Shelterbelts [توغو]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Unknown User
- المحرر: –
- المُراجع: Laura Ebneter
Brise vents vivants / Hélim Rangou Tinn
technologies_1338 - توغو
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
الشخص (الأشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Gbenonchi Mawussi
gmawussi@gmail.com
Ecole Supérieure d Agronomie, Université de Lomé (ESA UL)
Lomé
توغو
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Book project: SLM in Practice - Guidelines and Best Practices for Sub-Saharan Africa (SLM in Practice)اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Ecole Supérieure d'Agronomie, Université de Lomé (ESA) - توغو1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
22/08/2007
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
Shelterbelts made of leguminous trees and shrubs protect annual crops from wind erosion.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
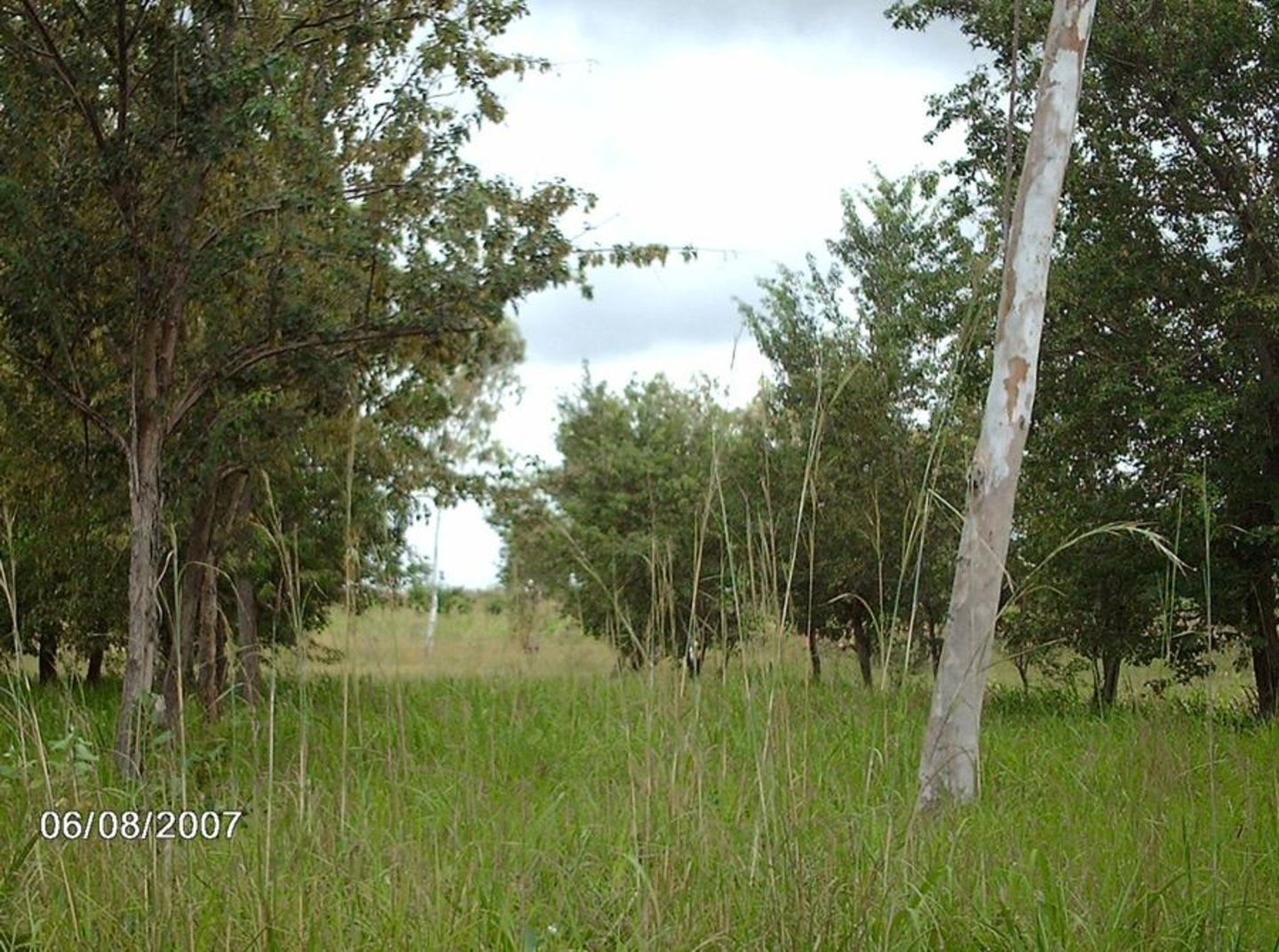
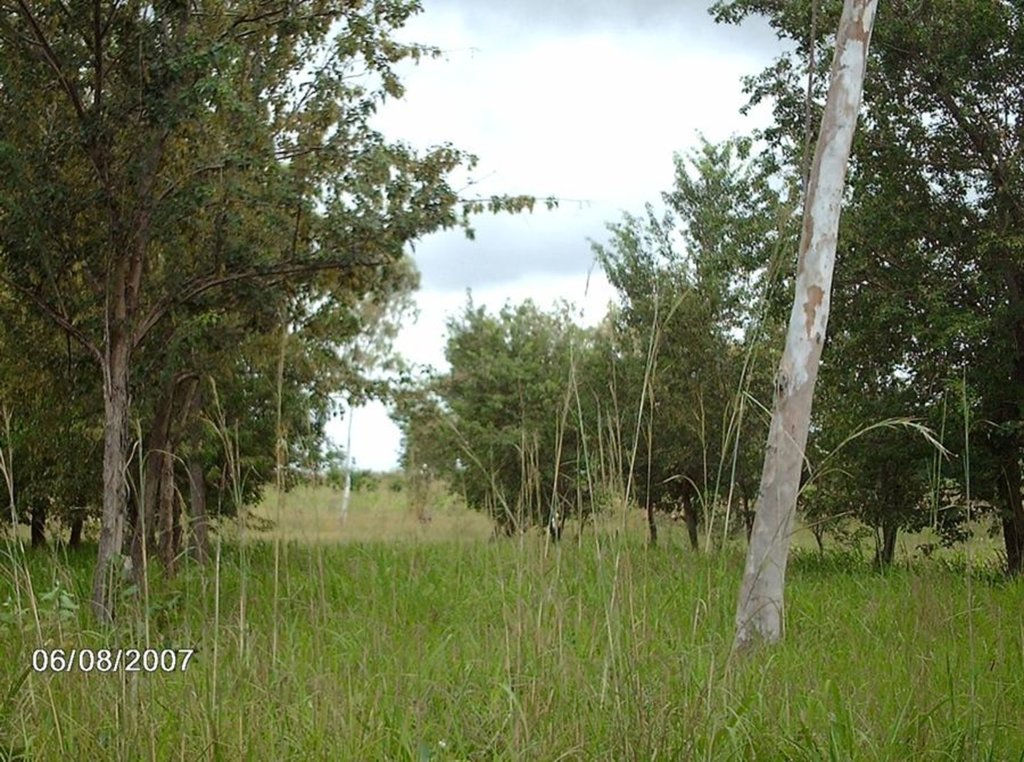
On the vast denuded plains of Pays Kabyé in northern Togo, barriers of leguminous trees (e.g. Cassia siamea or spectabilis; a medium sized tree growing between 10-20 m tall; Albizzia procera, Leucaena leucocephala) and shrubs (Cajanus cajan, Erythrina variegate) are established between fields cultivated with annual crops such as maize. The shelterbelts provide a good micro-climate and protect the crops against the counterproductive effects of wind speed such as wind erosion, soil water loss through evaporation and physical damage to crops. The shelterbelts’ effectiveness depends on their permeability, their spacing and the direction of planting in relation to the wind direction: A proportion of 40-50% of holes (openings, void) in relation to the total surface of the shelterbelt is desirable, and establishment of tree rows perpendicularly to the main wind direction is most effective. In order to reduce lateral turbulence the wind breaks need to reach a length of minimum 10 times their height. Shelterbelts protect 15-25 times their height on the leeward and 1-2 their height on the windward side. If the area to be protected is large, several wind breaks need to be established. The denser the shelterbelts are, the better the windbreaking effect, but the higher the competition with crops for nutrients, light and water. Frequent pruning helps to avoid too much competition and provides fuelwood. In case leguminous tree species are used, soil properties can be improved through nitrogen fixation and the provision of organic matter (leaves).
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
توغو
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Kara
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Tchitchao
Map
×3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- تحسين الإنتاج
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي ومنعه وعكسه
- خلق أثر اقتصادي مفيد
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

مختلطة (محاصيل/ رعي/ أشجار)، بما في ذلك الحراجة الزراعية
- الحراجة الزراعية
التعليقات:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): adverse effects of wind speed on soil humidity and crop yield
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): breaking of corn stalks and therefore decline of crop yield
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Mixed: Mf: Agroforestry
إذا تغير استخدام الأراضي بسبب التقنية، قم بالإشارة إلى استخدام الأرض قبل تنفيذ التقنية:
Cropland: Ca: Annual cropping
3.3 مزيد من المعلومات حول استخدام الأراضي
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 1
حدد:
Longest growing period in days: 180 Longest growing period from month to month: May-October
3.4 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- مصد الريح/حزام حماية
3.5 انتشار التقنية
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت التقنية منتشرة بالتساوي على منطقة ما، فحدد المنطقة التقريبية المغطاة:
- < 0.1 كم2 (10 هكتار)
التعليقات:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.8 km2.
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير النباتية
- V1: غطاء من الأشجار والشجيرات
التعليقات:
Main measures: vegetative measures
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -against wind
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة الناتج عن الرياح
- (Et): فقدان التربة السطحية
- (Eo): تأثيرات التدهور من مواقع أخرى

تدهور المياه
- (Ha): التجفيف
التعليقات:
Main type of degradation addressed: Et: loss of topsoil, Eo: offsite degradation effects, Ha: aridification
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- منع تدهور الأراضي
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
4.2 المواصفات الفنية/شروحات الرسم الفني
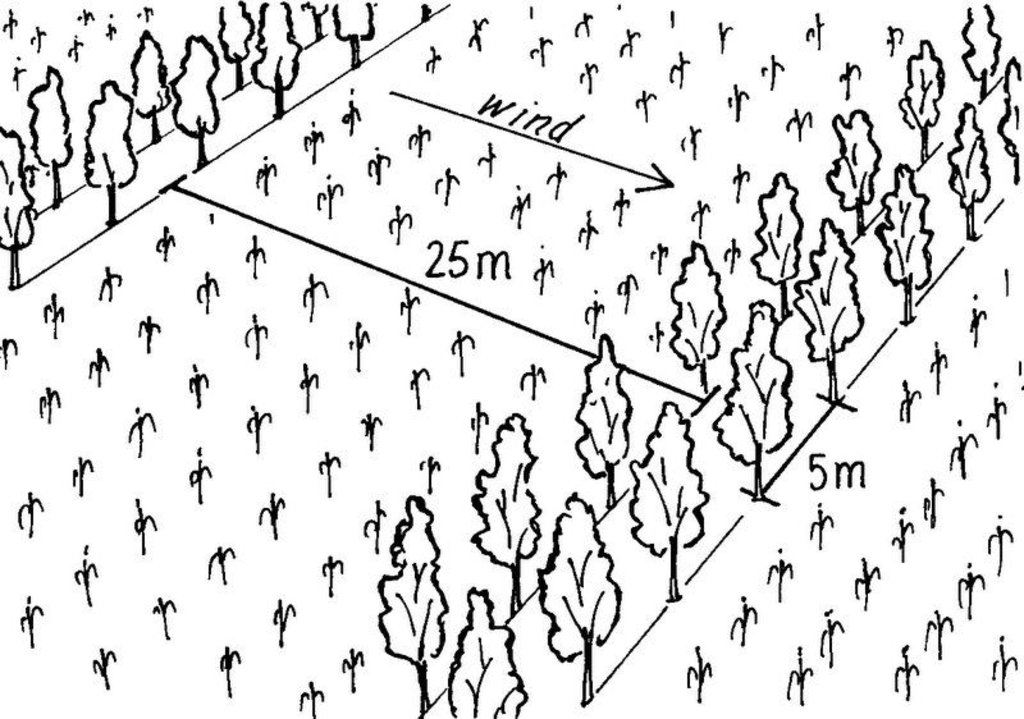
Spacing between windbreak rows is 20-25 m. The row of windbreak can be of a single tree line, of double tree lines, etc. depending on wind speed and scope of protection. The in between tree line spacing is 5 m (see photo). Plant density can range from 100 – 200 plants/ha depending on the number of tree lines planed within a windbreak.
Location: Tchitchao. Préfecture de la Kozah
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: reduction in wind speed
Aligned: -against wind
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 40
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 20.00
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 5.00
Trees/ shrubs species: Cassia siamea or spectabilis, Albizzia procera, Leucaena leucocephala, Cajanus cajan, Erythrina var
4.3 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
حدد كيفية احتساب التكاليف والمدخلات:
- حسب مساحة تنفيذ التقنية
الإشارة إلى حجم ووحدة المساحة:
0.8km2
حدد العملة المستخدمة لحساب التكاليف:
- دولار أمريكي
4.4 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Determine the area to be protected and alignment of shelterbelts (1,2, or 3 lines of trees); rows to be established perpendicular to main wind direction) | نباتية | during rainy season |
| 2. | Dig planting pits at a spacing of 2-3 meters | نباتية | during rainy season |
| 3. | Planting of seedlings (when conditions are favourable) | نباتية | during rainy season |
| 4. | Establish plant nursery | نباتية | during rainy season |
| 5. | Regular irrigation of young tree seedlings after plantation; Weeding; Reduce density to a spacing 5 m between trees | نباتية | during rainy season |
4.5 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 200,0 | 200,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Tools | ha | 1,0 | 86,0 | 86,0 | 100,0 |
| المواد النباتية | Seedlings | ha | 1,0 | 90,0 | 90,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 376,0 | |||||
التعليقات:
Duration of establishment phase: 36 month(s)
4.6 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Weeding (according to necessity / speed of regrowth) | نباتية | according to necessity / speed of regrowth |
| 2. | Pruning to avoid shading effect on crops |
4.7 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 139,0 | 139,0 | 100,0 |
| المواد النباتية | Seedlings | ha | 1,0 | 23,0 | 23,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 162,0 | |||||
التعليقات:
Machinery/ tools: hand tools such as hoe, machete and measuring tape
the indicated costs apply per hectare unit
4.8 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
The monetary costs include the purchase of seeds, cuttings or nursery plants and labour for the preparation and planting. In certain circumstances, it is necessary to protect young trees against browsing and other damage.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه رطبة
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التضاريس:
Landforms: Also hill slopes and plateau/plains (both ranked 2)
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- خشن / خفيف (رملي)
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- متوسطة (1-3%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Soil fertility: Medium
Soil drainage/infiltration: Medium (ranked 1) and good (ranked 2)
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- مختلط (كفاف/ تجاري)
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- أقل من % 10من كامل الدخل
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- ثري
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- فرد/أسرة معيشية
مستوى المكننة:
- عمل يدوي
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly Leaders / privileged
Population density: 200-500 persons/km2
1% of the land users are rich and own 100% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: these revenues are lower than for farmers who did not implement the wind breaks
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض المملوكة أو المستأجرة من قبل مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق صغير
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- فردية، يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- فردي
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
إنتاج الخشب
التعليقات/ حدد:
And forest products (fruits)
منطقة الإنتاج
التعليقات/ حدد:
Area occupied by tree hedges
الدخل والتكاليف
النفقات على المدخلات الزراعية
التعليقات/ حدد:
Collection of seedlings
دخل المزرعة
عبء العمل
التعليقات/ حدد:
Extra work
آثار اجتماعية واقتصادية أخرى
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
المعرفة بالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي/تدهور الأراضي
الآثار الايكولوجية
التربة
رطوبة التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Through evaporation
فقدان التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Loss of topsoil through wind erosion
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
مكافحة الآفات/الأمراض
التعليقات/ حدد:
Nesting sites for predatory birds
الحد من مخاطر المناخ والكوارث
سرعة الرياح
الآثار الايكولوجية الأخرى
Shade for crops
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
الرواسب المنقولة بواسطة الرياح
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 100-90%
التعليقات:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: There is no growing trend of spontaneous adoption in the region since the windbreak technology is little known by most farmers
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
|
Reduced wind speed How can they be sustained / enhanced? No exploitation or destruction of trees |
|
Soil conservation How can they be sustained / enhanced? Avoid burning the shelter belts |
|
Provision of forestry products How can they be sustained / enhanced? Reglementation of use of these products |
| High aestethic value of trees in the landscape |
|
Increased crop yield How can they be sustained / enhanced? Maintain the micro-climate generated by the shelter belts |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Reduced area for cultivation of crops | establish the minimum of shelterbelts necessary for optimal protection |
| Reduced crop yields alongside shelterbelts (competition for nutrients, light, water) | avoid dense planting of trees and shrubs; frequently prune the trees |
| Shelterbelts provide habitat for vermins / pests (rats, insects) | frequently hunt these animals |
| Increased labour inputs |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Care International au Togo. 1997. Agroforestry training and demonstrations in northern Togo. Final report to European Union B7-5040/93/21
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Louppe, D., H. Yossi. 1999. Les haies vives défensives en zones sèches et sub-humides d'Afrique de l'Ouest. Atelier Jachères, Dakar.
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Ariga, E. S., 1997. Availability and Role of Multipurpose Trees and Shrubs in Sustainable Agriculture in Kenya. Journal of Sustainable Agriculture 10:2/3, 25-35.
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية