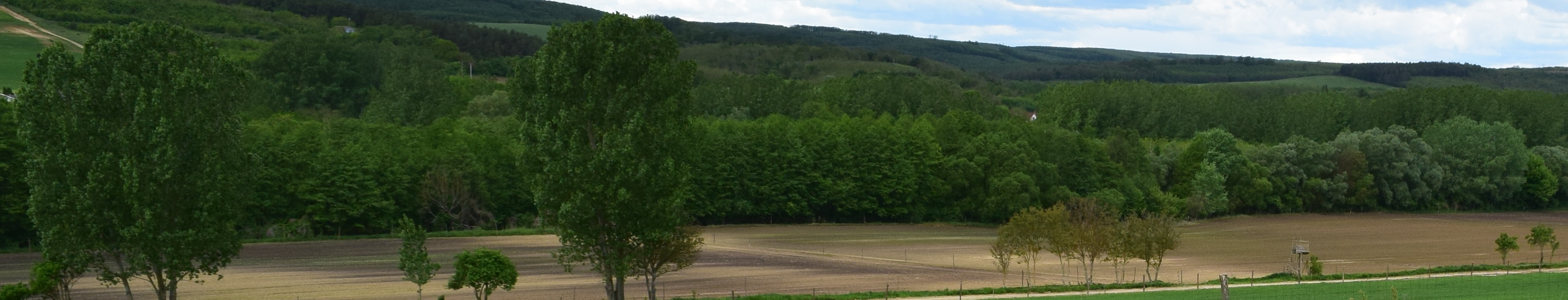
Afforestation of arable land [匈牙利]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Brigitta Szabó
- 编辑者: Piroska Kassai, Zoltan Toth
- 审查者: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Erdőtelepítés
technologies_5930 - 匈牙利
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
SLM专业人员:
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
OPtimal strategies to retAIN and re-use water and nutrients in small agricultural catchments across different soil-climatic regions in Europe (OPTAIN)1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
1.5 参考关于SLM方法(使用WOCAT记录的SLM方法)的调查问卷

Afforestation [海地]
Dans les mornes à Léogâne, la Croix Rouge Suisse (CRS) pratique la reforestation en participation communautaire.
- 编制者: Joana Eichenberger
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Afforestation is planting trees on previously non-forested land. Trees hold the soil and reduce runoff, and thus prevent erosion of the most fertile layers. It is an effective way to rehabilitate degraded lands, being a nature-based solution which addresses flood and soil erosion impacts.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
Afforestation is planting trees on previously non-forested land. Trees hold the soil and reduce runoff, and thus prevent erosion of the most fertile layers. It is an effective way to rehabilitate degraded lands, being a nature-based solution which addresses floods and soil erosion. As vegetation cover plays a crucial role in erosion and runoff rates, afforestation is considered among the best options for soil conservation. Water-related forest ecosystem services include the provision, filtration and regulation of water, along with stream ecosystem support and water-related hazard control, for example soil protection from runoff and erosion. In this context, forest management practices that involve vegetation cover modifications may have a substantial impact on the provision of water-related ecosystem services. Moreover, forest ecosystem interactions with water and energy cycles have been highlighted as the foundations for carbon storage, water resources distribution and terrestrial temperature balancing. Forest management may thus play a key role in meeting climate change mitigation goals as well (Rodrigues et al. 2020).
Afforestation is recommended in areas affected by severe erosion, especially where the slope exceeds 17% and deep gully erosion occurs. This can be a whole parcel or only a part of it. Planting mixed forest consisting of indigenous tree species is the most advantageous.
The main steps in planting/ maintaining trees are as follows:
•Site preparation: considerations include the most effective and cost-efficient methods; soil type, existing vegetation, time and financial constraints.
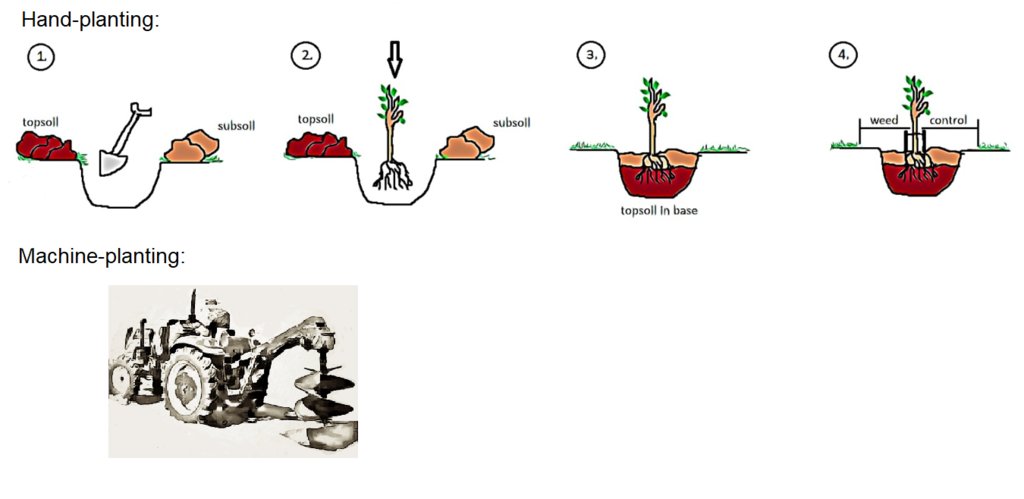
•Planting: machine-planting or hand-planting.
•Follow-up: monitoring survival, continuing control of competing vegetation, providing protection from animal damage, and monitoring for disease and insects.
•Harvesting/thinning: removing individual trees to reduce the woodland density. Through removing poorer quality trees, the stronger thrive.
Although the long-term environmental benefits of afforestation are significant, farmers generally do not like participating in afforestation programmes because it means a significant loss of income in the short/mid-term (even with the available subsidies/agricultural support).
2.3 技术照片
2.4 技术视频
注释、简短说明:
no video avalilable
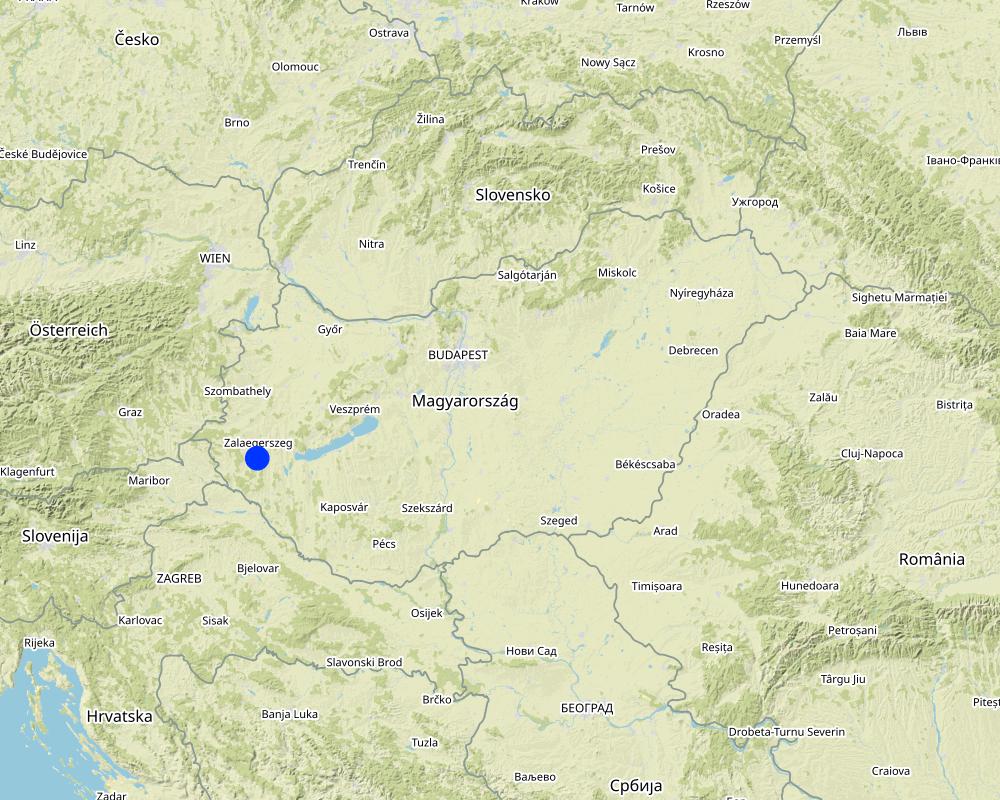
位置:
-
摄影师的名字:
-
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
匈牙利
区域/州/省:
Zala County
有关地点的进一步说明:
The site where the technology is applied is situated within the catchment of Felső-Válicka stream, which belongs to the Balaton catchment area in western Hungary.
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- 0.1-1 平方千米
技术现场是否位于永久保护区?:
否
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 10-50年前
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过土地使用者的创新
- 通过项目/外部干预
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 结合其他技术保护流域/下游区域
- 保持/提高生物多样性
- 适应气候变化/极端天气及其影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
否

农田
- 一年一作
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 谷类 - 大麦
- 谷物类 - 玉米
- 谷类 - 小麦(冬季)
- 油料作物 - 向日葵、菜籽、其他
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
采用间作制度了吗?:
否
采用轮作制度了吗?:
是
如果是,请具体说明:
wheat-maize-sunflower-barley
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?:
- 是(请在技术实施前填写以下有关土地利用的问题)
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
否

森林/林地
- 植树造林
植树造林:说明树种的起源和组成:
- 单一栽培的本地品种
- 混交品种
植树造林类型:
- 温带大陆林人工林
以上的树木是落叶树还是常绿树?:
- 落叶植物
产品和服务:
- 自然灾害防护
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 森林种植管理
- 改良的地面/植被覆盖
- 地表水管理(泉、河、湖、海)
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

植物措施
- V1:乔木和灌木覆盖层

管理措施
- M1:改变土地使用类型
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wg:冲沟侵蚀/沟蚀

生物性退化
- Bh:栖息地丧失
- Bq:数量/生物量减少

水质恶化
- Hs:地表水良变化
- Hp:地表水水质下降
- Hq:地下水水质下降
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 减少土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
1. Digging a hole
2. Planting the tree sapling
3. Covering with the soil, inverse back digging is recommended (topsoil in base)
4. Forming a weed free area at least 1 diameter around the tree and using stakes to stabilize the tree.
5. Spacing between trees is depending on tree sizes: at least 2,5 meter between small trees and at least 5 meter between larger trees.
作者:
Piroska Kassai
日期:
15/03/2023
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术区域
注明尺寸和面积单位:
hectare
具体说明成本计算所用货币:
- 美元
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
50
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | approval process (planning and obtaining permit) | any season |
| 2. | soil preparation | autumn |
| 3. | planting | autumn |
| 4. | wild fence construction | autumn |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | soil preparation | person day | 2.0 | 50.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | planting (4000 seedlings on 1 hectare) | person day | 3.0 | 50.0 | 150.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | wild fence construction | person day | 4.0 | 50.0 | 200.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | soil preparation | hiring cost/day | 1.0 | 400.0 | 400.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | planting | hiring cost/day | 1.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | wild fence construction | hiring cost/day | 2.0 | 100.0 | 200.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | seedlings | piece | 4000.0 | 0.1 | 400.0 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | wild fence raw material | meter | 400.0 | 2.5 | 1000.0 | 100.0 |
| 其它 | approval process (planning and obtaining permit) | per case | 1.0 | 400.0 | 400.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 2950.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 2950.0 | |||||
注释:
Subsidies are available for the establisment cost (~2000$/ha)
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Tillage/mechanical weeding | yearly |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Tillage/mechanical weeding | person day | 1.0 | 50.0 | 50.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Tillage/mechanical weeding- machine hiring cost | hiring cost/day | 1.0 | 300.0 | 300.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 350.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 350.0 | |||||
注释:
Financial supports are available for the maintanence cost of the forest and for the loss of farm income (in the case of land use change from cropland to forest)
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
tree species, existing vegetation, soil type
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
725.00
有关降雨的规范/注释:
Distribution of precipitation is uneven
农业气候带
- 半湿润
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 不相关
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
好
水质(未处理):
不良饮用水(需要处理)
水质请参考::
地表水
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
是
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 高
栖息地多样性:
- 高
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 商业/市场
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 丰富
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 机械化/电动
性别:
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 老年人
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 大规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 公司
土地使用权:
- 租赁
- 个人
用水权:
- 社区(有组织)
土地使用权是否基于传统的法律制度?:
是
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
注释/具体说明:
Crop production is not possible in afforested areas, but financial support is available to compensate for the loss of income
木材生产
注释/具体说明:
Wood production for industrial or energy purposes is possible in an afforested area, which also generates significant income
产品多样性
收入和成本
农业收入
注释/具体说明:
Farm income may decrease but financial compensatory supports are available in the afforestation programs.
收入来源的多样性
生态影响
水循环/径流
水质
地表径流
土壤
土壤水分
注释/具体说明:
As trees have a larger leaf area, surface roughness and deeper rooting systems than grassland or cropland, afforestation could usually result in reduced soil moisture content.
土壤流失
注释/具体说明:
The density of the vegetation cover greatly influences the degree of soil loss reduction
养分循环/补给
土壤有机物/地下C
酸度
注释/具体说明:
Especially under coniferous forests soil acidity increases, but this only matters if cropland use would be planned again on the area in the future
生物多样性:植被、动物
植被覆盖
动物多样性
栖息地多样性
减少气候和灾害风险
洪水影响
滑坡/泥石流
干旱影响
碳和温室气体的排放
火灾风险
风速
微气候
注释/具体说明:
Under trees reduced solar radiation, a more moderate temperature regime, higher humidity can be observed.
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
水资源可用性
地下水/河流污染
缓冲/过滤能力
风力搬运沉积物
注释/具体说明:
Trees as physical barriers can significantly decrease wind erosion
温室气体的影响
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 | |
| 季节性温度 | 夏季 | 增加 | 适度 |
| 季雨量 | 夏季 | 减少 | 适度 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 好 |
| 局地风暴 | 适度 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 热浪 | 适度 |
| 极端冬季条件 | 好 |
| 干旱 | 适度 |
| 森林火灾 | 非常不好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 滑坡 | 适度 |
生物灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 昆虫/蠕虫侵扰 | 适度 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
消极
长期回报:
中性/平衡
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
轻度消极
长期回报:
中性/平衡
6.5 技术采用
- 1-10%
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 0-10%
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
否
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Reduce soil erosion |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Reduce carbon emission |
| Reduce soil erosion and groundwater pollution |
| Improves microclimate |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Loss of crop yield, loss of income | |
| The appearance of wild animals in agricultural area improves the risk of crop damage on the surrounding croplands | Building fences |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
2
- 与土地使用者的访谈
2
- 与SLM专业人员/专家的访谈
1
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
26/10/2022
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Special Issue "Afforestation and Reforestation: Drivers, Dynamics, and Impacts" in Forests (ISSN 1999-4907).
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
https://www.mdpi.com/journal/forests/special_issues/afforestation_reforestation
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Rodrigues, A.R., Botequim, B., Tavares, C. et al. Addressing soil protection concerns in forest ecosystem management under climate change. For. Ecosyst. 7, 34 (2020)
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
https://doi.org/10.1186/s40663-020-00247-y
7.3 链接到网络上的相关信息
标题/说明:
European NWRM platform
URL:
nwrm.eu
标题/说明:
Creating a forest: A step by step guiding
URL:
https://erc.cals.wisc.edu/woodlandinfo
7.4 一般注释
-
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Afforestation [海地]
Dans les mornes à Léogâne, la Croix Rouge Suisse (CRS) pratique la reforestation en participation communautaire.
- 编制者: Joana Eichenberger
模块
无模块