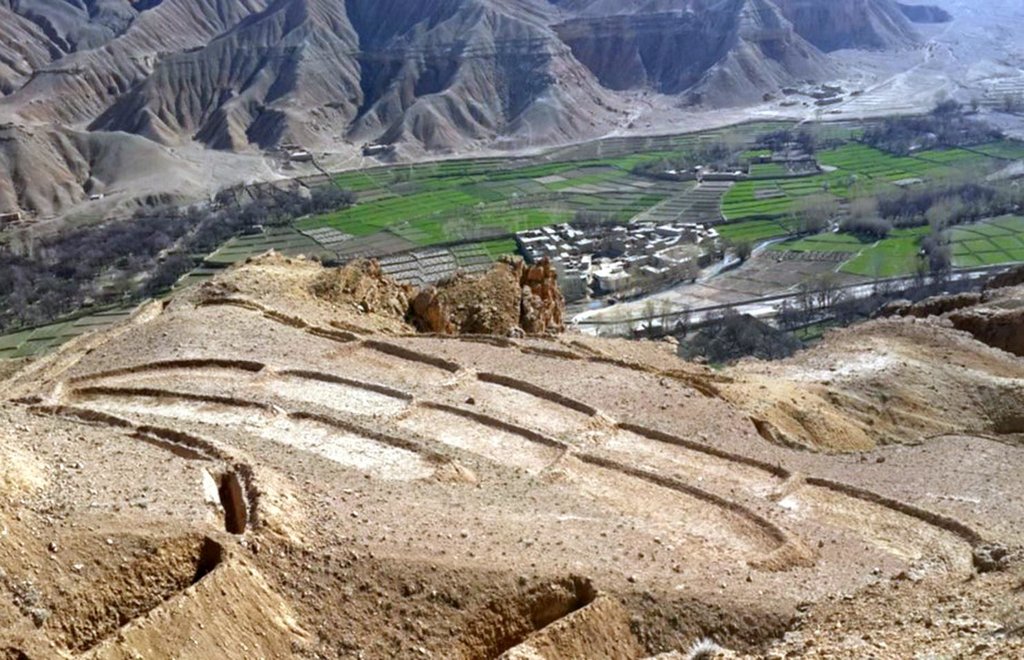
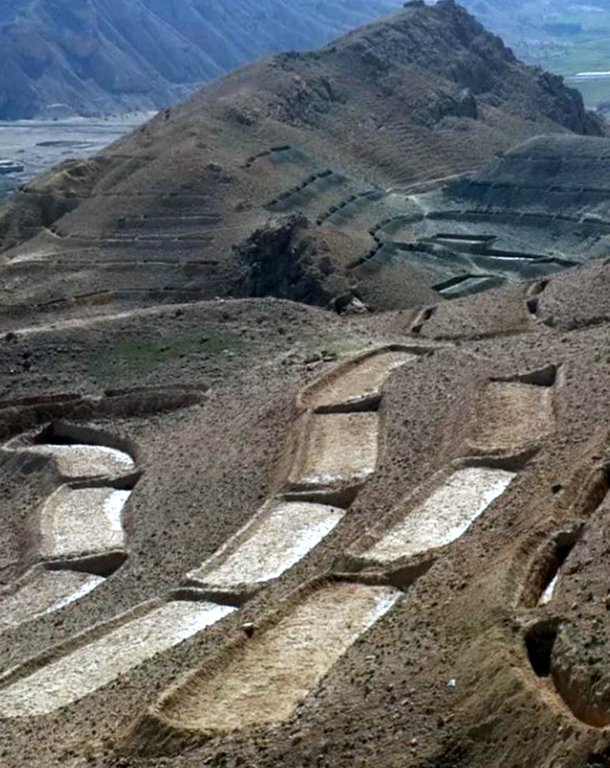
Terracing in Watershed [أفغانستان]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Aqila Haidery
- المحرر: –
- المُراجع: David Streiff
Kordak dar Abriza
technologies_1732 - أفغانستان
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Fuleki Blanka
Helvetas
اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
HELVETAS (Swiss Intercooperation)1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
19/04/2016
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.5 الإشارة إلى الاستبيان (الاستبيانات) حول مناهج الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي

Resilient Watershed Management Plan [طاجيكستان]
The participatory watershed management plan (WMP) is an interdisciplinary approach at community level to raise awareness on the watershed management concept and improve understanding of the watershed approach in planning and management of natural resource.
- جامع المعلومات: Askarsho Zevarshoev
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
Reshaping unproductive land into a series of levelled, gently-sloping platforms creates conditions suitable for cultivation and prevents accelerated erosion.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
The terracing in watershed fact-sheet is documented by Sustainable Land Management Project/HELVETAS Swiss Intercooperation which is funded by Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation (SDC).
Due to the enduring conflict and to the breakdown of common-pool resources management in upper catchments areas over the past decades, most pastures in Afghanistan are degraded.
Uncontrolled grazing of animals tilling grazing land to grow cereal crops are the main contributors to the loss of vegetation coverage in the upper catchments. One of the negative consequences is repeated flash floods each year causing loss and damage of agriculture lands, gardens, road, canal, infrastructure, houses and even lives. To decrease the severity of flash floods and extend vegetation in upper catchment areas, HELVETAS Swiss Intercooperation in Saighan district has established watershed activities.
Purpose of the Technology: Terrace construction was identified as an effective measure in degraded watershed areas to:
• control runoff and decrease flash flood;
• increase water infiltration;
• create the opportunity for income from cultivation of valuable crops in the terraces.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Having selected the watersheds and established watershed committees, watershed master plans were prepared and various structural and agronomical measures identified and estimated for each unit of land. Community laborers, trained by HELVETAS technical staff, constructed the terraces under supervision of watershed committee members. 600 terraces, each measuring 10 m x 3.6 m were constructed on seven hectares of land. To ensure maintenance, HELVETAS Swiss Intercooperation facilitated the creation of community saving systems and invested 10% of the project budget for maintenance of each watershed. It improved the capacity of watershed members, so after ending project support the community watershed committee would be able to manage maintenance of watershed measures.
Natural / human environment: Bamyan province is a remote province of Afghanistan with a high poverty rate. It has a semi-arid climate with cold winters and hot and dry summers. During winter, temperatures can drop below -22 degrees. Summer temperatures can reach 34 degrees in the month of July. The average annual rainfall in the area is about 230mm and some years can be very dry. 90% of the population relies on subsistence agriculture for their livelihoods and off-farm activities are marginal. The soil texture is clay, sandy loam and clay loam with moderate type of soil fertility, naked area of upper catchments causes that most of Saighan villages face to water scarcity during May to September and can’t grow valuable crops.The growing season in Saighan district is relatively short from April to October and farmers can produce only one crop per year. Farmers with access to irrigation water cultivate cash crops, for example potato and vegetables, in addition to staple crops (wheat) and fodder crops.Those without access to irrigation water cultivate wheat and fodder crops only. Water scarcity during May to September may result in a lack of high value crops.
The average annual income from one hectare in the area of having enough irrigation water is 250000 AFN (3676 USD) and in the area which has no enough irrigation water is 67500 AFN (992 USD).
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
أفغانستان
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Bamyan
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Saighan
2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ أقل من 10 سنوات (مؤخرًا)
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- من خلال المشاريع/ التدخلات الخارجية
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
Since 2010
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- تحسين الإنتاج
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي ومنعه وعكسه
- الحد من مخاطر الكوارث
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

أراضي الرعي
أراضي الرعي الواسع النطاق:
- الرعي المرتحل
التعليقات:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Harvest of shrubs and over grazing for over 20 years resulted in the lost vegetation cover. Top soil erosion is severe and gullies are visible.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Due to the lack of alternatives for fuel and lack of opportunities for income during decades war, people were compelled to use the natural resources in the upper catchment areas.
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Cropland: Cp: Perennial (non-woody) cropping
إذا تغير استخدام الأراضي بسبب التقنية، قم بالإشارة إلى استخدام الأرض قبل تنفيذ التقنية:
Grazing land: Ge: Extensive grazing land
3.3 مزيد من المعلومات حول استخدام الأراضي
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 1
حدد:
Longest growing period in days: 120; Longest growing period from month to month: March to July
كثافة الثروة الحيوانية (إذا كانت ذات صلة):
10-25 LU /km2
3.4 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- التدابير المتقاطعة للمنحدرات
3.5 انتشار التقنية
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت التقنية منتشرة بالتساوي على منطقة ما، فحدد المنطقة التقريبية المغطاة:
- 10-1 كم2
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير البنيوية
- S1: المصاطب المتدرجة
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح
التعليقات:
Main causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Shrub cutting), overgrazing (Over grazing and no management), droughts (3 years drought), population pressure, war and conflicts (3 decades of civil war)
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- اصلاح/إعادة تأهيل الأراضي المتدهورة بشدة
التعليقات:
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation, mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
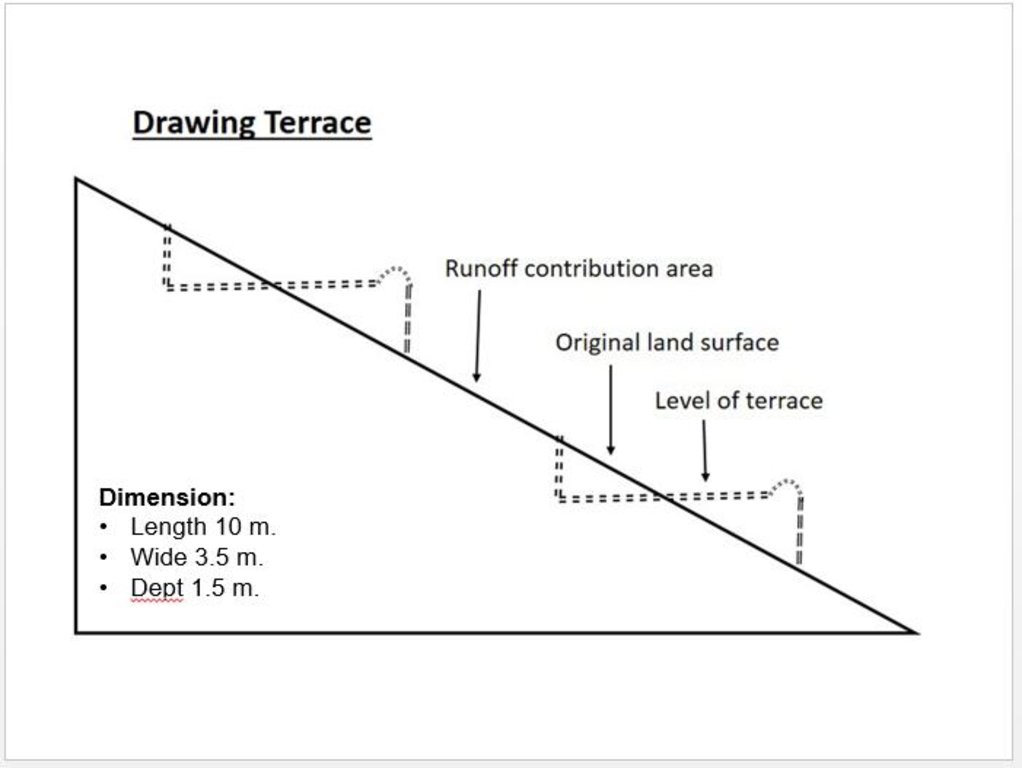
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
4.2 المواصفات الفنية/شروحات الرسم الفني
Technical drawing of a terrace built in the watershed for the mean of vegetation.
Almost all the terraces constructed on the hill sides has 10 m length, 3.5 m width and 1.5 m depth.
Location: Saighan. Bamyan
Date: 19/04/2016
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high (In order to design well)
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, reduction of slope angle, reduction of slope length, improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Terrace: forward sloping
Vertical interval between structures (m): 1.8
Spacing between structures (m): 0.5
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.3
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 3.6
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 10
Construction material (earth): Excuvation of soil and leveling
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 15-30%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 0%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 0%
Specification of dams/ pans/ ponds: Capacity 36m3
Catchment area: 36m2
4.3 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
حدد العملة المستخدمة لحساب التكاليف:
- دولار أمريكي
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
5.88
4.4 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Labor cost for the construction of the terraces | بنيوية أو هيكلية | 1 month |
4.5 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Labor cost for the construction of the terraces | persons/day | 1200,0 | 5,88 | 7056,0 | 10,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 7056,0 | |||||
4.6 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Repairing of few terraces after heavy rain falls | بنيوية أو هيكلية | 3 times a year |
4.7 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Repairing of few terraces | persons/day | 6,0 | 5,833333 | 35,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 35,0 | |||||
4.8 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
Labor cost is the determinate factors which was affecting the costs.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه قاحلة
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- متوسطة (1-3%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Soil fertility is low
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium
Soil water storage capacity is medium
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
50-5 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
ضعيف/ غير متوافر
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
للاستخدام الزراعي فقط (الري)
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- منخفض
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- مختلط (كفاف/ تجاري)
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- 10-50% من جميع الإيرادات
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- المجموعات/ المجتمع المحلي
الجنس:
- رجال
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: The culture doesn't allowed women to work as labor for construction works
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 0.5% - 1%
Relative level of wealth: rich, average, poor
10% of the land users are rich (Households who have land and livestock).
35% of the land users are average wealthy (Households who have land only).
45% of the land users are poor (Howseholds who have less or not land).
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض المملوكة أو المستأجرة من قبل مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق واسع
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- مجتمعي/قروي
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- مجتمعي (منظم)
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- مجتمعي (منظم)
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
60
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
80
التعليقات/ حدد:
Technology reduce flood and lower lands doesnt effect by floods
توافر المياه ونوعيتها
توافر مياه الري
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
20
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
25
التعليقات/ حدد:
Increasing under ground water by applying technology
الدخل والتكاليف
دخل المزرعة
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
0
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
50
التعليقات/ حدد:
Cultivation of cash crop in the terraces (farm income from uplands)
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الأمن الغذائي / الاكتفاء الذاتي
المعرفة بالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي/تدهور الأراضي
التخفيف من حدة الصراع
وضع الفئات المحرومة اجتماعيا واقتصاديا
livelihood and human well-being
التعليقات/ حدد:
The technology has effective role on reducing flash flood and as well through cultivation of valuable crops the community get more income from watershed area
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
حصاد / جمع المياه
الجريان السطحي
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
0
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
100
التعليقات/ حدد:
Leveled terraces infilter the water
مستوى المياه الجوفية/ الطبقة المائية الجوفية
التربة
رطوبة التربة
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
0
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
50
التعليقات/ حدد:
Technology let the water infilteration more
غطاء التربة
فقدان التربة
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
توافر المياه
الفيضان في اتجاه مجرى النهر
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
0
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
50
التعليقات/ حدد:
Control runoff
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | نوع التغير المناخي/ المتطرف | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة السنوية | زيادة | جيدا |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث الجوية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| عاصفة ممطرة محلية | ليس جيدا |
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| جفاف | جيدا |
الكوارث الهيدرولوجية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| فيضان عام (نهر) | ليس جيدا |
التعليقات:
The annual rainfall should be considered according to the slope of the area while designing terrace.
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي قليلا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
التعليقات:
The establishment cost of this technology seems to be high but once they are built they need very less maintenance cost with lots of benefits in the other hand.
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
- أكثر من 50%
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بتحديد الكمية (عدد الأسر المعيشية و/أو المساحةالمغطاة):
444 households covering 100 percent of the stated area
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 10-0%
التعليقات:
444 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Construction of terraces in the watershed requires lots of investment costs.
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
|
Good measure that is easy to be applied by the people. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Conducting training and workshops for capacity building of the community members. |
|
The application of this technology results to the control of runoff and reduction of the flash flood. How can they be sustained / enhanced? More vegetative measures should be considered. |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
|
A good technology for the better control of runoff and keeping the moisture. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Cultivation and sustainable maintenance of the plants in the terraces. |
|
Preparing and providing a good and proper place for cultivation and plantation. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Plantation of the local plants which has more resistance and are adaptable to the natural environment of Saighan district. |
|
Getting more income through cultivation of valuable crops. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Protection of cultivated seed from grazing animals |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Requires high investment and financial cost. | People should as well have contribution in the cost by providing the labor work. |
| In case the technical measures are not considered and applied properly it may increase infiltration and subsequently increases the soil moisture which may trigger landslide on slopes during rainfalls | High level of the technical staff and knowledge to be considered and as well the area should be studied and observed deeply. |
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط

Resilient Watershed Management Plan [طاجيكستان]
The participatory watershed management plan (WMP) is an interdisciplinary approach at community level to raise awareness on the watershed management concept and improve understanding of the watershed approach in planning and management of natural resource.
- جامع المعلومات: Askarsho Zevarshoev
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية