Освоение сильно каменистых склоновых земель под орошаемый абрикосовый сад. [Tajikistan]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Pjotr M Sosin
- Editor: –
- Reviewer: David Streiff
Табдил додани замини сангоб ба зардолу бог
technologies_1055 - Tajikistan
- Full summary as PDF
- Full summary as PDF for print
- Full summary in the browser
- Full summary (unformatted)
- Освоение сильно каменистых склоновых земель под орошаемый абрикосовый сад.: Maart 20, 2017 (inactive)
- Освоение сильно каменистых склоновых земель под орошаемый абрикосовый сад.: Julie 22, 2017 (inactive)
- Освоение сильно каменистых склоновых земель под орошаемый абрикосовый сад.: Aug. 21, 2019 (inactive)
- Освоение сильно каменистых склоновых земель под орошаемый абрикосовый сад.: Nov. 2, 2021 (public)
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
SLM specialist:
Name of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Tajik Soil Insitute (Tajik Soil Institute) - TajikistanName of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Tajik Academy of Agricultural Sciences (Tajik Academy of Agricultural Sciences) - Tajikistan1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
When were the data compiled (in the field)?
03/05/2011
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Ja
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
Освоение каменистых земель под орошаемое садоводство.
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
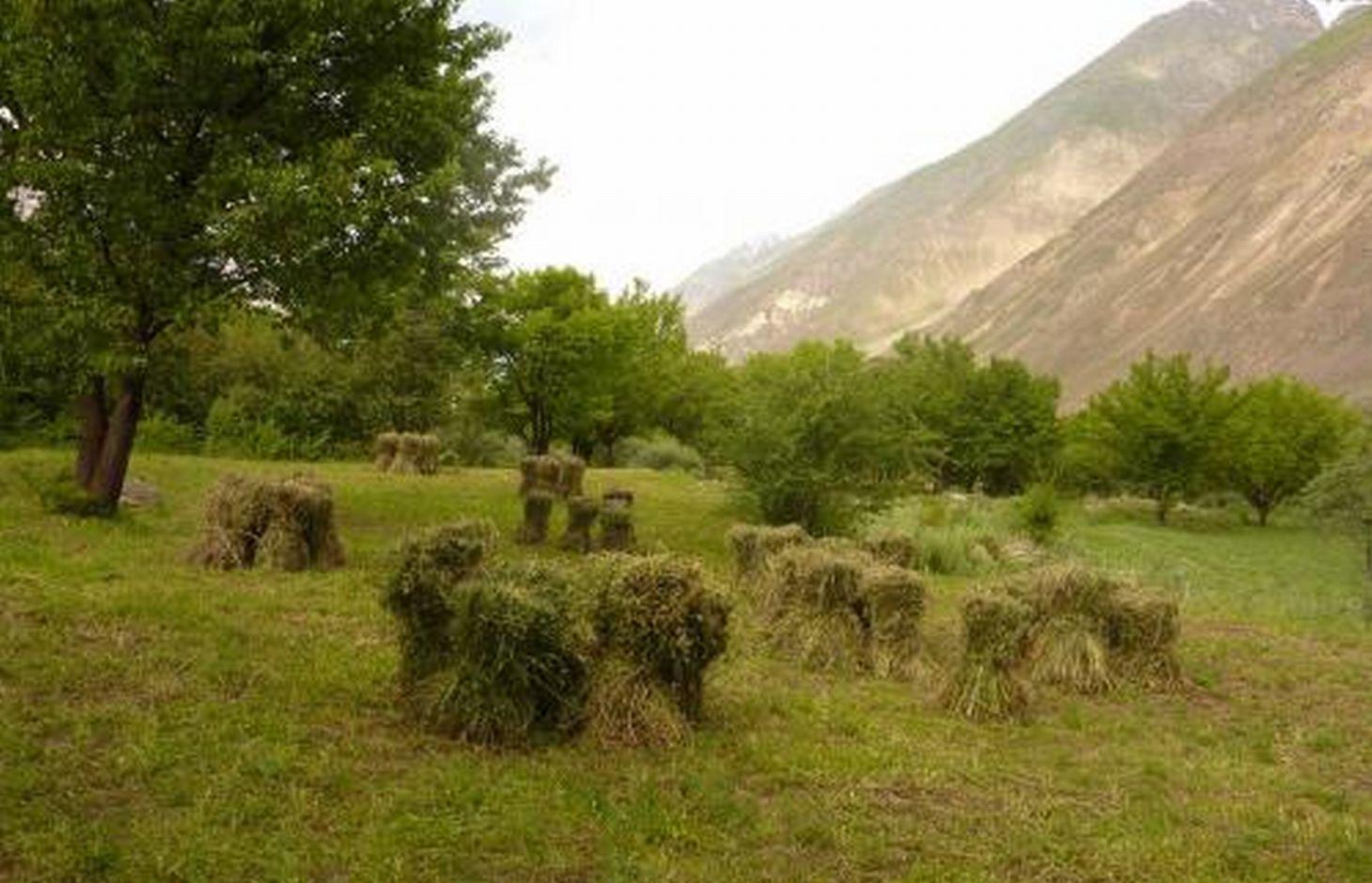
Сильно каменистый конус выноса до внедрения технологии использовался как низкопродуктивное пастбище. На участке внедрения технологии проведена камнеуборка. Камни и глыбы использовались для строительства ограждения (забора) вокруг участка. Часть камней складировалась в кучи на территории участка. Вдоль верхней границы участка построен оросительный канал. Из него на территорию участка, по горизонтали мезорельефа, проведены оросительные арыки. Планировка поверхности участка не проводилась из за сильной каменистости. Деревъя абрикоса посажены вдоль оросительных арыков. Междурядьях сада возделываются многолетние травы -эспарцет, люцерна. Камни убранные с площади участка использовались для строительство забора вокруг участка. Забор необходим для того, чтобы предотвратить проникновения на территорию сада мелко и крупно рогатого скота.
Purpose of the Technology: Цель технологии, повышение продуктивности сильно каменистых, склоновых земель конуса выноса с применением орошения и возделыванием комбинированных культур-абрикосового сада и многолетних трав.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Камне уборка на участке, строительство ограждения, строительство оросительного канала, проведение оросительных арыков по площади участка, посадка деревьев, вспашка междурядье и посев многолетних трав.
Natural / human environment: Участок расположен в аридной зоне на сильно каменистой почве конуса выноса, на левом берегу реки Ванч. До освоения этих земел поверхность почвы на 60% было покрыта камнями. Растительность была представлена эфемерами, имеющие короткий период вегетации. Эти земли использовались под летние низкопродуктивные выпаса.
2.3 Photos of the Technology
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
Tajikistan
Region/ State/ Province:
Таджикистан
Further specification of location:
ГБАО, Ванж, Жовид
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
If precise year is not known, indicate approximate date:
- 10-50 years ago
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- during experiments/ research
Comments (type of project, etc.):
Землепользователи принимали участие лишь в технической реализации технологии.
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- improve production
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied

Cropland
- Perennial (non-woody) cropping
- Tree and shrub cropping

Mixed (crops/ grazing/ trees), incl. agroforestry
- Agroforestry
Comments:
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Mixed: Mf: Agroforestry
If land use has changed due to the implementation of the Technology, indicate land use before implementation of the Technology:
Grazing land: Ge: Extensive grazing land
3.3 Further information about land use
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- full irrigation
Comments:
Water supply: полностью орошаемое, полностью орошаемое
Number of growing seasons per year:
- 1
Livestock density (if relevant):
1-10 УГ/км2
3.4 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- agroforestry
- improved ground/ vegetation cover
3.5 Spread of the Technology
Specify the spread of the Technology:
- evenly spread over an area
If the Technology is evenly spread over an area, indicate approximate area covered:
- 0.1-1 km2
Comments:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.2 m2.
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

vegetative measures
- V1: Tree and shrub cover
- V2: Grasses and perennial herbaceous plants

structural measures
- S6: Walls, barriers, palisades, fences

management measures
- M1: Change of land use type
Comments:
Main measures: vegetative measures
Secondary measures: structural measures, management measures
Type of agronomic measures: смешанное возделывание / междурядное возделывание, посадка бобовых в междурядьях, минимальная обработка
Type of vegetative measures: урегулированный: -контур
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

soil erosion by water
- Wt: loss of topsoil/ surface erosion

biological degradation
- Bc: reduction of vegetation cover
Comments:
Main type of degradation addressed: Вв (Wt): потеря верхнего слоя почвы / поверхностная эрозия
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Бр (Bc): уменьшение растительного покрова
Main causes of degradation: чрезмерный выпас, засуха, интенсивная эксплуатация населением
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- reduce land degradation
Comments:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
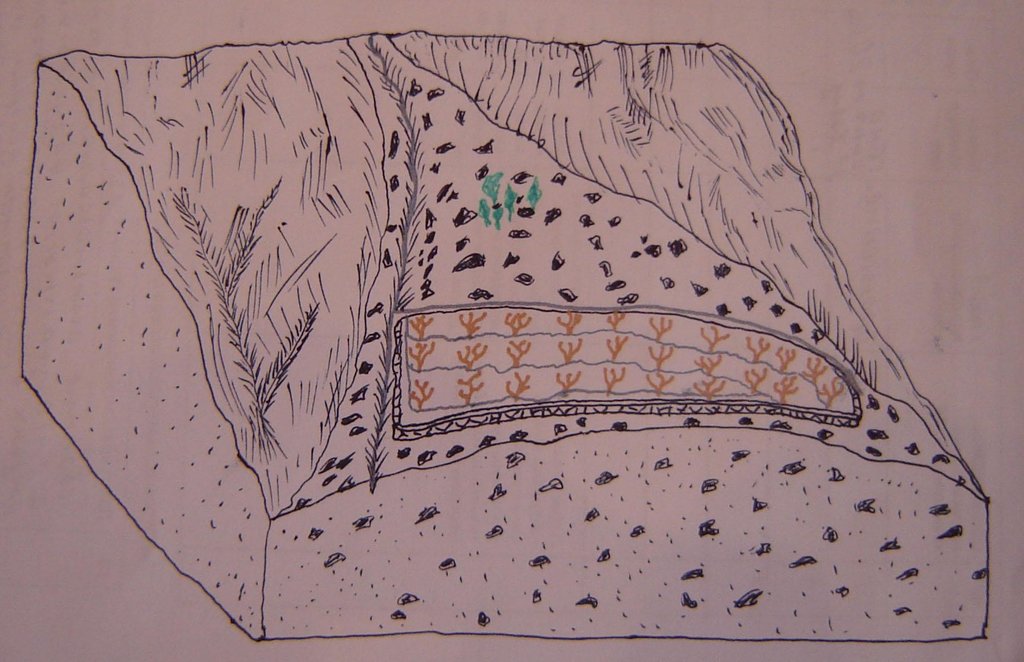
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
4.2 Technical specifications/ explanations of technical drawing
Схема размещения абрикосового сада на конусе выноса.
Location: Джамоат Джовид. Ванч, ГБАО
Date: 2010,06,16
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: средний
Technical knowledge required for land users: средний
Main technical functions: улучшение земляного покрова
Secondary technical functions: улучшение структуры верхнего слоя почвы (прессование), повышение органического вещества
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: Ф: фруктовые деревья / кустарники, К: многолетние культуры
Wall/ barrier
Vertical interval between structures (m): 1
Spacing between structures (m): 3000
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0,5
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 3000
Change of land use type
4.3 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
other/ national currency (specify):
Сомони
Indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (if relevant): 1 USD =:
4.5
Indicate average wage cost of hired labour per day:
7.00
4.4 Establishment activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Строительство забора | Structural | 1 год |
| 2. | Строительство оросительного канала | Structural | 1 год |
| 3. | Приобретение саженцев | Structural | 15 дней |
| 4. | Посадка саженцев | Structural | 2 месяц |
| 5. | Камнеуборка на площади 20га | Structural |
4.5 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | None | None | 3000.0 | 15.0 | 45000.0 | 30.0 |
| Labour | None | None | 1300.0 | 23.07692 | 30000.0 | 10.0 |
| Labour | None | None | 6400.0 | 1.0 | 6400.0 | 100.0 |
| Labour | None | None | 20.0 | 2625.0 | 52500.0 | 30.0 |
| Plant material | None | None | 6400.0 | 5.0 | 32000.0 | |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 165900.0 | |||||
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Agro-climatic zone
- arid
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- medium (loamy, silty)
Topsoil organic matter:
- medium (1-3%)
5.4 Water availability and quality
Ground water table:
> 50 m
Water quality (untreated):
good drinking water
5.5 Biodiversity
Species diversity:
- low
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Market orientation of production system:
- subsistence (self-supply)
Off-farm income:
- 10-50% of all income
Relative level of wealth:
- average
Individuals or groups:
- individual/ household
Level of mechanization:
- manual work
- animal traction
Gender:
- women
- men
Indicate other relevant characteristics of the land users:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly disadvantaged land users
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
5.7 Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
Is this considered small-, medium- or large-scale (referring to local context)?
- small-scale
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- state
Land use rights:
- leased
Comments:
Земля является собственностью госудаства, землепользователи арендуют участки
5.9 Access to services and infrastructure
health:
- poor
- moderate
- good
education:
- poor
- moderate
- good
technical assistance:
- poor
- moderate
- good
employment (e.g. off-farm):
- poor
- moderate
- good
markets:
- poor
- moderate
- good
energy:
- poor
- moderate
- good
roads and transport:
- poor
- moderate
- good
drinking water and sanitation:
- poor
- moderate
- good
financial services:
- poor
- moderate
- good
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-economic impacts
Production
fodder production
Water availability and quality
demand for irrigation water
Income and costs
farm income
economic disparities
Socio-cultural impacts
food security/ self-sufficiency
recreational opportunities
situation of socially and economically disadvantaged groups
Ecological impacts
Water cycle/ runoff
surface runoff
Soil
soil moisture
soil organic matter/ below ground C
Biodiversity: vegetation, animals
biomass/ above ground C
habitat diversity
Other ecological impacts
6.3 Exposure and sensitivity of the Technology to gradual climate change and climate-related extremes/ disasters (as perceived by land users)
Gradual climate change
Gradual climate change
| Season | Type of climatic change/ extreme | How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| annual temperature | increase | well |
Climate-related extremes (disasters)
Meteorological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| local rainstorm | not well |
Climatological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| drought | well |
Other climate-related consequences
Other climate-related consequences
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| reduced growing period | well |
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
negative
Long-term returns:
positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
slightly negative
Long-term returns:
very positive
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
- 10-50%
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many have did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 0-10%
Comments:
40% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
30 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Широкое внедрение технологии тормозится дефицитом денежных средств.
6.7 Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities of the Technology
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the land user’s view |
|---|
|
Не требует специальных инженерных сооружений How can they be sustained / enhanced? В течении использования технологии |
|
Для ограждения используется местный материал How can they be sustained / enhanced? В течении использования технологии |
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
|
Не требует специальных инженерных сооружений How can they be sustained / enhanced? В течении использования технологии |
|
Не используются дополнительные материалы и оборудование How can they be sustained / enhanced? В течении использования технологии |
|
Для ограждения используется местный материал How can they be sustained / enhanced? В течении использования технологии |
6.8 Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks of the Technology and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| Функционирование технологии зависит от обеспеченности оросительной водой | Внедрить водосберегающую технологию |
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks
No links
Modules
No modules