Bench Terracing [乌干达]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Philip Tibenderana
- 编辑者: Mirjam Nufer
- 审查者: Nicole Harari, Hanspeter Liniger, Alexandra Gavilano
Endinganire
technologies_616 - 乌干达
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Tear Fund Switzerland (Tear Fund Switzerland) - 瑞士1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
注释:
So far, where this technology has been applied, the water runoff has been reduced and the soils have been stabilised
1.5 参考关于SLM方法(使用WOCAT记录的SLM方法)的调查问卷

Catchment Based Integrated Water Resources Management [乌干达]
Catchment based integrated water resources management is a process which promotes the coordinated development and management of water, land and related resources in order to maximise economic and social welfare in an equitable manner without compromising the sustainability of vital eco systems
- 编制者: Philip Tibenderana
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
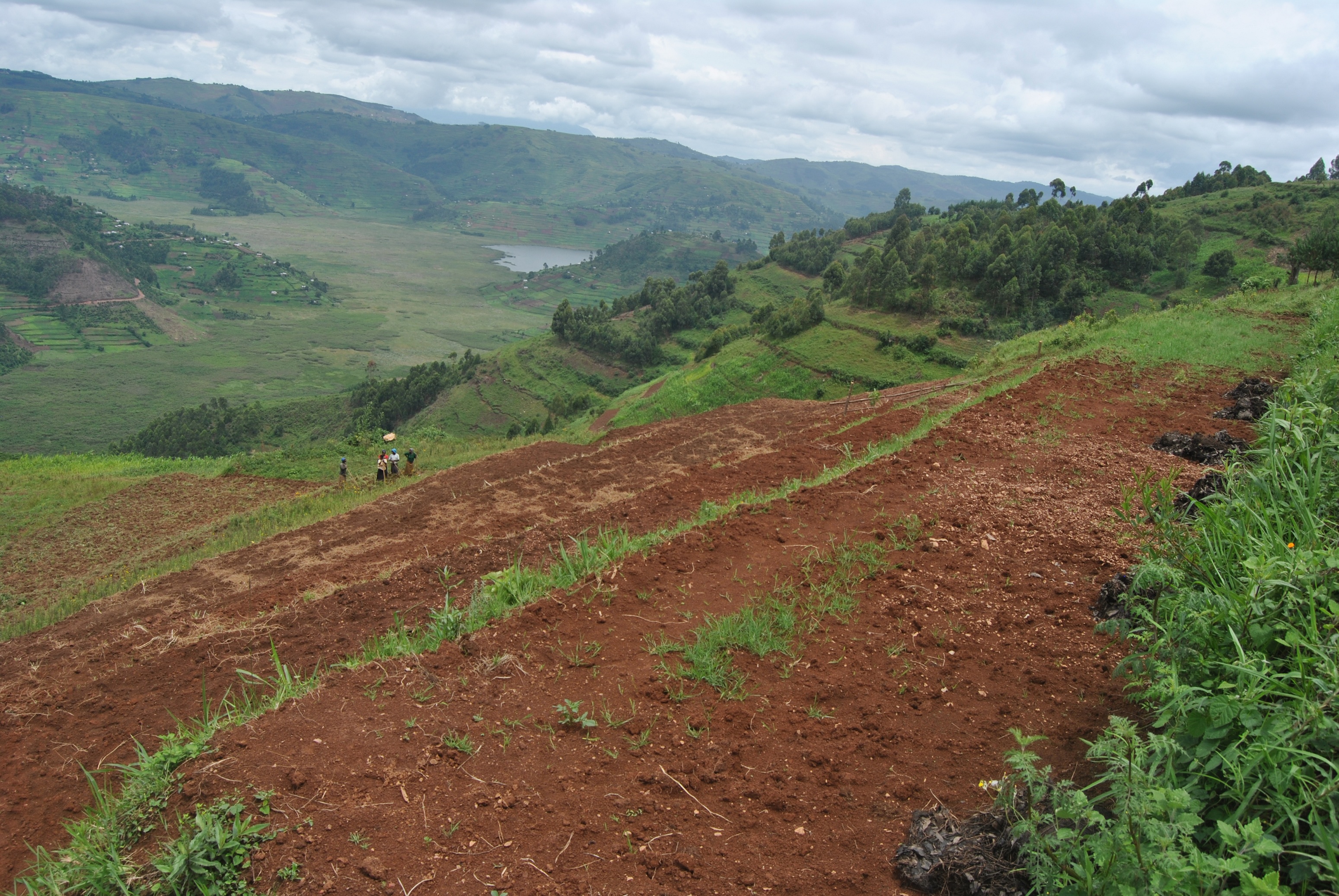
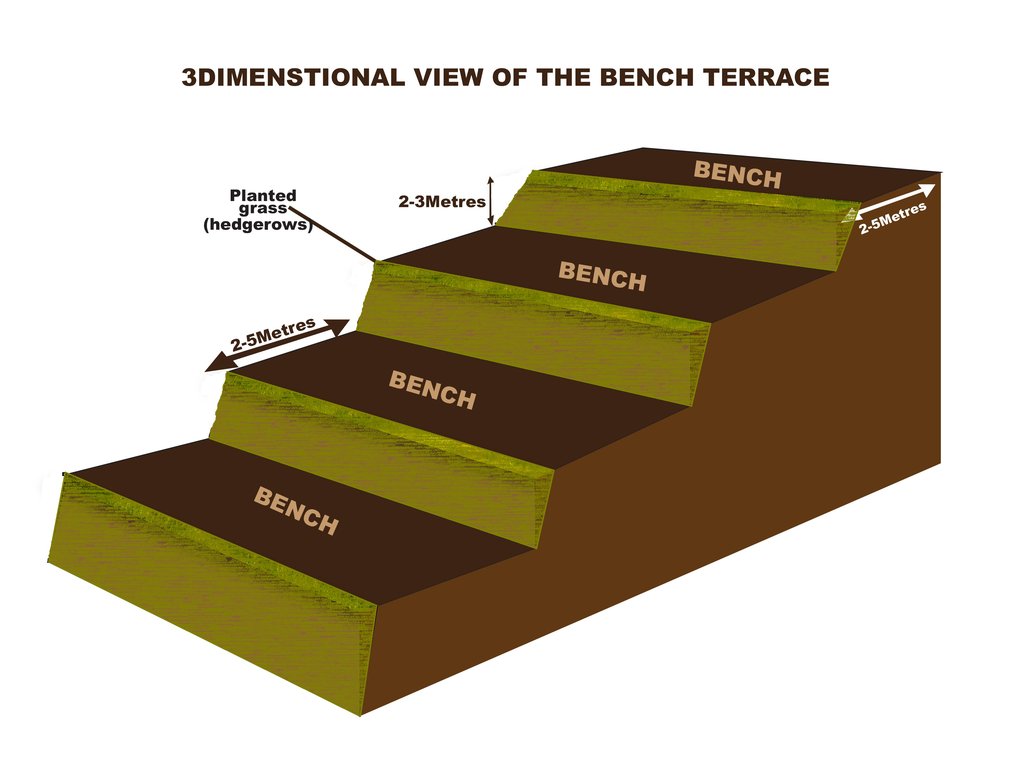
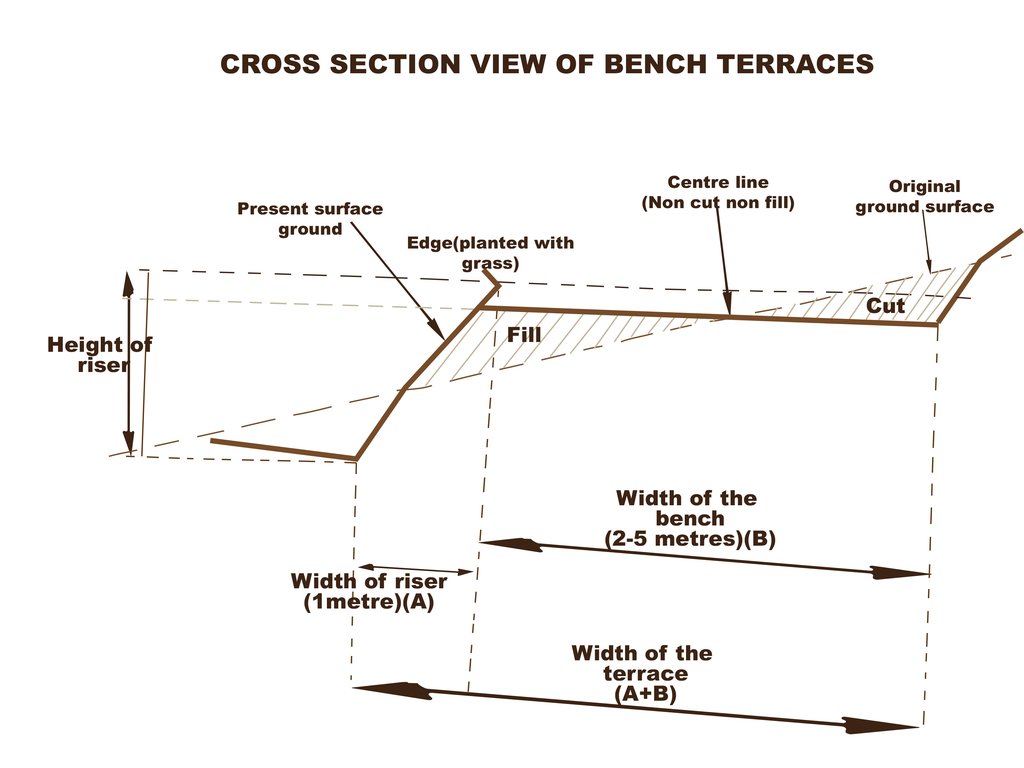
A bench terrace is an artificial horizontal strip dug across a steep landscape, with a riser ranging between 30 and 45 degrees. Bench terraces are constructed in series and help to minimize land degradation by rainwater runoff
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
A typical bench terrace takes the shape of a bench with a width of 3 to 5 meters and the height ranging from 1 to 2 meters, depending on the steepness of the slope, and the length is determined by the size of the plot, but typically 20 to 25 meters.
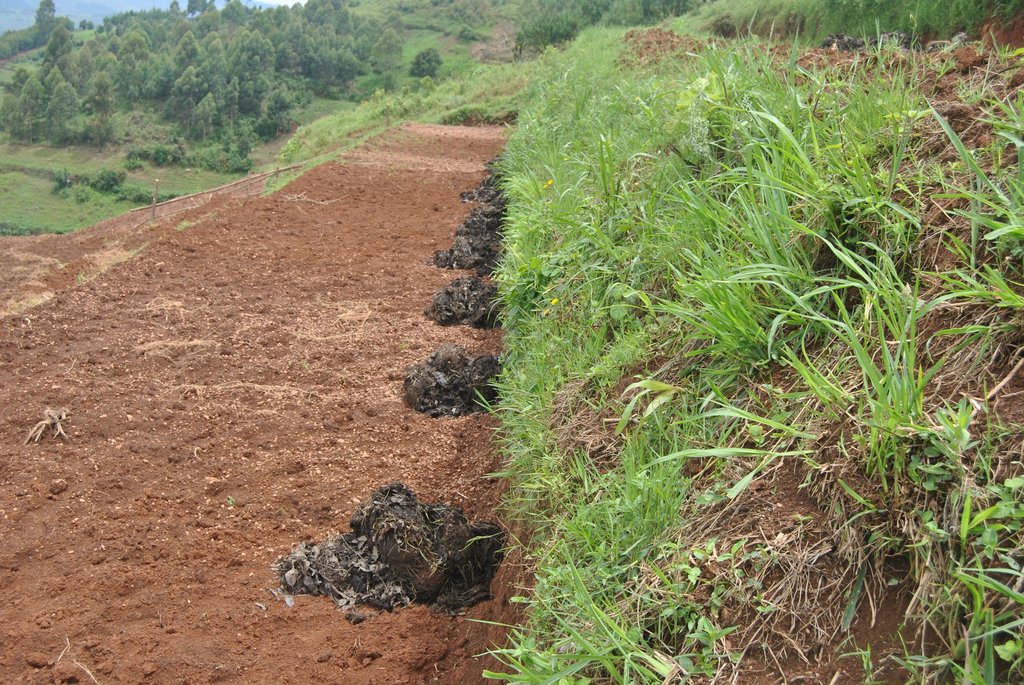
The top of the terrace riser is planted with a grass strip (referred to as a hedge row) commonly elephant grass or starria grass at a spacing of 200mm. The lower part of the riser is stabilized by planting creeping plant like couch grass to avoid erosion.
The technology is applied in already existing degraded farmlands, which are individually owned. An average farm size is less than half an acre.
This technology reduces the speed of water running down the slope during a downpour thereby reducing soil erosion and increasing water retention.
Areas which are prone to degradation by erosion are identified and later, the farmers are trained on benefits of this technology, how to construct and how to maintain the terraces by planting hegde rows.
This technology helps maintain the good top soil, which would have otherwise been washed down the slope into the valley, increases water retention, provides a flat ground for farm practices. All these ultimately increase crop yields.
What the land users dislike about this technology is that it is labour intensive. These labour intensive activities are done individually, on individual pieces of land using simple hand tools (hoes, spades and pick axes).
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
乌干达
区域/州/省:
South Western Region
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
注释:
This technology is implemented among farmers in a given area but is adopted by more farmers
Map
×2.6 实施日期
注明实施年份:
2015
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
The technology was introduced under the Integrated Water Resources Management Project to support farmers to mazimise land productivity
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 保护生态系统
- 结合其他技术保护流域/下游区域
- 降低灾害风险
- 适应气候变化/极端天气及其影响
- 减缓气候变化及其影响
- 创造有益的经济影响
- 创造有益的社会影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
是
具体说明混合土地使用(作物/放牧/树木):
- 农林业

农田
- 一年一作
- 多年一作(非木材)
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 谷类 - 大麦
- 谷物类 - 玉米
- 谷类 - 高粱
- 谷类 - 小麦(春季)
- 豆科牧草和豆类 - 豆子
- 豆科牧草和豆类 - 豌豆
- 根/块茎作物 - 土豆
- 烟草
- 蔬菜 - 叶菜(色拉、卷心菜、菠菜和其他)
每年的生长季节数:
- 2
具体说明:
September to January and March to June

牧场

森林/林地
- Trees, poles, fooder, firewood
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 改良的地面/植被覆盖
- 土壤肥力综合管理
- 横坡措施
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

植物措施
- V1:乔木和灌木覆盖层
- V2:草和多年生草本植物

结构措施
- S1:阶地
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wg:冲沟侵蚀/沟蚀
- Wm:块体运动/滑坡
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Dimensions are shown on the drawings
作者:
Kigezi Diocese Water and Sanitation Programme
日期:
12/12/2016
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术区域
注明尺寸和面积单位:
Acre
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Ugandan Shilling
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
3300.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
USD 2.1
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Mark out the plot of land to be terraced | After harvest of crops |
| 2. | Delineation of contours using the A-frame | After harvest of crops |
| 3. | Excavation (cut) and build up bench terrace by filling | After harvest of crops |
| 4. | Stabilising the riser by planting creeping grass and hedge rows | Onset of rains |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Construction of bench terraces in an area of 1 acre | person days | 324.0 | 2.1 | 680.4 | 30.0 |
| 设备 | Forked hoes | pieces | 1.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | |
| 设备 | Pick axes | pieces | 1.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | |
| 设备 | Spades | pieces | 1.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | |
| 植物材料 | Starria grass cuttings | sack | 80.0 | 7.0 | 560.0 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 1255.4 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 0.38 | |||||
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
Kigezi Diocese Water and Sanitation Programme
注释:
The cost of this technology is beyond the financial capacity of the land user hence the need for a subsidy
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Repair of damaged parts after heavy downpours | After rainy season |
| 2. | Maintenance of the hedge rows by triming and replanting empty spaces | Continuous |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Repair of broken parts of the terrace | days | 4.0 | 2.1 | 8.4 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Trimming of hedge rows | days | 8.0 | 2.1 | 16.8 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 25.2 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 0.01 | |||||
注释:
The initial investment of the equipment is adequate for maintenance at least for some years
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Establishment costs depend on the steepness of the slope, structure and deepness of the subsoil.
The maintenance costs depend of the degree of damage. Damages vary depending on the severity of rainfall. Soils that are more sandy are more likely to be swept than those that are clayey. The location of the terrace (whether up hill or down hill) will determine how badly the terrace will be damaged and hence the costs of repair. The steepness of the slope will also affect the extent to which the terraces are damaged
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
有关降雨的规范/注释:
Bi-modal rainfall pattern with long rainy season from Spetember to December then March to May
注明所考虑的参考气象站名称:
Kabale District Meterological Department
农业气候带
- 半湿润
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 不相关
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
> 50米
地表水的可用性:
好
水质(未处理):
不良饮用水(需要处理)
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
是
规律性:
偶然
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
Water quantity and quality is dependent on human activities and rainfall patterns
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
栖息地多样性:
- 中等
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 生计(自给)
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 贫瘠
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
性别:
- 女人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 青年人
- 中年人
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,未命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
用水权:
- 社区(有组织)
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
注释/具体说明:
The impact has come immediately with the first crop
作物质量
饲料生产
注释/具体说明:
Hedge rows are used as fodder
饲料质量
生产故障风险
产品多样性
注释/具体说明:
With terracing more variety of crops are being grown
生产区域
土地管理
收入和成本
农业投入费用
农业收入
收入来源的多样性
工作量
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
注释/具体说明:
It is expected to improve in the long term
健康状况
社区机构
SLM/土地退化知识
冲突缓解
生态影响
水循环/径流
地表径流
地下水位/含水层
注释/具体说明:
Recharge is hoped to increase in the long term as more farmers adopt the technology
土壤
土壤水分
土壤覆盖层
土壤流失
土壤堆积
注释/具体说明:
Soil which is trapped by the hedge rows
土壤有机物/地下C
注释/具体说明:
By use of manure
减少气候和灾害风险
洪水影响
注释/具体说明:
Flooding in the valley bottoms due to runoff
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
水资源可用性
注释/具体说明:
As more people adopt the technology, this is expected to increase
下游洪水
注释/具体说明:
Trend in downstream flooding is negative
下游淤积
注释/具体说明:
Trend in downstream siltation is negative
对邻近农田的破坏
注释/具体说明:
Soil which is washed down the slope
对公共/私人基础设施的破坏
注释/具体说明:
Especially on roads and water supply systems
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 未知 | |
| 季节性温度 | 旱季 | 增加 | 未知 |
| 季节性温度 | 湿季/雨季 | 增加 | 未知 |
| 年降雨量 | 减少 | 未知 | |
| 季雨量 | 湿季/雨季 | 减少 | 未知 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 好 |
| 局地雷暴 | 好 |
| 局地雹灾 | 好 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 陆地火灾 | 好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 非常好 |
| 山洪暴发 | 非常好 |
| 滑坡 | 非常好 |
生物灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 流行病 | 适度 |
| 昆虫/蠕虫侵扰 | 未知 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
非常积极
注释:
The adoption rate of this technology is gradual as people keep appreciating the benefits
6.5 技术采用
- 单例/实验
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
24 households (15 households were experimental and 9 have adopted)
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 91-100%
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
否
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Reduction of erosion damage by capturing or slowing down surface runoff |
| Trap and retain sediments from the slope above and accelerates re-vegetation process on the bare slopes |
| Creates a flat leveled ground for easier cultivation |
| The planted hedgerows provide fodder for the animals |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Increases soil moisture since the trapped water is retained as surface runoff is minimized |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Bench terraces cannot be constructed on slopes with sandy or rocky soils because they can collapse | N/A |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Bench terraces may cause sloughing if too much water infiltrates the soil | Suitable runoff outlets are created to carry away the excess runoff |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
Observation field visits to the constructed bench terraces
- 与土地使用者的访谈
Focus group discussion with 18 land users (5 females and 13 males)
- 与SLM专业人员/专家的访谈
Project implement staff
- 根据报告和其他现有文档进行编译
Integrated Water Resources Management project reports
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
07/09/2016
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Kigezi Diocese Water and Sanitation Programme, IWRM Annual Report (April 2015 - March 2016)
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
www.kigezi-watsan.ug
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Empowering communities through Water SMART agricultural practices
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
www.kigezi-watsan.ug
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
IWRM Pilot Report
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
www.kigezi-watsan.ug
7.3 链接到网络上的相关信息
标题/说明:
Bench terraces
URL:
www.fao.org/docrep/006/ad083e/ad083e07.htm
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Catchment Based Integrated Water Resources Management [乌干达]
Catchment based integrated water resources management is a process which promotes the coordinated development and management of water, land and related resources in order to maximise economic and social welfare in an equitable manner without compromising the sustainability of vital eco systems
- 编制者: Philip Tibenderana
模块
无模块