Recycling rice husks in Sri Lanka as a biochar-based slow-release urea fertilizer [ប្រទេសស្រីលង្កា]
- ការបង្កើត៖
- បច្ចុប្បន្នភាព
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Head Soil Science
- អ្នកកែសម្រួល៖ –
- អ្នកត្រួតពិនិត្យច្រើនទៀត៖ William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
“anguru kata” pohora
technologies_6184 - ប្រទេសស្រីលង្កា
ពិនិត្យមើលគ្រប់ផ្នែក
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់1. ព័ត៌មានទូទៅ
1.2 ព័ត៌មានលម្អិតពីបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ និងស្ថាប័នដែលចូលរួមក្នុងការវាយតម្លៃ និងចងក្រងឯកសារនៃបច្ចេកទេស
បុគ្គលសំខាន់ម្នាក់ (ច្រើននាក់)
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM:
Dissanayaka Lakmini
Coconut Research Institute
ប្រទេសស្រីលង្កា
អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
Senarathna Renuka
ប្រទេសស្រីលង្កា
អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
Nandasena Lekam Ralalage
ប្រទេសស្រីលង្កា
អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
Kirihamige Vimalawathi
ប្រទេសស្រីលង្កា
co-compiler:
Dharmakeerthi Saman
University of Peradeniya
ប្រទេសស្រីលង្កា
co-compiler:
ឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
Faculty of Agriculture, University of Peradeniya, Sri Lanka (AGRI.PDN) - ប្រទេសស្រីលង្កា1.3 លក្ខខណ្ឌទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈ វ៉ូខេត
អ្នកចងក្រង និង(បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ)យល់ព្រមទទួលយកនូវលក្ខខណ្ឌនានាទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈវ៉ូខេត:
បាទ/ចា៎
1.4 សេចក្តីប្រកាសស្តីពីចីរភាពនៃការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស
តើបច្ចេកទេសដែលបានពណ៌នានេះមានបញ្ហាដែលផ្តោតលើការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី, បើដូច្នេះវាមិនអាចត្រូវបានប្រកាសថាជាបច្ចេកទេសនៃការគ្រប់គ្រងប្រកបដោយចីរភាពទេ?
ទេ
មតិយោបល់:
Urea is the type of nitrogen fertilizer available in Sri Lanka. Urea is readily soluble in water and hydrolyses to ammonia which in turn is converted to nitrate by microorganisms. Nitrate can be lost by leaching, volatilization, and denitrification in paddy fields. However, slow release fertilizer (SRF) releases the N in urea slowly to the soil and allows efficient uptake by the crop at the right time. Hence, it reduces the negative environmental impacts associated with N losses and also maintains adequate productivity in rice cultivation. In addition, this technology reduces CO2 emissions from rice husks to the atmosphere.
2. ការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស SLM
2.1 ការពណ៌នាដោយសង្ខេបពីបច្ចេកទេស
និយមន័យបច្ចេកទេស:
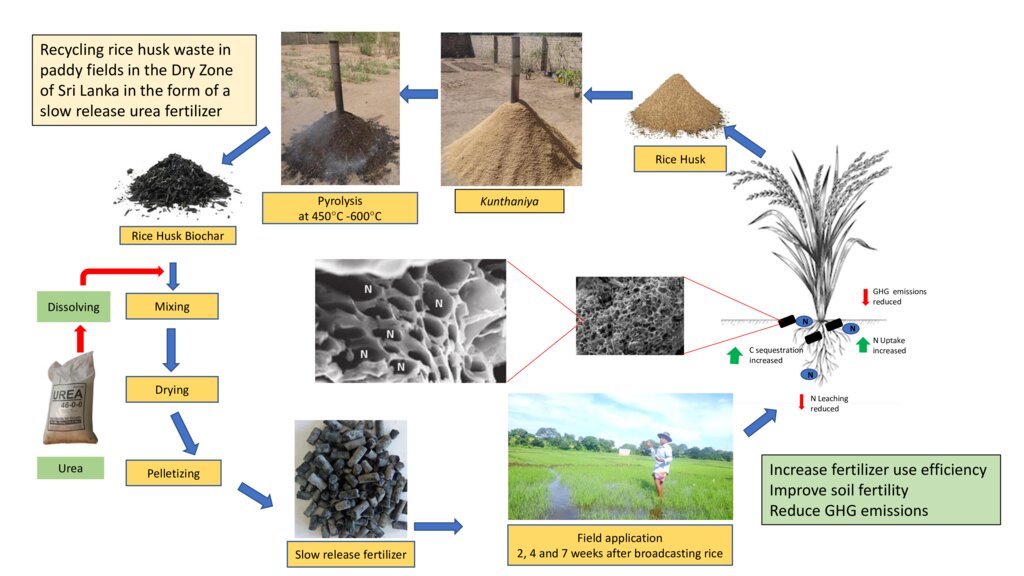
Rice husks, a waste product generated in rice mills, can release its carbon as a greenhouse gas (GHG) to the atmosphere through burning or decomposition. Converting it into biochar and intercalating (filled) with urea can produce a slow-release nitrogen (N) fertiliser that improves N-use efficiency while minimizing GHG emissions.
2.2 ការពណ៌នាលម្អិតពីបច្ចេកទេស
ការពណ៌នា:
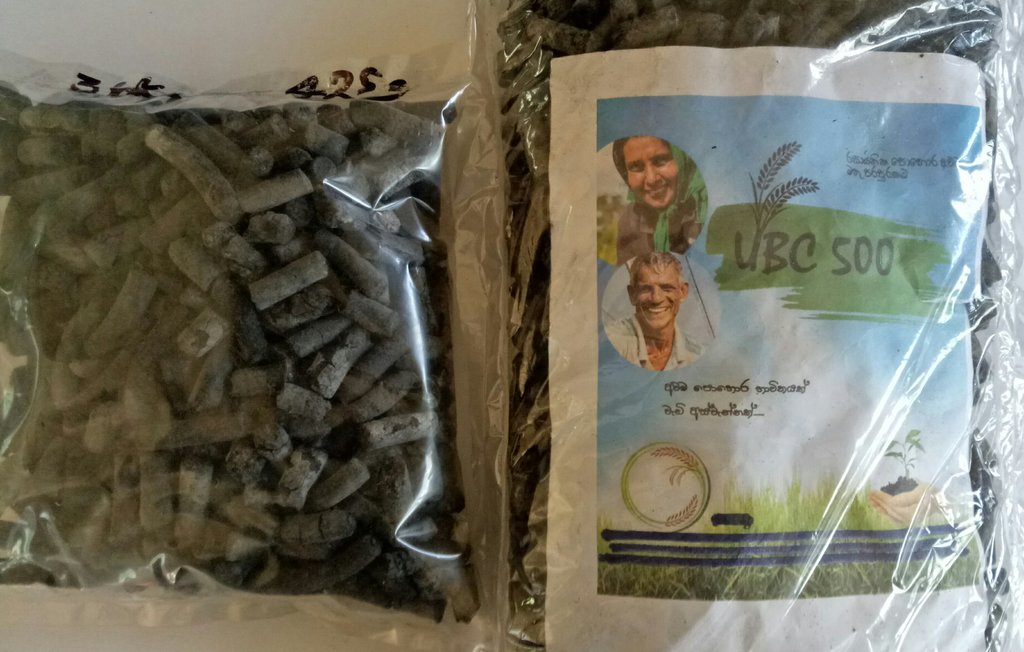
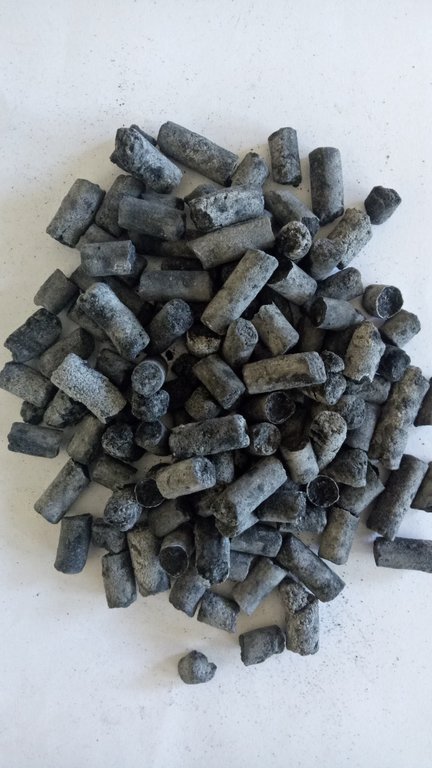
Rice husks are often considered as a waste, and its carbon is released to the atmosphere as carbon dioxide (CO2) which is a greenhouse gas (GHG) through either decomposition or burning as a biofuel. However, rice husks can be converted into biochar – where its carbon is stable - with a large number of micro and sub-micron size pores in a honeycomb-like structure. Rice husk biochar was produced using an improved batch pyrolizer, “Kunthaniya”, at a temperature of between 450°C and 650°C. Pore spaces in rice husk biochar can be intercalated (filled) with urea and then, slow-release fertilizer (SRF) pellets can be produced through the use of a suitable biodegradable binder. This SRF has found to be more efficient in improving the N-use efficiency, hence the urea requirement of paddy fields in Sri Lanka can be reduced by about 25%, further contributing to environment sustainability. It has been well documented that biochar can improve soil physical, chemical and biological properties in a sustainable manner. This process is a contribution to creative recycling of agricultural waste.
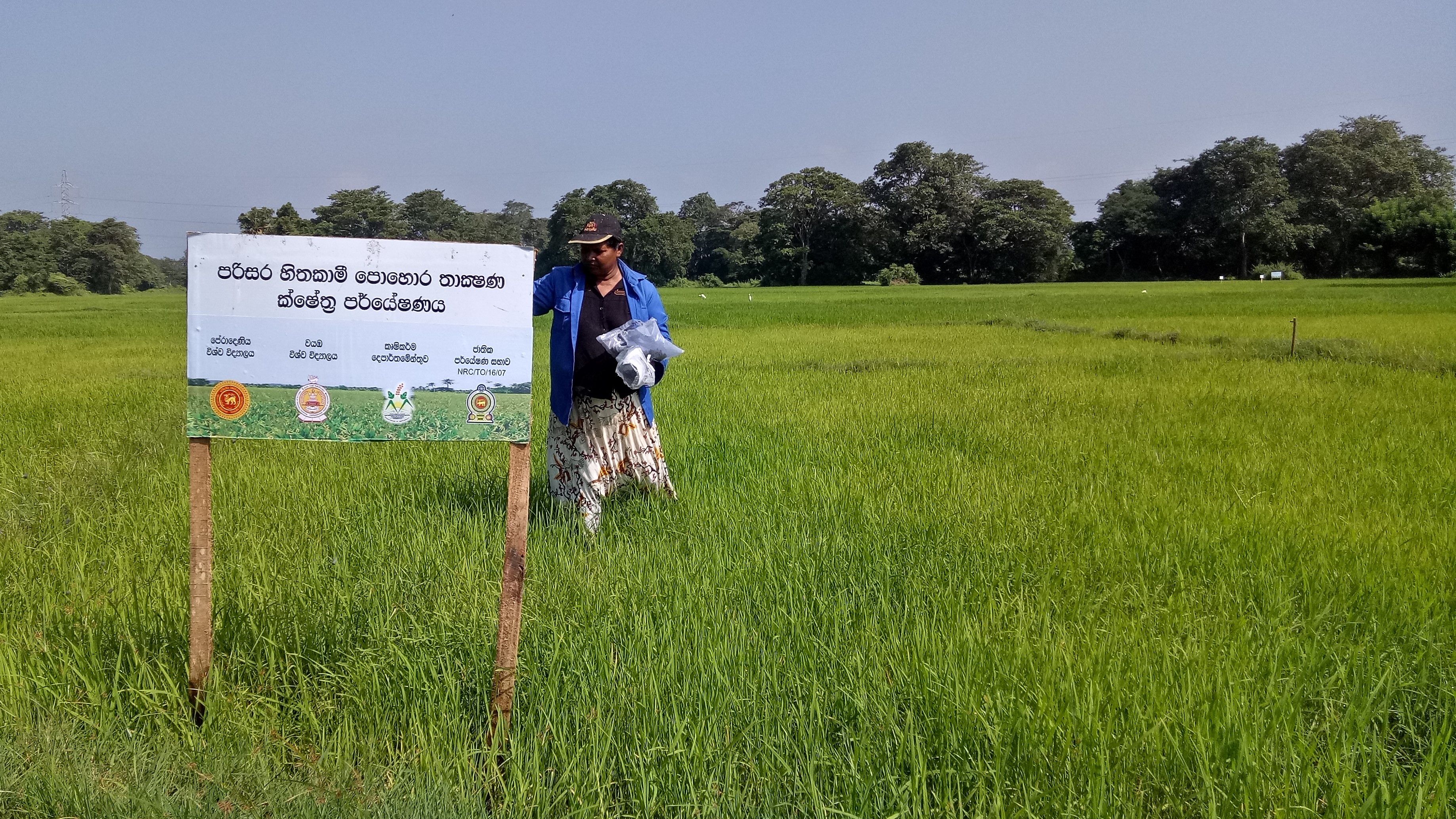
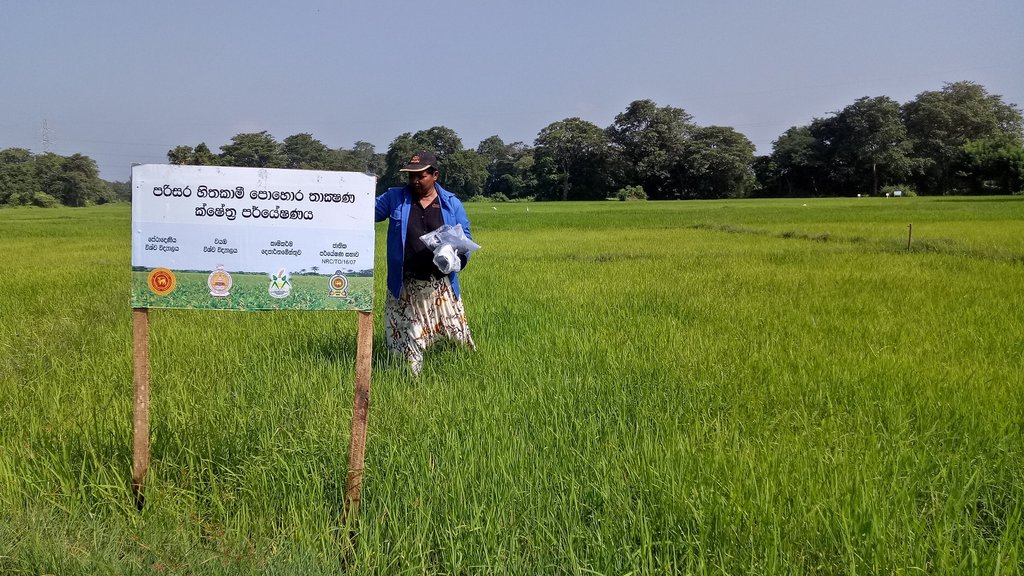
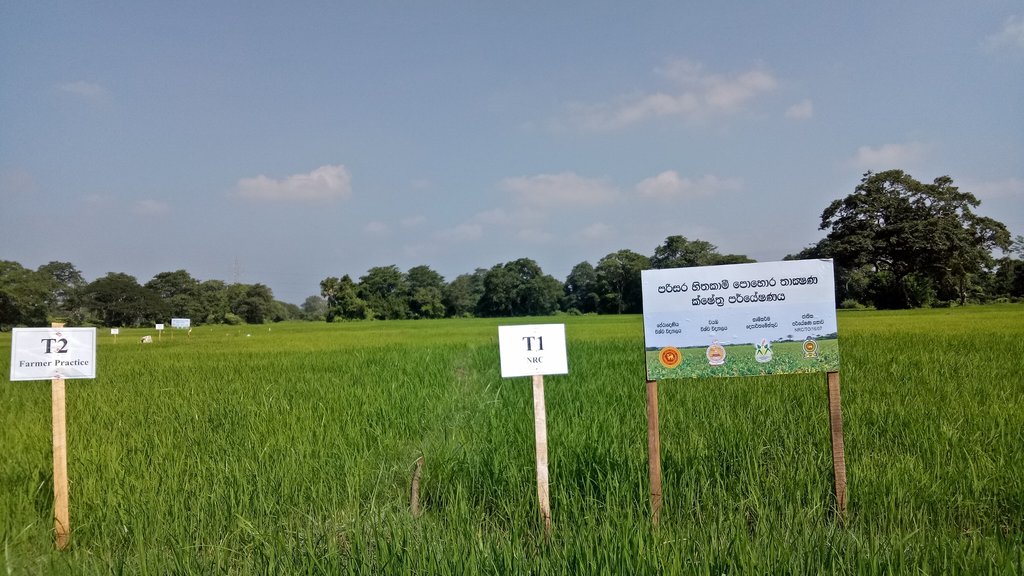
The SRF technology was evaluated against current farmer practice in rice cultivated area in Mahakanumulla village, Anuradhapura district, Sri Lanka. The area belongs to the Dry Zone of Sri Lanka (mean annual rainfall <1750mm). Rice is cultivated during two seasons, yala (May-September) and maha (December – February): the yala season is generally drier. Farmers rely on irrigation water supplied from a small village tank. The SRF was transported to farmers’ fields and applied at 2 weeks (@ 100 kg/ha), at 4 weeks (@ 170 kg/ha) and 7 weeks (@ 145 kg/ha) after direct seeding.
Farmers indicated that the granule size was large and light, hence they had some concerns about even distribution of fertilizer. They perceive that plants receive N slowly compared to granular urea - suggesting the slow releasing nature of the new technology. They did not observe any yield difference. Obtaining rice husks in large quantities from rice mills to produce biochar can sometimes be difficult in some areas of the country due to competition for use in the poultry industry. Some farmers may be discouraged to implement this technology due to lack of knowledge: this can be overcome through extension officers operating at field level.
This new technology qualifies as a sustainable land management practice in number of ways. First it increases N-use efficiency in paddy fields, second it reduces the urea requirement by 25% while sustaining productivity, third it recycles agricultural wastes in paddy fields, fourth, repeated application of SRF improves soil fertility through rice husk biochar, and finally it reduces GHG emissions.
2.3 រូបភាពនៃបច្ចេកទេស
កំណត់សម្គាល់ទូទៅនៃរូបថត/រូភាព:
The photos show the application of SRF on farmers fields and the physical nature of the SRF.
2.5 ប្រទេស/តំបន់/ទីតាំងកន្លែង ដែលបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានអនុវត្ត និងបានគ្រប់ដណ្តប់ដោយការវាយតម្លៃនេះ
ប្រទេស:
ប្រទេសស្រីលង្កា
តំបន់/រដ្ឋ/ខេត្ត:
North Central Province
បញ្ជាក់បន្ថែមពីលក្ខណៈនៃទីតាំង:
Mahakanumulla village, Thirappane
បញ្ជាក់ពីការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស:
- អនុវត្តនៅកន្លែងជាក់លាក់មួយ/ ប្រមូលផ្តុំនៅតំបន់តូចៗ
តើបច្ចេកទេស (មួយ ឬច្រើន) ទាំងនោះស្ថិតនៅក្នុងតំបន់ការពារជាអចិន្ត្រៃយ៍ណាមួយដែរឬទេ?
ទេ
Map
×2.6 កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត
បង្ហាញឆ្នាំនៃការចុះអនុវត្ត:
2021
2.7 ការណែនាំពីបច្ចេកទេស
សូមបញ្ជាក់តើបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានណែនាំឱ្យអនុវត្តដោយរបៀបណា:
- ពេលកំពុងពិសោធន៍
- តាមរយៈគម្រោង / អន្តរាគមន៍ពីខាងក្រៅ
3. ចំណាត់ថ្នាក់នៃបច្ចេកទេស SLM
3.1 គោលបំណងចម្បង (១ ឬច្រើន) នៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
- ធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងនូវផលិតកម្ម
- កាត់បន្ថយ, បង្ការ, ស្តារឡើងវិញនូវការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
- កាត់បន្ថយការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ និងផលប៉ះពាល់របស់វា
- បង្កើតផលប្រយោជន៍សេដ្ឋកិច្ច
- បង្កើតផលប្រយោជន៍សង្គម
3.2 ប្រភេទដីប្រើប្រាស់មួយប្រភេទ (ច្រើនប្រភេទ) ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
ដីប្រើប្រាស់ចម្រុះនៅលើដីតែមួយ:
ទេ

ដីដាំដំណាំ
- ដំណាំប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
ដំណាំប្រចាំឆ្នាំ - បញ្ជាក់ប្រភេទដំណាំ:
- ធញ្ញជាតិ - ស្រូវ (តំបន់ដីសើម)
ប្រព័ន្ធដាំដុះដំណាំប្រចាំឆ្នាំ:
ដាំដំណាំបន្តបន្ទាប់ពីស្រូវវស្សា
ចំនួនសារដែលដាំដំណាំក្នុងមួយឆ្នាំ:
- 2
សូមបញ្ជាក់:
yala and maha seasons
តើជាការអនុវត្តន៍ដំណាំចន្លោះ?
ទេ
តើជាការអនុវត្តន៍ដំណាំវិលជុំ?
ទេ
3.3 បន្ទាប់ពីអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើដីប្រើប្រាស់មានការប្រែប្រួលដែររឺទេ?
បន្ទាប់ពីអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើដីប្រើប្រាស់មានការប្រែប្រួលដែររឺទេ?
- ទេ (បន្តទៅសំណួរ 3.4)
3.4 ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹក
ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹកនៅកន្លែងអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស:
- ទឹកភ្លៀង និងប្រព័ន្ធស្រោចស្រព
មតិយោបល់:
Rice farmers in Mahakanumulla mainly depend on irrigation water supplied from a small tank located above the rice fields. However, farmers do not irrigate rice fields if they receive adequate rainfall. But, increasingly, farmers depend on irrigation water due to decreasing rainfall during the growing season.
3.5 ក្រុម SLM ដែលបច្ចេកទេសស្ថិតនៅក្នុង
- ការគ្រប់គ្រងជីជាតិដីតាមបែបចម្រុះ
- ការគ្រប់គ្រងកាកសំណល់/ ការគ្រប់គ្រងទឹកកង្វក់
3.6 វិធានការ SLM ដែលបញ្ចូលនូវបច្ចេកទេស

វិធានការក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ
- A2: សារធាតុសរីរាង្គ/ជីជាតិដី
- A3: ការរក្សាស្រទាប់ដីខាងលើ
- A6: ការគ្រប់គ្រងកាកសំណល់
A3: ប្រព័ន្ធភ្ជួររាស់ខុសៗគ្នា:
A 3.3: Full tillage (< 30% soil cover)
A6: បញ្ជាក់ពីការគ្រប់គ្រងកាកសំណល់:
A 6.4: រក្សាទុក
មតិយោបល់:
Application of SRF to the crop at the required growth stages to improve the soil fertility and, thus, crop productivity.
3.7 កំណត់ប្រភេទនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដីសំខាន់ៗដែលបច្ចេកទេសនេះបានដោះស្រាយ

ការធ្លាក់ចុះសារធាតុគីមីក្នុងដី
- Cn: ការថយចុះជីជាតិ និងកាត់បន្ថយបរិមាណសារធាតុសរីរាង្គ (មិនកើតឡើងដោយការហូរច្រោះទេ)
- Cp: ការបំពុលដី

ការបាត់បង់ទឹក
- Hp: ការថយចុះគុណភាពទឹកនៅលើផ្ទៃដី
- Hq: ការថយចុះគុណភាពទឹកនៅក្រោមដី
មតិយោបល់:
The SRF technology improves soil fertility by reducing nitrogen (N) loss from the soil due to leaching. And it also reduces accumulation of excess N in surface and ground water bodies, preventing water pollution.
3.8 ការពារ កាត់បន្ថយ ឬស្តារឡើងវិញនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
បញ្ជាក់ពីគោលដៅរបស់បច្ចេកទេស ដែលផ្តោតទៅការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី:
- ការកាត់បន្ថយការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
មតិយោបល់:
The use of conventional N fertilizers to cultivate rice for a long period of time causes higher N losses from the soil and results a potential risk of environment pollution. Application as an SRF reduces the losses of N from the soil, increases crop nutrient uptake and increases crop productivity. The reduced losses mitigate soil fertility degradation and deterioration of water quality.
4. បច្ចេកទេសជាក់លាក់ សកម្មភាពអនុវត្ត ធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
4.1 គំនូសបច្ចេកទេសនៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
លក្ខណៈពិសេសនៃបច្ចេកទេស (ទាក់ទងនឺងគំនូរបច្ចេកទេស):
Production of SRF: Rice husks were pyrolyzed using a locally modified “Kunthaniya” (a batch pyrolyser) to produce rice husk biochar. The temperature of the pyrolyser was around 450°C to 600°C with a heating rate of less than 20°C per hour. Pore structures were saturated using a urea solution through capillary action. The urea-intercalated rice husk biochar is then mixed with a biodegradable organic substance and pelletized using a medium scale pelletizer and dried to increase its mechanical properties such as resistance to disintegration and shear forces.
Field Experiment : Five paddy farmers were randomly selected from the command area of a small tank in the Mahakanumulla Village Tank Cascade System in the Dry Zone of Sri Lanka. The produced SRF was applied at a rate of 75% of recommended N in three split applications. Yields in SRF applied areas were compared against the current farmer practice. Experimental evidence showed that there is no yield reduction despite the reduction of nitrogen input into their fields.
ឈ្មោះអ្នកនិពន្ធ:
H.P.G.T.N. Kulasinghe
4.2 ព័ត៌មានទូទៅដែលពាក់ព័ន្ធនឹងការគណនាធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
កំណត់របៀបនៃការគណនាថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូល:
- ក្នុងតំបន់អនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
កំណត់ទំហំ និងឯកត្តាផ្ទៃដី:
1ha
ផ្សេងៗ/ រូបិយប័ណ្ណជាតិ (បញ្ជាក់):
LKR
បើពាក់ព័ន្ធសូមកំណត់អត្រាប្តូរប្រាក់ពីដុល្លាទៅរូបិយប័ណ្ណតំបន់ (ឧ. 1 ដុល្លារ = 79.9 រៀលនៃរូបិយប័ណ្ណប្រេស៊ីល) ៖ 1 ដុល្លារ =:
275,0
កំណត់ថ្លៃឈ្នួលជាមធ្យមនៃការជួលកម្លាំងពលកម្មក្នុងមួយថ្ងៃ:
1500
4.3 សកម្មភាពបង្កើត
| សកម្មភាព | រយៈពេល (រដូវកាល) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Collection of paddy husk from rice milling stations | 2 months before cultivation |
| 2. | Pyrolyzing of paddy husk using a pyrolizer or a kunthani | 6 weeks before cultivation |
| 3. | Mixing with urea, ERP and other ingredients and pelletizing | 4 weeks before cultivation |
| 4. | Drying the pellets (SRF) | 2 weeks before cultivation |
| 5. | Packing and transporting SRF to the rice fields | 1 week before cultivation |
មតិយោបល់:
One of the major raw materials to produce SRF is rice husks and it can be supplied from rice milling stations, generally available year-round. However, there is competition for rice husks in the market because of demand from the poultry industry. Hence, finding rice husks is sometimes difficult in some areas of the country.
4.4 ថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូលដែលត្រូវការសម្រាប់ការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Manufacturing SRF | Labour days | 2,5 | 1500,0 | 3750,0 | |
| ជី និងសារធាតុពុល | Urea | kg | 200,0 | 270,0 | 54000,0 | |
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | Binding materials 1 | kg | 10,0 | 25,0 | 250,0 | |
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | Binding materials 2 | kg | 10,0 | 250,0 | 2500,0 | |
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | Rice husk biochar | kg | 200,0 | 50,0 | 10000,0 | |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស | 70500,0 | |||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 256,36 | |||||
ប្រសិនបើអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីមិនមានថ្លៃដើម 100% សូមបញ្ជាក់ថានរណាដែលចំណាយថ្លៃដើមដែលនៅសល់:
Project funded by the National Research Council of Sri Lanka (Grant No. : NRC TO-16/07)
មតិយោបល់:
SRF was given to the farmer, free, for application. The cost of SRF was borne by the project funded by the National Research Council of Sri Lanka (Grant No. : NRC TO-16/07)
4.5 សកម្មភាពថែទាំ
| សកម្មភាព | ពេលវេលា/ ភាពញឹកញាប់ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Application of first dose of SRF | 2 weeks after direct seeding of rice |
| 2. | Application of second dose of SRF | 4 weeks after direct seeding of rice |
| 3. | Application of third dose of SRF | 7 weeks after direct seeding of rice |
មតិយោបល់:
Application of correct amount of SRF at the correct growth stage of the rice crop is important for efficient uptake of N to the crop and reduce losses.
4.6 កំណត់ថ្លៃដើមសម្រាប់ការថែទាំ/ សកម្មភាពរបស់បច្ចេកទេស (ក្នុងរយៈពេលមួយឆ្នាំ)
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Labour for SRF application | Labour days | 3,0 | 1500,0 | 4500,0 | 100,0 |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេស | 4500,0 | |||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 16,36 | |||||
4.7 កត្តាសំខាន់បំផុតដែលមានឥទ្ធិពលដល់ការចំណាយ
ពណ៌នាពីកត្តាប៉ះពាល់ចម្បងៗទៅលើថ្លៃដើម:
Labour availability and finding raw materials are the major factors that affect the cost.
5. លក្ខណៈបរិស្ថានធម្មជាតិ និងមនុស្ស
5.1 អាកាសធាតុ
បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
- < 250 មម
- 251-500 មម
- 501-750 មម
- 751-1,000 មម
- 1,001-1,500 មម
- 1,501-2,000 មម
- 2,001-3,000 មម
- 3,001-4,000 មម
- > 4,000 មម
កំណត់បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀង (បើដឹង) ជា មីលីម៉ែត្រ:
1400,00
លក្ខណៈពិសេស/ មតិយោបល់លើរដូវភ្លៀង:
The Mahakanumulla area receives monsoon rainfall during two distinct seasons, namely yala (May – September) and maha (December – February), hence a bimodal rainfall pattern can be observed. The highest amount of rainfall is received during the maha season, in which most of the rainfall comes from the North-eastern monsoonal rains. Lesser rainfall is received from the South-west monsoonal rains, during the yala season. Hence prolonged dry periods are observed during the yala season. Other than that, this area receives rainfall from two inter-monsoonal rains (March-April and October-November).
បញ្ជាក់ឈ្មោះឯកសារយោងនៃស្ថានីយឧតុនិយម:
Mahailuppallama, Anuradhapura
តំបន់កសិអាកាសធាតុ
- មានភ្លៀងតិចតួច
Recorded minimum and maximum temperatures in the area are 20.8°C and 29.5°C respectively
5.2 សណ្ឋានដី
ជម្រាលជាមធ្យម:
- រាបស្មើ (0-2%)
- ជម្រាលតិចតួច (3-5%)
- មធ្យម (6-10%)
- ជម្រាលខ្ពស់បន្តិច (11-15%)
- ទីទួល (16-30%)
- ទីទួលចោត (31-60%)
- ទីទួលចោតខ្លាំង (>60%)
ទម្រង់ដី:
- ខ្ពង់រាប
- កំពូលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលទួល
- ជម្រាលជើងភ្នំ
- បាតជ្រលងភ្នំ
តំបន់តាមរយៈកម្ពស់ :
- 0-100 ម
- 101-500 ម
- 501-1,000 ម
- 1,001-1,500 ម
- 1,501-2,000 ម
- 2,001-2,500 ម
- 2,501-3,000 ម
- 3,001-4,000 ម
- > 4,000 ម
បញ្ជាក់ថាតើបច្ចេកទេសនេះត្រូវបានអនុវត្តន៍នៅក្នុង:
- មិនពាក់ព័ន្ធទាំងអស់
មតិយោបល់ និងបញ្ចាក់បន្ថែមអំពីសណ្ឋានដី :
The altitude of the area is 112m. An undulating pattern of topography is a distinct feature of this landscape. The rice is cultivated mainly in the valley area of the catena and other upland crops are cultivated in the crest area of the catena.
5.3 ដី
ជម្រៅដីជាមធ្យម:
- រាក់ខ្លាំង (0-20 សម)
- រាក់ (21-50 សម)
- មធ្យម (51-80 សម)
- ជ្រៅ (81-120 សម)
- ជ្រៅខ្លាំង (> 120 សម)
វាយនភាពដី (ស្រទាប់លើ):
- គ្រើម/ មានពន្លឺ (ខ្សាច់)
វាយនភាពដី (> 20 សម ស្រទាប់ក្នុង):
- មធ្យម (ល្បាយ, ល្បាប់)
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គនៅស្រទាប់ដីខាងលើ:
- មធ្យម (1-3%)
បើអាចសូមភ្ជាប់ការពណ៌នាពីដីឱ្យបានច្បាស់ ឬព័ត៌មានដែលអាចទទួលបាន ឧ. ប្រភេទដី, pH ដី/ ជាតិអាស៊ីត, សមត្ថភាពផ្លាស់ប្តូរកាចុង, វត្តមាននីត្រូសែន, ភាពប្រៃ ។ល។:
Rice growing soils of the Mahakanumulla area are classified as Alfisols (Typic endoaquaalf). The soil is poorly drained. The pH of the soil is in the neutral range (6.05-7.23). Soil EC (55.5-143.0 µs/cm, 1:2.5 soil:water) values did not show any occurrence of soil salinity. Av. P content of the soil (Olsen P) was low for rice growth (<5 mg/kg) and ranged from 2.9-3.5 mg/kg. Av. K content of the soils was medium to high for rice growth and ranged from 61.3-99 mg/kg.
5.4 ទឹកដែលអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន និងគុណភាពទឹក
នីវ៉ូទឹកក្រោមដី:
< 5 ម
ទឹកលើដីដែលអាចទាញយកប្រើប្រាស់បាន:
ល្អ
គុណភាពទឹក (មិនបានធ្វើប្រត្តិកម្ម):
ទឹកសម្រាប់តែការធ្វើកសិកម្ម (ស្រោចស្រព)
គុណភាពទឹក គឺផ្តោតទៅលើ៖:
ទាំងទឹកក្រោមដី និងលើផ្ទៃដី
តើមានបញ្ហាភាពទឹកប្រៃហូរចូលមកដែរឬទេ?
ទេ
តើទឹកជំនន់កំពុងកើតមាននៅតំបន់នេះដែររឺទេ?
ទេ
មតិយោបល់ និងលក្ខណៈពិសេសផ្សេងៗទៀតលើគុណភាព និងបរិមាណទឹក :
The amount of water supplied through the irrigation is limited during the dry season (yala). The water quality is affected by soil macro-nutrients (N, P, K) added as fertilizers to the soil. Due to the undulating topography of the landscape, those soil nutrients can wash-off from higher positions to lower positions due to surface runoff and leaching into the ground water and accumulating in the water bodies in the lower positions of the catena.
5.5 ជីវៈចម្រុះ
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃប្រភេទ:
- កម្រិតមធ្យម
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃទីជម្រក:
- កម្រិតមធ្យម
មតិយោបល់ និងលក្ខណៈពិសេសផ្សេងទៀតលើជីវចម្រុះ:
Number of different tree species, wild animals, birds, insects and aquatic life can be observed around Mahakanumulla village. Forest patches can be identified mostly around the small tank, and those areas are habitats for multiple wild animals and birds.
5.6 លក្ខណៈនៃអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីដែលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
នៅមួយកន្លែង ឬពនេចរ :
- នៅមួយកន្លែង
ទីផ្សារនៃប្រព័ន្ធផលិតកម្ម:
- ពាក់កណ្តាលពាណិជ្ជកម្ម (ផ្គត់ផ្គង់ខ្លួនឯង/ ពាណិជ្ជកម្ម)
ចំណូលក្រៅកសិកម្ម:
- 10-50% នៃចំណូល
កម្រិតជីវភាព:
- មិនល្អ
ឯកជន ឬក្រុម:
- ធ្វើខ្លួនឯង/ គ្រួសារ
កម្រិតប្រើប្រាស់គ្រឿងយន្ត:
- ប្រើកម្លាំងពលកម្ម
- គ្រឿងយន្ត/ ម៉ាស៊ីន
យេនឌ័រ:
- ស្ត្រី
- បុរស
អាយុរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- វ័យកណ្តាល
សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីលក្ខណៈពាក់ព័ន្ធផ្សេងទៀតអំពីអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
Most of the land users are dependent on full time rice farming. But some land users use rice farming as a secondary source of income and do other jobs in the city. Most of the younger generation in the village are migrating for jobs in the cities.
5.7 ទំហំផ្ទៃដីជាមធ្យមនៃដីប្រើប្រាស់ដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី ក្នុងការអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
- < 0.5 ហិកតា
- 0.5-1 ហិកតា
- 1-2 ហិកតា
- 2-5 ហិកតា
- 5-15 ហិកតា
- 15-50 ហិកតា
- 50-100 ហិកតា
- 100-500 ហិកតា
- 500-1,000 ហិកតា
- 1,000-10,000 ហិកតា
- > 10,000 ហិកតា
តើផ្ទៃដីនេះចាត់ទុកជាទំហំកម្រិតណាដែរ ខ្នាតតូច មធ្យម ឬខ្នាតធំ (ធៀបនឹងបរិបទតំបន់)?
- ខ្នាតតូច
មតិយោបល់:
Rice is cultivated over a large area. However, single farmer manage relatively small fields (0.5-1 ha or 2-5 ha). The fields managed by farmers are located adjacent to each other.
5.8 ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ដី និងកម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក
ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី:
- ឯកជន មានកម្មសិទ្ធ
កម្មសិទ្ធិប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- ឯកជន
កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក:
- ជាក្រុម (មានដែនកំណត់)
តើកម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ដី គឺផ្អែកលើប្រព័ន្ធច្បាប់បែបបុរាណ?
ទេ
5.9 ការប្រើប្រាស់សេវាកម្ម និងហេដ្ឋារចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ
សុខភាព:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការអប់រំ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ជំនួយបច្ចេកទេស:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការងារ (ឧ. ការងារក្រៅកសិដ្ឋាន):
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទីផ្សារ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ថាមពល:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ផ្លូវ និងការដឹកជញ្ជូន:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទឹកផឹក និងអនាម័យ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
សេវាកម្មហិរញ្ញវត្ថុ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
មតិយោបល់:
The villagers of Mahaknumulla have access for most of the resources like infrastructure and energy/electricity/fuel. But most of the villagers/landusers complain about technical assistant/support for agricultural practices, finding markets for their produce and availability of good quality drinking water. The villagers go to nearby shops to buy day-to-day needs, but they have to go to the town, which is 8-10km away, for other services such as health and financial services.
6. ផលប៉ះពាល់ និងការសន្និដ្ឋាន
6.1 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្នុងបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ផលប៉ះពាល់លើសេដ្ឋកិច្ចសង្គម
ផលិតផល
ផលិតកម្មដំណាំ
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
6.5 t/ha (two seasons)
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
6.9 t/ha (two seasons)
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Although farmers could not observe a yield increase , experimental evidence suggests upto10% yield increase compared to farmer fertilizer management. A decrease in yield however not observed by farmers despite 25% reduction in N input. The above figures are for average of five farmers over two seasons.
គុណភាពដំណាំ
ហានិភ័យនៃភាពបរាជ័យរបស់ផលិតកម្ម
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃផលិតផល
ផ្ទៃដីផលិតកម្ម
ការគ្រប់គ្រងដី
ទឹកដែលអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន និងគុណភាពទឹក
ទឹកបរិភោគដែលអាចទាញយកមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន
គុណភាពទឹកបរិភោគ
ទឹកដែលអាចប្រើប្រាស់បានសម្រាប់ការចិញ្ចឹមសត្វ
គុណភាពទឹកសម្រាប់ការចិញ្ចឹមសត្វ
ទឹកប្រើប្រាស់សម្រាប់ស្រោចស្រព
គុណភាពទឹកស្រោចស្រព
តម្រូវការទឹកសម្រាប់ស្រោចស្រព
ចំណូល និងថ្លៃដើម
ការចំណាយលើធាតុចូលកសិកម្ម
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
LKR 60,750.00/ha for urea
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
LKR 70,500/ha for SRF
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
LKR 270/kg urea and LKR 167/kg of SRF. Expenses were calculated assuming all other costs are constants under two situations
ចំណូលក្នុងកសិដ្ឋាន
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
LKR 520,000/ha
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
LKR 552,000/ha
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
LKR 80/kg of paddy. Average yields mentioned above was used to calculate the farm income. Therefore, farm income is expected to be increased more than the expenses in SRF applied fields.
ភាពសម្បូរបែបប្រភពប្រាក់ចំណូល
ភាពខុសគ្នាផ្នែកសេដ្ឋកិច្ច
បន្ទុកការងារ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Although a longer time is required for SRF application because of higher bulk volume (175kg more), this application cost is negligible
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើវប្បធម៌សង្គម
សន្តិសុខស្បៀង/ ភាពគ្រប់គ្រាន់ខ្លួនឯង
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Expected improvements in productivity due to SRF application could strengthen the food security
ស្ថានភាពសុខភាព
កម្មសិទ្ធដីប្រើប្រាស់/ ទឹក
ឱកាសវប្បធម៍
ឱកាសនៃការបង្កើតថ្មី
ស្ថាប័នសហគមន៍
ស្ថាប័នជាតិ
ចំណេះដឹង SLM / ការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Farmers gain awareness through extension programmes when implementing the SRF technology
ការកាត់បន្ថយជម្លោះ
ស្ថានភាពក្រុមដែលមានបញ្ហាក្នុងសង្គម និងសេដ្ឋកិច្ច
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើអេកូឡូស៊ី
វដ្តទឹក/លំហូរ
បរិមាណទឹក
គុណភាពទឹក
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
N accumulation in water bodies is reducing due to lower N losses of SRF
ការប្រមូលស្តុកទុកទឹក
លំហូរទឹកលើផ្ទៃដី
ប្រព័ន្ធបង្ហូរទឹក
នីវ៉ូទឹកក្រោមដី/ ដង្ហើមទឹក
រំហួត
ដី
សំណើមដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
It is expected to have a better moisture content as a result of accumulation of biochar with repeated application of SRF
គម្របដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Experimental evidence suggests that soil cover is more with rice plants that grow better and tiller more due to better N utilization for crop growth
ការបាត់បង់ដី
ការកើនឡើងដី
ដីប្រេះ
ដីហាប់
វដ្តនៃសារធាតុចិញ្ចឹម/ការទទួលបាន
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
N uptake: 167 kg of N/ha
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
N uptake: 219 kg of N/ha
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Higher uptake of N by rice plants due to SRF application, nutrient recycling is expected to be improved. The above values were obtained from 5 farmer fields in the year 2021.
ភាពប្រៃ
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
Electrical Conductivity : 0.11 dS/m
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
Electrical Conductivity : 0.09 dS/m
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
The above values were obtained from 5 farmer fields in the year 2021.
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គដី/ការបូនក្រោមដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
SRF contains biochar which is a good source to improve the soil C.
ជាតិអាស៊ីត
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
pH : 7.42
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
pH : 7.38
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
The above values were obtained from 5 farmer fields in the year 2021.
ជីវចម្រុះ៖ ដំណាំ, សត្វ
ដំណាំគម្រប
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Efficient uptake of N cause to improve the crop growth, thereby vegetation cover
ជីវម៉ាស/ កាបូនលើដី
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
5.2 t/ha (straw) + 8.1 (grain)
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
6.0 t/ha (straw) + 8.7 t/ha (grain)
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Higher crop growth results higher biomass production. The above values were obtained from 5 farmer fields in the year 2021.
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃរុក្ខជាតិ
ប្រភេទរាតត្បាត
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃសត្វ
ប្រភេទសត្វមានប្រយោជន៍
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃទីជំរក
ការគ្រប់គ្រងកត្តាចង្រៃ/ ជំងឺ
ការកាត់បន្ថយហានិភ័យនៃគ្រោះមហន្តរាយ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ
ផលប៉ះពាល់នៃទឹកជំនន់
ដីបាក់/ លំហូរកំទិចកំទី
ផលប៉ះពាល់នៃគ្រោះរាំងស្ងួត
ផលប៉ះពាល់នៃព្យុះស៊ីក្លូន/ព្យុះភ្លៀង
ការបំភាយនៃកាបូន និងឧស្ម័នផ្ទះកញ្ចក់
ហានិភ័យនៃភ្លើងឆេះព្រៃ
ល្បឿនខ្យល់
អាកាសធាតុ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Because of the better growth of the rice plants micro climate in the paddy fields is expected to be improved.
បញ្ជាក់ពីការប៉ាន់ស្មាននៃផលប៉ះពាល់ក្នុងបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស (វាស់វែង):
Plant growth parameters and yield
6.2 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្រៅបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ទឹកដែលអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន
លំហូរទឹកដែលអាចប្រើប្រាស់បាននៅរដូវប្រាំង
ទឹកជំនន់ខ្សែទឹកខាងក្រោម
កំណកល្បាប់ខ្សែទឹកខាងក្រោម
ទឹកក្រោមដី/ ការបំពុលទឹកទន្លេ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
N accumulation in water bodies is expected to be reduced due to lower N losses from SRF
Buffering/សមត្ថភាពចម្រោះ
ខ្យល់នាំយកនូវធូរលី
ខូចខាតដល់ស្រែអ្នកជិតខាង
ខូចខាតដល់ហេដ្ឋារចនាសម្ព័ន្ធសាធារណៈ/ឯកជន
ផលប៉ះពាល់នៃឧស្ម័នផ្ទះកញ្ចក់
6.3 ភាពប្រឈម និងភាពរួសនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ/ គ្រោះមហន្តរាយ (ដែលដឹងដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
| រដូវកាល | កើនឡើង ឬថយចុះ | លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| សីតុណ្ហភាពប្រចាំឆ្នាំ | កើនឡើង | មិនស្គាល់ | |
| បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំឆ្នាំ | ថយចុះ | មិនស្គាល់ |
6.4 ការវិភាគថ្លៃដើម និងអត្ថប្រយោជន៍
តើផលចំណេញ និងថ្លៃដើមត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
ប៉ះពាល់តិចតួចបំផុត
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមានតិចតួច
តើផលចំណេញ និងការថែទាំ/ ជួសជុលត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
វិជ្ជមាន
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមានតិចតួច
6.5 ការទទួលយកបច្ចេកទេស
- តែមួយករណី /ពិសោធន៍
បើអាច សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីបរិមាណ (ចំនួនគ្រួសារ និង/ ឬតំបន់គ្របដណ្តប់):
5 farmers/households
6.6 ការបន្សុំា
តើថ្មីៗនេះ បច្ចេកទេសនេះត្រូវបានកែតម្រូវដើម្បីបន្ស៊ាំទៅនឹងស្ថានភាពប្រែប្រួលដែរឬទេ?
ទេ
6.7 ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៃបច្ចេកទេស
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៅកន្លែងរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
|---|
| This technology uses less chemical fertilizer and therefore it is good for their health and environment |
| This technology gives better crop growth and slightly higher yield |
| Biochar could improve the fertility of the soil |
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាស ទស្សនៈរបស់បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ |
|---|
| SRF reduces the N losses from the soil and allows the rice crop to uptake N effectively from soil at required growth stages. Efficient N uptake promotes the crop growth and increase the productivity. |
| Reduced N losses of SRF directly influence the water quality by reducing the losses of N through surface runoff and leaching and avoid accumulation in water bodies at the lower positions of the landscape. |
| Rice husks, which is are good source of C, are utilized for SRF production; hence it promotes C sequestration as it is added back to the soil as biochar. It improves the soil organic carbon pool and promotes carbon sequestration in soil. |
| Utilizing rice husks by returning back to the rice fields is an effective solution for rice waste management. |
| If the SRF production technology can be transferred to farmers, their societies can produce the SRF by themselves from the wastes generated in small scale rice mills. |
6.8 ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យនៃបច្ចេកទេស និងវិធីសាស្ត្រដោះស្រាយ
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| Additional cost despite reduced chemical fertilizer | increased crop yields can partially compensate this. They can produce their own SRF if the production technology is transferred to them |
| Uneven distribution of nitrogen in the field | Changing the water management practices that have been currently adopted by farmers |
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកចងក្រងឬបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| The raw materials need to be formulated accurately to get the benefits of the technology. Hence, technical knowledge and experience is required when preparing SRF. | Proper guidance and technical support from the beginning to the end of the process is essential. This can be achieved through educating and training extension officers to teach and disseminate knowledge for farmers. |
7. ឯកសារយោង និងវេបសាយ
7.1 វិធីសាស្ត្រ/ ប្រភពនៃព័ត៌មាន
- តាមការចុះទីវាល ការស្រាវជ្រាវនៅទីវាល
More than 10 field visits
- ការសម្ភាសន៍ជាមួយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
Interviewed 5 farmers
តើពេលណាដែលទិន្នន័យបានចងក្រង (នៅទីវាល)?
08/05/2021
មតិយោបល់:
Plant growth measurements were collected 7 weeks after broadcasting rice and yield data collected after 3 ½ months after broadcasting.
7.2 ឯកសារយោងដែលបានចេញផ្សាយ
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Preparation of Biochar as a Soil Amendment from Rice Husk and Corn Cob by Slow Pyrolysis Process, S.T. Munasinghe, R.S. Dharmakeerthi, P. Weerasinghe and L.G.S. Madusanka, ISSN 0041-3224
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
Tropical Agriculturist Journal
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Changes in Structural and Chemical Properties of Rice Husk Biochar Co-pyrolysed with Eppawala Rock Phosphate under Different Temperatures, D.K.R.P.L. Dissanayake, R.S. Dharmakeerthi, A.K. Karunarathna and W.S. Dandeniya, ISSN: 2706-0233
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
Tropical Agricultural Research Journal
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Biochar Based Slow-Release Urea Fertilizer: Production and Assessing the Effects on Growth of Lowland Rice and Nitrogen Dynamics in an Alfisol, M.K.N.W. Jayarathna, R.S. Dharmakeerthi and W.M.U.K. Rathnayaka, ISSN: 2706-0233
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
Tropical Agricultural Research Journal
7.3 ការភ្ជាប់ទៅកាន់ព័ត៌មានពាក់ព័ន្ធលើប្រព័ន្ធអនឡាញ
ចំណងជើង/ ពណ៌នា:
Changes in Structural and Chemical Properties of Rice Husk Biochar Co-pyrolysed with Eppawala Rock Phosphate under Different Temperatures
វេបសាយ:
http://192.248.43.153/bitstream/1/3160/2/PGIATAR_30_1_19.pdf
ចំណងជើង/ ពណ៌នា:
Biochar Based Slow-Release Urea Fertilizer: Production and Assessing the Effects on Growth of Lowland Rice and Nitrogen Dynamics in an Alfisol
វេបសាយ:
https://tar.sljol.info/articles/abstract/10.4038/tar.v32i2.8464/
7.4 មតិយោបល់ទូទៅ
The WOCAT questionnaire on SLM technologies covers all the aspects that can affect on the sustainability of natural and human environment.
ការតភ្ជាប់ និងម៉ូឌុល
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់ការតភ្ជាប់
គ្មានការតភ្ជាប់
ម៉ូឌុល
គ្មានម៉ូឌុល