Vegetative erosion control and cons. Crop. System [泰国]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Samran Sombatpanit
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
Rabob karn pluek puet choeng anurak
technologies_999 - 泰国
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
Intapan Pitarg
Land development departement Regional Office 6
泰国
SLM专业人员:
Kanchanakul Nualsri
Department of Land Development
泰国
SLM专业人员:
Kanchanakul Vasuthep
Department of Land Development
泰国
SLM专业人员:
Boonchee Sawatdee
泰国
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Land Development Department (Land Development Department) - 泰国有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
World Association of Soil and Water Conservation (WASWC) - 中国1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
A conservation cropping system utilizing vegetative method for controlling erosion
2.2 技术的详细说明
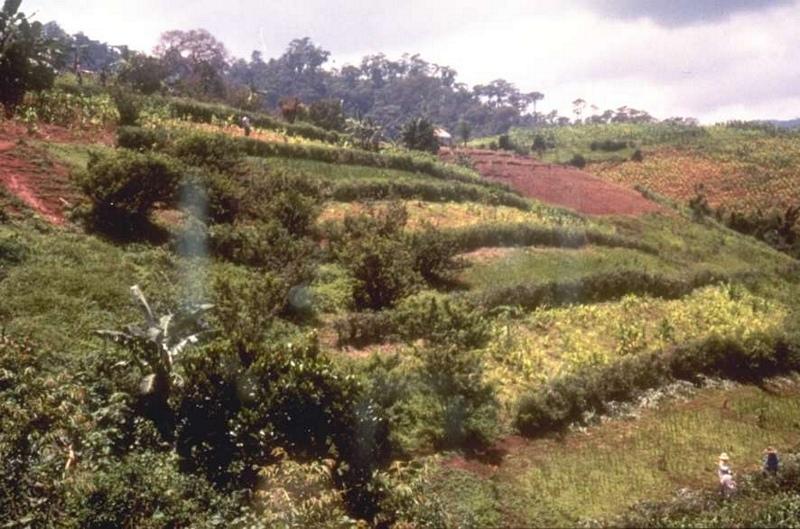
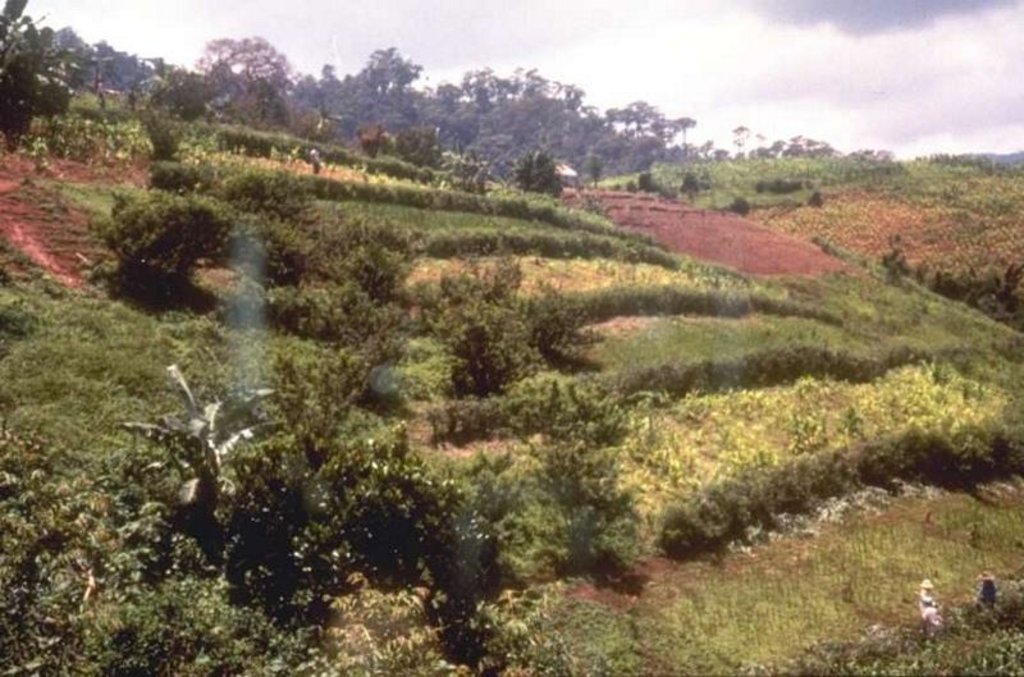
说明:
To make the contour hedgerow by grass and legunminous plants across the slope together with integrated cropping system, comprising of field crop, vegetables and bush-type crops and fruit trees. Other components include contour cultivation, incorporation of crop residues, soil amendments, reduced tillage, stressing on cropping more than once a year.
2.3 技术照片
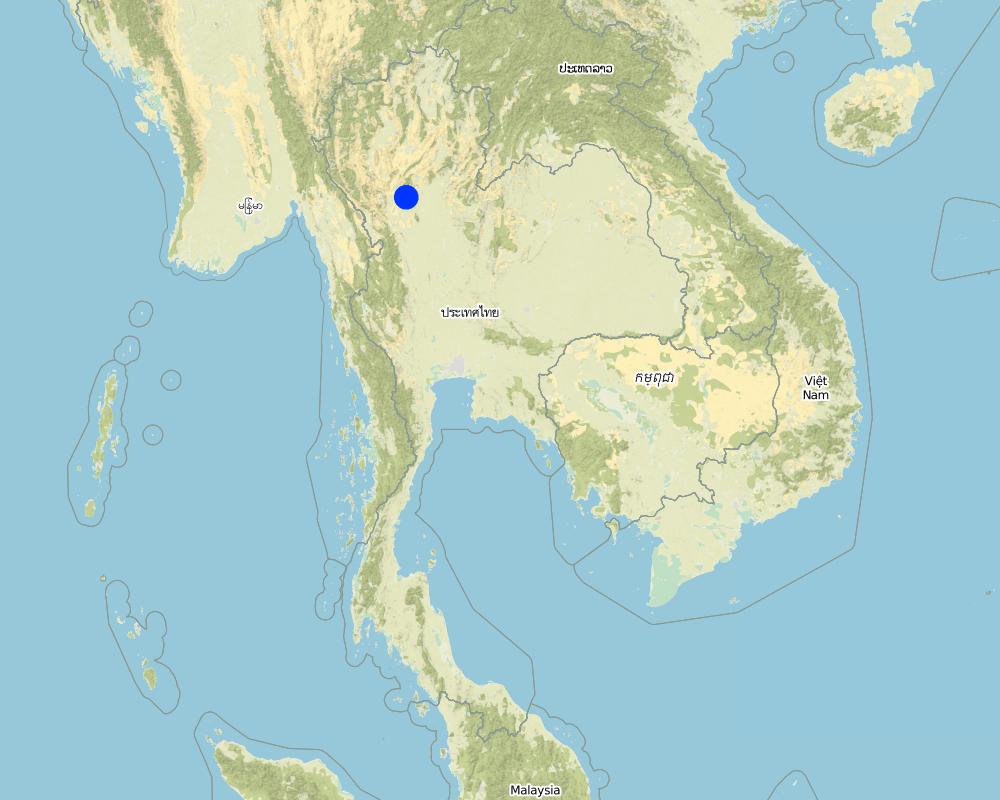
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
泰国
区域/州/省:
Upper North
有关地点的进一步说明:
Upper North
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- 100-1,000 平方千米
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 1000 km2.
This technology is being implemented in several areas. The extent of mplemented areas is not exactly known at the this time but can be known in the future.
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
Alley cropping with leguminous hedgerow was introduced from IITA, Nigeria. Grass strip was introduced from Australia.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
是
具体说明混合土地使用(作物/放牧/树木):
- 农林业

农田
- 一年一作
- 多年一作(非木材)
- 乔木与灌木的种植
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 谷类 - 水稻(旱地)
- 豆科牧草和豆类 - 其他
- corn
乔木和灌木种植 - 指定作物:
- 芒果、山竹果、番石榴
- Lychee, Longan, Jack fruit
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 180 Longest growing period from month to month: May - Oct

牧场

森林/林地
- Leucaena, cajanus, flemingo, tephrosia, glyricidia
产品和服务:
- 木材
- 水果和坚果
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): 1. Farmers lack of technology about SWC and soil improvement. Farmers need support in credits and marketing. 3. Poveerty.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): 1. Weed problems. 2. Soil fertility decline resulting in decreased crop yield. 3. Soil erosion. 4. Lack of labour.
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 最小的土壤扰动
- 横坡措施
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A3:土壤表面处理
A3:区分耕作制度:
A 3.2: Reduced tillage (> 30% soil cover)
注释:
Main measures: vegetative measures
Secondary measures: agronomic measures
Type of agronomic measures: mixed cropping / intercropping, mulching, green manure, minimum tillage, contour tillage
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)

水质恶化
- Ha:干旱化
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, Ha: aridification
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
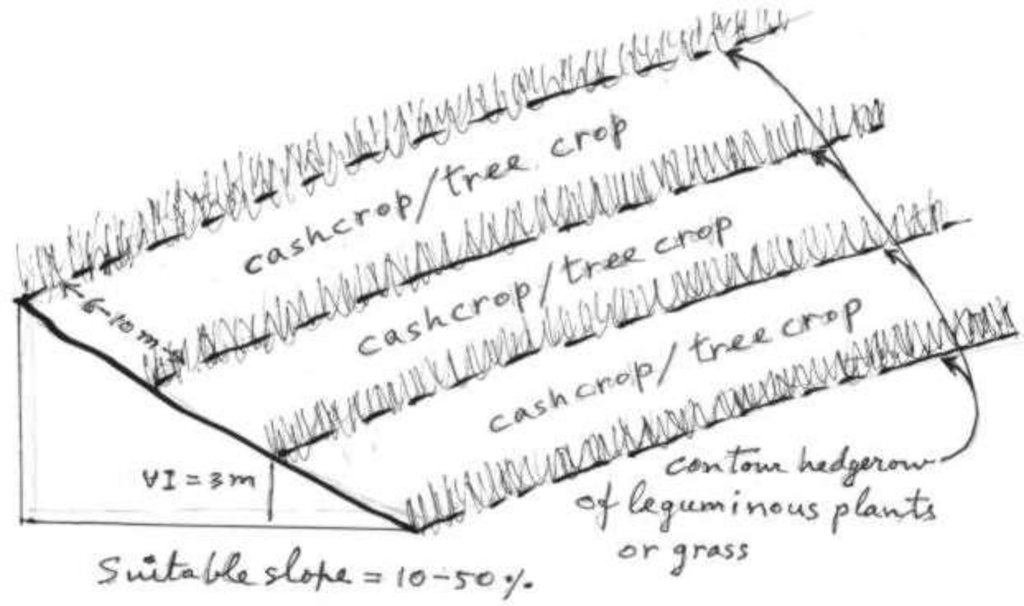
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
General dimension of the technology
Upper North
Date: 8/6/00
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: high
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, reduction of slope length, improvement of ground cover, increase in organic matter, increase of infiltration, increase in soil fertility
Secondary technical functions: increase of surface roughness, increase / maintain water stored in soil, water harvesting / increase water supply, water spreading
Green manure
Material/ species: Leucaena leucocephala, Cajanus cajan
Remarks: From lopping branches of legumes
Vegetative measure: Contour
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 3
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 5-12
Vegetative measure: Grass strip
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 3
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 5-12
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Trees/ shrubs species: Leucaena, cajanus, flemingo, tephrosia, glyricidia
Fruit trees / shrubs species: Mango, Jack fruit, Longan, Lychee, etc.
Grass species: Vetiver, ruzi, setaria, bahia, napier
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 30.00%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is (see figure below): 20.00%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 0.00%
作者:
Samran Sombatpanit, Bangkok, Thailand
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Baht
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
37.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
2.70
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Contour establishment | beforginning of rainy season |
| 2. | Establishing hedgerow area | beforginning of rainy season |
| 3. | Planting hedgerow plants | beforginning of rainy season |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 54.0 | 54.0 | |
| 设备 | Equipment - hour | ha | 1.0 | 5.4 | 5.4 | |
| 植物材料 | Seeds | ha | 1.0 | 6.0 | 6.0 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 65.4 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 1.77 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Weeding | Before rainy season / Two times per crop |
| 2. | Land preparation | Before rainy season / Once a year |
| 3. | Crop planting | Before rainy season / Once a year |
| 4. | Fertilizer application | Before rainy season / Once per crop |
| 5. | Loppinging /mulching | as required /2-3 times per year |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 64.8 | 64.8 | |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 64.8 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 1.75 | |||||
注释:
Machinery/ tools: Tractor, hand hoe, macheter
Calculation of the cost will involve only those related to SWC. The hedgerow area per ha is 1000 m2 which requires approximately one hour of tractor's work, the rental charge of which is 200 Baht per hour.
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
The cost depends very much on the degree of slope, which determines the number of hedgerows per specific area.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
有关降雨的规范/注释:
Annual rainfall: Also 1500-2000 mm (ranked 2) and 750-1000 mm (ranked 3)
农业气候带
- 半湿润
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Altitudinal zone: Also 501-1000 m a.s.l. (ranked 2) and 1001-1500 m a.s.l. (ranked 3)
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil depth on average: Also deep (ranked 2)
Soil fertility: Medium
Soil drainage/infiltration: Good
Soil water storage capacity: Medium
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 生计(自给)
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 非常贫瘠
- 贫瘠
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
10% of the land users are average wealthy and own 10% of the land.
10% of the land users are poor and own 10% of the land.
80% of the land users are poor and own 80% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Poor land users used to work as labourers to earn extra income.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,未命名
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 自由进入(无组织)
- 个人
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
注释/具体说明:
Timber trees & fruit trees
饲料质量
木材生产
生产区域
注释/具体说明:
For establishing hedgerows
土地管理
收入和成本
农业收入
经济差异
工作量
其它社会经济效应
Input constraints
社会文化影响
社区机构
国家机构
冲突缓解
生态影响
水循环/径流
地表径流
SLM之前的数量:
20
SLM之后的数量:
10
多余水的排放
土壤
土壤水分
土壤覆盖层
土壤流失
SLM之前的数量:
20
SLM之后的数量:
5
养分循环/补给
生物多样性:植被、动物
植物多样性
动物多样性
栖息地多样性
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
旱季稳定可靠的水流
下游洪水
下游淤积
地下水/河流污染
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
非常积极
6.5 技术采用
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
15100, 100% area covered
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 0-10%
注释:
99% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
15000 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: estimates
1% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
100 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Number of participating farmers increases according to the government's budget and work plan. The technology has been widely accepted all over the country and in many parts of the world.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| The technology can: 1. Improve soil fertility and productivity. |
| 2. Increase income |
| 3. Attain sustainable land use. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
The technology can: 1. Reduce soil loss/runoff How can they be sustained / enhanced? Try to integrate annual cash crops and fruit trees. |
| 2. Improve soil fertility |
| 3. Conserve soil moisture |
|
4. Increase yield/income 5. Preserve the environment |
|
6. Easily implemented by farmers 7. Requires low cost. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| 1. Require more labour to create and maintain. | 1. Grow fast-growing tree species. |
| 2. Certain part of the land especially that occupied by the hedgerows cannot be used to grow crop. | 2. Hire more labourers from the increased income. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| It is more labour intensive than normal farming practices. | Good labour management |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Sajjapongse, A., C. Anecksamphant and S. Boonchee, ASALAND management of Sloping Lands Network. Special Lecture, LDD Technical Meeting, February 15-18, 2000, Chiang Mai.. 2000.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Department of Land Development, Bangkok 10900, Thailand
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Other documents from IBSRAM and other development projects assisted by foreign countries. 1990-1999.
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块