Crop Residue Management [埃塞俄比亚]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: GERBA LETA
- 编辑者: Noel Templer, Julia Doldt, Kidist Yilma, Tabitha Nekesa, Ahmadou Gaye, Siagbé Golli
- 审查者: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Sally Bunning
Hafte Midhani
technologies_6644 - 埃塞俄比亚
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
土地使用者:
Woyessa Habtamu
Farmer
埃塞俄比亚
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Soil protection and rehabilitation for food security (ProSo(i)l)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
CIAT International Center for Tropical Agriculture (CIAT International Center for Tropical Agriculture) - 肯尼亚1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
1.5 参考关于SLM方法(使用WOCAT记录的SLM方法)的调查问卷

Integrated Soil Fertility Management (ISFM) [埃塞俄比亚]
The Integrated Soil Fertility Management (ISFM) approach has been adopted under the Integrated Soil Fertility Management Project (ISFM+). It was introduced as a quick-win solution to increase both crop and biomass production through the incremental promotion of varied but complementary technology packages.
- 编制者: GERBA LETA
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
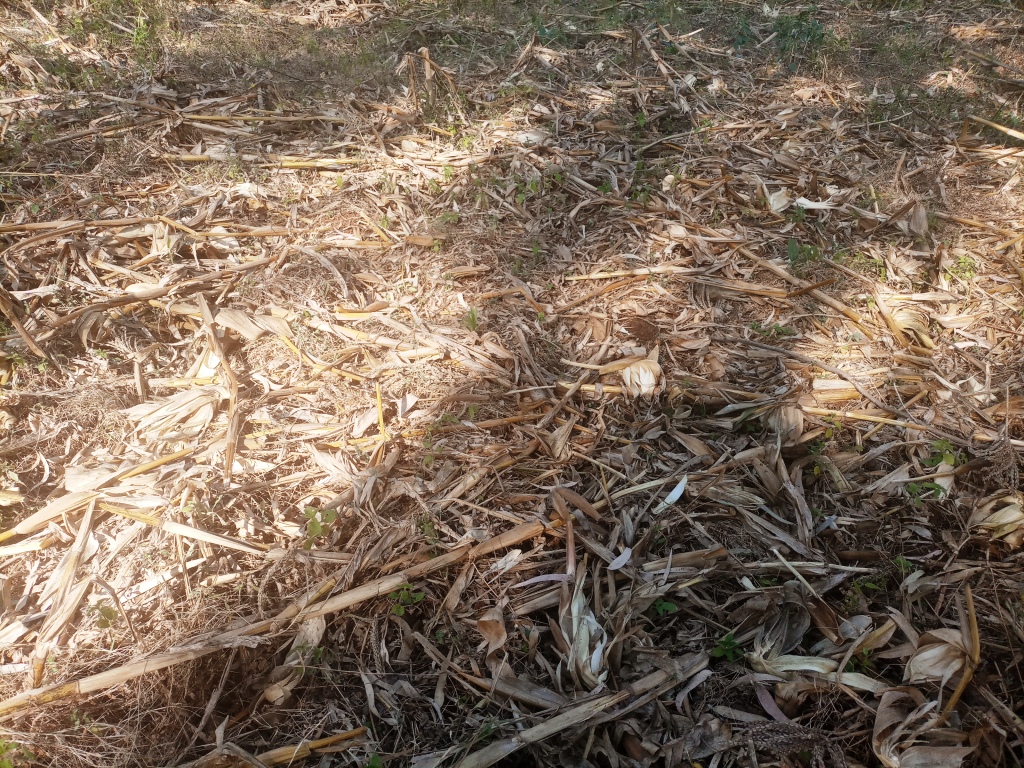
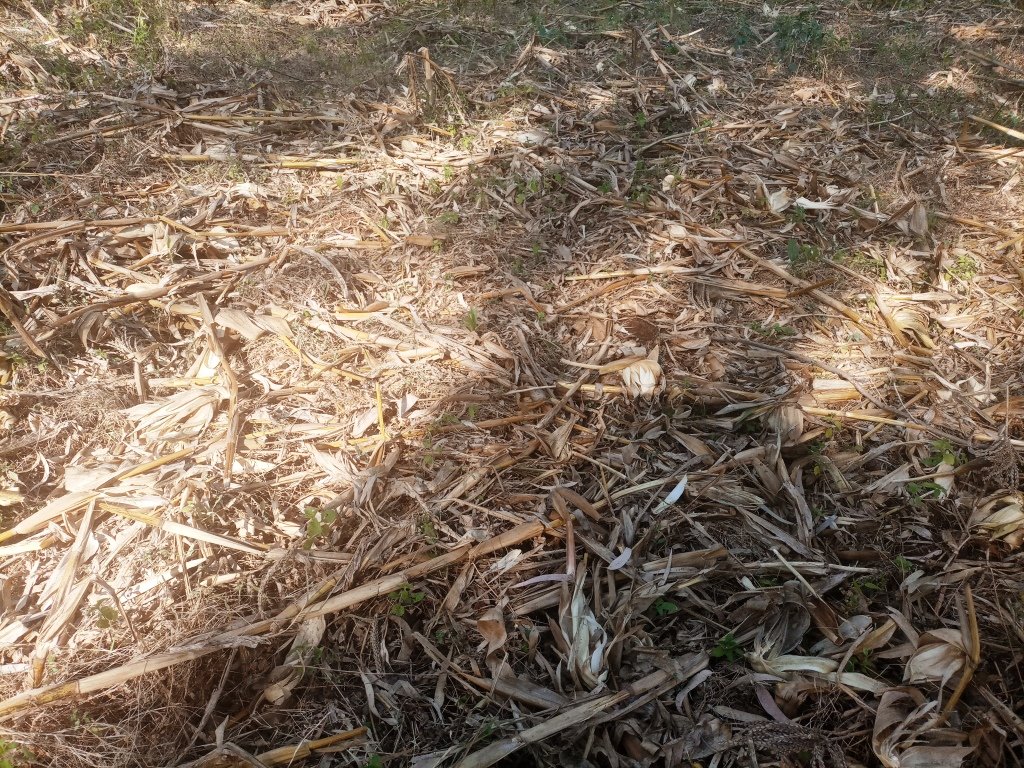
Crop residue management involves leaving stover and other trash from cereal crops (including tef, wheat and maize), as well as haulms of legumes, in the field. Crop residues keep the soil covered, retain organic matter and moisture in the soil, and help to ensure better production.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
Crop residue management involves leaving stover and other trash from cereal crops (including tef, wheat and maize), as well as haulms of legumes, in the field. Crop residue (CR) management is integral to soil health: it yields multiple benefits such as mitigating the risks of soil loss to water erosion, reducing the decomposition of organic matter and storing extra carbon. It also increases the fertility status of degraded soils and helps to improve soil structure and moisture properties. Degraded soils are at risk of tillage, water, and wind erosion. Soils degrade quickly when not covered and when no effort is made to increase organic matter levels or improve soil structure. Crop residue management plays an important role in arresting soil degradation and improving soil properties, and eventually increasing crop production. Therefore, it has positive economic and ecological functions. The aim of applying this technology is to improve soil fertility, reduce soil acidity and demands for synthetic fertilizers. Overall, crop residue management allows land users to sustainably use their land over a long period without losing its productive potential. In this part of Ethiopia, land users used to leave maize and millet stover in the fields but this is challenged by the prevalence of free (open access) grazing. Thus, controlling grazing is one prerequisite to ensuring adoption of the technology. Monocropping also reduces biomass production. Land users appreciate the extra grain yields from crop residue-rich farms. CR management also retains moisture and enables early tillage operations. In summary, the application of appropriate CR management provides multiple benefits. It mitigates the risks of erosion, reduces excessive mining of CR, reduces the rate of decomposition of organic matter, increases the fertility status of degraded soils, and increases crop production and sustainable productivity.
2.3 技术照片
关于照片的一般说明:
The photo portrays one of the many crop residue management practices applied on different crops.
2.4 技术视频
注释、简短说明:
Videos of this technology is not documented.
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
埃塞俄比亚
区域/州/省:
Oromia
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- 0.1-1 平方千米
技术现场是否位于永久保护区?:
否
Map
×2.6 实施日期
注明实施年份:
2015
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 作为传统系统的一部分(> 50 年)
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
Integrated Soil Fertility Management Project (ISFM+) of the GIZ.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 保护生态系统
- 保持/提高生物多样性
- 创造有益的经济影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
否

农田
- 一年一作
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 谷类 - 小麦(春季)
- 谷物类 - 玉米
- 谷类 - 小米
- cereals - Tef
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
采用间作制度了吗?:
否
采用轮作制度了吗?:
是
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?:
- 否(继续问题3.4)
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 农畜综合管理
- 改良的地面/植被覆盖
- 土壤肥力综合管理
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A2:有机质/土壤肥力
- A3:土壤表面处理
- A6:残株管理
- A7:其它
A3:区分耕作制度:
A 3.3: Full tillage (< 30% soil cover)
A6:对残株管理作出具体说明:
A 6.4:保留

管理措施
- M2:改变管理/强度级别
注释:
With tillage, the crop residue is incorporated well into the soil system. It improves soil structure by contributing organic matter with the benefits of facilitating infiltration and reducing surface runoff.
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)
- Ca:酸化

物理性土壤退化
- Pc:压实
- Ps:有机土壤沉降,土壤沉降

生物性退化
- Bc:植被覆盖的减少
- Bq:数量/生物量减少
- Bs:质量和物种组成/多样性的下降
- Bl:土壤寿命损失
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
注释:
It ensures the sustainable productivity potential of the soil.
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术区域
注明尺寸和面积单位:
4 sanga
如果使用本地面积单位,注明转换系数为1公顷(例如1公顷=2.47英亩):1公顷=:
1ha
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
ETB
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
53.12
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Mowing the crop by leaving some proportion on the ground. | Harvesting |
| 2. | Keep of livestock grazing | Dry season |
| 3. | Plow over the crop residue early on. | Late in the dry season. |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
注释:
The technology needs changing the mindset of the land users than the money/finance for the establishment and maintenance of it. Uniform distribution of rainfall is essential to plan the plowing time to incorporate the residue well into the soil.
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Keep the farm with crop residue intact from livestock | During off-season. |
注释:
Prohibiting the use of a proportion of crop residue for fuel, construction, and livestock feed is enough to put in place the technology.
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
如果您无法分解上表中的成本,请估算维护该技术所需要的总成本。:
2500.0
注释:
Allocated some money just to keep off the interference of livestock to the farmland during the off-season. The cost can be covered by land users themselves but need awareness creation on SLM using crop residue as one of the best practices.
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Change of the cost is related to the inflation and economic instability.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
1947.00
有关降雨的规范/注释:
The area received summer maximum rainfall.
注明所考虑的参考气象站名称:
Bedele
农业气候带
- 半湿润
The uniform distribution of rainfall is helpful to incorporate the residue in time.
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Since the farming at stallholder level is manual using traction power, the introduction of this technology is not obstructed by the topography as long as the land is under farming.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
好
水质(未处理):
良好饮用水
水质请参考::
地表水
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
否
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
栖息地多样性:
- 中等
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
- 畜力牵引
性别:
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 青年人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
The land users engage in livestock business as off-farm income.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 州
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
用水权:
- 自由进入(无组织)
- 社区(有组织)
土地使用权是否基于传统的法律制度?:
是
具体说明:
The land is inherited from the predecessors, though there was a land reallocation program in the past.
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
注释:
Land users are benefited from various financial institutions to access credit and other services. Various credit institutions and revolving funds were mentioned my the land users.
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
作物质量
饲料生产
注释/具体说明:
The purpose is to use less of crop residue for soil amendment than as fodder.
饲料质量
注释/具体说明:
The purpose is to reduces
畜牧生产
生产故障风险
注释/具体说明:
As it improves soil structure, moisture retention capacity, etc., the practice reduces risks of crop failure.
产品多样性
生产区域
土地管理
水资源可用性和质量
饮用水的可用性
饮用水的质量
收入和成本
农业投入费用
农业收入
收入来源的多样性
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
健康状况
注释/具体说明:
The health condition is convergent with considerable harvest and food security.
SLM/土地退化知识
生态影响
水循环/径流
水量
水质
地表径流
多余水的排放
地下水位/含水层
注释/具体说明:
The health condition is convergent with considerable harvest and food security.
蒸发
注释/具体说明:
The ground cover by crop residues inevitably contributes to the reduction of evaporation.
土壤
土壤水分
土壤覆盖层
土壤流失
土壤堆积
土壤结壳/密封
土壤压实
养分循环/补给
注释/具体说明:
Improves on a gradual basis.
土壤有机物/地下C
酸度
生物多样性:植被、动物
植被覆盖
生物量/地上C
有益物种
栖息地多样性
害虫/疾病控制
注释/具体说明:
Crop residue may host some insects but obstruct the movement of others.
减少气候和灾害风险
干旱影响
注释/具体说明:
Increasing the moisture retention capacity of the soil improves crops' resilience to droughts and other adversity.
碳和温室气体的排放
注释/具体说明:
Accumulation of crop residue increases carbon storage via the reduction of emissions.
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
水资源可用性
注释/具体说明:
No facts are available to support the allegation. Besides, it needs long-term observation and documentation.
旱季稳定可靠的水流
下游洪水
下游淤积
温室气体的影响
注释/具体说明:
Impact of greenhouse gases reduced with accumulation of crop residues.
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 | |
| 季节性温度 | 旱季 | 增加 | 好 |
| 年降雨量 | 减少 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
生物灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 流行病 | 未知 |
| 昆虫/蠕虫侵扰 | 不好 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 延长生长期 | 好 |
| 缩短生长期 | 非常好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
非常积极
注释:
Actually, the technology demands only labor costs for the protection of the farmland from grazing the leftover and to avoid illegal burning of crop residues.
6.5 技术采用
- 11-50%
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 91-100%
注释:
Land users adopted the practice and plow over the crop residue when the first shower of rainfall intercepted.
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
否
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| It improves soil fertility on gradual basis. |
| It assists to reduce soil acidity. |
| Increases production and productivity. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Absorbs and retain soil moisture for the crop to rely on for growth and grain filling as a coping mechanism to the unpredictable distribution of rainfall. |
| It reduces soil temperature and smother the weeds. |
| Sequesters carbon, a beneficial for climate change/variability. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Create tillage inconvenience as mechanization is less common among smallholders. | Using the excessive residue as trash line support the purpose of soil and water conservation. |
| Free grazing system and multiple uses of crop residue challenges retention of crop residue. | Institutionalizing controlled grazing system is of paramount important. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Less fodder available for the livestock and other multiple uses of crop residues. | Limit the amount of crop residue to be retained on the farm to 15 to 30 percent of the total non-grain biomass produced in the farm. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
2
- 与土地使用者的访谈
1
- 与SLM专业人员/专家的访谈
1
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
06/02/2023
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Renard, C. 1997. Crop Residues in Sustainable Mixed Crop/Livestock Farming Systems. CAB International, Walingford. ISBN 0 851991777
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
https://core.ac.uk › download ›
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
IIRR and ACT. 2005. Conservation Agriculture. A manual for farmers and extension workers in Africa. International Institute of Rural Agriculture, Nairobi; African Conservation Tillage Network, Harare.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
http://www.act-africa.org ›
7.3 链接到网络上的相关信息
标题/说明:
Best management practices: residue management
URL:
http://omaf.gov.on.ca/english/environment/bmp/AF179.pdf
7.4 一般注释
Similar to any other technologies. some questions in the questionnaire are not relevant to this particular technology. Meaning, the technology doesn't address every issue stated therein.
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Integrated Soil Fertility Management (ISFM) [埃塞俄比亚]
The Integrated Soil Fertility Management (ISFM) approach has been adopted under the Integrated Soil Fertility Management Project (ISFM+). It was introduced as a quick-win solution to increase both crop and biomass production through the incremental promotion of varied but complementary technology packages.
- 编制者: GERBA LETA
模块
无模块