Water Source Protection [不丹]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: ONGPO LEPCHA
- 编辑者: Haka Drukpa
- 审查者: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Chhu Ka Soongchop (ཆུ་བརྐ་སྲུང་སྐྱོབ།)
technologies_6842 - 不丹
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
土地使用者:
Dorji Sangay
Yakpugang Community
不丹
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Strengthening national-level institutional and professional capacities of country Parties towards enhanced UNCCD monitoring and reporting – GEF 7 EA Umbrella II (GEF 7 UNCCD Enabling Activities_Umbrella II)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
National Soil Services Centre, Department of Agriculture, Ministry of Agriculture & Livestock (NSSC) - 不丹1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
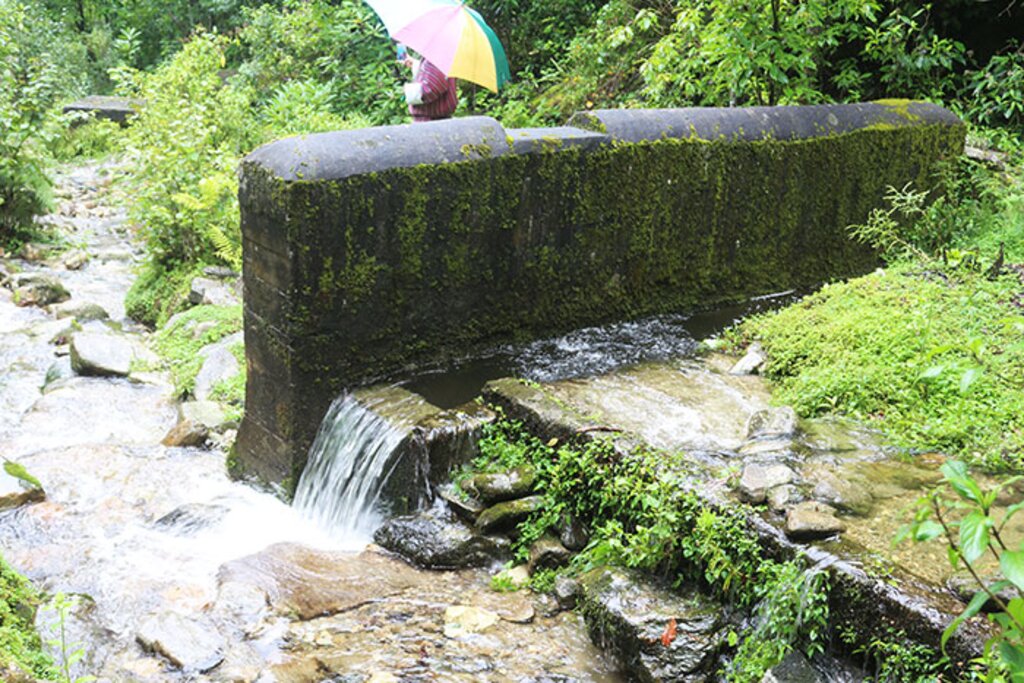
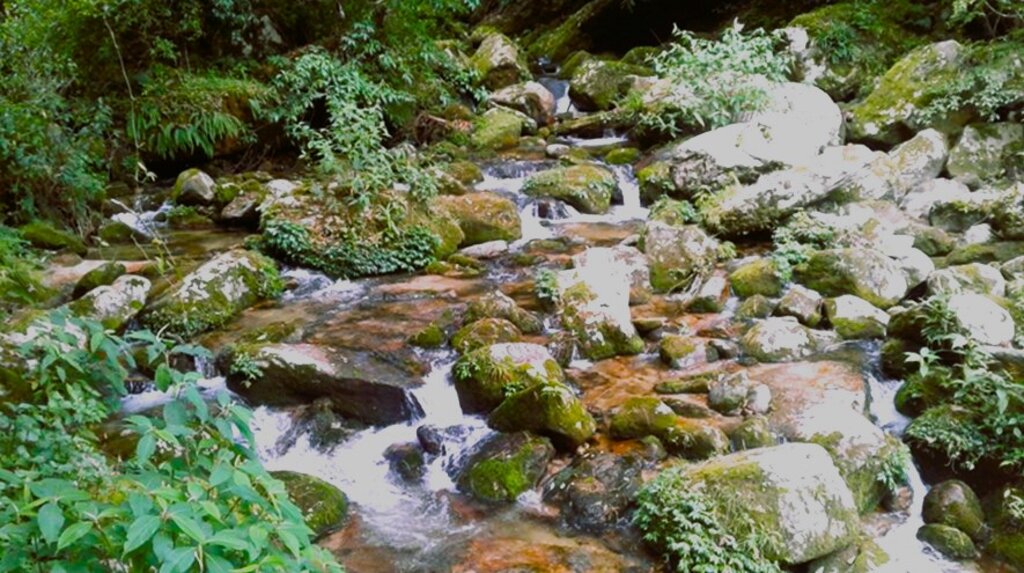
Water source protection involves protecting lakes, rivers, springs, or man-made reservoirs to avoid water pollution and damage by livestock and wild animals. In the past, the emphasis was on fencing and improving vegetation cover at the discharge point itself, but a recent focus is on groundwater recharge areas.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
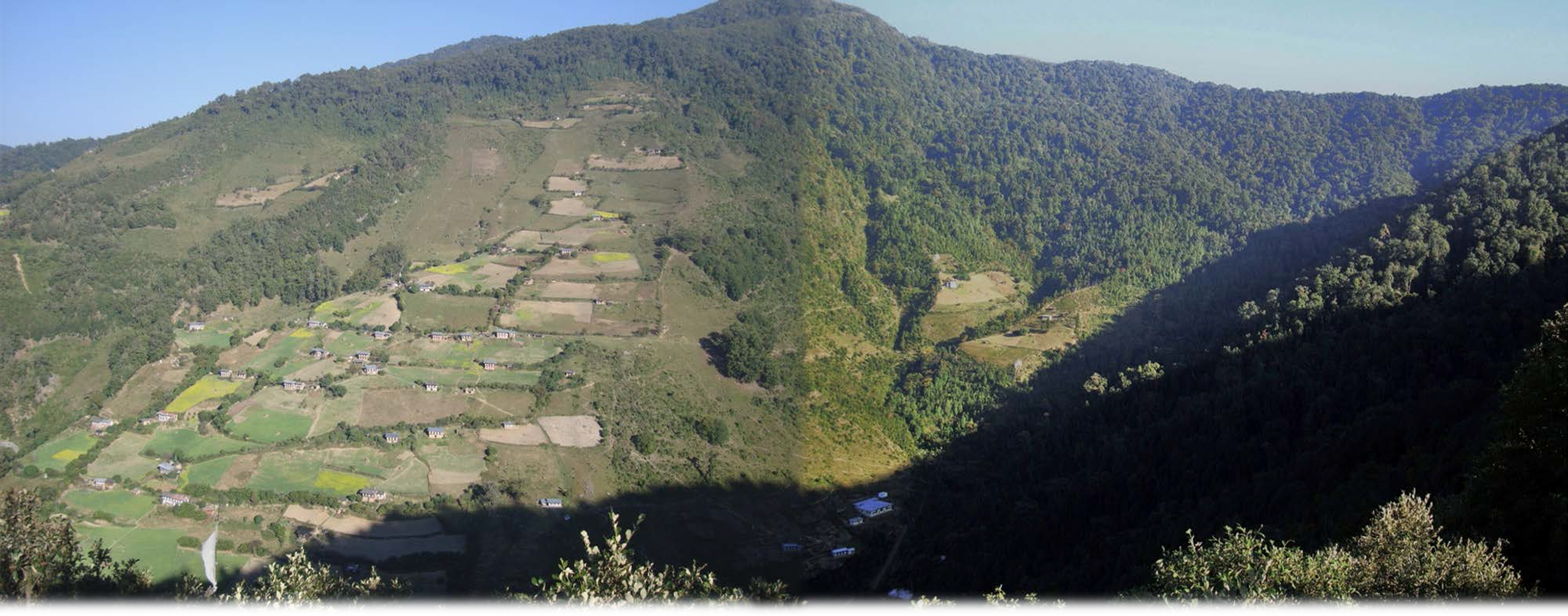
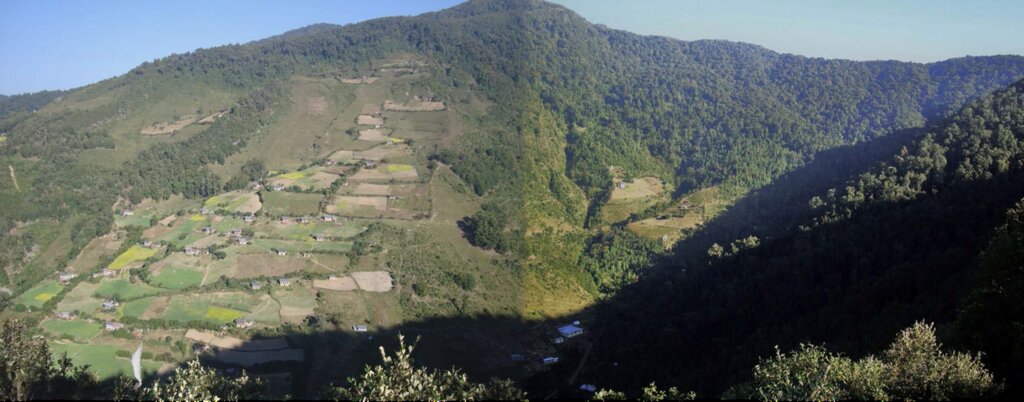
Water source protection involves protecting lakes, rivers, springs or man-made reservoirs to avoid water pollution and damage by livestock and wild animals. In the past this included fencing and enhancing vegetation cover at the discharge point – that is, where the water starts flowing. However, today, water source protection also focuses on improving groundwater recharge areas. The water source protection technology has many benefits. In addition to providing a clean and regular supply of drinking and irrigation water, it also enhances the vegetation cover of the catchment area.
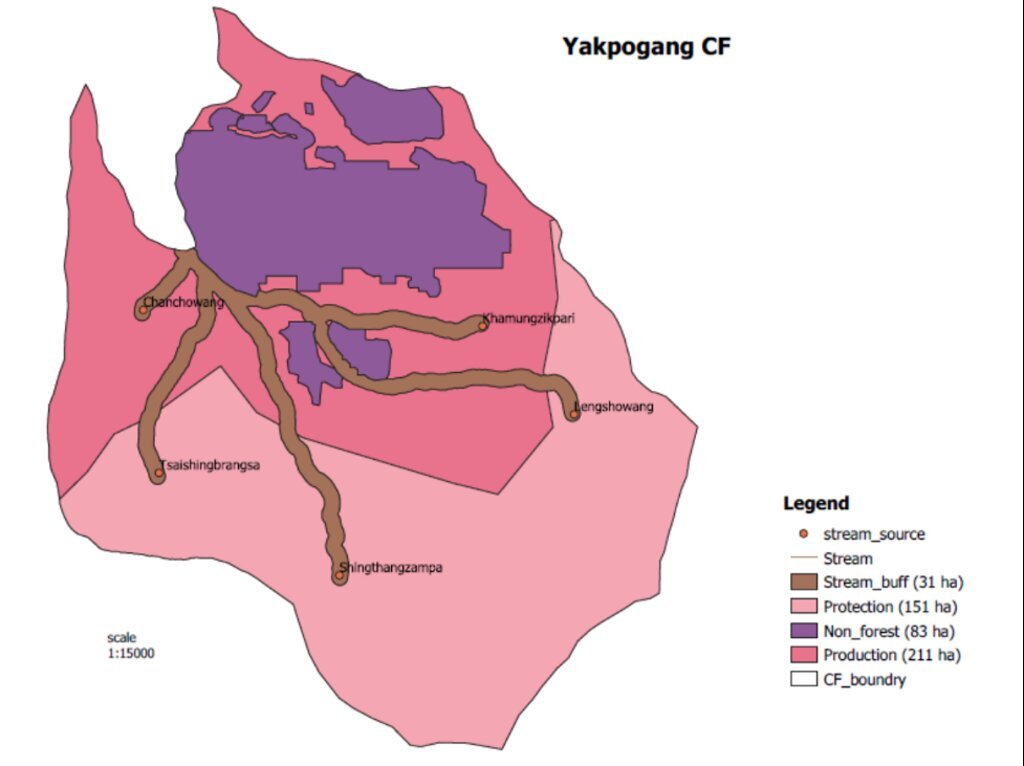
Strategies target maintaining adequate water levels in underground water reservoirs to ensure a continuous flow of streams and springs. In Yakpugang Community Forest, the technology has been applied specifically in the southern mountainous part of the village. An area of 638 acres (255 hectares) has been established as the recharge zone, and three springs have been identified for source protection. Native tree species have been planted annually in the degraded watershed to improve forest conditions. The main purpose is to protect the quality and quantity of the water for both drinking and irrigation purposes. The technology is supported by an approach that involves collective efforts of the community who realize that if their drinking and irrigation water supply is to be sustainable, they must work together.
The main purpose is to ensure a continuous supply of water for drinking and irrigation to the community. This is achieved through managing the catchment areas where rainwater soaks through the ground to reach a groundwater reservoir, and one of the key interventions is protecting the water sources from wild animals and livestock.
The water source protection technology involves 1) meeting different stakeholders, 2) signing agreements between the stakeholders, 3) site selection and survey, 4) planting of native tree species, and 5) conducting annual monitoring and evaluation. Inputs like fencing materials, planting materials, and human resources are required for the implementation and maintenance of the technology.
The technology is liked because it helps provide a continuous supply of both clean drinking and irrigation water. Furthermore, protecting water sources by the community is rewarded in monetary form by the nearby town as part of the Payment for Environmental Services (PES). This incentive helps the community to generate income which is ploughed back into the improvement and maintenance of water sources. What is disliked is the reduction in grazing land since the land users are not allowed to graze their cattle inside the water source areas.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
不丹
区域/州/省:
Mongar Dzongkhag (District)
有关地点的进一步说明:
Yakpugang village
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 适用于特定场所/集中在较小区域
技术现场是否位于永久保护区?:
否
Map
×2.6 实施日期
注明实施年份:
2007
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
The project was conducted with technical assistance from SNV Bhutan and and funded through Blue Moon Funding with Watershed Management Division of the Department of Forests and Park Services. Later Mongar Regional Referral Hospital was also involved as one of the major water users.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 保护生态系统
- 结合其他技术保护流域/下游区域
- 降低灾害风险
- 适应气候变化/极端天气及其影响
- 创造有益的社会影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
否

农田
- 一年一作
- 乔木与灌木的种植
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 蔬菜 - 叶菜(色拉、卷心菜、菠菜和其他)
- 蔬菜 - 根茎类蔬菜(胡萝卜、洋葱、甜菜等)
- Chillies
乔木和灌木种植 - 指定作物:
- 仁果类(苹果、梨子、柑橘等)
- 核果(桃、杏、樱桃、李子等)
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Vegetables are cultivated in one growing season, however, fruit trees are perennial.
采用间作制度了吗?:
否
采用轮作制度了吗?:
是
如果是,请具体说明:
The cole crops are rotated with root vegetables and legumes.

水道、水体、湿地
- 排水管道、水道
主要产品/服务:
Irrigation channels for farming and drinking water pipes
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?:
- 否(继续问题3.4)
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 混合雨水灌溉
注释:
The community was benefited greatly from the technology, and thus farming is mostly irrigated and rainfed is done, when rain falls in the area.
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 改良的地面/植被覆盖
- 灌溉管理(包括供水、排水)
- 地表水管理(泉、河、湖、海)
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

植物措施
- V1:乔木和灌木覆盖层
- V2:草和多年生草本植物
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wg:冲沟侵蚀/沟蚀

水质恶化
- Ha:干旱化
- Hs:地表水良变化
- Hp:地表水水质下降
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 减少土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
GIS map of the recharge zone of the Yakpugang spings
Yakpugang village, Mongar Gewog (Block), Mongar Dzongkhag (District), Bhutan
作者:
Ugyen Norten
日期:
07/10/2023
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术单元
指定单位:
Recharge zone of 638 acres (255 hectares)
指定单位面积(如相关):
638 acres (255 hectares)
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
82.08
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
1000
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Community meeting | Conducted several times |
| 2. | Survey of the recharge zone and site selection | The survey took around 2 to 3 weeks |
| 3. | Agreement between the stakeholders | Agreement done thrice |
| 4. | Native tree species plantation around the watershed | Based on a specified date and each individuals from household came |
注释:
The establishment activities were done with the technical assistance from SNV Bhutan and the Department of Forests and Park Services since the water source falls under the community forest.
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
如果您无法分解上表中的成本,请估算建立该技术所需要的总成本。:
258500.0
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
The project was funded through Blue Moon in collaboration with Watershed Management Division of the Department of Forests and Park Services and Global Environment Facility (GEF) was also involved.
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Clearing of the water source | Thrice annually |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Community Forest members | person/day. | 102.0 |
注释:
Since the water source is a community asset, an individual from each household goes to the water source area for annual maintenance. This happens three times a year, and no cost goes into it except labour contribution from each household during which they bring their own tools and food.
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
None.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
有关降雨的规范/注释:
The data was used from the nearest weather station of the National Center for Hydrology and Meteorology (NCHM).
注明所考虑的参考气象站名称:
https://www.nchm.gov.bt/home/pageMenu/906
农业气候带
- 半湿润
Warm temperate zone
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 凹陷情况
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 高(>3%)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地表水的可用性:
好
水质(未处理):
良好饮用水
水质请参考::
地表水
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
否
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
Water quantity and quality have been greatly improved with the intervention of water source protection. These three water sources provide drinking water to Mongar town and Mongar hospital.
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 高
栖息地多样性:
- 高
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- > 收入的50%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 机械化/电动
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 中年人
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
注释:
Total land is 1.5 acres and total cultivated and is 1 acre
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
用水权:
- 社区(有组织)
土地使用权是否基于传统的法律制度?:
是
具体说明:
The traditional legal system in our country is as per the Land Act and Land Rules and Regulations which dictate the land use in the country.
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
SLM之前的数量:
15 baskets of maize
SLM之后的数量:
20 to 25 baskets maize
注释/具体说明:
There has been an increase in the amount of maize, which has been credited to the increase in the amount of water than in the past.
作物质量
注释/具体说明:
According to the land user, crop quality has been relatively better after the implementation of the technology than in the past.
生产故障风险
注释/具体说明:
Due to the presence of water in the community, production has decreased.
产品多样性
SLM之前的数量:
maize and some other cereals and vegetables were grown
SLM之后的数量:
maize together with cole crops, tubers and fruits are grown
生产区域
SLM之前的数量:
1 acres
SLM之后的数量:
1.5 acres
注释/具体说明:
In the past, the lack of water would lead the land users to keeping some of the land fallow.
水资源可用性和质量
饮用水的可用性
SLM之前的数量:
Water would be scarce periodically
SLM之后的数量:
Water is now available throughout the community
注释/具体说明:
Drinking water availability has increased compared to the past. This is mainly due to the protection of water sources. In addition, now community members also go for regular clearing of irrigation channels, drinking water pipelines, and sources to keep the supply steady.
饮用水的质量
注释/具体说明:
Quality in terms of cleanliness of drinking water was reported to have enhanced because in the past nearby streams from where they get their drinking water used to get polluted by rainwater, animals, etc.
家畜用水的可用性
SLM之前的数量:
Water would be taken to the nearby streams
SLM之后的数量:
Water is now provided near there house
注释/具体说明:
Since supply is continuous the water availability for livestock also increased.
家畜用水的质量
注释/具体说明:
Water for livestock are also improved than in the past.
灌溉用水的可用性
SLM之前的数量:
Focused more on growing crops requiring less water
SLM之后的数量:
Now grows variety of diverse crops
注释/具体说明:
Since the water flow is continuous, there is enough water to carry out multiple cropping.
灌溉用水的质量
注释/具体说明:
Water quality for irrigation is better than the past
收入和成本
农业收入
SLM之前的数量:
focuses mostly on commercialising maize
SLM之后的数量:
now commercialises diverse vegetable crops as well
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
注释/具体说明:
The availability of water in the community, allowed for the land users to grow a diverse vegetable crops in large amount.
健康状况
SLM之前的数量:
Community members prone to water related disease
SLM之后的数量:
Water is relatively cleaner
土地使用权/用水权
注释/具体说明:
Agreement for water source protection is conducted after every end of the agreement year, where water use rights are also discussed.
生态影响
水循环/径流
水量
SLM之前的数量:
water from the source would dry up most of the times
SLM之后的数量:
water in the water source is almost always filled.
水质
SLM之前的数量:
Would be dirty due to wild animals and grazing cattle
SLM之后的数量:
Since water source is protected, water is relatively cleaner
减少气候和灾害风险
干旱影响
SLM之前的数量:
in the past, drought would occur periodically
SLM之后的数量:
Even during the absence of rain, water is still available
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
地下水/河流污染
SLM之前的数量:
Would normally be polluted due to wild animals and grazing cattles
SLM之后的数量:
Water is now clean and also drinkable
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 适度 | |
| 年降雨量 | 增加 | 适度 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 适度 |
| 局地雷暴 | 非常好 |
| 局地雹灾 | 好 |
| 局地风暴 | 好 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 好 |
| 森林火灾 | 不好 |
| 陆地火灾 | 不好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 不好 |
| 山洪暴发 | 不好 |
| 滑坡 | 非常不好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
注释:
The income earned from the project goes into community development and the community forest, and the expense for the project is already funded.
6.5 技术采用
- > 50%
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
102 households
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 0-10%
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
否
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Continuous supply of both drinking water and irrigation water |
| Water is supplied to Mongar town, and income is earned from it under Payment for Environmental Services (PES) arrangement b |
| Has helped in community development and improvement of community forest |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Water quality is preserved, and pollution and contamination of the water sources are prevented. |
| The plantation of native tree species helps conserve the ecosystem. |
| Long-term sustainability and enhanced climate resilience of the water source |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Decreased grazing land | Shift the grazing area outside the community forest or establish improved pasture land in their registered land |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
One household
- 与土地使用者的访谈
One individual
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
11/07/2023
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Norten, U. (2021). Impact of Water Management strategies- Payment for Ecosystem Services (PES) in Bhutan. International Journal of Science and Innovative Research, 2(8), 109-144.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
https://ijesir.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/11/0100072IJESIRnew.pdf
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
WWF. (2017). Valuing Ecosystem Services in Chamkharchhu Sub Basin: Mapping Sediment Using InVEST. WWF.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
https://wwfasia.awsassets.panda.org/downloads/final_invest_report_final_draft_may_17_spread_compressed_2.pdf
7.3 链接到网络上的相关信息
标题/说明:
Source Water Protection
URL:
https://www.nrcs.usda.gov/programs-initiatives/source-water-protection
标题/说明:
Water Source Protection
URL:
https://sswm.info/arctic-wash/module-4-technology/further-resources-water-sources/water-source-protection
标题/说明:
Basic Information about Source Water Protection
URL:
https://www.epa.gov/sourcewaterprotection/basic-information-about-source-water-protection
标题/说明:
Conserving water resources with PES, an example from Yakpugang
URL:
https://kuenselonline.com/conserving-water-resources-with-pes-an-example-from-yakpugang/
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块