Recycling rice husks in Sri Lanka as a biochar-based slow-release urea fertilizer [斯里兰卡]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Head Soil Science
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
“anguru kata” pohora
technologies_6184 - 斯里兰卡
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
SLM专业人员:
Dissanayaka Lakmini
Coconut Research Institute
斯里兰卡
土地使用者:
Senarathna Renuka
斯里兰卡
土地使用者:
Nandasena Lekam Ralalage
斯里兰卡
土地使用者:
Kirihamige Vimalawathi
斯里兰卡
co-compiler:
Dharmakeerthi Saman
University of Peradeniya
斯里兰卡
co-compiler:
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Faculty of Agriculture, University of Peradeniya, Sri Lanka (AGRI.PDN) - 斯里兰卡1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
注释:
Urea is the type of nitrogen fertilizer available in Sri Lanka. Urea is readily soluble in water and hydrolyses to ammonia which in turn is converted to nitrate by microorganisms. Nitrate can be lost by leaching, volatilization, and denitrification in paddy fields. However, slow release fertilizer (SRF) releases the N in urea slowly to the soil and allows efficient uptake by the crop at the right time. Hence, it reduces the negative environmental impacts associated with N losses and also maintains adequate productivity in rice cultivation. In addition, this technology reduces CO2 emissions from rice husks to the atmosphere.
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
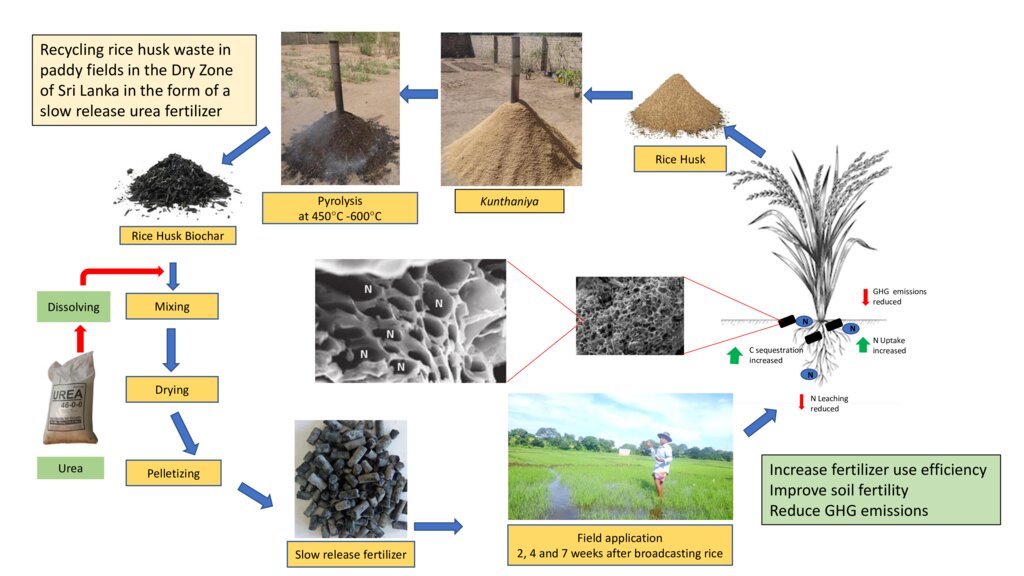
Rice husks, a waste product generated in rice mills, can release its carbon as a greenhouse gas (GHG) to the atmosphere through burning or decomposition. Converting it into biochar and intercalating (filled) with urea can produce a slow-release nitrogen (N) fertiliser that improves N-use efficiency while minimizing GHG emissions.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
Rice husks are often considered as a waste, and its carbon is released to the atmosphere as carbon dioxide (CO2) which is a greenhouse gas (GHG) through either decomposition or burning as a biofuel. However, rice husks can be converted into biochar – where its carbon is stable - with a large number of micro and sub-micron size pores in a honeycomb-like structure. Rice husk biochar was produced using an improved batch pyrolizer, “Kunthaniya”, at a temperature of between 450°C and 650°C. Pore spaces in rice husk biochar can be intercalated (filled) with urea and then, slow-release fertilizer (SRF) pellets can be produced through the use of a suitable biodegradable binder. This SRF has found to be more efficient in improving the N-use efficiency, hence the urea requirement of paddy fields in Sri Lanka can be reduced by about 25%, further contributing to environment sustainability. It has been well documented that biochar can improve soil physical, chemical and biological properties in a sustainable manner. This process is a contribution to creative recycling of agricultural waste.
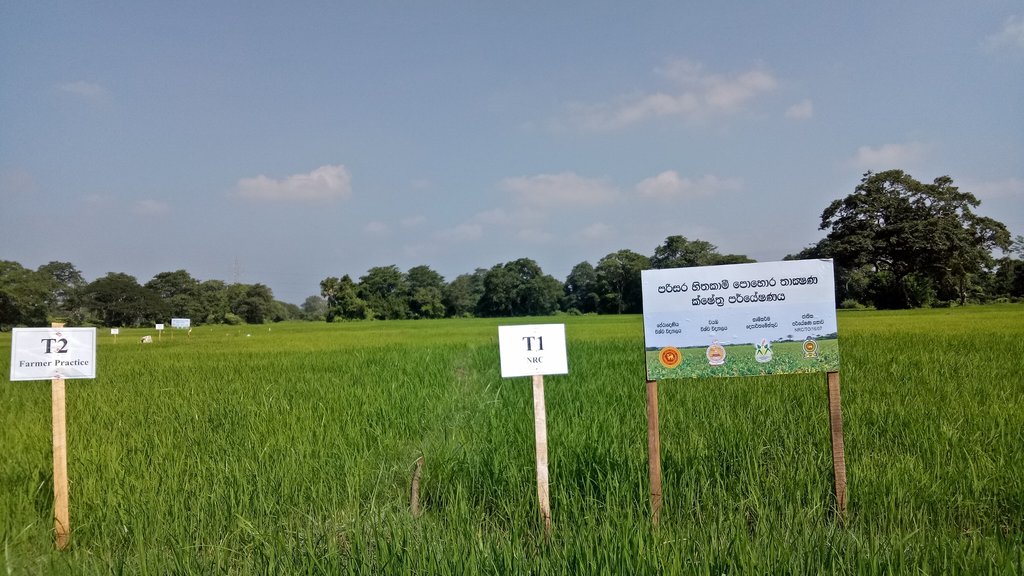
The SRF technology was evaluated against current farmer practice in rice cultivated area in Mahakanumulla village, Anuradhapura district, Sri Lanka. The area belongs to the Dry Zone of Sri Lanka (mean annual rainfall <1750mm). Rice is cultivated during two seasons, yala (May-September) and maha (December – February): the yala season is generally drier. Farmers rely on irrigation water supplied from a small village tank. The SRF was transported to farmers’ fields and applied at 2 weeks (@ 100 kg/ha), at 4 weeks (@ 170 kg/ha) and 7 weeks (@ 145 kg/ha) after direct seeding.
Farmers indicated that the granule size was large and light, hence they had some concerns about even distribution of fertilizer. They perceive that plants receive N slowly compared to granular urea - suggesting the slow releasing nature of the new technology. They did not observe any yield difference. Obtaining rice husks in large quantities from rice mills to produce biochar can sometimes be difficult in some areas of the country due to competition for use in the poultry industry. Some farmers may be discouraged to implement this technology due to lack of knowledge: this can be overcome through extension officers operating at field level.
This new technology qualifies as a sustainable land management practice in number of ways. First it increases N-use efficiency in paddy fields, second it reduces the urea requirement by 25% while sustaining productivity, third it recycles agricultural wastes in paddy fields, fourth, repeated application of SRF improves soil fertility through rice husk biochar, and finally it reduces GHG emissions.
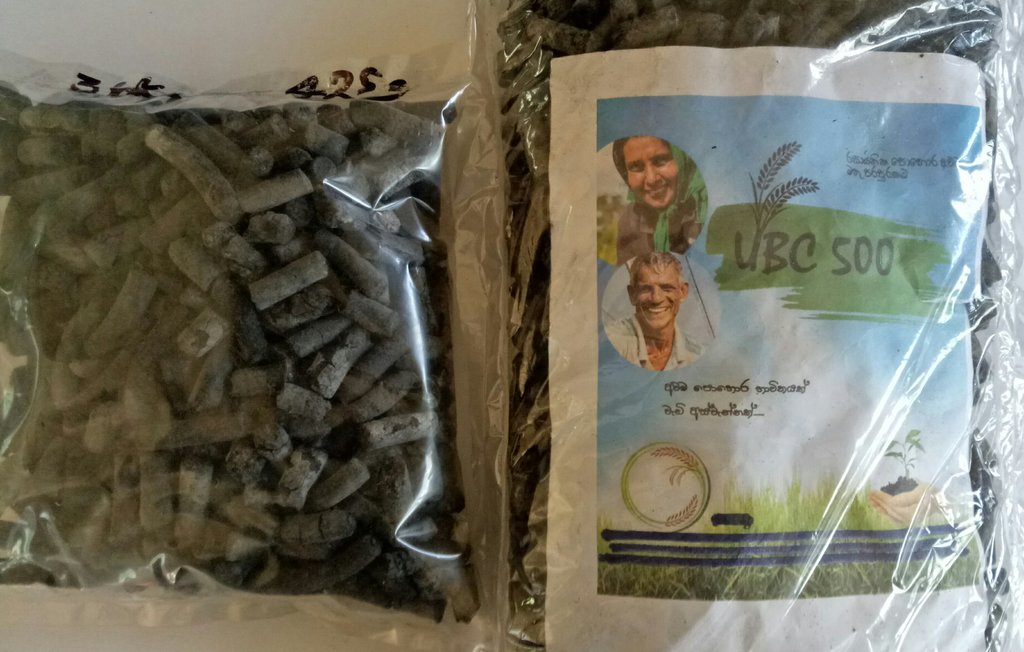
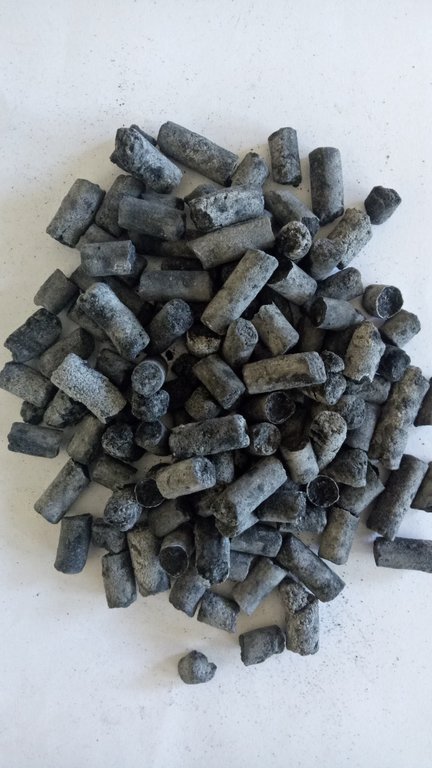
2.3 技术照片
关于照片的一般说明:
The photos show the application of SRF on farmers fields and the physical nature of the SRF.
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
斯里兰卡
区域/州/省:
North Central Province
有关地点的进一步说明:
Mahakanumulla village, Thirappane
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 适用于特定场所/集中在较小区域
技术现场是否位于永久保护区?:
否
Map
×2.6 实施日期
注明实施年份:
2021
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 在实验/研究期间
- 通过项目/外部干预
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 减缓气候变化及其影响
- 创造有益的经济影响
- 创造有益的社会影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
否

农田
- 一年一作
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 谷类 - 水稻(湿地)
年作制度:
连作湿地稻
每年的生长季节数:
- 2
具体说明:
yala and maha seasons
采用间作制度了吗?:
否
采用轮作制度了吗?:
否
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?:
- 否(继续问题3.4)
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 混合雨水灌溉
注释:
Rice farmers in Mahakanumulla mainly depend on irrigation water supplied from a small tank located above the rice fields. However, farmers do not irrigate rice fields if they receive adequate rainfall. But, increasingly, farmers depend on irrigation water due to decreasing rainfall during the growing season.
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 土壤肥力综合管理
- 废物管理/废水管理
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A2:有机质/土壤肥力
- A3:土壤表面处理
- A6:残株管理
A3:区分耕作制度:
A 3.3: Full tillage (< 30% soil cover)
A6:对残株管理作出具体说明:
A 6.4:保留
注释:
Application of SRF to the crop at the required growth stages to improve the soil fertility and, thus, crop productivity.
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)
- Cp:土壤污染

水质恶化
- Hp:地表水水质下降
- Hq:地下水水质下降
注释:
The SRF technology improves soil fertility by reducing nitrogen (N) loss from the soil due to leaching. And it also reduces accumulation of excess N in surface and ground water bodies, preventing water pollution.
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
注释:
The use of conventional N fertilizers to cultivate rice for a long period of time causes higher N losses from the soil and results a potential risk of environment pollution. Application as an SRF reduces the losses of N from the soil, increases crop nutrient uptake and increases crop productivity. The reduced losses mitigate soil fertility degradation and deterioration of water quality.
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Production of SRF: Rice husks were pyrolyzed using a locally modified “Kunthaniya” (a batch pyrolyser) to produce rice husk biochar. The temperature of the pyrolyser was around 450°C to 600°C with a heating rate of less than 20°C per hour. Pore structures were saturated using a urea solution through capillary action. The urea-intercalated rice husk biochar is then mixed with a biodegradable organic substance and pelletized using a medium scale pelletizer and dried to increase its mechanical properties such as resistance to disintegration and shear forces.
Field Experiment : Five paddy farmers were randomly selected from the command area of a small tank in the Mahakanumulla Village Tank Cascade System in the Dry Zone of Sri Lanka. The produced SRF was applied at a rate of 75% of recommended N in three split applications. Yields in SRF applied areas were compared against the current farmer practice. Experimental evidence showed that there is no yield reduction despite the reduction of nitrogen input into their fields.
作者:
H.P.G.T.N. Kulasinghe
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术区域
注明尺寸和面积单位:
1ha
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
LKR
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
275.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
1500
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Collection of paddy husk from rice milling stations | 2 months before cultivation |
| 2. | Pyrolyzing of paddy husk using a pyrolizer or a kunthani | 6 weeks before cultivation |
| 3. | Mixing with urea, ERP and other ingredients and pelletizing | 4 weeks before cultivation |
| 4. | Drying the pellets (SRF) | 2 weeks before cultivation |
| 5. | Packing and transporting SRF to the rice fields | 1 week before cultivation |
注释:
One of the major raw materials to produce SRF is rice husks and it can be supplied from rice milling stations, generally available year-round. However, there is competition for rice husks in the market because of demand from the poultry industry. Hence, finding rice husks is sometimes difficult in some areas of the country.
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Manufacturing SRF | Labour days | 2.5 | 1500.0 | 3750.0 | |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Urea | kg | 200.0 | 270.0 | 54000.0 | |
| 施工材料 | Binding materials 1 | kg | 10.0 | 25.0 | 250.0 | |
| 施工材料 | Binding materials 2 | kg | 10.0 | 250.0 | 2500.0 | |
| 施工材料 | Rice husk biochar | kg | 200.0 | 50.0 | 10000.0 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 70500.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 256.36 | |||||
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
Project funded by the National Research Council of Sri Lanka (Grant No. : NRC TO-16/07)
注释:
SRF was given to the farmer, free, for application. The cost of SRF was borne by the project funded by the National Research Council of Sri Lanka (Grant No. : NRC TO-16/07)
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Application of first dose of SRF | 2 weeks after direct seeding of rice |
| 2. | Application of second dose of SRF | 4 weeks after direct seeding of rice |
| 3. | Application of third dose of SRF | 7 weeks after direct seeding of rice |
注释:
Application of correct amount of SRF at the correct growth stage of the rice crop is important for efficient uptake of N to the crop and reduce losses.
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour for SRF application | Labour days | 3.0 | 1500.0 | 4500.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 4500.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 16.36 | |||||
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Labour availability and finding raw materials are the major factors that affect the cost.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
1400.00
有关降雨的规范/注释:
The Mahakanumulla area receives monsoon rainfall during two distinct seasons, namely yala (May – September) and maha (December – February), hence a bimodal rainfall pattern can be observed. The highest amount of rainfall is received during the maha season, in which most of the rainfall comes from the North-eastern monsoonal rains. Lesser rainfall is received from the South-west monsoonal rains, during the yala season. Hence prolonged dry periods are observed during the yala season. Other than that, this area receives rainfall from two inter-monsoonal rains (March-April and October-November).
注明所考虑的参考气象站名称:
Mahailuppallama, Anuradhapura
农业气候带
- 半干旱
Recorded minimum and maximum temperatures in the area are 20.8°C and 29.5°C respectively
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 不相关
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
The altitude of the area is 112m. An undulating pattern of topography is a distinct feature of this landscape. The rice is cultivated mainly in the valley area of the catena and other upland crops are cultivated in the crest area of the catena.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Rice growing soils of the Mahakanumulla area are classified as Alfisols (Typic endoaquaalf). The soil is poorly drained. The pH of the soil is in the neutral range (6.05-7.23). Soil EC (55.5-143.0 µs/cm, 1:2.5 soil:water) values did not show any occurrence of soil salinity. Av. P content of the soil (Olsen P) was low for rice growth (<5 mg/kg) and ranged from 2.9-3.5 mg/kg. Av. K content of the soils was medium to high for rice growth and ranged from 61.3-99 mg/kg.
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
< 5米
地表水的可用性:
好
水质(未处理):
仅供农业使用(灌溉)
水质请参考::
地下水和地表水
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
否
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
The amount of water supplied through the irrigation is limited during the dry season (yala). The water quality is affected by soil macro-nutrients (N, P, K) added as fertilizers to the soil. Due to the undulating topography of the landscape, those soil nutrients can wash-off from higher positions to lower positions due to surface runoff and leaching into the ground water and accumulating in the water bodies in the lower positions of the catena.
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
栖息地多样性:
- 中等
关于生物多样性的注释和进一步规范:
Number of different tree species, wild animals, birds, insects and aquatic life can be observed around Mahakanumulla village. Forest patches can be identified mostly around the small tank, and those areas are habitats for multiple wild animals and birds.
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 贫瘠
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
- 机械化/电动
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 中年人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Most of the land users are dependent on full time rice farming. But some land users use rice farming as a secondary source of income and do other jobs in the city. Most of the younger generation in the village are migrating for jobs in the cities.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
注释:
Rice is cultivated over a large area. However, single farmer manage relatively small fields (0.5-1 ha or 2-5 ha). The fields managed by farmers are located adjacent to each other.
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
用水权:
- 社区(有组织)
土地使用权是否基于传统的法律制度?:
否
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
注释:
The villagers of Mahaknumulla have access for most of the resources like infrastructure and energy/electricity/fuel. But most of the villagers/landusers complain about technical assistant/support for agricultural practices, finding markets for their produce and availability of good quality drinking water. The villagers go to nearby shops to buy day-to-day needs, but they have to go to the town, which is 8-10km away, for other services such as health and financial services.
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
SLM之前的数量:
6.5 t/ha (two seasons)
SLM之后的数量:
6.9 t/ha (two seasons)
注释/具体说明:
Although farmers could not observe a yield increase , experimental evidence suggests upto10% yield increase compared to farmer fertilizer management. A decrease in yield however not observed by farmers despite 25% reduction in N input. The above figures are for average of five farmers over two seasons.
作物质量
生产故障风险
产品多样性
生产区域
土地管理
水资源可用性和质量
饮用水的可用性
饮用水的质量
家畜用水的可用性
家畜用水的质量
灌溉用水的可用性
灌溉用水的质量
灌溉用水需求
收入和成本
农业投入费用
SLM之前的数量:
LKR 60,750.00/ha for urea
SLM之后的数量:
LKR 70,500/ha for SRF
注释/具体说明:
LKR 270/kg urea and LKR 167/kg of SRF. Expenses were calculated assuming all other costs are constants under two situations
农业收入
SLM之前的数量:
LKR 520,000/ha
SLM之后的数量:
LKR 552,000/ha
注释/具体说明:
LKR 80/kg of paddy. Average yields mentioned above was used to calculate the farm income. Therefore, farm income is expected to be increased more than the expenses in SRF applied fields.
收入来源的多样性
经济差异
工作量
注释/具体说明:
Although a longer time is required for SRF application because of higher bulk volume (175kg more), this application cost is negligible
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
注释/具体说明:
Expected improvements in productivity due to SRF application could strengthen the food security
健康状况
土地使用权/用水权
文化机会
娱乐机会
社区机构
国家机构
SLM/土地退化知识
注释/具体说明:
Farmers gain awareness through extension programmes when implementing the SRF technology
冲突缓解
社会经济弱势群体的情况
生态影响
水循环/径流
水量
水质
注释/具体说明:
N accumulation in water bodies is reducing due to lower N losses of SRF
水的回收/收集
地表径流
多余水的排放
地下水位/含水层
蒸发
土壤
土壤水分
注释/具体说明:
It is expected to have a better moisture content as a result of accumulation of biochar with repeated application of SRF
土壤覆盖层
注释/具体说明:
Experimental evidence suggests that soil cover is more with rice plants that grow better and tiller more due to better N utilization for crop growth
土壤流失
土壤堆积
土壤结壳/密封
土壤压实
养分循环/补给
SLM之前的数量:
N uptake: 167 kg of N/ha
SLM之后的数量:
N uptake: 219 kg of N/ha
注释/具体说明:
Higher uptake of N by rice plants due to SRF application, nutrient recycling is expected to be improved. The above values were obtained from 5 farmer fields in the year 2021.
盐度
SLM之前的数量:
Electrical Conductivity : 0.11 dS/m
SLM之后的数量:
Electrical Conductivity : 0.09 dS/m
注释/具体说明:
The above values were obtained from 5 farmer fields in the year 2021.
土壤有机物/地下C
注释/具体说明:
SRF contains biochar which is a good source to improve the soil C.
酸度
SLM之前的数量:
pH : 7.42
SLM之后的数量:
pH : 7.38
注释/具体说明:
The above values were obtained from 5 farmer fields in the year 2021.
生物多样性:植被、动物
植被覆盖
注释/具体说明:
Efficient uptake of N cause to improve the crop growth, thereby vegetation cover
生物量/地上C
SLM之前的数量:
5.2 t/ha (straw) + 8.1 (grain)
SLM之后的数量:
6.0 t/ha (straw) + 8.7 t/ha (grain)
注释/具体说明:
Higher crop growth results higher biomass production. The above values were obtained from 5 farmer fields in the year 2021.
植物多样性
外来入侵物种
动物多样性
有益物种
栖息地多样性
害虫/疾病控制
减少气候和灾害风险
洪水影响
滑坡/泥石流
干旱影响
飓风、暴雨的影响
碳和温室气体的排放
火灾风险
风速
微气候
注释/具体说明:
Because of the better growth of the rice plants micro climate in the paddy fields is expected to be improved.
对现场影响的评估(测量)进行具体说明:
Plant growth parameters and yield
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
水资源可用性
旱季稳定可靠的水流
下游洪水
下游淤积
地下水/河流污染
注释/具体说明:
N accumulation in water bodies is expected to be reduced due to lower N losses from SRF
缓冲/过滤能力
风力搬运沉积物
对邻近农田的破坏
对公共/私人基础设施的破坏
温室气体的影响
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 未知 | |
| 年降雨量 | 减少 | 未知 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
稍微积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
稍微积极
6.5 技术采用
- 单例/实验
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
5 farmers/households
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
否
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| This technology uses less chemical fertilizer and therefore it is good for their health and environment |
| This technology gives better crop growth and slightly higher yield |
| Biochar could improve the fertility of the soil |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| SRF reduces the N losses from the soil and allows the rice crop to uptake N effectively from soil at required growth stages. Efficient N uptake promotes the crop growth and increase the productivity. |
| Reduced N losses of SRF directly influence the water quality by reducing the losses of N through surface runoff and leaching and avoid accumulation in water bodies at the lower positions of the landscape. |
| Rice husks, which is are good source of C, are utilized for SRF production; hence it promotes C sequestration as it is added back to the soil as biochar. It improves the soil organic carbon pool and promotes carbon sequestration in soil. |
| Utilizing rice husks by returning back to the rice fields is an effective solution for rice waste management. |
| If the SRF production technology can be transferred to farmers, their societies can produce the SRF by themselves from the wastes generated in small scale rice mills. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Additional cost despite reduced chemical fertilizer | increased crop yields can partially compensate this. They can produce their own SRF if the production technology is transferred to them |
| Uneven distribution of nitrogen in the field | Changing the water management practices that have been currently adopted by farmers |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| The raw materials need to be formulated accurately to get the benefits of the technology. Hence, technical knowledge and experience is required when preparing SRF. | Proper guidance and technical support from the beginning to the end of the process is essential. This can be achieved through educating and training extension officers to teach and disseminate knowledge for farmers. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
More than 10 field visits
- 与土地使用者的访谈
Interviewed 5 farmers
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
08/05/2021
注释:
Plant growth measurements were collected 7 weeks after broadcasting rice and yield data collected after 3 ½ months after broadcasting.
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Preparation of Biochar as a Soil Amendment from Rice Husk and Corn Cob by Slow Pyrolysis Process, S.T. Munasinghe, R.S. Dharmakeerthi, P. Weerasinghe and L.G.S. Madusanka, ISSN 0041-3224
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Tropical Agriculturist Journal
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Changes in Structural and Chemical Properties of Rice Husk Biochar Co-pyrolysed with Eppawala Rock Phosphate under Different Temperatures, D.K.R.P.L. Dissanayake, R.S. Dharmakeerthi, A.K. Karunarathna and W.S. Dandeniya, ISSN: 2706-0233
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Tropical Agricultural Research Journal
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Biochar Based Slow-Release Urea Fertilizer: Production and Assessing the Effects on Growth of Lowland Rice and Nitrogen Dynamics in an Alfisol, M.K.N.W. Jayarathna, R.S. Dharmakeerthi and W.M.U.K. Rathnayaka, ISSN: 2706-0233
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Tropical Agricultural Research Journal
7.3 链接到网络上的相关信息
标题/说明:
Changes in Structural and Chemical Properties of Rice Husk Biochar Co-pyrolysed with Eppawala Rock Phosphate under Different Temperatures
URL:
http://192.248.43.153/bitstream/1/3160/2/PGIATAR_30_1_19.pdf
标题/说明:
Biochar Based Slow-Release Urea Fertilizer: Production and Assessing the Effects on Growth of Lowland Rice and Nitrogen Dynamics in an Alfisol
URL:
https://tar.sljol.info/articles/abstract/10.4038/tar.v32i2.8464/
7.4 一般注释
The WOCAT questionnaire on SLM technologies covers all the aspects that can affect on the sustainability of natural and human environment.
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块