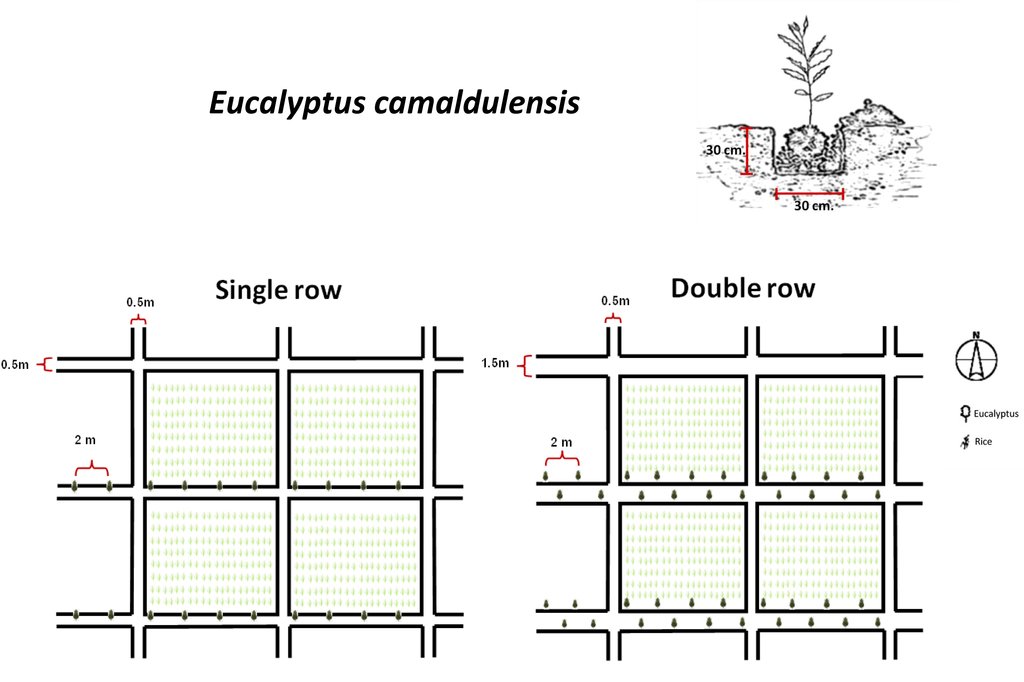
Eucalyptus camaldulensis variety H4 is salt tolerant and has the ability to lower shallow saline groundwater levels; as a result salinity is controlled. Planting eucalyptus on one or two sides of the rice bund in an east-west direction (in single or double rows) at a spacing of 2 m between trees is the most effective technique and well accepted by farmers.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
Eucalyptus camaldulensis cultivation on rice bunds to lower shallow saline groundwater levels in low-lying areas is a technology used on salt-affected land. The LDD Perennial Tree Planting project to promote the technology of planting Eucalyptus camaldulensis on rice bunds has been implemented since 1996. The land user interviewed cultivates a moderately salt-affected rice field at Ban Muang Pia District, Khon Kaen Province. The land is used for rice production both glutinous (variety RD 6) and non-glutinous fragrant rice (Hom Mali 105). The average yield of rice is 200-250 kg/rai (1 ha = 6.25 rai). The farmers have planted eucalyptus on bunds in the rice cultivated areas on about 10,000 rai in more than 10 years with the objectives of remedying and preventing salination by lowering shallow saline groundwater levels, through "bio-drainage" as well as increasing income and better utilization of lands on rice bunds for growing trees.
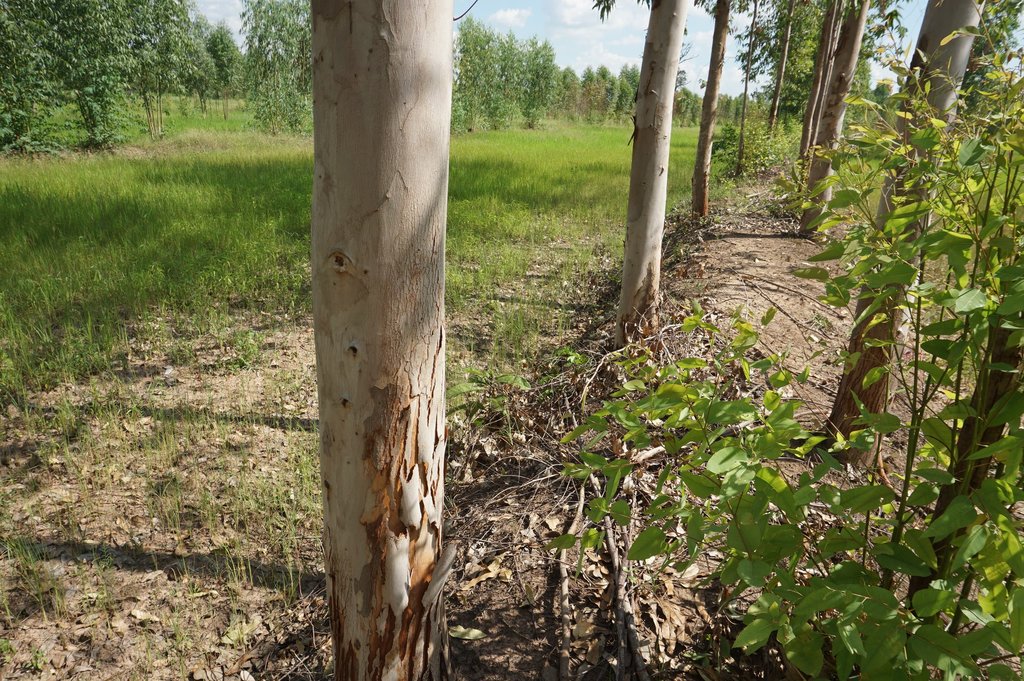
The technology of eucalyptus cultivation on rice bunds has been implemented in farmers' fields in the low-lying salt-affected rice area common in the Northeast of Thailand. It is widely accepted by farmers through the joint partnership between the Land Development Department (LDD), Siam Forestry Co., Ltd. and the local district administration. Eucalyptus seedlings are provided by LDD and are planted in a single or double rows - double rows with trees planted on two sides of the rice bunds in a zigzag manner following an east-west direction to prohibit a shadow effect. The spacing between the trees in a row is 2 m: the rice bund was adapted to be 1.5 m wide and 0.5 m high. This provides more space and convenient access to the rice field. The project provides labour costs for farmers to prepare the land before planting. Many farmers outside the project transplanted their own eucalyptus seedlings on the bunds of 0.5 m or more in width. Farmers buy the seedlings at 1 THB each and plant in pits of 0.3 x 0.3 x 0.3 m with 0.5 kg compost and 0.5 kg rice husks from farm by-products. This technology is well accepted by farmers because of the effective control of salinity in the rice fields as well as the higher income obtained from selling eucalyptus wood. Farmers observed the dead patchy spots of rice plants with salt crusts before planting eucalyptus: after 2 cutting cycles no salt patches were observed anymore, and rice yields increased noticeably. There was also extra income from selling poles of eucalyptus every 4 years. The average yield of eucalyptus trees of 2.5-3.0 inches in diameter was 16 tons per rai for the first cutting.
Based on 7 years (2 crops of eucalyptus coppicing), the average additional income was 1,087 THB/rai/yr (according to the farmers' and Siam Forest's information). The main investment was in the first year of planting; later on, the maintenance cost was on labour for weeding, pruning and thinning to 3 stems after coppice/cutting, including adding 15-15-15 fertilizer for each tree. The average income is increased through better rice yields. The benefits of the technology according to interviews are creating a cooler microclimate from eucalyptus trees and changes in biodiversity through better soil quality resulting in more species of flora and fauna such as grasses, wildflowers, dragonflies, earthworms in the rice field and on the bund. Some farmers wanted more trees by planting at closer spacing of 1 m, but this resulted in too great a density of trees thus consuming more surface water and competing with rice for water consumptive use.
2.3 技术照片
2.4 技术视频
注释、简短说明:
The video shows the area of eucalyptus growing on the rice bund.
日期:
01/10/2018
位置:
Ban Muang Pia, Khon Kaen
摄影师的名字:
Supranee Sritumboon
注释、简短说明:
Farmer interview and SLM discussion.
日期:
01/10/2018
位置:
Ban Muang Pia, Khon Kaen
摄影师的名字:
Supranee Sritumboon
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
泰国
区域/州/省:
Khon Kaen
有关地点的进一步说明:
Ban Phai
注释:
The SLM Technology site for planting eucalyptus in a rice production area.
Map
×2.6 实施日期
注明实施年份:
1996
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
- by other land users
注释(项目类型等):
The project initiated by the government (Land Development Department) collaborated with private enterprises (Siam Forestry Co., Ltd.), local administration, communities and land users.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 保持/提高生物多样性
- 创造有益的经济影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
- 多年一作(非木材)
主要农作物(经济作物及粮食作物):
Rice
注释:
Planting eucalyptus for additional income and more intensive utilization of land on the rice bunds.
如果由于技术的实施而导致土地用途发生变化,则在技术实施前说明土地利的用途。:
Before planting eucalyptus, rice was the only crop. Due to the shallow saline groundwater of the area, rice had shown symptoms of being salt-affected; however after planting eucalyptus trees, these symptoms disappeared.
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
注释:
Average annual rainfall is 1,200-1,300 mm.
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Land use is for rice production; the technology is planting Eucalyptus camaldulensis on rice bunds.
牲畜密度(如相关):
Only few cattle, swine, and boar are in the land user's farm.
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 农业林学
- 地下水管理
- desalination
3.5 技术传播
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果该技术均匀地分布在一个区域上,请注明覆盖的大致区域。:
- 1-10 平方千米
注释:
The technology has spread over the area of 10,000 rai (1 ha = 6.25 rai) owned by farmers/land users both under and outside the supported project of planting eucalyptus on rice bunds.
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A2:有机质/土壤肥力
- A5:种子管理,改良品种

其它措施
注释:
Eucalyptus camaldulensis H4 is the salt-tolerant variety used for lowering shallow saline groundwater.
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)
- Cs:盐化/碱化

物理性土壤退化
- Pc:压实
- Pk:熟化和结壳

生物性退化
- Bc:植被覆盖的减少
- Bq:数量/生物量减少
- Bs:质量和物种组成/多样性的下降
- Bl:土壤寿命损失

水质恶化
- Hg:地下水/含水层水位的变化
- Hq:地下水水质下降
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
注释:
Decreased saline groundwater levels to control salinity distribution in rice cultivated areas.
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
1. Seedling of Eucalyptus camaldulensis H4, a salt-tolerant variety, were planted. The age of seedlings was 3-month old. The rice bund was regulated to 0.5 m wide for planting eucalyptus in single row or 1.5 m wide for planting in double rows (in a zigzag manner), 0.5 m high with a spacing of 2 m between the trees along an east-west direction. The number of trees was 80/rai or 500/ha for double rows planting.
2. Planting technique: 0.5 kg of compost mixed with 0.5 kg of rice husks was applied at the bottom of a pit of 0.3 x 0.3 x 0.3 m before seedlings were planted.
4.3 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术区域
注明尺寸和面积单位:
own by one selected land user
如果使用本地面积单位,请注明换算系数为1公顷:
1 hectare = 6.25 rai
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
THB
注明美元与当地货币的汇率(如相关):1美元=:
32.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
300 THB
4.4 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Site selection of salt-affected area | 结构性的 | May-July |
| 2. | Land preparation; bunds construction and seedling preparation | 结构性的 | May-July |
| 3. | Public hearing, joint meeting between farmers and researchers | 其它措施 | May-July |
| 4. | Demonstration plot | 农业学的 | May-July |
| 5. | Model establishment (Eucalyptus planting method) | 农业学的 | May-July |
| 6. | Joint monitoring, evaluation and follow up for planting | 其它措施 | After planting |
注释:
No irrigation water therefore the planting time depends on the period of early rainy season which will be from May to July.
4.5 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour cost for planting eucalyptus (labour wage per day = 300 THB, 1 rai required a labour cost of 600 THB) | Rai | 1.0 | 600.0 | 600.0 | |
| 植物材料 | Eucalyptus seedling cost (80 trees/rai), 1 THB for each seedling | Seedling | 80.0 | 1.0 | 80.0 | |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Compost cost 3.5 THB/kg, 0.5 kg/pit | kg | 40.0 | 3.5 | 140.0 | |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Rice husk cost 4 THB/kg, 0.5 kg/pit | kg | 40.0 | 4.0 | 160.0 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 980.0 | |||||
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
Land Development Department
注释:
Labour cost for land preparation and planting borne by LDD and seedlings borne by Siam Forestry Co., Ltd.; compost and rice husk were from farm by-products.
4.6 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Thinning and pruning after first year of planting | 农业学的 | 2 times/rain season |
| 2. | Weeding after first year of planting | 农业学的 | 2 times/rain season |
| 3. | Fertilizer application after first year of planting | 农业学的 | 2 times/rain season |
| 4. | Cutting and selling logs | 农业学的 | 4th and 7th year |
注释:
Four years after planting, the poles will be cut and sold. After cutting, the tree coppices, then thinning is needed in order to leave not more than 3 stems, necessary for better growth of the tree trunks. Weeding is important during rainy season to control competition for fertilizer.
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour cost of weeding, pruning, thinning, and fertilizer application for 150 THB/time, 2 times/rai/yr, based on the labour wage of 300 THB/day | Time | 2.0 | 150.0 | 300.0 | |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Cost of 15-15-15 chemical fertilizer (13 THB/kg, application rate 50 g/tree; 50 g x 80 trees per rai = 4 kg/rai | kg | 4.0 | 13.0 | 52.0 | |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 352.0 | |||||
注释:
Land users do the job by themselves without hiring labourers. Furthermore, the fertilizer application will be the same fertilizer and timing as is used for rice. No extra fertilizer needed for trees because the trees will consume fertilizer from the rice field.
4.8 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Maintenance cost of weeding, pruning, thinning and fertilizer application was 428 THB/rai/yr. Calculation is based on 7 years of planting. Four years after planting, the logs were sold for additional income 5,714.3 THB/rai. On the 7th year, the logs were sold at 4,285.7 THB/rai.
(Income from 2 times of Eucalyptus sale; 4th year = 40,000 THB, 7th year = 30,000 THB. Therefore, total income for 7 years = 10,000 THB/rai. Benefit from Eucalyptus planting = 10,000–2,388 (planting cost + 4 years of maintenance cost) = 7,612 THB/7 years = 1,087 THB/rai/yr.)
Compost and rice husk are from farm by-products and the labour costs are from land users. The income thereore will be higher than 1,087 THB/rai as estimated.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
1200.00
有关降雨的规范/注释:
Average annual rainfall from 2003-2012
注明所考虑的参考气象站名称:
Meteorological Department
农业气候带
- 半干旱
Average temperature 21-36 degree Celsius, relative humidity is 75%
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 不相关
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
The geography is in the lower basin of Korat Plateau in the Northeast of Thailand.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Texture of top soil is sandy loam and more than 20 cm below the surface is sandy clay loam; pH = 7 and increasing with depth up to 8.5; soil salinity is moderately to highly affected which is identified by the salt crusts on the soil surface; very low P and K.
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
< 5米
地表水的可用性:
匮乏/没有
水质(未处理):
不良饮用水(需要处理)
水的盐度有问题吗?:
是
具体说明:
Slightly saline
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
否
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
Shallow saline groundwater exists because of the low-lying discharge area and the source of the salt is under the surface of the land.
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 低
栖息地多样性:
- 低
关于生物多样性的注释和进一步规范:
Before planting eucalyptus, species and habitat were low. After 7 years, dragonfly, earthworms, birds, rats, and wildflowers that were not seen before now are found.
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
性别:
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 老年人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Diligent farmer seeking more income by raising few cattle, swine, and boar.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
注释:
Farmers/ land owners outside the project have been planting eucalyptus on rice bunds and get additional income.
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
- rainfed
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
SLM之前的数量:
Rice production before planting eucalyptus 150-200 kg/rai
SLM之后的数量:
Rice production after planting eucalyptus 200-250 kg/rai
注释/具体说明:
The increase in rice production was due to being less saline condition of the field.
作物质量
SLM之前的数量:
More unfilled grain of rice
SLM之后的数量:
Less unfilled grain of rice
注释/具体说明:
Increased about 10%
饲料生产
SLM之前的数量:
Less stubble
SLM之后的数量:
More stubble
注释/具体说明:
Increased about 10%
畜牧生产
SLM之后的数量:
10%
产品多样性
SLM之前的数量:
Only rice was grown before SLM
SLM之后的数量:
Rice and Eucalyptus
注释/具体说明:
Increased about 50%, Eucalyptus grown in east-west direction only.
生产区域
SLM之前的数量:
0%
SLM之后的数量:
50%
注释/具体说明:
Rice bunds were unused before planting eucalyptus.
土地管理
SLM之前的数量:
0%
SLM之后的数量:
10%
注释/具体说明:
Planting trees hinder access to the rice field.
水资源可用性和质量
饮用水的质量
SLM之后的数量:
No effect
注释/具体说明:
From rain water
家畜用水的可用性
注释/具体说明:
Depend upon rainfall
家畜用水的质量
注释/具体说明:
Depends upon rain water
灌溉用水的可用性
注释/具体说明:
No supplementary water available
灌溉用水的质量
注释/具体说明:
Under rainfed only
灌溉用水需求
注释/具体说明:
Remain unchanged
收入和成本
农业投入费用
SLM之前的数量:
0%
SLM之后的数量:
20%
注释/具体说明:
Increased about 20% (the cost for planting trees in the first year and the maintenance cost of later years).
农业收入
SLM之前的数量:
0
SLM之后的数量:
Approximately 1,000 THB/rai/yr
注释/具体说明:
Additional income from selling eucalyptus logs besides rice
收入来源的多样性
SLM之前的数量:
Income from only rice
SLM之后的数量:
Income from both rice and logs
注释/具体说明:
Extra income from selling swine and boar
工作量
SLM之前的数量:
0%
SLM之后的数量:
10%
注释/具体说明:
Increased about 10% by planting tree and subsequent maintainence.
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
SLM之前的数量:
0%
SLM之后的数量:
10%
注释/具体说明:
Self-sufficiency increased through obtaining higher income.
健康状况
SLM之前的数量:
0%
SLM之后的数量:
10%
注释/具体说明:
Change in microclimate affected in cooler atmosphere
娱乐机会
SLM之前的数量:
0%
SLM之后的数量:
10%
注释/具体说明:
Due to change in microclimate and biodiversity
社区机构
SLM之前的数量:
0%
SLM之后的数量:
20%
注释/具体说明:
More communication among land users community and local administration.
国家机构
SLM之前的数量:
0%
SLM之后的数量:
10%
注释/具体说明:
National institutions are more recognized by land users.
SLM/土地退化知识
SLM之前的数量:
0%
SLM之后的数量:
50%
注释/具体说明:
Land users observed less salination.
生态影响
水循环/径流
多余水的排放
SLM之前的数量:
0%
SLM之后的数量:
10%
注释/具体说明:
Saline groundwater level decreased due to the bio-drainage by eucalyptus trees.
地下水位/含水层
SLM之前的数量:
Ave. groundwater level < 1 m
SLM之后的数量:
Ave. groundwater level > 1 m
注释/具体说明:
Lower groundwater level after 7 years of planting eucalyptus
蒸发
SLM之前的数量:
0%
SLM之后的数量:
10%
注释/具体说明:
Cooler atmosphere
土壤
土壤水分
SLM之前的数量:
0%
SLM之后的数量:
10%
注释/具体说明:
Due to shading
土壤覆盖层
SLM之前的数量:
0%
SLM之后的数量:
10%
注释/具体说明:
Shading effect and plant residues
土壤结壳/密封
SLM之前的数量:
0%
SLM之后的数量:
10%
注释/具体说明:
Due to better soil properties from crop residues and earthworm activities
土壤压实
SLM之前的数量:
0%
SLM之后的数量:
10%
注释/具体说明:
Due to better soil properties from crop residues and earthworm activities
养分循环/补给
SLM之前的数量:
0%
SLM之后的数量:
10%
盐度
SLM之前的数量:
0%
SLM之后的数量:
30%
注释/具体说明:
Rice production as well as quality of rice increased (and also more percentage of full grains) due to the decrease in salinity level.
生物多样性:植被、动物
植被覆盖
SLM之前的数量:
0%
SLM之后的数量:
50%
注释/具体说明:
Rice bunds are used for planting eucalyptus only along east-west direction.
生物量/地上C
SLM之前的数量:
0%
SLM之后的数量:
80%
注释/具体说明:
Biomass from eucalyptus trees
植物多样性
SLM之前的数量:
0%
SLM之后的数量:
60%
注释/具体说明:
From eucalyptus trees and more local species of grasses and wildflowers
动物多样性
SLM之前的数量:
0%
SLM之后的数量:
50%
注释/具体说明:
Earthworms, birds, rats, ants, etc.
有益物种
SLM之前的数量:
0%
SLM之后的数量:
10%
注释/具体说明:
Native earthworms
栖息地多样性
SLM之前的数量:
0%
SLM之后的数量:
20%
注释/具体说明:
Dragonfly, earthworms, birds and rats
减少气候和灾害风险
干旱影响
SLM之前的数量:
0%
SLM之后的数量:
10%
注释/具体说明:
Due to cooler atmosphere of the planting sites
碳和温室气体的排放
SLM之前的数量:
0%
SLM之后的数量:
20%
注释/具体说明:
Eucalyptus trees absorb greenhouse gases.
微气候
SLM之前的数量:
0%
SLM之后的数量:
20%
注释/具体说明:
Cooler and greener atmosphere
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
地下水/河流污染
SLM之前的数量:
0%
SLM之后的数量:
10%
注释/具体说明:
Reduced groundwater level
温室气体的影响
SLM之前的数量:
0%
SLM之后的数量:
10%
注释/具体说明:
The planted Eucalyptus trees absorb greenhouse gases.
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 不好 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 延长生长期 | 不好 |
| 缩短生长期 | 不好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
稍微积极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
非常积极
注释:
The cost of planting trees in the first year was the only main cost. The maintenance cost starts from second year on until the year of cutting and selling logs. After coppicing, maintenance cost starts again until the next cutting. Therefore the benefits will be higher with more cycles of cutting.
6.5 技术采用
- 10-50%
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
1,600 ha
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发地采用该技术,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 10-50%
注释:
Farmers and land users acknowledge the benefit of the technology that results in decreasing salinity, increasing rice production, and additional income from trees.
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
是
其它(具体说明):
closer spacing of trees
具体说明技术的适应性(设计、材料/品种等):
Planting eucalyptus has been adapted from growing eucalyptus on rice bunds of 1.5 m wide to 0.5 m wide to save labor cost of land preparation and plant the seedlings on one row instead of 2 rows.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Decrease saline groundwater level resulting in rice yield increase. |
| Get higher income from increasing rice yield and eucalyptus poles. |
| The microclimate in the area has been improved and the air is cooler and the land is greener. |
| Increased indirect returns due to land is greener and used as animal fodders for cattle, swine, and boar. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Decreased saline groundwater level then prevented further salination as a result to protect the land degradation. |
| Increasing farmer's income. |
| To establish better environment for more biodiversity especially earthworms used to disappear now are found and their activities induce better soil properties. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| More birds and rats damage rice yield. | No solution |
| The officers do not visit whenever the land users need help. | The officers need to contact the land users and give advice more often. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Farmers do not understand how eucalyptus trees could decrease saline groundwater level. | Explain, illustrate and demonstrate the cause and effect of salinity. |
| There are pros and cons of planting eucalyptus because the leaves may damage the soil and their shading effect may decrease rice yield. | Organize farmer group visit to some successful sites that no adverse effects have been found. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
Visit 1 farmer/ land user's land
- 与土地使用者的访谈
Interview with 1 farmer
- 与SLM专业人员/专家的访谈
The Land Development Department officers and planners (6)
- 根据报告和其他现有文档进行编译
Reports from the Soil Salinity Research and Development Group of the Land Development Department (2)
- projects
The Land Development Department's implementation projects (3)
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Land Development Department
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
http://www.ldd.go.th/
7.3 链接到网络上可用的相关信息
标题/说明:
Planting Eucalyptus on bunds: Better way for the Northeast farmers
URL:
http://www.ldd.go.th/
标题/说明:
Eucalyptus : New opportunity by Siam Forestry
URL:
http://www.scgpackaging.com/others/forestry/eucalyptus/TH
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Advisory system for planting Eucalyptus camaldulensis on rice … [泰国]
The Thai government promotes planting of Eucalyptus camaldulensis on rice bunds to lower the saline groundwater level and prevent the spread of salt in soils - through cooperation of farmers, land owners, Siam Forestry Co., Ltd., Subdistrict Administration Organization, Land Development Department, and with specialists/ technical advisors.
- 编制者: Areerat Wangkaew
模块
无模块