Planting Eucalyptus on rice bunds to lower saline groundwater [Thaïlande]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Areerat Wangkaew
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateurs : Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Samran Sombatpanit, Pitayakon Limtong, William Critchley
Planting perennial salt-tolerant trees in salt-affected areas of the Northeast of Thailand.
technologies_4099 - Thaïlande
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Personne(s)-ressource(s) clé(s)
exploitant des terres:
Chuenchai Sayan
+66-99-0254108
Ban Muang Pia, Muang Pia Sub-district, Ban Phai District, Khon Kaen 40110
Thaïlande
Spécialiste GDT:
Sritumboon Supranee
ssritumboon@yahoo.com
Land Development Department
2003, 61 Phaholyothin Road, Ladyao, Chatuchak, Bangkok 10900
Thaïlande
Spécialiste GDT:
Pothinam Pornpana
laosuwan18@hotmail.com
Land Development Department
2003, 61 Phaholyothin Road, Ladyao, Chatuchak, Bangkok 10900
Thaïlande
Spécialiste GDT:
Rophandung Weera
weerop@hotmail.com
Land Development Department
2003, 61 Phaholyothin Road, Ladyao, Chatuchak, Bangkok 10900
Thaïlande
Spécialiste GDT:
Srihaban Pranee
pranee.782@gmail.com
Land Development Department
2003, 61 Phaholyothin Road, Ladyao, Chatuchak, Bangkok 10900
Thaïlande
Spécialiste GDT:
Jakkarach Usa
usa.kl@hotmail.com
Land Development Department
2003, 61 Phaholyothin Road, Ladyao, Chatuchak, Bangkok 10900
Thaïlande
Spécialiste GDT:
Janplang Chettaruj
joeshua9@hotmail.com
Land Development Department
2003, 61 Phaholyothin Road, Ladyao, Chatuchak, Bangkok 10900
Thaïlande
National consultant:
Arunin Somsri
ssarunin@gmail.com
Land Development Department
2003, 61 Phaholyothin Road, Ladyao, Chatuchak, Bangkok 10900
Thaïlande
Nom du projet qui a facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Decision Support for Mainstreaming and Scaling out Sustainable Land Management (GEF-FAO / DS-SLM)Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Land Development Department LDD (Land Development Department LDD) - Thaïlande1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Quand les données ont-elles été compilées (sur le terrain)?
01/10/2018
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.4 Déclaration sur la durabilité de la Technologie décrite
Est-ce que la Technologie décrite ici pose problème par rapport à la dégradation des terres, de telle sorte qu'elle ne peut pas être déclarée comme étant une technologie de gestion durable des terres?
Non
Commentaires:
The technology is environmentally suited and very well accepted by the land users.
1.5 Référence au(x) questionnaire(s) sur les Approches de GDT

Advisory system for planting Eucalyptus camaldulensis on rice … [Thaïlande]
The Thai government promotes planting of Eucalyptus camaldulensis on rice bunds to lower the saline groundwater level and prevent the spread of salt in soils - through cooperation of farmers, land owners, Siam Forestry Co., Ltd., Subdistrict Administration Organization, Land Development Department, and with specialists/ technical advisors.
- Compilateur : Areerat Wangkaew
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
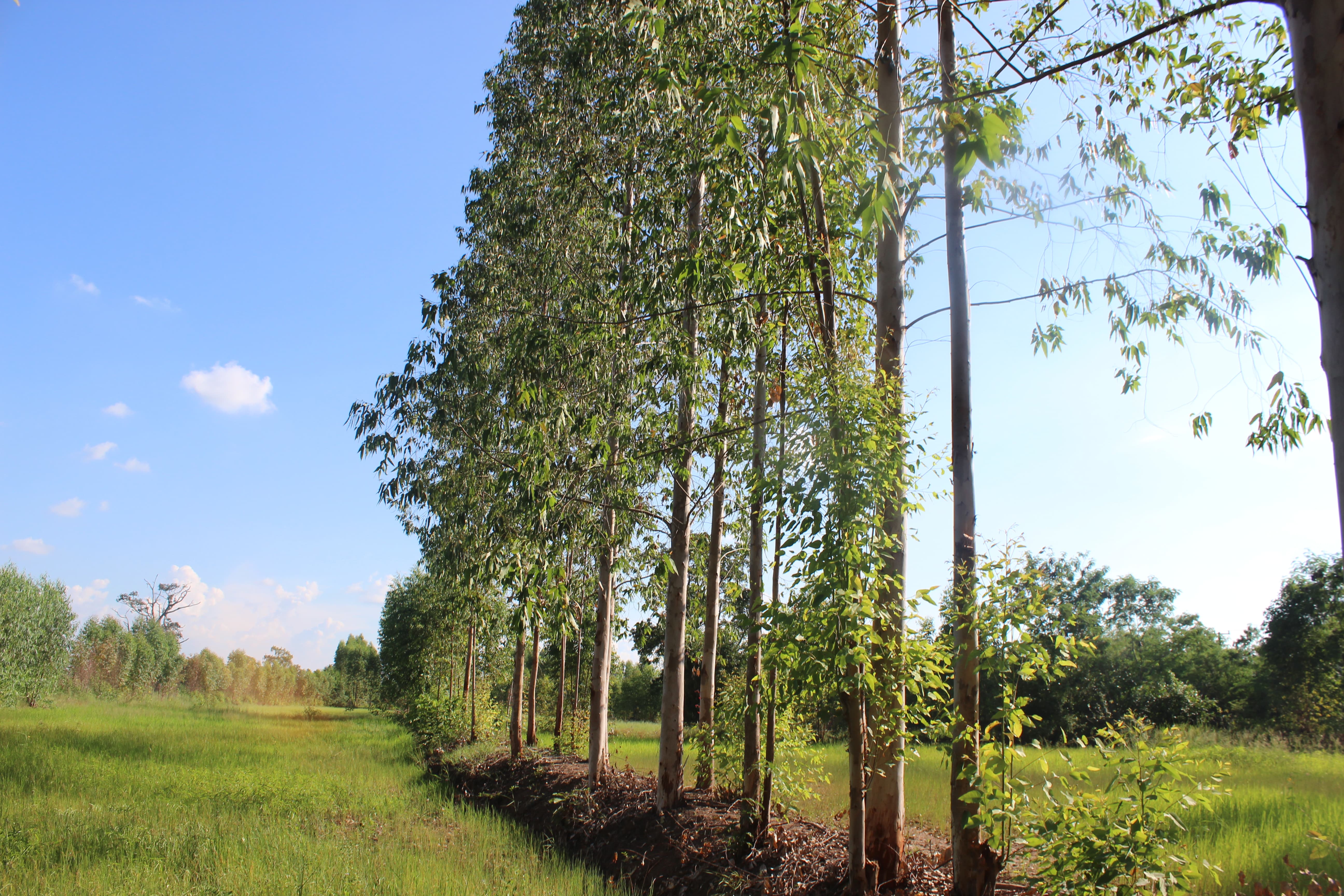
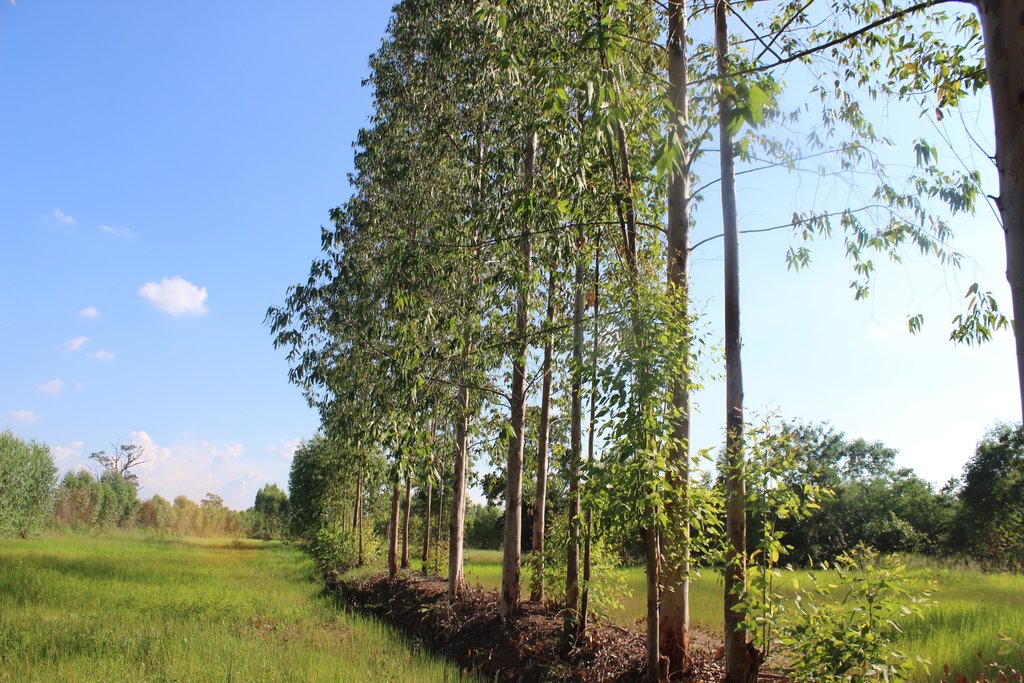
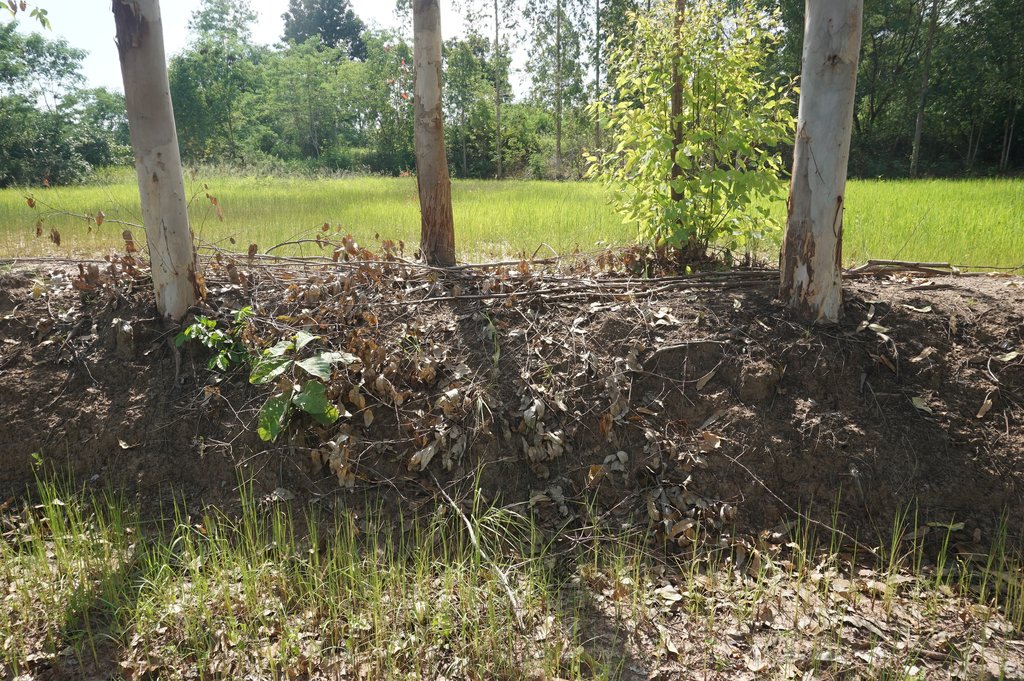
Eucalyptus camaldulensis variety H4 is salt tolerant and has the ability to lower shallow saline groundwater levels; as a result salinity is controlled. Planting eucalyptus on one or two sides of the rice bund in an east-west direction (in single or double rows) at a spacing of 2 m between trees is the most effective technique and well accepted by farmers.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
Eucalyptus camaldulensis cultivation on rice bunds to lower shallow saline groundwater levels in low-lying areas is a technology used on salt-affected land. The LDD Perennial Tree Planting project to promote the technology of planting Eucalyptus camaldulensis on rice bunds has been implemented since 1996. The land user interviewed cultivates a moderately salt-affected rice field at Ban Muang Pia District, Khon Kaen Province. The land is used for rice production both glutinous (variety RD 6) and non-glutinous fragrant rice (Hom Mali 105). The average yield of rice is 200-250 kg/rai (1 ha = 6.25 rai). The farmers have planted eucalyptus on bunds in the rice cultivated areas on about 10,000 rai in more than 10 years with the objectives of remedying and preventing salination by lowering shallow saline groundwater levels, through "bio-drainage" as well as increasing income and better utilization of lands on rice bunds for growing trees.
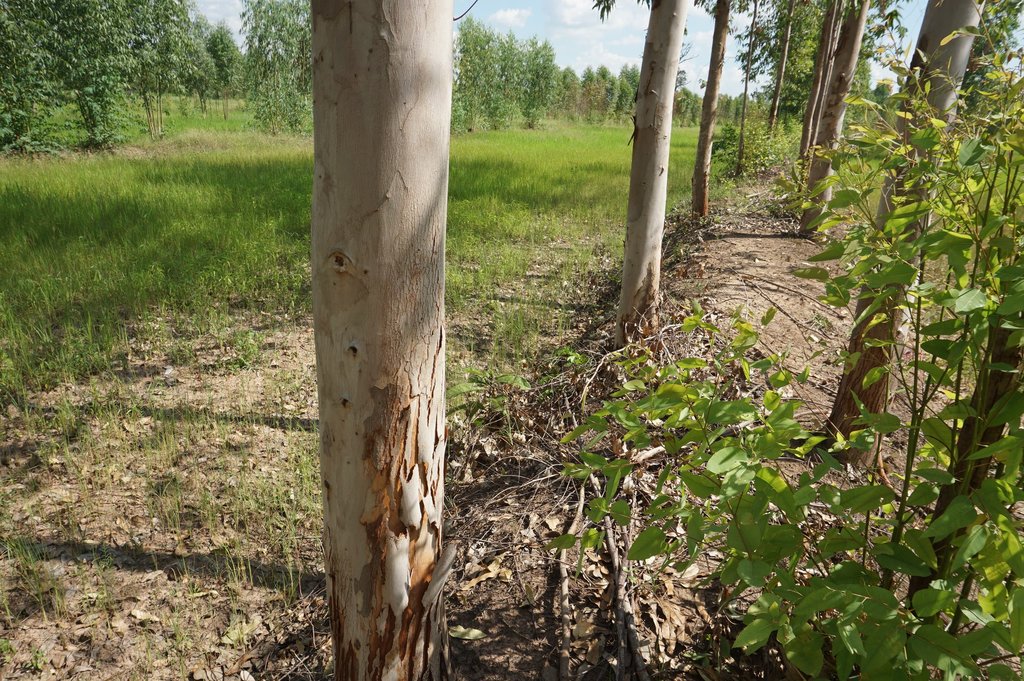
The technology of eucalyptus cultivation on rice bunds has been implemented in farmers' fields in the low-lying salt-affected rice area common in the Northeast of Thailand. It is widely accepted by farmers through the joint partnership between the Land Development Department (LDD), Siam Forestry Co., Ltd. and the local district administration. Eucalyptus seedlings are provided by LDD and are planted in a single or double rows - double rows with trees planted on two sides of the rice bunds in a zigzag manner following an east-west direction to prohibit a shadow effect. The spacing between the trees in a row is 2 m: the rice bund was adapted to be 1.5 m wide and 0.5 m high. This provides more space and convenient access to the rice field. The project provides labour costs for farmers to prepare the land before planting. Many farmers outside the project transplanted their own eucalyptus seedlings on the bunds of 0.5 m or more in width. Farmers buy the seedlings at 1 THB each and plant in pits of 0.3 x 0.3 x 0.3 m with 0.5 kg compost and 0.5 kg rice husks from farm by-products. This technology is well accepted by farmers because of the effective control of salinity in the rice fields as well as the higher income obtained from selling eucalyptus wood. Farmers observed the dead patchy spots of rice plants with salt crusts before planting eucalyptus: after 2 cutting cycles no salt patches were observed anymore, and rice yields increased noticeably. There was also extra income from selling poles of eucalyptus every 4 years. The average yield of eucalyptus trees of 2.5-3.0 inches in diameter was 16 tons per rai for the first cutting.
Based on 7 years (2 crops of eucalyptus coppicing), the average additional income was 1,087 THB/rai/yr (according to the farmers' and Siam Forest's information). The main investment was in the first year of planting; later on, the maintenance cost was on labour for weeding, pruning and thinning to 3 stems after coppice/cutting, including adding 15-15-15 fertilizer for each tree. The average income is increased through better rice yields. The benefits of the technology according to interviews are creating a cooler microclimate from eucalyptus trees and changes in biodiversity through better soil quality resulting in more species of flora and fauna such as grasses, wildflowers, dragonflies, earthworms in the rice field and on the bund. Some farmers wanted more trees by planting at closer spacing of 1 m, but this resulted in too great a density of trees thus consuming more surface water and competing with rice for water consumptive use.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.4 Vidéos de la Technologie
Commentaire, brève description:
The video shows the area of eucalyptus growing on the rice bund.
Date:
01/10/2018
Lieu:
Ban Muang Pia, Khon Kaen
Nom du vidéaste:
Supranee Sritumboon
Commentaire, brève description:
Farmer interview and SLM discussion.
Date:
01/10/2018
Lieu:
Ban Muang Pia, Khon Kaen
Nom du vidéaste:
Supranee Sritumboon
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Thaïlande
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Khon Kaen
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Ban Phai
Commentaires:
The SLM Technology site for planting eucalyptus in a rice production area.
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Indiquez l'année de mise en œuvre:
1996
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- par le biais de projets/ d'interventions extérieures
- by other land users
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
The project initiated by the government (Land Development Department) collaborated with private enterprises (Siam Forestry Co., Ltd.), local administration, communities and land users.
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- améliorer la production
- réduire, prévenir, restaurer les terres dégradées
- conserver/ améliorer la biodiversité
- créer un impact économique positif
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

Terres cultivées
- Cultures annuelles
- Cultures pérennes (non ligneuses)
Principales cultures (vivrières et commerciales):
Rice
Commentaires:
Planting eucalyptus for additional income and more intensive utilization of land on the rice bunds.
Si l'utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie, indiquez l'utilisation des terres avant la mise en œuvre de la Technologie:
Before planting eucalyptus, rice was the only crop. Due to the shallow saline groundwater of the area, rice had shown symptoms of being salt-affected; however after planting eucalyptus trees, these symptoms disappeared.
3.3 Informations complémentaires sur l'utilisation des terres
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- pluvial
Commentaires:
Average annual rainfall is 1,200-1,300 mm.
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 1
Précisez:
Land use is for rice production; the technology is planting Eucalyptus camaldulensis on rice bunds.
Densité d'élevage/ chargement (si pertinent):
Only few cattle, swine, and boar are in the land user's farm.
3.4 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- agroforesterie
- gestion des eaux souterraines
- desalination
3.5 Diffusion de la Technologie
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- répartie uniformément sur une zone
Si la Technologie est uniformément répartie sur une zone, indiquez la superficie couverte approximative:
- 1-10 km2
Commentaires:
The technology has spread over the area of 10,000 rai (1 ha = 6.25 rai) owned by farmers/land users both under and outside the supported project of planting eucalyptus on rice bunds.
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

pratiques agronomiques
- A2: Matière organique/ fertilité du sol
- A5: Gestion des semences, amélioration des variétés

autres mesures
Commentaires:
Eucalyptus camaldulensis H4 is the salt-tolerant variety used for lowering shallow saline groundwater.
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

dégradation chimique des sols
- Cn: baisse de la fertilité des sols et réduction du niveau de matière organique (non causée par l’érosion)
- Cs: salinisation/ alcalinisation

dégradation physique des sols
- Pc: compaction
- Pk: scellage et encroûtement

dégradation biologique
- Bc: réduction de la couverture végétale
- Bq: baisse de la quantité/ biomasse
- Bs: baisse de la qualité et de la composition/ diversité des espèces
- Bl: perte de la vie des sols

dégradation hydrique
- Hg: changement du niveau des nappes phréatiques (eaux souterraines) et des aquifères
- Hq: baisse de la qualité des eaux souterraines
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- réduire la dégradation des terres
- restaurer/ réhabiliter des terres sévèrement dégradées
Commentaires:
Decreased saline groundwater levels to control salinity distribution in rice cultivated areas.
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
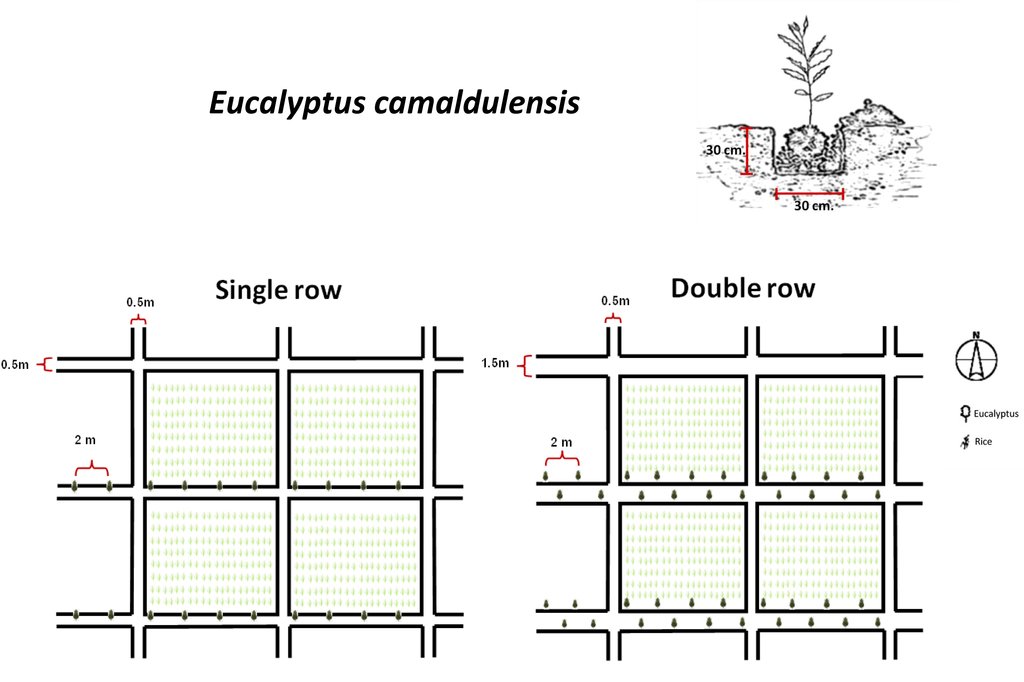
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
4.2 Spécification/ explications techniques du dessin technique
1. Seedling of Eucalyptus camaldulensis H4, a salt-tolerant variety, were planted. The age of seedlings was 3-month old. The rice bund was regulated to 0.5 m wide for planting eucalyptus in single row or 1.5 m wide for planting in double rows (in a zigzag manner), 0.5 m high with a spacing of 2 m between the trees along an east-west direction. The number of trees was 80/rai or 500/ha for double rows planting.
2. Planting technique: 0.5 kg of compost mixed with 0.5 kg of rice husks was applied at the bottom of a pit of 0.3 x 0.3 x 0.3 m before seedlings were planted.
4.3 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
Spécifiez la manière dont les coûts et les intrants ont été calculés:
- par superficie de la Technologie
Indiquez la taille et l'unité de surface:
own by one selected land user
Si vous utilisez une unité locale de superficie, indiquez le facteur de conversion pour un hectare:
1 hectare = 6.25 rai
autre/ monnaie nationale (précisez):
THB
Indiquer le taux de change du dollars en monnaie locale (si pertinent): 1 USD= :
32,0
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
300 THB
4.4 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Site selection of salt-affected area | Structurel | May-July |
| 2. | Land preparation; bunds construction and seedling preparation | Structurel | May-July |
| 3. | Public hearing, joint meeting between farmers and researchers | Autres mesures | May-July |
| 4. | Demonstration plot | Agronomique | May-July |
| 5. | Model establishment (Eucalyptus planting method) | Agronomique | May-July |
| 6. | Joint monitoring, evaluation and follow up for planting | Autres mesures | After planting |
Commentaires:
No irrigation water therefore the planting time depends on the period of early rainy season which will be from May to July.
4.5 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % du coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Labour cost for planting eucalyptus (labour wage per day = 300 THB, 1 rai required a labour cost of 600 THB) | Rai | 1,0 | 600,0 | 600,0 | |
| Matériel végétal | Eucalyptus seedling cost (80 trees/rai), 1 THB for each seedling | Seedling | 80,0 | 1,0 | 80,0 | |
| Engrais et biocides | Compost cost 3.5 THB/kg, 0.5 kg/pit | kg | 40,0 | 3,5 | 140,0 | |
| Engrais et biocides | Rice husk cost 4 THB/kg, 0.5 kg/pit | kg | 40,0 | 4,0 | 160,0 | |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 980,0 | |||||
Si le coût n'est pas pris en charge à 100% par l'exploitant des terres, indiquez qui a financé le coût restant:
Land Development Department
Commentaires:
Labour cost for land preparation and planting borne by LDD and seedlings borne by Siam Forestry Co., Ltd.; compost and rice husk were from farm by-products.
4.6 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Thinning and pruning after first year of planting | Agronomique | 2 times/rain season |
| 2. | Weeding after first year of planting | Agronomique | 2 times/rain season |
| 3. | Fertilizer application after first year of planting | Agronomique | 2 times/rain season |
| 4. | Cutting and selling logs | Agronomique | 4th and 7th year |
Commentaires:
Four years after planting, the poles will be cut and sold. After cutting, the tree coppices, then thinning is needed in order to leave not more than 3 stems, necessary for better growth of the tree trunks. Weeding is important during rainy season to control competition for fertilizer.
4.7 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % du coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Labour cost of weeding, pruning, thinning, and fertilizer application for 150 THB/time, 2 times/rai/yr, based on the labour wage of 300 THB/day | Time | 2,0 | 150,0 | 300,0 | |
| Engrais et biocides | Cost of 15-15-15 chemical fertilizer (13 THB/kg, application rate 50 g/tree; 50 g x 80 trees per rai = 4 kg/rai | kg | 4,0 | 13,0 | 52,0 | |
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 352,0 | |||||
Commentaires:
Land users do the job by themselves without hiring labourers. Furthermore, the fertilizer application will be the same fertilizer and timing as is used for rice. No extra fertilizer needed for trees because the trees will consume fertilizer from the rice field.
4.8 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
Maintenance cost of weeding, pruning, thinning and fertilizer application was 428 THB/rai/yr. Calculation is based on 7 years of planting. Four years after planting, the logs were sold for additional income 5,714.3 THB/rai. On the 7th year, the logs were sold at 4,285.7 THB/rai.
(Income from 2 times of Eucalyptus sale; 4th year = 40,000 THB, 7th year = 30,000 THB. Therefore, total income for 7 years = 10,000 THB/rai. Benefit from Eucalyptus planting = 10,000–2,388 (planting cost + 4 years of maintenance cost) = 7,612 THB/7 years = 1,087 THB/rai/yr.)
Compost and rice husk are from farm by-products and the labour costs are from land users. The income thereore will be higher than 1,087 THB/rai as estimated.
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifiez la pluviométrie moyenne annuelle (si connue), en mm:
1200,00
Spécifications/ commentaires sur les précipitations:
Average annual rainfall from 2003-2012
Indiquez le nom de la station météorologique de référence considérée:
Meteorological Department
Zone agro-climatique
- semi-aride
Average temperature 21-36 degree Celsius, relative humidity is 75%
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Indiquez si la Technologie est spécifiquement appliquée dans des:
- non pertinent
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la topographie:
The geography is in the lower basin of Korat Plateau in the Northeast of Thailand.
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- grossier/ léger (sablonneux)
Texture du sol (> 20 cm sous la surface):
- moyen (limoneux)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- faible (<1%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Texture of top soil is sandy loam and more than 20 cm below the surface is sandy clay loam; pH = 7 and increasing with depth up to 8.5; soil salinity is moderately to highly affected which is identified by the salt crusts on the soil surface; very low P and K.
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Profondeur estimée de l’eau dans le sol:
< 5 m
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
faible/ absente
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
faiblement potable (traitement nécessaire)
La salinité de l'eau est-elle un problème? :
Oui
Précisez:
Slightly saline
La zone est-elle inondée?
Non
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la qualité et la quantité d'eau:
Shallow saline groundwater exists because of the low-lying discharge area and the source of the salt is under the surface of the land.
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- faible
Diversité des habitats:
- faible
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la biodiversité:
Before planting eucalyptus, species and habitat were low. After 7 years, dragonfly, earthworms, birds, rats, and wildflowers that were not seen before now are found.
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Sédentaire ou nomade:
- Sédentaire
Orientation du système de production:
- mixte (de subsistance/ commercial)
Revenus hors exploitation:
- 10-50% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- moyen
Individus ou groupes:
- individu/ ménage
Niveau de mécanisation:
- travail manuel
Genre:
- hommes
Age des exploitants des terres:
- personnes âgées
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Diligent farmer seeking more income by raising few cattle, swine, and boar.
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres détenues ou louées par les exploitants appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- petite dimension
Commentaires:
Farmers/ land owners outside the project have been planting eucalyptus on rice bunds and get additional income.
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- individu, avec titre de propriété
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- individuel
- rainfed
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
énergie:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
Quantité avant la GDT:
Rice production before planting eucalyptus 150-200 kg/rai
Quantité après la GDT:
Rice production after planting eucalyptus 200-250 kg/rai
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The increase in rice production was due to being less saline condition of the field.
qualité des cultures
Quantité avant la GDT:
More unfilled grain of rice
Quantité après la GDT:
Less unfilled grain of rice
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Increased about 10%
production fourragère
Quantité avant la GDT:
Less stubble
Quantité après la GDT:
More stubble
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Increased about 10%
production animale
Quantité après la GDT:
10%
diversité des produits
Quantité avant la GDT:
Only rice was grown before SLM
Quantité après la GDT:
Rice and Eucalyptus
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Increased about 50%, Eucalyptus grown in east-west direction only.
surface de production
Quantité avant la GDT:
0%
Quantité après la GDT:
50%
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Rice bunds were unused before planting eucalyptus.
gestion des terres
Quantité avant la GDT:
0%
Quantité après la GDT:
10%
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Planting trees hinder access to the rice field.
Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
qualité de l'eau potable
Quantité après la GDT:
No effect
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
From rain water
disponibilité de l'eau pour l'élevage
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Depend upon rainfall
qualité de l'eau pour l'élevage
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Depends upon rain water
disponibilité de l'eau d'irrigation
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
No supplementary water available
qualité de l'eau d'irrigation
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Under rainfed only
demande pour l'eau d'irrigation
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Remain unchanged
Revenus et coûts
dépenses pour les intrants agricoles
Quantité avant la GDT:
0%
Quantité après la GDT:
20%
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Increased about 20% (the cost for planting trees in the first year and the maintenance cost of later years).
revenus agricoles
Quantité avant la GDT:
0
Quantité après la GDT:
Approximately 1,000 THB/rai/yr
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Additional income from selling eucalyptus logs besides rice
diversité des sources de revenus
Quantité avant la GDT:
Income from only rice
Quantité après la GDT:
Income from both rice and logs
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Extra income from selling swine and boar
charge de travail
Quantité avant la GDT:
0%
Quantité après la GDT:
10%
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Increased about 10% by planting tree and subsequent maintainence.
Impacts socioculturels
sécurité alimentaire/ autosuffisance
Quantité avant la GDT:
0%
Quantité après la GDT:
10%
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Self-sufficiency increased through obtaining higher income.
situation sanitaire
Quantité avant la GDT:
0%
Quantité après la GDT:
10%
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Change in microclimate affected in cooler atmosphere
possibilités de loisirs
Quantité avant la GDT:
0%
Quantité après la GDT:
10%
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Due to change in microclimate and biodiversity
institutions communautaires
Quantité avant la GDT:
0%
Quantité après la GDT:
20%
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
More communication among land users community and local administration.
institutions nationales
Quantité avant la GDT:
0%
Quantité après la GDT:
10%
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
National institutions are more recognized by land users.
connaissances sur la GDT/ dégradation des terres
Quantité avant la GDT:
0%
Quantité après la GDT:
50%
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Land users observed less salination.
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
drainage de l'excès d'eau
Quantité avant la GDT:
0%
Quantité après la GDT:
10%
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Saline groundwater level decreased due to the bio-drainage by eucalyptus trees.
nappes phréatiques/ aquifères
Quantité avant la GDT:
Ave. groundwater level < 1 m
Quantité après la GDT:
Ave. groundwater level > 1 m
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Lower groundwater level after 7 years of planting eucalyptus
évaporation
Quantité avant la GDT:
0%
Quantité après la GDT:
10%
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Cooler atmosphere
Sols
humidité du sol
Quantité avant la GDT:
0%
Quantité après la GDT:
10%
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Due to shading
couverture du sol
Quantité avant la GDT:
0%
Quantité après la GDT:
10%
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Shading effect and plant residues
encroûtement/ battance du sol
Quantité avant la GDT:
0%
Quantité après la GDT:
10%
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Due to better soil properties from crop residues and earthworm activities
compaction du sol
Quantité avant la GDT:
0%
Quantité après la GDT:
10%
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Due to better soil properties from crop residues and earthworm activities
cycle/ recharge des éléments nutritifs
Quantité avant la GDT:
0%
Quantité après la GDT:
10%
salinité
Quantité avant la GDT:
0%
Quantité après la GDT:
30%
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Rice production as well as quality of rice increased (and also more percentage of full grains) due to the decrease in salinity level.
Biodiversité: végétale, animale
Couverture végétale
Quantité avant la GDT:
0%
Quantité après la GDT:
50%
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Rice bunds are used for planting eucalyptus only along east-west direction.
biomasse/ au dessus du sol C
Quantité avant la GDT:
0%
Quantité après la GDT:
80%
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Biomass from eucalyptus trees
diversité végétale
Quantité avant la GDT:
0%
Quantité après la GDT:
60%
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
From eucalyptus trees and more local species of grasses and wildflowers
diversité animale
Quantité avant la GDT:
0%
Quantité après la GDT:
50%
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Earthworms, birds, rats, ants, etc.
espèces bénéfiques
Quantité avant la GDT:
0%
Quantité après la GDT:
10%
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Native earthworms
diversité des habitats
Quantité avant la GDT:
0%
Quantité après la GDT:
20%
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Dragonfly, earthworms, birds and rats
Réduction des risques de catastrophe et des risques climatiques
impacts de la sécheresse
Quantité avant la GDT:
0%
Quantité après la GDT:
10%
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Due to cooler atmosphere of the planting sites
émissions de carbone et de gaz à effet de serre
Quantité avant la GDT:
0%
Quantité après la GDT:
20%
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Eucalyptus trees absorb greenhouse gases.
microclimat
Quantité avant la GDT:
0%
Quantité après la GDT:
20%
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Cooler and greener atmosphere
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
pollution des rivières/ nappes phréatiques
Quantité avant la GDT:
0%
Quantité après la GDT:
10%
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Reduced groundwater level
impact des gaz à effet de serre
Quantité avant la GDT:
0%
Quantité après la GDT:
10%
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The planted Eucalyptus trees absorb greenhouse gases.
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Extrêmes climatiques (catastrophes)
Catastrophes climatiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| sécheresse | pas bien |
Autres conséquences liées au climat
Autres conséquences liées au climat
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| prolongement de la période de croissance | pas bien |
| réduction de la période de croissance | pas bien |
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
légèrement positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
Commentaires:
The cost of planting trees in the first year was the only main cost. The maintenance cost starts from second year on until the year of cutting and selling logs. After coppicing, maintenance cost starts again until the next cutting. Therefore the benefits will be higher with more cycles of cutting.
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
- 10-50%
Si disponible, quantifiez (nombre de ménages et/ou superficie couverte):
1,600 ha
Parmi tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle ou aucun paiement?
- 10-50%
Commentaires:
Farmers and land users acknowledge the benefit of the technology that results in decreasing salinity, increasing rice production, and additional income from trees.
6.6 Adaptation
La Technologie a-t-elle été récemment modifiée pour s'adapter à l'évolution des conditions?
Oui
autre (précisez):
closer spacing of trees
Spécifiez l'adaptation de la Technologie (conception, matériaux/ espèces, etc.):
Planting eucalyptus has been adapted from growing eucalyptus on rice bunds of 1.5 m wide to 0.5 m wide to save labor cost of land preparation and plant the seedlings on one row instead of 2 rows.
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
| Decrease saline groundwater level resulting in rice yield increase. |
| Get higher income from increasing rice yield and eucalyptus poles. |
| The microclimate in the area has been improved and the air is cooler and the land is greener. |
| Increased indirect returns due to land is greener and used as animal fodders for cattle, swine, and boar. |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
| Decreased saline groundwater level then prevented further salination as a result to protect the land degradation. |
| Increasing farmer's income. |
| To establish better environment for more biodiversity especially earthworms used to disappear now are found and their activities induce better soil properties. |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| More birds and rats damage rice yield. | No solution |
| The officers do not visit whenever the land users need help. | The officers need to contact the land users and give advice more often. |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Farmers do not understand how eucalyptus trees could decrease saline groundwater level. | Explain, illustrate and demonstrate the cause and effect of salinity. |
| There are pros and cons of planting eucalyptus because the leaves may damage the soil and their shading effect may decrease rice yield. | Organize farmer group visit to some successful sites that no adverse effects have been found. |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
- visites de terrain, enquêtes sur le terrain
Visit 1 farmer/ land user's land
- interviews/entretiens avec les exploitants des terres
Interview with 1 farmer
- interviews/ entretiens avec les spécialistes/ experts de GDT
The Land Development Department officers and planners (6)
- compilation à partir de rapports et d'autres documents existants
Reports from the Soil Salinity Research and Development Group of the Land Development Department (2)
- projects
The Land Development Department's implementation projects (3)
7.2 Références des publications disponibles
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Land Development Department
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
http://www.ldd.go.th/
7.3 Liens vers les informations pertinentes disponibles en ligne
Titre/ description:
Planting Eucalyptus on bunds: Better way for the Northeast farmers
URL:
http://www.ldd.go.th/
Titre/ description:
Eucalyptus : New opportunity by Siam Forestry
URL:
http://www.scgpackaging.com/others/forestry/eucalyptus/TH
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens

Advisory system for planting Eucalyptus camaldulensis on rice … [Thaïlande]
The Thai government promotes planting of Eucalyptus camaldulensis on rice bunds to lower the saline groundwater level and prevent the spread of salt in soils - through cooperation of farmers, land owners, Siam Forestry Co., Ltd., Subdistrict Administration Organization, Land Development Department, and with specialists/ technical advisors.
- Compilateur : Areerat Wangkaew
Modules
Aucun module trouvé