River training dam [塔吉克斯坦]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Margaux Tharin
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Alexandra Gavilano, Alvin Chandra, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Дамбаи Обпартоб
technologies_698 - 塔吉克斯坦
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
土地使用者:
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Book project: where people and their land are safer - A Compendium of Good Practices in Disaster Risk Reduction (DRR) (where people and their land are safer)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
CARITAS (Switzerland) - 瑞士1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
The river training dam is a disaster mitigation structure protecting downstream areas from flash floods and mudflows. It consists of a channel dug and wire net gabions built to train the river and is hence cheap to establish and maintain. There is a substantial community contribution as labour is an important part of the input costs. The dam enables the rehabilitation of unproductive land in the downstream catchment areas, reduction of crop pests, increase in crop diversity and land productivity, and an overall improvement of livelihoods for downstream communities through reduced vulnerability to disasters.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
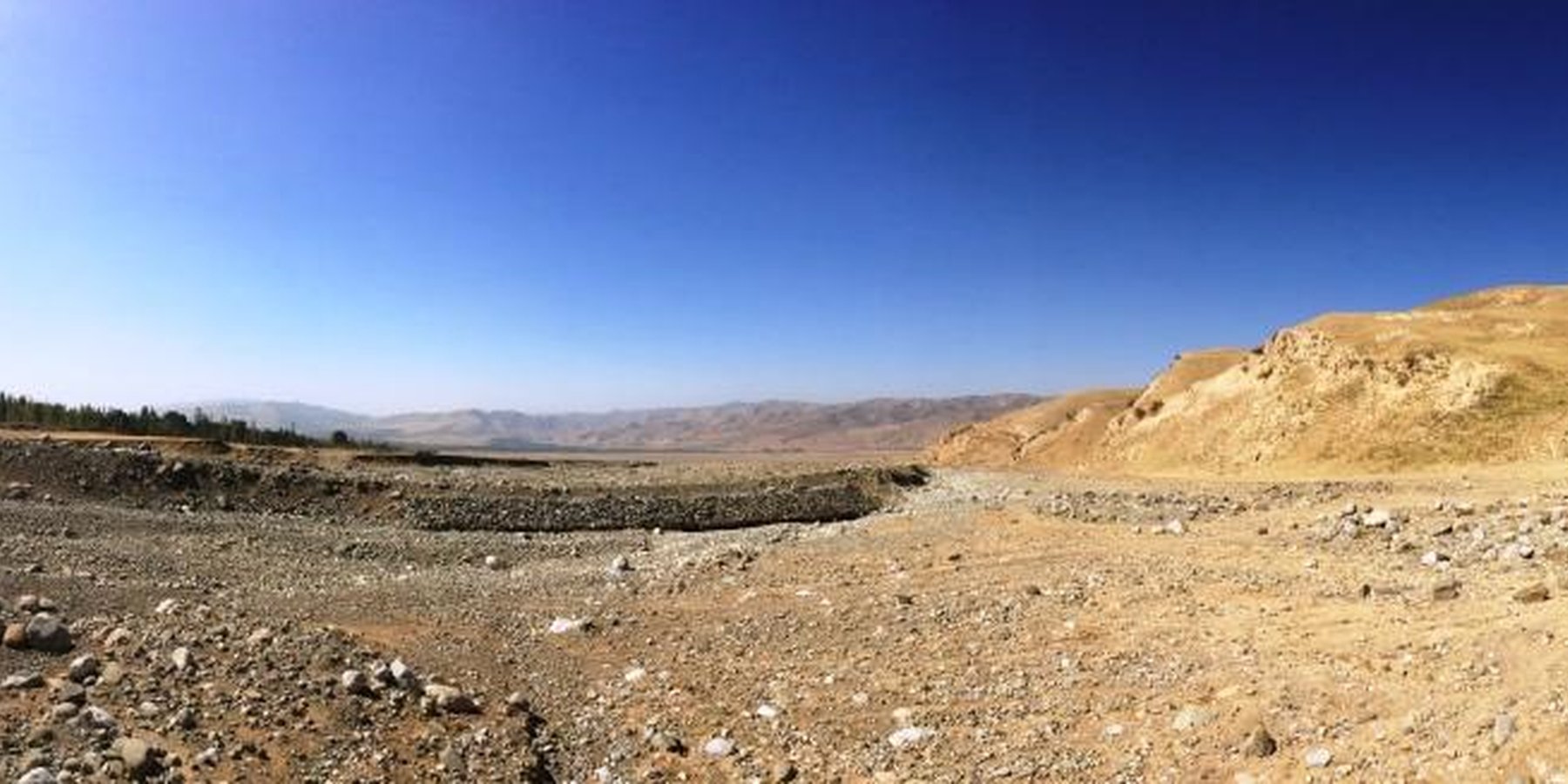
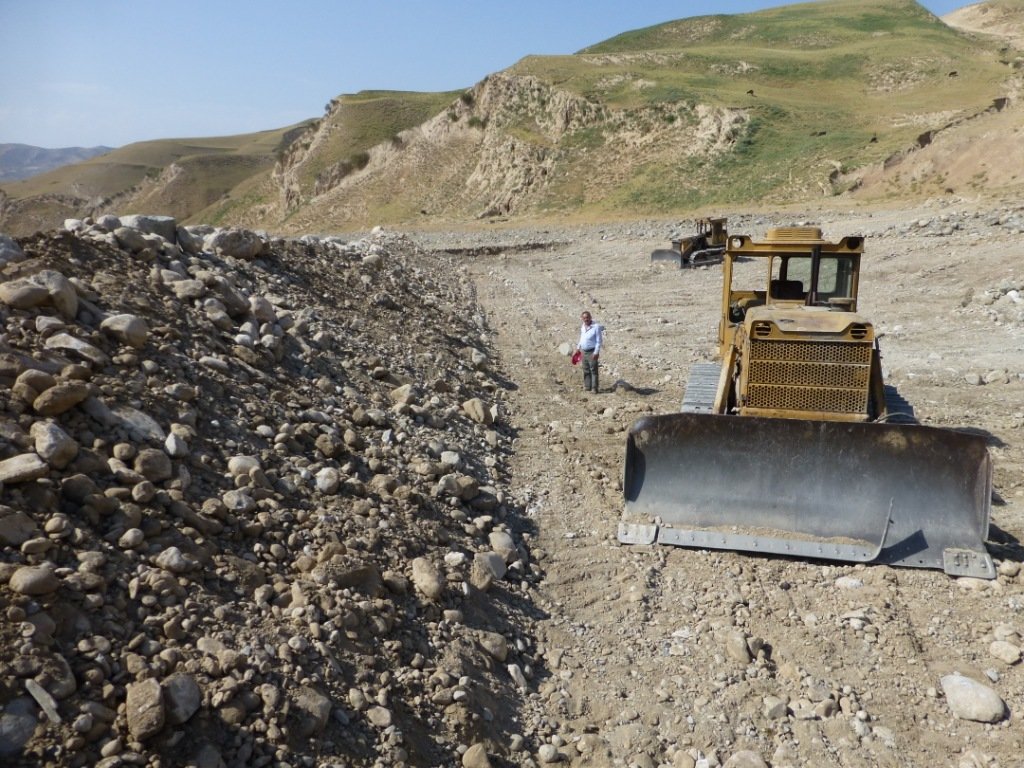
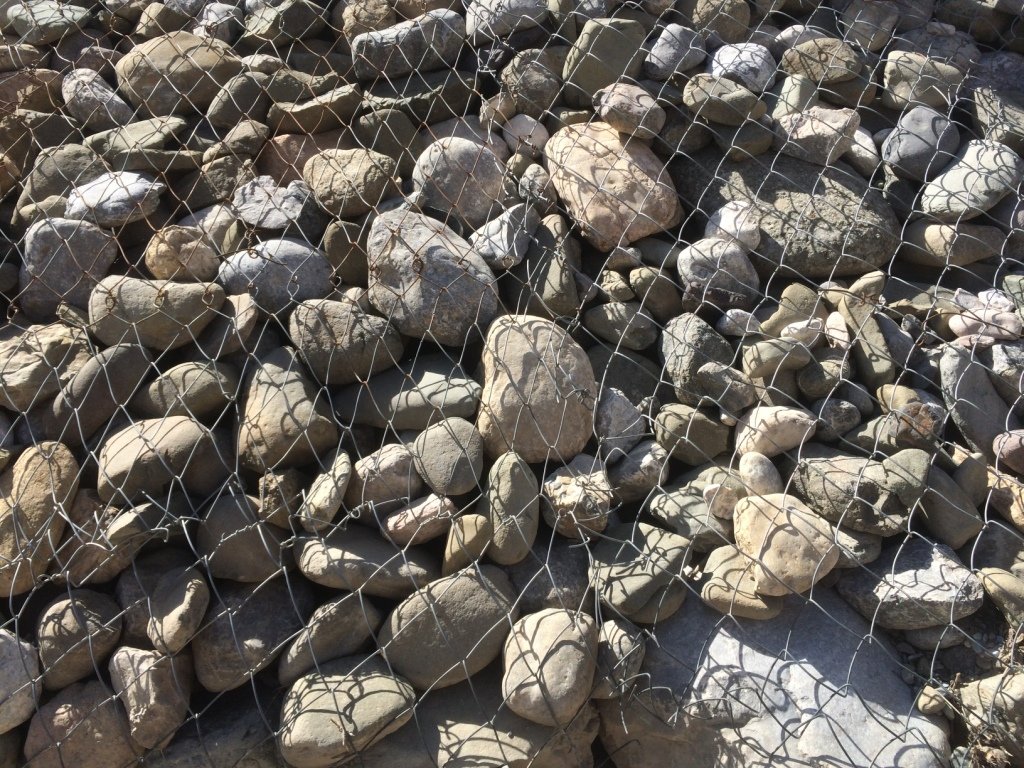
The river training dam is a disaster mitigation structure constructed in the middle zone of the watershed of Obishur (Southern Tajikistan), at 1400 metres above sea level. It is diverting the water from the river fan naturally flowing through Kulchashma village into a different direction and river outlet (Yakhsu river). The dike is a simple structure consisting of a 400m-long and 4m-high channel dug by bulldozer consolidated by a 60m-long and 3m-wide gabion protecting a sharp curve of the river. The material needed is limited to stones and wire net, and the construction as well as maintenance costs are hence low and don't need a too high amount of labour, provided by the communities as in-kind contribution. The structure is built to resist a pressure of up to 72 m3/sec. Given the annual frequency and strength of the local floods, the Kulchashma river training dam has an estimated life expectancy of 30 years. The land users proposed to establish the dam in order to protect the 250 households and 270 ha of land downstream being regularly affected by the floods. In particular, people, houses, roads and other infrastructure, crop and pasture land as well as animals and other assets were highly exposed to the risk of flood. The agricultural production, constituting the main part of people’s income was hindered by the regular occurrence of disasters. The establishment of the river training dam resulted in the rehabilitation of unproductive land in the river fan and its use as pasture and arable land which the community mainly uses for agroforestry. The occurrence of crop pests decreased, the crop diversity was increased, the crop and land productivity improved, thereby enhancing the land users’ food security and overall income. The dam also allowed vulnerable community members to access land and build houses. The construction of buildings behind the dam is however risky and communities tend to forget or ignore that a risk of failure of the dam persists, and that its life expectancy is limited. But first of all, the personal safety of the community members is now improved and they are happy to be able to sleep without the fear of regular floods.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
塔吉克斯坦
区域/州/省:
Khatlon Region, Muminabad District
有关地点的进一步说明:
Kulchashma Jamoat, Kulchashma village
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 适用于特定场所/集中在较小区域
注释:
water diversion and drainage
Map
×2.6 实施日期
注明实施年份:
2014
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过土地使用者的创新
注释(项目类型等):
The adoption of the technology was proposed by the land users.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 结合其他技术保护流域/下游区域
- 降低灾害风险
- 创造有益的经济影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

牧场
粗放式放牧:
- 半游牧畜牧业
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 混合雨水灌溉
注释:
Irrigation - main irrigation channels also received water diverted by the dam.
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 引水和排水
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

结构措施
- S3:分级沟渠、渠道、水道
- S5:大坝、集水斗、水池
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wg:冲沟侵蚀/沟蚀
- Wr:河岸侵蚀
- Wo:场外劣化效应

生物性退化
- Bc:植被覆盖的减少
- Bh:栖息地丧失
- Bq:数量/生物量减少
- Bl:土壤寿命损失
- Bp:害虫/疾病增加,捕食者减少

水质恶化
- Hs:地表水良变化
- Hp:地表水水质下降
- Hq:地下水水质下降
注释:
Improvement of groundwater quality is not the focus of the project but the technology has an impact on this type of natural degradation process.
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
注释:
Flood sediments are diverted by the dam and its accumulation in the lower zone of the watersheds is prevented, thereby allowing the rehabilitation of arable land downstream.
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Specify how costs and inputs were calculated:
per Technology unit
Specify unit:
Dam
Specify dimensions of unit (if relevant):
400m-long dug channel and 60m-long gabion
Specify currency used for cost calculations:
USD
作者:
Sady Odinashoev
日期:
01/08/2013
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术单元
指定单位:
Dam
指定单位面积(如相关):
400m-long dug channel and 60m-long gabion
具体说明成本计算所用货币:
- 美元
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | 400m-long channel digging (bulldozer) | August-October |
| 2. | Stone collection | October (10 days) |
| 3. | Construction of gabions | November (15 days) |
注释:
Establishment activities to be completed before the cold and snow/rain season.
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Construction of wire net gabions | person-hours | 1400.0 | 1.5 | 2100.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Bulldozer driving | person-hours | 150.0 | 1.5 | 225.0 | |
| 设备 | Bulldozer rent | day | 15.0 | 63.0 | 945.0 | |
| 设备 | Fuel for bulldozer | litre | 2250.0 | 1.35 | 3037.5 | |
| 设备 | Diesel oil for bulldozer | litre | 68.0 | 2.13 | 144.84 | |
| 设备 | Spindle oil for bulldozer | litre | 45.0 | 2.0 | 90.0 | |
| 施工材料 | wire net (diametre 4mm) | m2 | 625.0 | 1.6 | 1000.0 | |
| 施工材料 | wire (diametre 3mm) | kg | 26.0 | 1.6 | 41.6 | |
| 其它 | Gearbox oil for bulldozer | litre | 22.0 | 2.5 | 55.0 | |
| 其它 | Solid oil for bulldozer | litre | 22.0 | 3.0 | 66.0 | |
| 其它 | Gas for bulldozer | litre | 22.0 | 1.4 | 30.8 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 7735.74 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 7735.74 | |||||
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
Rent of bulldozer + bulldozer driving covered by local district government. All other costs covered by project.
注释:
Cost-sharing for establishment and maintenance activities is agreed upon when determining the design and implementation of the dam as part of the project conditions.
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Fixing of wire net gabions | March, annually |
注释:
Maintenance activities to be conducted before peak rain/snowmelt/flood season.
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Fixing wire net (by Self Help Group) | hour | 40.0 | 0.8 | 32.0 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | wire net | kg | 7.0 | 1.0 | 7.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 39.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 39.0 | |||||
注释:
All maintenance costs covered by land users.
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
- Geography (steep hills to dig a diverting channel increases the establishment costs)
- Geology (quality/type of soil affects the time needed for digging)
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
有关降雨的规范/注释:
Varies very much from year to year.
注明所考虑的参考气象站名称:
Muminabad meteo station (1200 m a.s.l.)
农业气候带
- 半干旱
Average temperatures:
Spring:10-32°C
Summer: 20-35°C
Autumn: 10-32°C
Winter: -5-+5°C
Average yearly temperature: 11.1°C
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 凹陷情况
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
On southern (sunny) side of the hills, loess type of soil. On northern (shady) side of the hills, humus type of soil
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
> 50米
地表水的可用性:
过量
水质(未处理):
良好饮用水
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
是
规律性:
偶然
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
Seasonal floods/high runoff in spring time, when heavy rain coincides with snowmelt.
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
栖息地多样性:
- 中等
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 生计(自给)
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
- 机械化/电动
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 青年人
- 中年人
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 中等规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 州
土地使用权:
- 租赁
用水权:
- 社区(有组织)
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
SLM之前的数量:
No production
SLM之后的数量:
Self-use + surplus sold on market
注释/具体说明:
6000 kg onions/ ha
作物质量
注释/具体说明:
35-40% increase
饲料生产
注释/具体说明:
On average 50% increase of fodder. Additionally, fodder crop seeds (lucerne) can be sold; increases land users' income.
饲料质量
畜牧生产
生产故障风险
注释/具体说明:
One of the main and most important impact
产品多样性
生产区域
注释/具体说明:
25-30% increase in production area in lowlands (downstream) through rehabilitation of unproductive land which was previously regularly flooded and covered by sediments.
土地管理
注释/具体说明:
Trees newly planted are used for riverbed protection and fuelwood production
水资源可用性和质量
饮用水的可用性
注释/具体说明:
Floods do not contaminate spring drinking waters with sediments
饮用水的质量
灌溉用水的可用性
注释/具体说明:
Irrigation channel not destroyed by annual floods anymore.
收入和成本
农业投入费用
注释/具体说明:
Pests decreased.
农业收入
注释/具体说明:
Through rehabilitation of unproductive land in river fan.
收入来源的多样性
其它社会经济效应
orchards
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
注释/具体说明:
Cultivation of wheat plots and vegetables for self-use and sale
健康状况
土地使用权/用水权
注释/具体说明:
Previously unused land in the river fan is now registered as pasture land with a land certificate for the use of the community, and new houses where also built on this land.
娱乐机会
社区机构
注释/具体说明:
Taxes can be collected with the registration and certification of pasture land and with the authorisation of house construction.
SLM/土地退化知识
社会经济弱势群体的情况
注释/具体说明:
With dam constructed, economically disadvantaged people have space for building a house on the rehabilitated land.
生态影响
水循环/径流
地表径流
多余水的排放
土壤
土壤覆盖层
土壤流失
土壤堆积
养分循环/补给
土壤有机物/地下C
生物多样性:植被、动物
植被覆盖
植物多样性
害虫/疾病控制
减少气候和灾害风险
洪水影响
滑坡/泥石流
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
旱季稳定可靠的水流
下游洪水
下游淤积
对邻近农田的破坏
对公共/私人基础设施的破坏
对场外影响(测量)的评估进行具体说明:
In the last three years no flood affected the downstream village. 330ha of land situated downstream of the dam has been rehabilitated, cleaned from big stones, and used fully as pasture. No sediment flood affected the use of this rehabilitated land.
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年降雨量 | 增加 | 好 | |
| 季雨量 | 春季 | 增加 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 非常好 |
| 山洪暴发 | 非常好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
非常积极
注释:
From the land-user perspective, the benefit assessment of the establishment costs could only be done in relation to the land-users' contribution (i.e. 10% of establishment costs in cash or USD 600 , plus labour).
Because the dam was constructed less than 10 years ago, the long-terms returns cannot be assessed yet.
6.5 技术采用
- > 50%
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
250 households and 270 ha covered, i.e. 50% of Kulchashma village's population.
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 0-10%
注释:
This low percentage is explained by the fact that a structural measure like a dam construction is a big collective investment and can only be initiated as a group with coordination.
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
否
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| The construction and maintenance of a river training dam prevents further land degradation caused by floods, allows the rehabilitation of unused land to create new pastures, and above all increases people's and livestock's safety. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| General improvement of life quality, including life safety and opportunities to protect assets and improve livelihoods. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| None | n/a |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Downstream communities feel safe behind the dam and tend to ignore the risk of failure in extreme conditions (beyond the coping capacity of the dam). As a consequence, people build houses in places still at risk in the river fan. | Strengthened governance (no authorisation of construction in the river fan/behind the dam in the risk zone). |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 与土地使用者的访谈
5 land users
- 与SLM专业人员/专家的访谈
1
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
11/10/2016
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块