Укрепление берегов рек с помощью камней и габионов [Tajikistan]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: German Kust
- Editor: –
- Reviewer: David Streiff
Strengthening of the river banks with stones and gabions (English)
technologies_1362 - Tajikistan
- Full summary as PDF
- Full summary as PDF for print
- Full summary in the browser
- Full summary (unformatted)
- Укрепление берегов рек с помощью камней и габионов: Maart 21, 2017 (inactive)
- Укрепление берегов рек с помощью камней и габионов: Julie 31, 2017 (inactive)
- Укрепление берегов рек с помощью камней и габионов: Feb. 14, 2020 (inactive)
- Укрепление берегов рек с помощью камней и габионов: Nov. 2, 2021 (public)
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
SLM specialist:
Tajikistan
Name of project which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Community Agriculture and Watershed Management project in Tajikistan (WB / CAWMP)1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
When were the data compiled (in the field)?
22/05/2011
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Ja
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
Укрепление берегов рек и противоселевые мероприятия с помощью камней и габионов
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
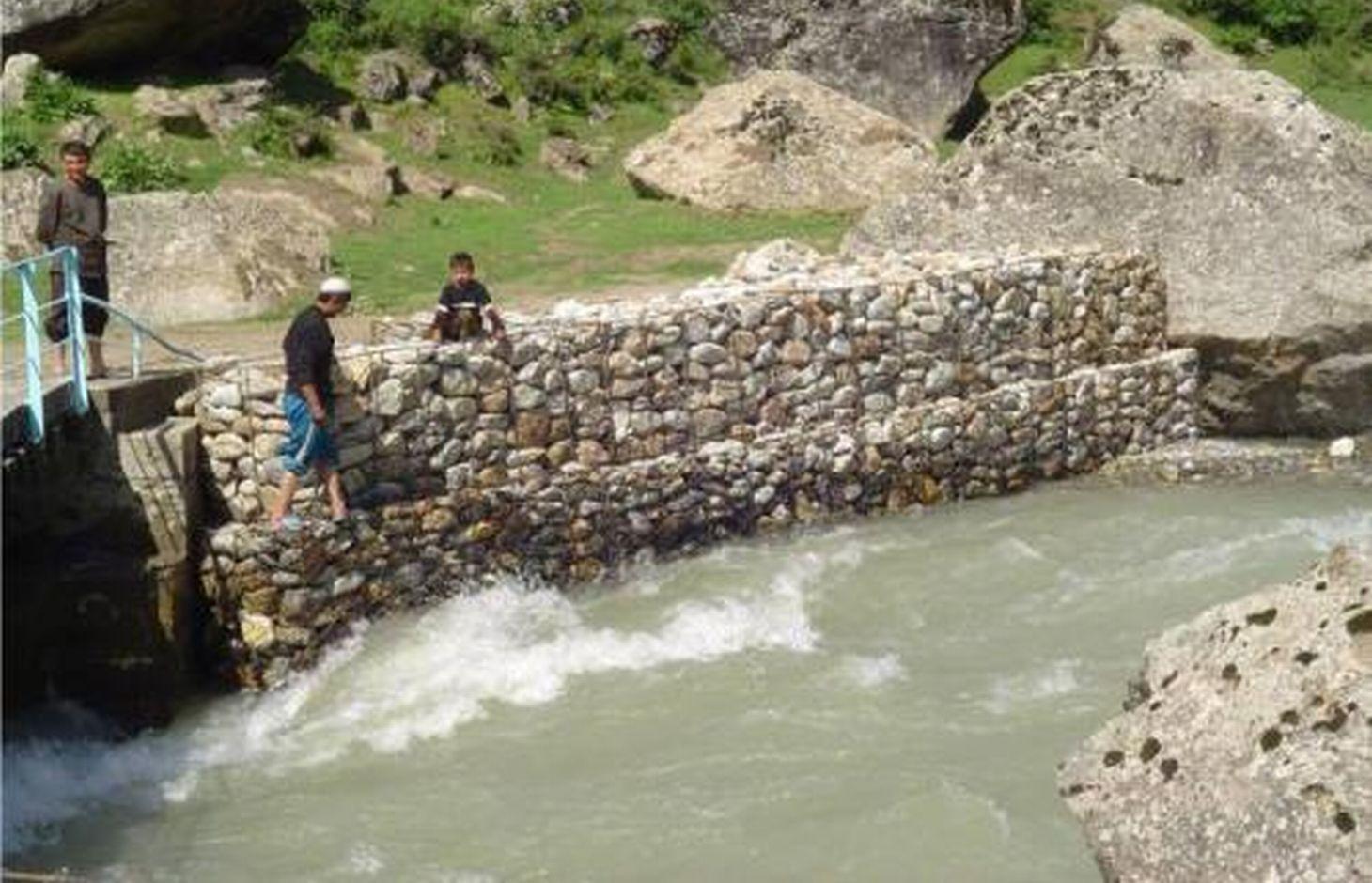
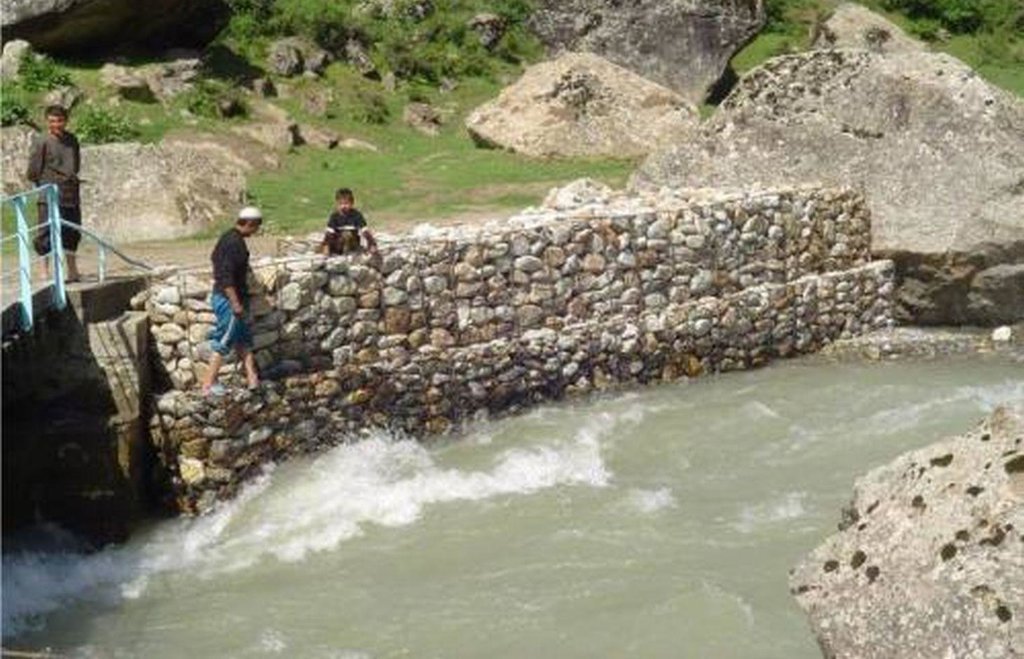
Технология состоит в сборе камней , в основном среднего размера (20-40 см в диаметре) и укладке их особым способом в местах, подверженных наиболее сильному воздействия течения реки и размыванию для предотвращения от дальнейшего размывания земель, занятых поселениями или сельскохозяйственными полями. Традиционно применяется два типа укладки камней: (1) в виде габионов, то есть вертикальных стен из камней, скрепленных проволокой, (2) в виде каменной кладки на матах из ветвей деревьев и кустарников
Purpose of the Technology: Предотвращение размыва берегов речными и селевыми потоками
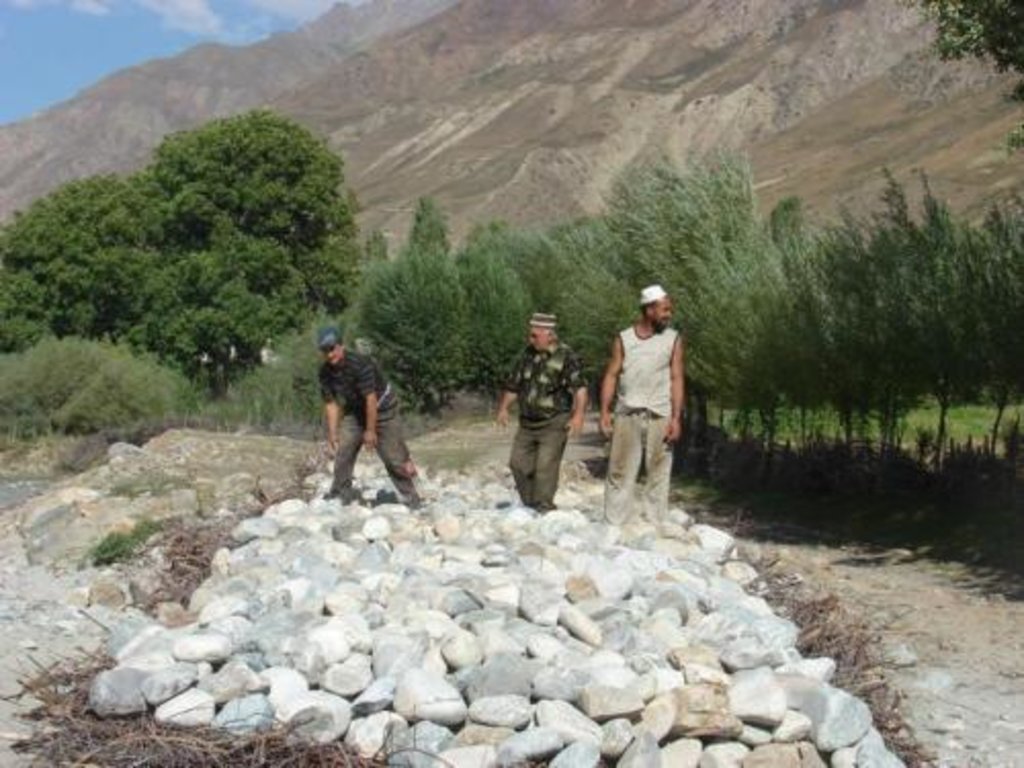
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: сбор камней\ветвей деревьев, их укладка особым способом, скрепление камней ветвями или проволокой
Natural / human environment: берега рек \ сельские поселения
2.3 Photos of the Technology
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
Tajikistan
Region/ State/ Province:
Таджикистан
Further specification of location:
Таджикабадский район, джамоаты Ширинчашма и Шогадоев
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
If precise year is not known, indicate approximate date:
- more than 50 years ago (traditional)
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- as part of a traditional system (> 50 years)
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- protect a watershed/ downstream areas – in combination with other Technologies
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied

Cropland
- Annual cropping

Mixed (crops/ grazing/ trees), incl. agroforestry
- Silvo-pastoralism
Comments:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): размывание берегов речными и селевыми потоками, уменьшение полезной площади земель
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): размывание берегов речными и селевыми потоками, уменьшение полезной площади земель
Mixed: (eg agro-pastoralism, silvo-pastoralism): Yes
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Other: Os: Settlements, infrastructure networks
Livestock is grazing on crop residues
Constraints of settlement / urban: риск сноса части территории
If land use has changed due to the implementation of the Technology, indicate land use before implementation of the Technology:
Other: Os: Settlements, infrastructure networks
3.3 Further information about land use
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- mixed rainfed-irrigated
Comments:
Water supply: смешанное богарно-орошаемое, смешанное богарно-орошаемое
Number of growing seasons per year:
- 1
3.4 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- surface water management (spring, river, lakes, sea)
3.5 Spread of the Technology
Specify the spread of the Technology:
- evenly spread over an area
If the Technology is evenly spread over an area, indicate approximate area covered:
- 1-10 km2
Comments:
всего выполнено 6 подпроектов по берегоукреплению в рамках проекта Всемирного Банка CAWMP. В данном описании приводятся данные в основном для Таджикабадского района
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

vegetative measures
- V1: Tree and shrub cover

structural measures
- S6: Walls, barriers, palisades, fences

management measures
- M3: Layout according to natural and human environment
Comments:
Main measures: structural measures
Secondary measures: vegetative measures, management measures
Type of vegetative measures: урегулированный: -линейныи, в блоках
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

soil erosion by water
- Wr: riverbank erosion
Comments:
Main type of degradation addressed: Вр (Wr): эрозия берегов реки
Main causes of degradation: сильные / чрезмерные дожди (интенсивность/количество), наводнение
Secondary causes of degradation: чрезмерное использование растительного покрова для бытовых целей, другие природные причины (лавина, извержение вулкана, сели, высоко уязвимые природные ресурсы, экстремальная топография и т.д.) укажите какие (сели)
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- prevent land degradation
Comments:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation, rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
4.2 Technical specifications/ explanations of technical drawing
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: средний (должен иметь инженерное образование (гидротехническое))
Technical knowledge required for land users: средний (должен иметь успешный опыт создания такого рода сооружений)
Main technical functions: стабилизация почвы (например, с помощью корней деревьев против оползней)
Secondary technical functions: контроль над концентрированными стоками: запруда / замедление, контроль над концентрированными стоками: дрена / отводка
Aligned: -linear
Vegetative material: Д: деревья / кустарники
In blocks
Vegetative material: Д: деревья / кустарники
Trees/ shrubs species: деревья и кустарники высаживаются после установлния габионов
Wall/ barrier
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 1-3
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0,5-5
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 5-20
Construction material (earth): при создании каменной кладки на матах из веток землей и наносами постепенно забиваются маты
Construction material (stone): основной материал, противостоящий водным и селевым потокам
Construction material (wood): ветки деревьев используются для создания матов и скрепления камней
Construction material (other): металлическая проволока используется для скрепления камней
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
Change of land use practices / intensity level: опасные ранее земли введены в использование
Layout change according to natural and human environment: сбережение участков земель, ранее опасных для поселения и сельского хозяйства
4.4 Establishment activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | сбор черенков | Vegetative | |
| 2. | черенки тополя или ивы и облепихи | Vegetative | |
| 3. | посадка черенков | Vegetative | |
| 4. | сбор и транспортировка камней | Structural | |
| 5. | сбор и транспортировка веток деревьев | Structural | |
| 6. | укладка растительных матов и\или камней | Structural | |
| 7. | скрепление камней в габионах | Structural | |
| 8. | Проектирование сооружения | Management | |
| 9. | Организация работ | Management |
4.6 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing/ frequency | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | замена разрушенных участков камней и крепления | Structural | |
| 2. | посадка черенков | Structural | |
| 3. | Контроль состояния сооружений | Management | |
| 4. | Ремонтные мероприятия | Management |
4.7 Costs and inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
Comments:
Затраты в размере 200-800 долларов США рассчитаны на 1 погонный метр среднестатистического сооружения при полностью ручном труде
4.8 Most important factors affecting the costs
Describe the most determinate factors affecting the costs:
время года, дальность транспортировки камней, высота сооружения, ширина толщина сооружения, возможность механизации работ
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Agro-climatic zone
- sub-humid
- semi-arid
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
5.4 Water availability and quality
Availability of surface water:
excess
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Market orientation of production system:
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial
Off-farm income:
- > 50% of all income
Relative level of wealth:
- poor
Individuals or groups:
- groups/ community
Level of mechanization:
- manual work
- mechanized/ motorized
Gender:
- women
- men
Indicate other relevant characteristics of the land users:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
5.7 Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
Is this considered small-, medium- or large-scale (referring to local context)?
- small-scale
Comments:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology: < 0.5 ha, 0.5-1 ha, 1-2 ha
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- communal/ village
- individual, titled
Land use rights:
- communal (organized)
- individual
5.9 Access to services and infrastructure
health:
- poor
- moderate
- good
education:
- poor
- moderate
- good
technical assistance:
- poor
- moderate
- good
employment (e.g. off-farm):
- poor
- moderate
- good
markets:
- poor
- moderate
- good
energy:
- poor
- moderate
- good
roads and transport:
- poor
- moderate
- good
drinking water and sanitation:
- poor
- moderate
- good
financial services:
- poor
- moderate
- good
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-economic impacts
Production
production area
Income and costs
workload
Socio-cultural impacts
food security/ self-sufficiency
community institutions
conflict mitigation
Ecological impacts
Soil
soil loss
Climate and disaster risk reduction
flood impacts
6.2 Off-site impacts the Technology has shown
damage on neighbours' fields
6.3 Exposure and sensitivity of the Technology to gradual climate change and climate-related extremes/ disasters (as perceived by land users)
Gradual climate change
Gradual climate change
| Season | Type of climatic change/ extreme | How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| annual temperature | increase | well |
Climate-related extremes (disasters)
Meteorological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| local rainstorm | not well |
| local windstorm | well |
Climatological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| drought | well |
Hydrological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| general (river) flood | not well |
Other climate-related consequences
Other climate-related consequences
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| reduced growing period | well |
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Long-term returns:
positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Long-term returns:
positive
Comments:
Экономическую пользу трудно оценить, поскольку предотвращенные риски могут быть очень затратными по восстановительным мероприятиям при критических ситуациях
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
- more than 50%
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many have did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 0-10%
Comments:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
76 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: указано количество семей, применивших эту технологию в рамках проекта CAWMP
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: эти технологии традиционны в Таджикистане, но высокозатратны, поэтому нужны стимулирующие средства на ее применение
6.7 Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities of the Technology
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the land user’s view |
|---|
| меньше опасность критических ситуаций |
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
|
относительная дешевизна местных материалов (фактически оплачивается только их транспортировка) How can they be sustained / enhanced? всегда |
|
инженерная простота сооружений How can they be sustained / enhanced? пока есть опытные мастера и инженеры |
|
возможность снизить риски землепользования на критических участках How can they be sustained / enhanced? пока поддерживаются существующие сооружения |
6.8 Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks of the Technology and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the land user’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| сооружения могут быть уничтожены сильным селем или паводком | делать сооружения крепче |
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| сооружения могут быть уничтожены сильным селем или паводком | делать сооружения крепче, применять более совершенные технологии укрепления |
7. References and links
7.2 References to available publications
Title, author, year, ISBN:
база данных проекта Community agriculture and Watershed Management project
Available from where? Costs?
Группа управления проектом, бесплатно
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks
No links
Modules
No modules