ការដាំដំណាំវិលជុំនៅចន្លោះរងស្វាយដោយប្រើប្រព័ន្ធតំណក់ទឹក [كمبوديا]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Be Gechkim
- المحررون: Navin Chea, Sophea Tim
- المراجعون: TOM SAY, SO Than, Ursula Gaemperli
បន្លែសរីរាង្គ
technologies_2236 - كمبوديا
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
الشخص (الأشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات
مستخدم الأرض:
ប្រុស ហ៊ួ
(+855) 97 69 14 569
Fb: កសិដ្ឋានមាន់ស្រែក្រចេះ / Page: សហគមន៍បៃតងចម្រុះ
កសិករ
ភូមិសោបក្រោម ឃុំសោប ស្រុកព្រែកប្រសព្វ ខេត្តក្រចេះ
كمبوديا
ប្រធានទទួលបន្ទុករួមការិយាល័យកសិកម្ម រុក្ខាប្រមាញ់ និងនេសាទ ស្រុកព្រែកប្រសព្វ:
ភ្នាក់ងារផ្សព្វផ្សាយឃុំនៅសាលាឃុំសោប:
សុភ័ក្រ សុង
(+855) 97 94 23 388
មិនមានអ៊ីម៉ែល
ឃុំសោប ស្រុកព្រែកប្រសព្វ ខេត្តក្រចេះ
ភូមិព្រែករកា ឃុំសោប ស្រុកព្រែកប្រសព្វ ខេត្តក្រចេះ
كمبوديا
ប្រធានការិយាល័យកសិកម្ម រុក្ខាប្រមាញ់ និងនេសាទ ស្រុកសំបូរ:
មន្ត្រីការិយាល័យកសិកម្ម រុក្ខាប្រមាញ់ និងនេសាទ ស្រុកចិត្របុរី:
សារ៉ាវុធ លី
(+855) 89 796 786
saravuthly123@gmail.com
មន្ត្រីការិយាល័យកសិកម្ម រុក្ខាប្រមាញ់ និងនេសាទ ស្រុកចិត្របុរី
ភូមិខ្សារ ឃុំដារ ស្រុកចិត្របុរី ខេត្តក្រចេះ
كمبوديا
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Scaling-up SLM practices by smallholder farmers (IFAD)اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Royal University of Agriculture (RUA) - كمبوديا1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
12/04/2017
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.4 إعلان بشأن استدامة التقنية الموصوفة
هل التقنية الموصوفة هنا تمثل مشكلة فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي، بحيث لا يمكن إعلانها تقنية مستدامة لإدارة الأراضي؟:
كلا
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
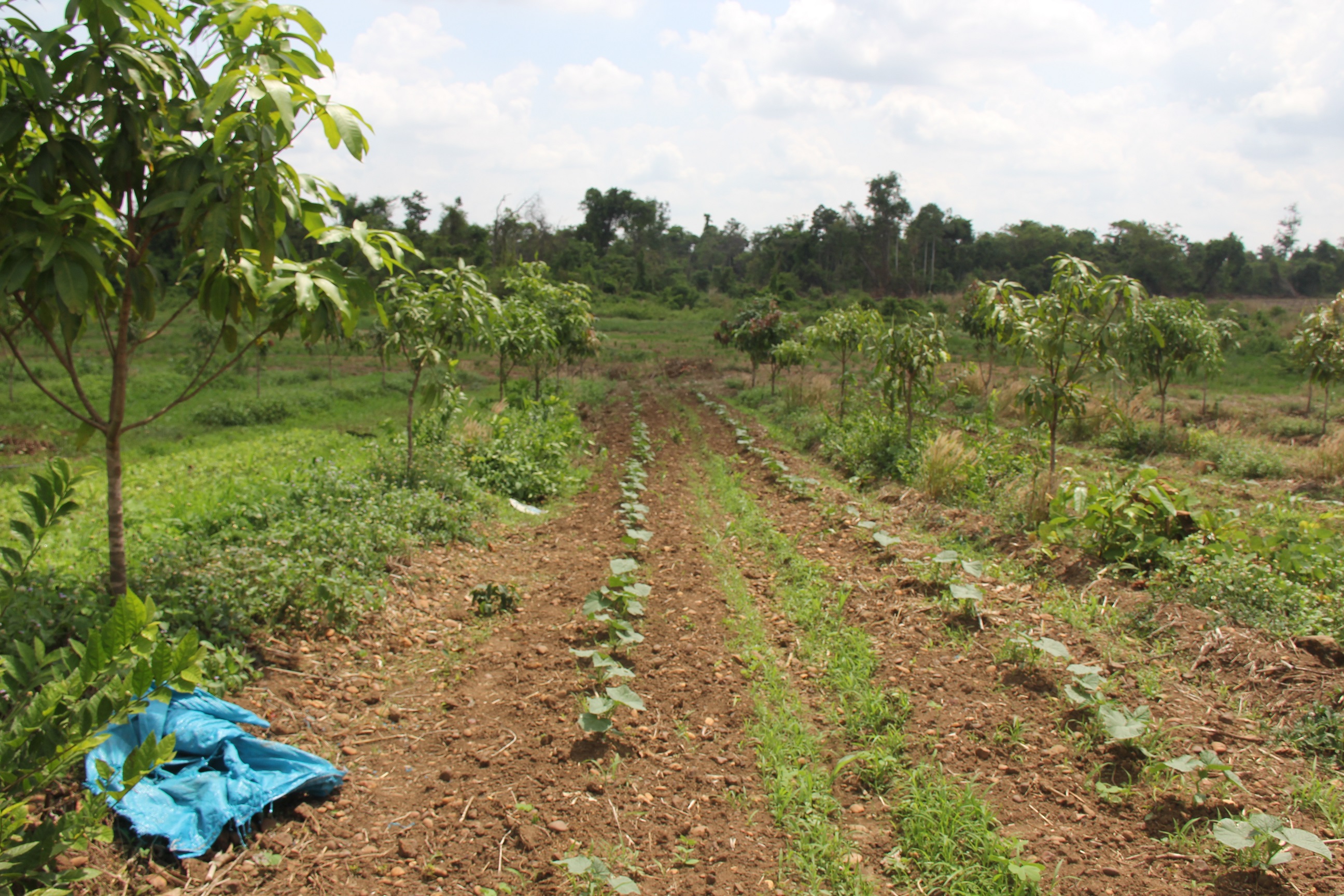
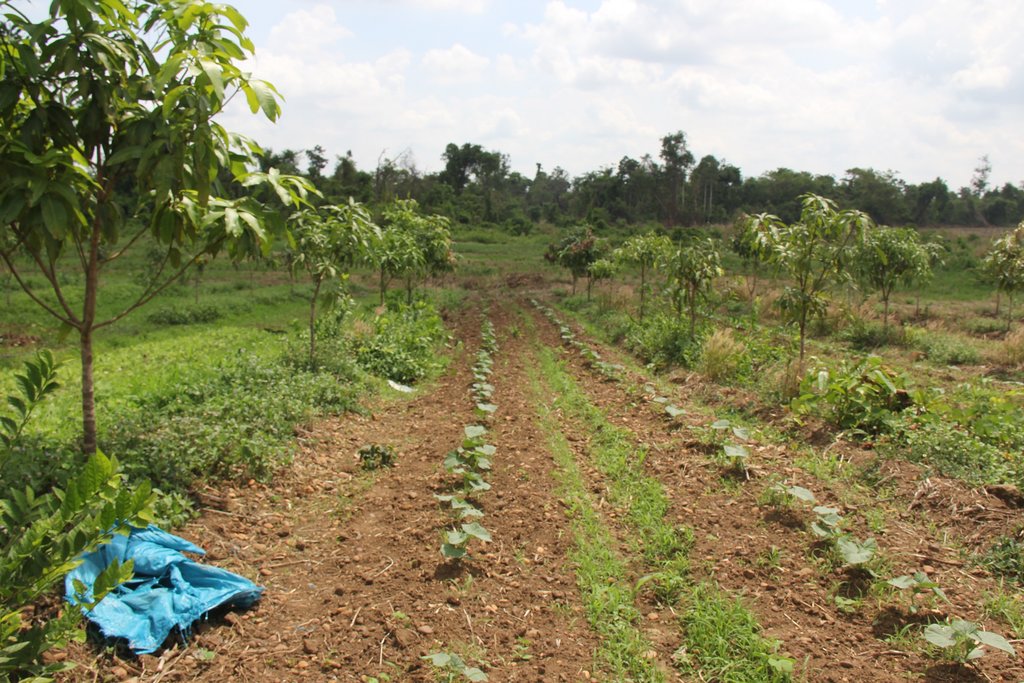
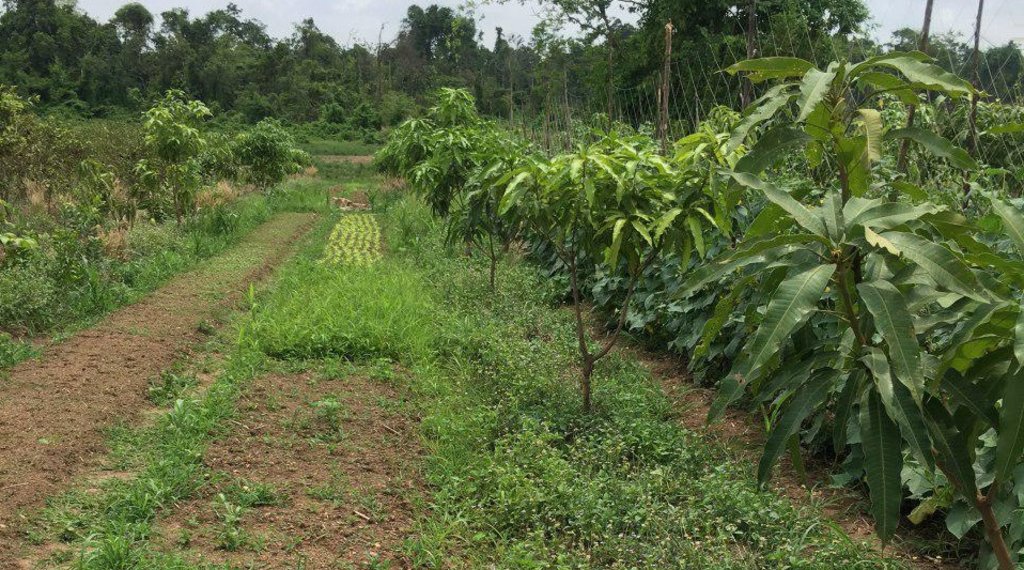
ការដាំបន្លែជាលក្ខណៈវិលជុំ នៅតាមចន្លោះជួរស្វាយ គឺជាទម្រង់មួយនៃកសិរុក្ខកម្ម។ ការអនុវត្តនេះ គឺដើម្បីបង្កើនទិន្នផល និងប្រាក់ចំណូលសម្រាប់គ្រួសារ ក្នុងអំឡុងពេលដែលស្វាយនៅតូចមិនទាន់ផ្តល់ផល។ គោលបំណងផ្សេងទៀតនៃបច្ចេកទេស គឺការបង្កើតគម្របដីជាអចិន្ត្រៃយ៍មិនឱ្យស្មៅចង្រៃលូតលាស់ បន្ថយការបាត់បង់សំណើមដី និងទប់ស្កាត់ការហូរច្រោះ ហើយគោលបំណងចុងក្រោយ គឺការរួមផ្សំជាមួយប្រព័ន្ធតំណក់ទឹកដែលជួយបន្ស៊ាំទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ។
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
កសិរុក្ខកម្ម គឺជាការអនុវត្តដាំដំណាំ និង/ឬចិញ្ចឹមសត្វនៅលើផ្ទៃដីតែមួយដោយដាំដុះលាយជាមួយនឹងដើមឈើ ដូចជាឈើហូបផ្លែ ដូង ឫស្សី និងដើមឈើផ្សេងទៀត ដើម្បីបង្កើនផលិតភាពកសិកម្ម និងទទួលបានអត្ថប្រយោជន៍ផ្សេងៗទៀត (MoE et al., 2016)។ កសិរុក្ខកម្មដើរតួនាទីយ៉ាងសំខាន់ក្នុងការផ្តល់ផលប្រយោជន៍ដល់ប្រព័ន្ធអេកូឡូស៊ី និងសេដ្ឋកិច្ច ដូចជា ការប្រមូលផលឈើ និងដំណាំរួមផ្សំ ធ្វើឲ្យដីកាន់តែមានជីជាតិ កាត់បន្ថយការប្រើប្រាស់ជី និងថ្នាំគីមីដែលនាំឲ្យថ្លៃដើមផលិតថយចុះ បន្ស៊ាំបានកាន់តែប្រសើរទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ (MoE et al., 2016) ក៏ដូចជាការជួយកាត់បន្ថយហានិភ័យនៃការខូចខាតផលដំណាំផងដែរ (FA and DANIDA, 2005)។
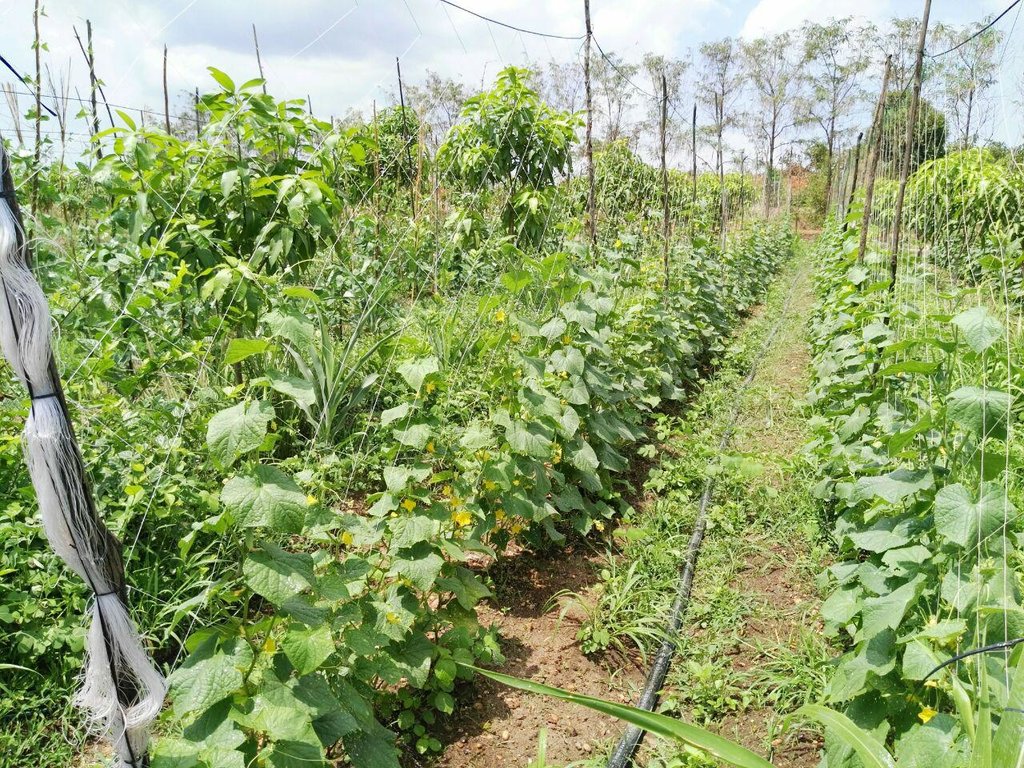
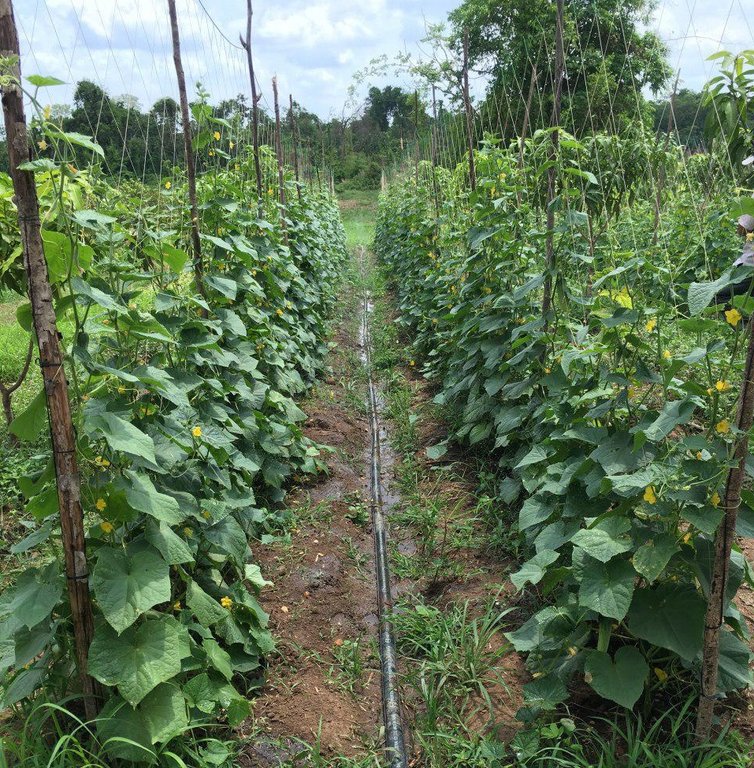
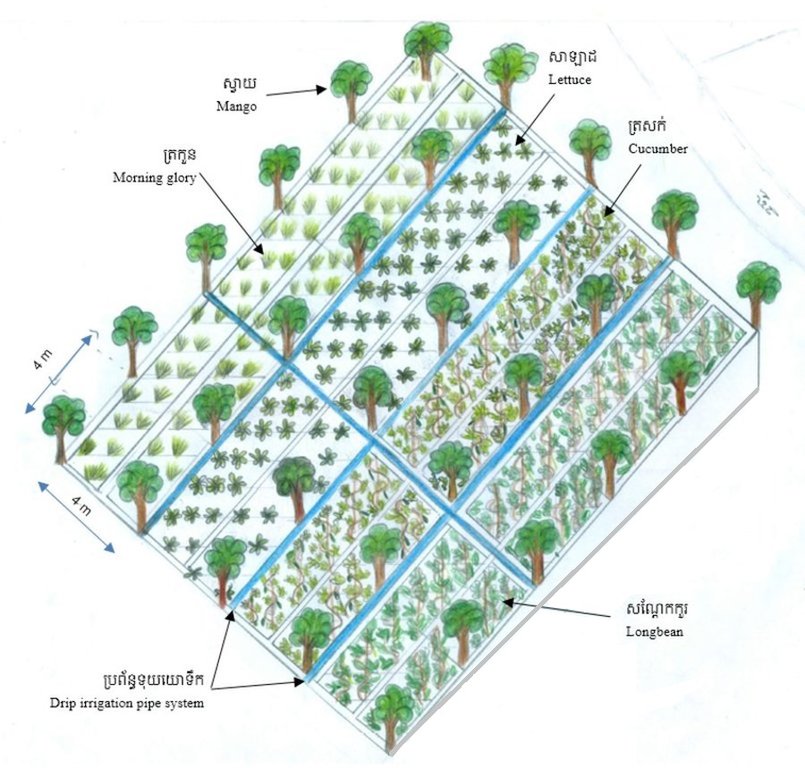
លោក ហួរ គឺជាកសិករមួយរូបក្នុងចំណោមកសិករច្រើននាក់ដែលបានផ្លាស់ប្តូរពីកសិកម្មឯកវប្បកម្មមកអនុវត្តប្រព័ន្ធកសិរុក្ខកម្ម។ រូបគាត់ និងក្រុមគ្រួសារ រស់នៅភូមិសោបក្រោម ឃុំ សោប ស្រុក ព្រែកប្រសព្វ ខេត្តក្រចេះ ដែលជាខេត្តមួយស្ថិតនៅប៉ែកឦសាននៃប្រទេសកម្ពុជា។ លើផ្ទៃដីដាំដុះទំហំ ២១០០ម៉ែត្រការ៉េ នៅតំបន់ជម្រាលភ្នំ គាត់មានស្វាយសរុបចំនួន ១៣៥ដើម ដោយដាំជា ៩ជួរ ហើយចន្លោះជួរ និងចន្លោះដើមមានប្រវែង ៤ម៉ែត្រដូចគ្នា។ តាមចន្លោះជួរស្វាយមានដាំបន្លែឆ្លាស់គ្នាជាច្រើនប្រភេទ ដូចជាសណ្តែកកួរ ត្រសក់ ត្រកួន ស្ពៃ និងសាលាដ ។ ស្វាយត្រូវបានដាំបន្ទាប់ពីភ្ជួរដីហាលរយៈ ១៥ថ្ងៃ ដោយជីករណ្តៅទំហំ ០,៥ម៉ែត្របួនជ្រុង ជាមួយជម្រៅ ០,៥ម៉ែត្រ និងបំពេញដោយលាមកគោ អង្កាម និងកន្ទក់ដែលបានផ្អាប់ទុក ១៥ថ្ងៃ ក្នុងមួយរណ្តៅប្រមាណជា ២ ទៅ ៣ គ.ក្រ។ កសិករបានប្រើប្រព័ន្ធស្រោចស្រពជាតំណក់ទឹក ដោយរាយទុយោដល់គល់ស្វាយ និងតាមបណ្តោយរងបន្លែទាំងអស់។ ការរៀបចំរងបន្លែ គឺប្រែប្រួលតាមរដូវកាល នៅរដូវប្រាំងគេលើករងកម្ពស់ ១០សង់ទីម៉ែត្រ ហើយនៅរដូវវស្សាគេលើករងកម្ពស់ ២០សង់ទីម៉ែត្រ ដើម្បីកុំឱ្យជាំទឹក។ ជាងនេះទៅទៀតការធ្វើកសិកម្មបែបនេះមិនមានការចំណាយច្រើន ហើយថែមទាំងជួយបង្កើនប្រាក់ចំណូលនៅពេលដំណាំអាយុកាលវែងមិនទាន់បានទទួលផល។ លើសពីនេះកសិករបានប្រើជីកំប៉ុស្តិ៍ទឹក និងថ្នាំសំលាប់សត្វល្អិតផ្សំពីធម្មជាតិ ដែលគាត់បានផលិតដោយខ្លួនឯង ធ្វើឲ្យគ្មានផលប៉ះពាល់អវិជ្ជមានដល់បរិស្ថានផងទៀតផង។ ការធ្វើជីកំប៉ុស្តិ៍ទឹក គឺគាត់ប្រើកម្ទេចកម្ទីត្រី កន្ទក់ និងស្ករក្រហម លាយជាមួយទឹក រួចរក្សាទុករយៈពេល ១៥ថ្ងៃ ទើបយកមកលាយទឹកបាញ់លើបន្លែ។ ចំណែកឯថ្នាំកំចាត់សត្វល្អិតត្រូវបានផ្សំពីសមាសធាតុរុក្ខជាតិផ្សេងៗដែលមានក្លិនក្រពុលខ្លាំង និងរសល្វីង ដូចជា សំបកស្លែង ក្តុល ស្តៅ វល្លិ៍បណ្តូលពេជ្រ និងរំដេង ដោយចិញ្ច្រាំវាឱ្យម៉ត់ ហើយលាយជាមួយស្ករក្រហម និងទឹក រួចបន្ទាប់មកត្រាំវាទុករយៈពេល ១៥ថ្ងៃ។ សម្រាប់ការប្រើប្រាស់ គឺត្រូវលាយទឹកថ្នាំចំណុះ ១លីត្រ ជាមួយទឹក ២៥លីត្រ។
សរុបមកបច្ចេកទេសកសិរុក្ខកម្មនេះបានផ្តល់នូវអត្ថប្រយោជន៍ច្រើនយ៉ាង។ ការដាំដំណាំបែបនេះអាចបង្កើនសេដ្ឋកិច្ចដោយការប្រមូលផលដំណាំផ្សេងៗគ្នា ទាំងក្នុងរដូវប្រាំង និងរដូវវស្សា ជាពិសេសក្នុងរយៈពេល ៣ឆ្នាំ ដំបូងដែលស្វាយមិនទាន់បានផ្តល់ផល ដូច្នេះ គឺទប់ទល់បាននឹងការចំណាយផ្សេងៗក្នុងកសិដ្ឋាន។ ការអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសនេះក៏ផ្តល់នូវភាពត្រជាក់ដល់ដីតាមរយៈម្លប់នៃដើមស្វាយ កាត់បន្ថយការបាត់បង់សំណើមដី ទប់ស្កាត់ការហូរច្រោះ ព្រមទាំងជួយបន្ស៊ាំទៅនឹងភាពហួតហែងដែលបណ្តាលមកពីការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុទៀតផង។ លើសពីនេះ ការអនុវត្តបែបនេះ គឺមិនទុកឱ្យដីនៅទំនេរចោលនាំឱ្យដុះស្មៅចង្រៃដែលជាជម្រកនៃការកកើតសត្វល្អិត និងជំងឺផ្សេងៗ ជាមូលហេតុនាំឱ្យបាត់បង់អត្ថប្រយោជន៍ផ្នែកសេដ្ឋកិច្ច។
បើមើលមួយភ្លែត វាអាចជាគុណវិបត្តិមួយដែរ ដែលកសិករត្រូវចំណាយច្រើនក្នុងគ្រាដំបូង ឧទាហរណ៍ដូចជាការតម្លើងប្រព័ន្ធតំណក់ទឹកជាដើម ប៉ុន្តែគេអាចប្រើបានក្នុងរយៈពេលច្រើនឆ្នាំ និងបន្ថយការចំណាយលើកម្លាំងពលកម្មស្រោចស្រព។ ចំពោះដំណាំបន្លែ កសិករមានភាពប្រឈមជាមួយនឹងតម្លៃបន្លែលើទីផ្សារមិនទៀងទាត់ ប្រសិនបើតម្លៃទីផ្សារមានស្ថេរភាព នោះកសិករនឹងទទួលបានចំណូលកាន់តែច្រើនសម្រាប់ការលើកកម្ពស់ជីវភាពគ្រួសារ។ ដូចនេះស្ថាប័នពាក់ព័ន្ធគួរយកចិត្តទុកដាក់លើបញ្ហាទីផ្សារនេះផងដែរ។
2.3 صور التقنية
2.4 فيديوهات عن التقنية
تعليقات، وصف موجز:
មិនមាន
اسم مصور الفيديو:
មិនមាន
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
كمبوديا
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
ភូមិសោបក្រោម ឃុំសោប ស្រុកព្រែកប្រសព្វ ខេត្តក្រចេះ
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
اذكر سنة التنفيذ:
2015
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- من خلال المشاريع/ التدخلات الخارجية
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
ជំនួយបច្ចេកទេសពីកម្មវិធីផ្សព្វផ្សាយបច្ចេកទេសកសិកម្មថ្មីដែលធន់ទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ (ASPIRE)
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- تحسين الإنتاج
- خلق أثر اقتصادي مفيد
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

مختلطة (محاصيل/ رعي/ أشجار)، بما في ذلك الحراجة الزراعية
- الحراجة الزراعية
المنتجات / الخدمات الرئيسية:
មានស្វាយ ត្រសក់ ស្ពៃ សណ្តែកកួរ និងសាលាដ
إذا تغير استخدام الأراضي بسبب التقنية، قم بالإشارة إلى استخدام الأرض قبل تنفيذ التقنية:
ជាប្រភេទដីព្រៃមិនសូវសម្បូរជីជាតិ
3.3 مزيد من المعلومات حول استخدام الأراضي
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- مختلط بعلي-مروي
التعليقات:
ប្រើប្រាស់ទឹកពីទំនប់ស្រែងៀត
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 1
حدد:
ជាប្រភេទដំណាំរយៈពេលវែង និងមានដំណាំផ្សេងៗចន្លោះមុនពេលទទួលផលស្វាយ
3.4 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- أنظمة التناوب (تعاقب المحاصيل، البور، الزراعة المتنقلة)
- تحسين الغطاء الأرضي/النباتي
- إدارة الري (بما في ذلك إمدادات المياه والصرف الصحي)
3.5 انتشار التقنية
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت التقنية منتشرة بالتساوي على منطقة ما، فحدد المنطقة التقريبية المغطاة:
- < 0.1 كم2 (10 هكتار)
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير الزراعية
- A1: الغطاء النباتي/التربة

التدابير البنيوية
- S7: معدات حصاد المياه/الإمداد/الري
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح

التدهور الكيميائي للتربة
- (Cn): تراجع الخصوبة وانخفاض محتوى المادة العضوية (غير ناتج عن الانجراف)

التدهور البيولوجي
- (Bc): تناقص الغطاء النباتي
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
- اصلاح/إعادة تأهيل الأراضي المتدهورة بشدة
التعليقات:
គាត់អាចដាំដំណាំដែលជួយបង្ការការហូរច្រោះដោយសារទឹកភ្លៀងនៅក្នុងរដូវរស្សា ពីមុនដីនេះជាដីព្រៃសឹករេចរិល។
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
4.2 المواصفات الفنية/شروحات الرسم الفني
បច្ចេកទេសនេះត្រូវបានអនុវត្តលើផ្ទៃដីដាំដុះទំហំ ២១០០ម៉ែត្រការ៉េ (ទទឹង ៣៥ ម៉ែត្រ x បណ្តោយ ៦០ ម៉ែត្រ) នៅតំបន់ជម្រាលភ្នំ។ ក្នុងទំហំផ្ទៃដីនេះមានដាំស្វាយសរុបចំនួន ១៣៥ដើម (ចំនួន ៩ជួរ ហើយចន្លោះជួរ និងចន្លោះដើមមានទំហំ ៤ម៉ែត្រ) និងមានដាំបន្លែដូចជាសណ្តែកកួរ ត្រសក់ ត្រកួន សាលាដ ស្ពៃ ឆ្លាស់គ្នានៅតាមចន្លោះជួរស្វាយ។ ប្រព័ន្ធស្រោចស្រពដោយតំណក់ត្រូវបានពង្រាយលើផ្ទៃដីទាំងមូល ដោយរាយទុយោតំណក់ទឹកដល់គ្រប់គល់ស្វាយ និងតាមរងដំណាំ។
4.3 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
حدد كيفية احتساب التكاليف والمدخلات:
- حسب مساحة تنفيذ التقنية
الإشارة إلى حجم ووحدة المساحة:
២១០០ ម៉ែត្រការ៉េ
عملة أخرى/ عملة وطنية (حدد):
រៀល
أشر إلى سعر الصرف من الدولار الأمريكي إلى العملة المحلية (إذا كان ذا صلة): 1 دولار أمريكي =:
4000,0
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
២០០០០រៀល
4.4 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | ភ្ជួរដីហាល | زراعية | ខែមេសា |
| 2. | បណ្តុះកូនស្វាយ | زراعية | ខែមេសា |
| 3. | ជីករណ្តៅ និងរៀបប្រព័ន្ធទុយោ | بنيوية أو هيكلية | ខែមេសា |
| 4. | ធ្វើថ្នាំសំលាប់សត្វល្អិត និងជីទឹក | تدابير أخرى | ខែមេសា |
| 5. | ដាំកូនស្វាយ | زراعية | ខែកញ្ញា |
| 6. | វាយដី និងលើករង | زراعية | ខែមេសា |
4.5 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | ភ្ជួរ និងរាស់ដី | នាក់/ថ្ងៃ | 3,0 | 20000,0 | 60000,0 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | ជីករណ្តៅ | នាក់/ថ្ងៃ | 5,4 | 20000,0 | 108000,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | ប្រព័ន្ធដំណក់ទឹក | ឈុត | 1,0 | 800000,0 | 800000,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | ក្បាលចម្រោះ | គ្រឿង | 1,0 | 120000,0 | 120000,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | ចបជីក | ចប | 2,0 | 15000,0 | 30000,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | គោយន្ត | គ្រឿង | 1,0 | 4800000,0 | 4800000,0 | 100,0 |
| المواد النباتية | ដើមស្វាយ | ដើម | 135,0 | 5000,0 | 675000,0 | 100,0 |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | ជីត្រី | លីត្រ | 200,0 | 300,0 | 60000,0 | 100,0 |
| مواد البناء | សំណាញ់សម្រាប់ធ្វើទ្រើង | ដុំ | 18,0 | 15000,0 | 270000,0 | 100,0 |
| مواد البناء | ឫស្សីទ្រើង | សរុប | 1,0 | 100000,0 | 100000,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 7023000,0 | |||||
التعليقات:
ទាក់ទងនឹងចំណាយ "ការជីករណ្តៅ" កសិករបានបញ្ជាក់ថាតម្លៃ ៨០០ រៀលសម្រាប់រន្ធមួយ (៨០០ X ១៣៥ រណ្តៅ = ១០៨០០០) ហើយនៅក្នុងតារាងចំណាយខាងលើត្រូវបានគណនាជានាក់/ថ្ងៃ។
4.6 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | បណ្តុះកូនបន្លែ | زراعية | ខែមេសា |
| 2. | ស្ទូងបន្លែ | زراعية | ខែមេសា |
| 3. | ធ្វើទ្រើង (វល្លិ៍) | تدابير أخرى | ខែមេសា |
| 4. | ធ្វើស្មៅ | زراعية | ១០ថ្ងៃដំបូង |
| 5. | បាញ់ថ្នាំការពារ | زراعية | ពេលមានសត្វល្អិត |
| 6. | ដូរទុយោ | تدابير أخرى | ពេលធ្លុះធ្លាយ |
4.7 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | លើករង | នាក់/ថ្ងៃ | 3,0 | 20000,0 | 60000,0 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | ស្ទូងបន្លែ ឬដាំ | នាក់/ថ្ងៃ | 2,0 | 20000,0 | 40000,0 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | ធ្វើស្មៅ | នាក់/ថ្ងៃ | 9,0 | 20000,0 | 180000,0 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | បាញ់ថ្នាំការពារ | នាក់/ថ្ងៃ | 1,0 | 20000,0 | 20000,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | ទុយោ | ដុំ | 3,0 | 100000,0 | 300000,0 | 100,0 |
| المواد النباتية | ពូជត្រសក់ | កញ្ចប់ | 4,0 | 10000,0 | 40000,0 | 100,0 |
| المواد النباتية | ពូជសណ្តែកកួរ | កញ្ចប់ | 1,0 | 3500,0 | 3500,0 | 100,0 |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | ថ្នាំកំចាត់សត្វល្អិត | លីត្រ | 20,0 | 2000,0 | 40000,0 | 100,0 |
| غير ذلك | ដូរទុយោ | នាក់/ថ្ងៃ | 1,0 | 20000,0 | 20000,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 703500,0 | |||||
التعليقات:
ការថែទាំគិតត្រឹមរយៈពេល ៣ខែប៉ុណ្ណោះអាស្រ័យតាមវដ្តដំណាំដែលដាំក្រោមដើមស្វាយ។
4.8 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
ត្រូវចំណាយដើមទុនច្រើនទៅលើប្រព័ន្ធទុយោ។
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
حدد متوسط هطول الأمطار السنوي (إذا كان معروفًا)، بالملليمتر:
1138,20
المواصفات/التعليقات على هطول الأمطار:
បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងនៅឆ្នាំ ២០១៥ គឺ ១១៣៨,២ មម ឆ្នាំ ២០១៤ គឺ ១៦៩៦,៥ មម និងឆ្នាំ២០១៣ គឺ ១៦៦១,៨ មម។
الإشارة إلى اسم محطة الأرصاد الجوية المرجعية المعنية:
ក្រសួងធនធានទឹក និងឧតុនិយម នាយកដ្ឋានឧតុនិយមឆ្នាំ2015
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه رطبة
អាសធាតុក្តៅហើយសើម មាន 2រដូវ គឺរដូវប្រាំង និងវស្សា។
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
وضح ما إذا كانت التقنية مطبقة على وجه التحديد في:
- غير ذات صلة
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- خشن / خفيف (رملي)
قوام التربة (> 20 سم تحت السطح):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- عالية (>3%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
ដីគ្រួស និងថ្ម
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
50-5 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
جيد
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
للاستخدام الزراعي فقط (الري)
هل تعتبر ملوحة الماء مشكلة؟:
كلا
هل تحدث فيضانات في المنطقة؟:
كلا
تعليقات ومواصفات أخرى بشأن نوعية المياه وكميتها:
អាចទទួលបានតែទឹកសម្រាប់កសិកម្មប៉ុណ្ណោះ ដែលទាញពីទំនប់ស្រែងៀត។
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- منخفض
تنوع الموائل:
- منخفض
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
مستقر أو مرتحل:
- غير المترحل
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- تجاري/سوق
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- 10-50% من جميع الإيرادات
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- متوسط
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- فرد/أسرة معيشية
مستوى المكننة:
- عمل يدوي
- ميكانيكية/ مزودة بمحرك
الجنس:
- رجال
عمر مستخدمي الأرضي:
- متوسط العمر
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض المملوكة أو المستأجرة من قبل مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق متوسط
التعليقات:
ខ្នាតមធ្យមដោយសារគាត់មានដីទំហំ ៣០ហិកតា និងមានអ្នកមានដីច្រើនហិកតារហូតដល់ ៥០ហិកតា។
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- فردية، يوجد سند ملكية
- ដីរានព្រៃ
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- فردي
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- فردي
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
التعليقات/ حدد:
ជាក់ស្តែងកសិករដាំដំណាំច្រើនប្រភេទជាងពីមុននៅលើផ្ទៃដីដដែល ដូចនេះគាត់អាចប្រមូលផលបន្តបន្ទាប់ពីដំណាំទាំងនោះ ដូចជាដំណាំអាយុកាលវែង និងដំណាំប្រចាំឆ្នាំ។
خطر فشل الإنتاج
التعليقات/ حدد:
តាមរយៈការដាំដំណាំរយៈពេលវែង និងដំណាំរយៈពេលខ្លីជាមួយគ្នា បានជួយកាត់បន្ថយហានិភ័យនៃភាពបរាជ័យបាន។
تنوع المنتج
التعليقات/ حدد:
ដោយសារមានដាំដំណាំជាប្រព័ន្ធចម្រុះដែលមានដំណាំច្រើនប្រភេទចម្រុះគ្នា។
منطقة الإنتاج
التعليقات/ حدد:
ដីកាលដើមឡើយជាប្រភេទដីព្រៃសឹករេចរិល ប៉ុន្តែឥលូវគាត់អាចដាំដំណាំបានតាមបច្ចេកទេស SLM នេះ។
إدارة الأراضي
التعليقات/ حدد:
គាត់ដាំដំណាំច្រើនប្រភេទ ហើយប្រើប្រាស់តែជីធម្មជាតិ និងថ្នាំពុលការពារដំណាំផ្សំពីរុក្ខជាតិដែលបានផលិតដោយគាត់ផ្ទាល់។
الدخل والتكاليف
النفقات على المدخلات الزراعية
التعليقات/ حدد:
បច្ចុប្បន្ននេះគាត់មិនចាំបាច់ទិញជីថ្នាំគីមីទៀតទេ ហើយគាត់ព្យាយាមប្រើប្រាស់ថ្នាំសំលាប់សត្វល្អិតដែលផលិតដោយខ្លួនឯង។
دخل المزرعة
التعليقات/ حدد:
គាត់អាចទទួលបានចំណូលពេញមួយឆ្នាំពីព្រោះគាត់បានដាំទាំងដំណាំអាយុកាលវែង និងខ្លី។
تنوع مصادر الدخل
التعليقات/ حدد:
តាមរយៈការដាំដំណាំច្រើនជាងមួយប្រភេទលើផ្ទៃដីដដែលបណ្តាលឱ្យគាត់ទទួលបានប្រភពចំណូលកើនឡើងប៉ុន្តែតិចតួចប៉ុណ្ណោះ។
عبء العمل
التعليقات/ حدد:
គម្របដីល្អដែលបានពីការដាំដំណាំឆ្លាស់បានជួយបញ្ជៀសការដុះលូតលាស់នៃស្មៅចង្រៃ និងជួយកាត់បន្ថយកម្លាំងពលកម្មក្នុងធ្វើស្មៅផងដែរ។
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الأمن الغذائي / الاكتفاء الذاتي
التعليقات/ حدد:
គាត់ដាំដំណាំច្រើនជាងមុនធ្វើឱ្យសន្តិសុខស្បៀងកាន់តែប្រសើរ។
الوضع الصحي
التعليقات/ حدد:
ការបំពុលបរិស្ថានត្រូវបានកាត់បន្ថយដោយសារគាត់ប្រើប្រាស់តែជីធម្មជាតិ និងថ្នាំពុលការពារដំណាំផ្សំពីរុក្ខជាតិប៉ុណ្ណោះ។ ដូចនេះស្ថានភាពសុខភាពកាន់តែប្រើសើរឡើង។
المعرفة بالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي/تدهور الأراضي
التعليقات/ حدد:
ចំណេះដឹងដែលពាក់ព័ន្ធនឹងដី គឺគាត់ទទួលបានពីបទពិសោធន៍របស់គាត់ និងតាមរយៈឯកសារ ឬវីដេអូលើប្រព័ន្ធអ៊ីនធឺណេត។
الآثار الايكولوجية
التربة
رطوبة التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
មានដំណាំគម្របដីកាន់តែច្រើន គឺបានជួយកាត់បន្ថយរំហួតតាមនោះដែរ។
غطاء التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
តាមរយៈការដាំបន្លែឆ្លាស់គ្នាបានធ្វើឱ្យគម្របដីល្អប្រសើរ
تراص التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
ឫសរបស់ដំណាំស្វាយបានចាក់ចូលទៅក្នុងដីធ្វើឱ្យដីផុសល្អ
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
الغطاء النباتي
التعليقات/ حدد:
ដោយសារតែមានដំណាំគម្របដីជាអចិន្ត្រៃយ៍ពេញមួយឆ្នាំ
الأنواع الدخيلة الغازية
التعليقات/ حدد:
ប្រភេទរាតត្បាត គឺត្រូវបានកាត់បន្ថយតាមរយៈការដាំដំណាំវិលជុំ និងការប្រើប្រាស់ថ្នាំពុលការពារដំណាំផ្សំពីរុក្ខជាតិ។
الأنواع المفيدة
التعليقات/ حدد:
ប្រភេទសត្វមានប្រយោជន៍កើនឡើងពីព្រោះតែការប្រើប្រាស់ជីកំប៉ុស្តិ៍ទឹក។
مكافحة الآفات/الأمراض
التعليقات/ حدد:
ថ្នាំសម្លាប់សត្វល្អិតផ្សំពីធម្មជាតិដែលគាត់ផលិតដោយខ្លួនគាត់ គឺមានប្រសិទ្ធភាពខ្ពស់។
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
تعليقات بشأن تقييم الأثر:
មិនមានផលប៉ះពាល់ខាងក្រៅបរិវេណគួរឱ្យកត់សម្គាល់ទេ
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | نوع التغير المناخي/ المتطرف | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة السنوية | زيادة | جيدا | |
| درجة الحرارة الموسمية | موسم الرطوبة/ الأمطار | زيادة | جيدا |
| درجة الحرارة الموسمية | فصل جاف | زيادة | جيدا |
| هطول الأمطار السنوي | انخفاض | باعتدال | |
| هطول الأمطار الموسمية | موسم الرطوبة/ الأمطار | زيادة | جيدا |
| تغير مناخ تدريجي آخر | ភ្លៀងធ្លាក់មានការប្រែម្រួល មានការរាំងរហូតដល់ខែ០៧ ទើបភ្លៀង |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث الجوية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| عاصفة ممطرة محلية | باعتدال |
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| موجة حر | ليس جيدا |
| موجة باردة | جيدا |
| ظروف شتاء قاسية | باعتدال |
الكوارث البيولوجية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| أمراض وبائية | جيدا |
| الإصابة بالحشرات/الديدان | جيدا |
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| មិនមានបញ្ហាដោយសារមានប្រភពទឹក និងប្រព័ន្ធស្រោចស្រព |
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
- حالات فردية/تجريبية
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 100-90%
التعليقات:
ដោយសារមិនមានតម្រូវការថែទាំច្រើន និងចេញកម្លាំងពលកម្មច្រើន។
6.6 التكيف
هل تم تعديل التقنية مؤخرًا لتتكيف مع الظروف المتغيرة؟:
كلا
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
| មិនចំណាយកម្លាំងពលកម្មច្រើន/កាត់បន្ថយបន្ទុកការងារតាមរយៈការប្រើប្រព័ន្ធតំណក់ទឹក |
| មានបន្លែច្រើនមុខអាចតម្រូវទៅតាមទីផ្សារ |
| កុំឱ្យដីទំនេរចោល និងមានស្មៅដុះច្រើន |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
| កាត់បន្ថយកម្លាំងពលកម្ម ដោយមានរៀបចំប្រព័ន្ធទុយោសម្រាប់ការស្រោចស្រព និងដាក់ជី |
| មិនប៉ះពាល់បរិស្ថាន ដោយមិនត្រូវការម៉ាស៊ីន/ឥន្ធនៈផ្សេងៗសម្រាប់ស្រោចស្រពដោយប្រើប្រព័ន្ធបូមទឹកស្វ័យប្រវត្តិដែលដំណើរការដោយកម្លាំងទឹកហូរ។ |
| ការគ្រប់គ្រងដីបានល្អប្រសើរ ដោយអន្តរកម្មរវាងដំណាំ និងដើមឈើ |
| ការដាំដំណាំវិលជុំជួយរក្សាស្ថេរភាពជីជាតិដី និងបង្កើនគម្របដី |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| ខ្វះខាតដើមទុនមួយចំនួន | កម្ចីពីស្ថាប័នមីក្រូហិរញ្ញវត្ថុ ឬរដ្ឋក្នុងអត្រាការប្រាក់ទាប ឬរដ្ឋ ជួយគាំទ្របន្ថែម។ |
| ទីផ្សារមិនមានស្ថេរភាព | ចងក្រងជាក្រុមកសិករ និងស្វែងរកការគាំទ្រពីអង្គការ និងមន្ទីរដើម្បីជួយរកបណ្តាញទីផ្សារ។ |
| ចំណាយទុនច្រើនពេលចាប់ផ្តើមដំបូងសម្រាប់ការរៀបចំប្រព័ន្ធស្រោចស្រពដោយតំណក់ទឹក។ | គួរមានការគាំទ្រជាបដិភាគពីគម្រោង និងរដ្ឋ |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| នៅពេលស្វាយធំបែកមែកសាខាបាំងពន្លឺវានឹងមិនអាចដាំដំណាំបានទៀតទេ។ | ដាំដំណាំផ្សេងៗដែលមិនសូវត្រូវការពន្លឺ និងធន់ពេលនៅក្រោមម្លប់។ |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
- زيارات ميدانية، مسوحات ميدانية
១ កន្លែង
- مقابلات مع مستخدمي الأراضي
១ នាក់
- مقابلات مع المتخصصين/الخبراء في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
៤ នាក់
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Yang S. and Pean S. (2012) Organic fertilizer: Technology principle and farmer experiences. Cambodian Center for Study and Development in Agriculture: Phnom Penh. (In Khmer)
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
CEDAC and price is about 10000 Riel
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
FA and DANIDA (2005). Guidelines for Site Selection and Tree Planting in Cambodia. Forestry Administration. Retrieved on May 15 2017 from
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
http://treeseedfa.org/guidelines_site_eng.htm
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
MoE, Adaptation Fund and UNEP (2016). Agroforestry System: “Enhancing Climate Change Resilience of Rural Communities Living in Protected Areas in Cambodia”. Ministry of Environment.
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية