Water Spreading (typical example from Hashatribab) [السودان]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Abdalla Osman Eisa
- المحرر: –
- المراجعون: Deborah Niggli, Alexandra Gavilano
Sidud (Local Arabic) - Tarrit (Beja dialect) for earth dams
technologies_1292 - السودان
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Soil Conservation, Land Use and Water Adminstratio (Soil Conservation, Land Use and Water Adminstratio) - السودان1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.4 إعلان بشأن استدامة التقنية الموصوفة
هل التقنية الموصوفة هنا تمثل مشكلة فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي، بحيث لا يمكن إعلانها تقنية مستدامة لإدارة الأراضي؟:
كلا
1.5 الإشارة إلى الاستبيان (الاستبيانات) حول مناهج الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي (موثقة باستخدام WOCAT)

Water Spreading (typical example from Hashatribab) [السودان]
Construction of water spreading system on khor and wadi with machinery jointly government and farmers in dam compaction and pitching.
- جامع المعلومات: Abdalla Osman Eisa
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
Water Spreading (or Spate Irrigation system) conducted through the construction of earth dam structures at the khor cross section.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
Water Spreading (or Spate Irrigation) can be done through the construction of an angled bank or weir – with a spillway in case of excess flow – to divert a “khor” (ephemeral stream) and spread it (using spaced contour bunds) for crop production.
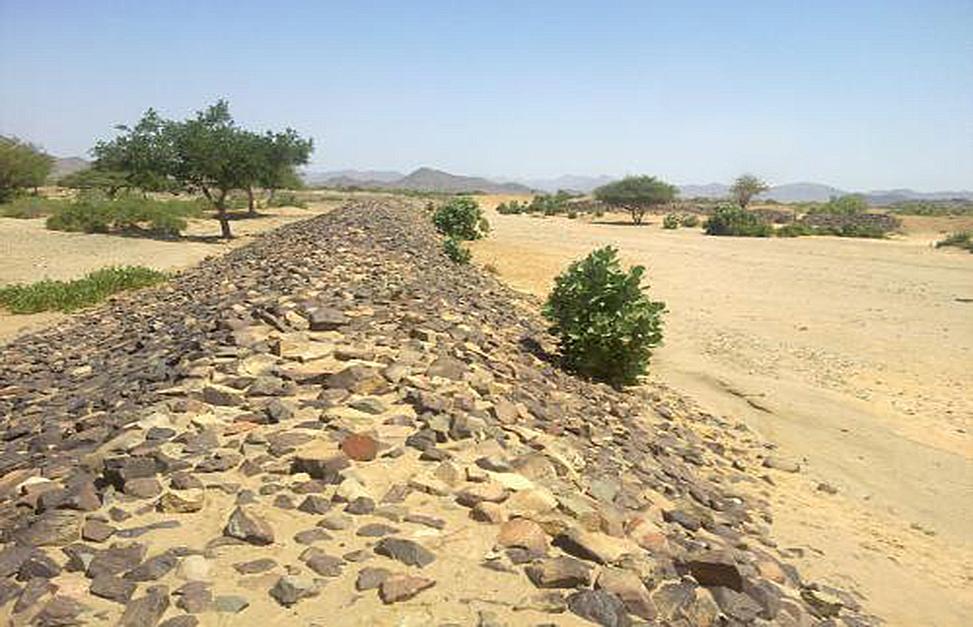
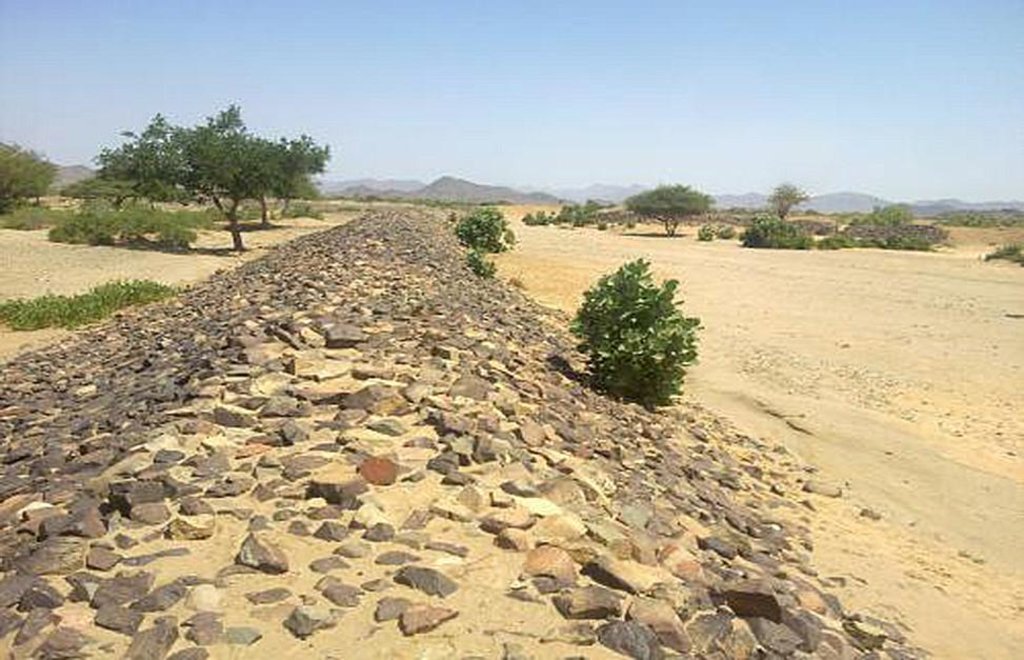
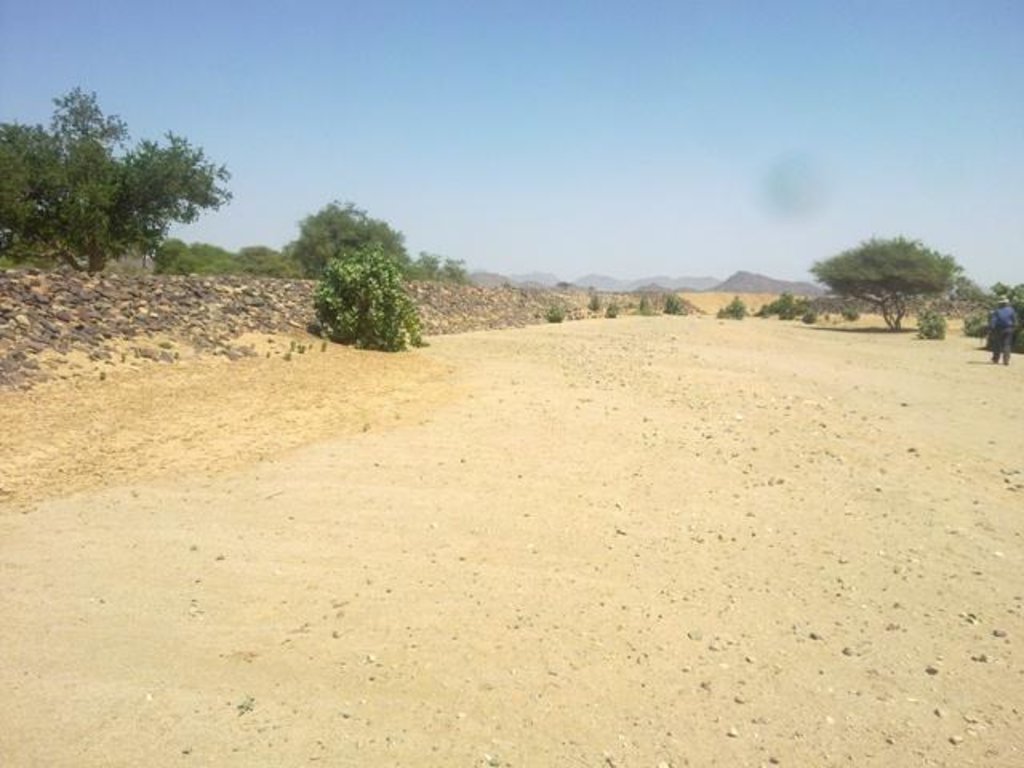
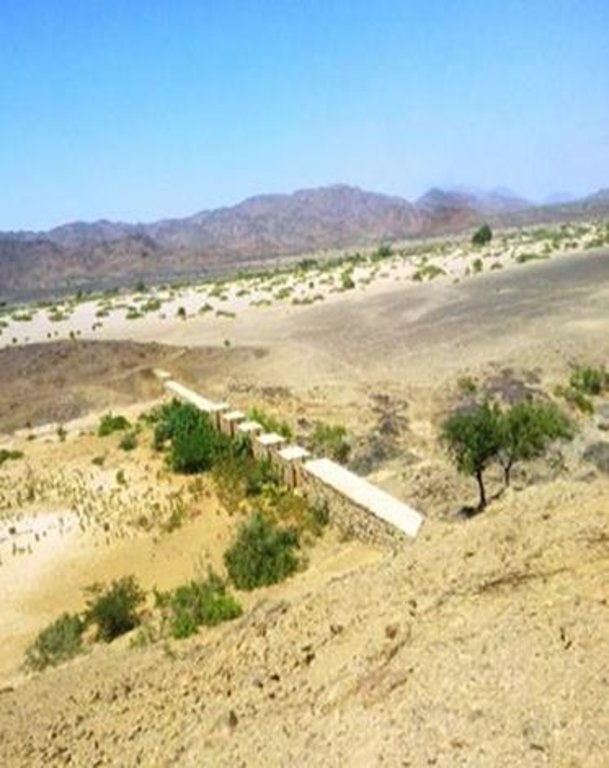
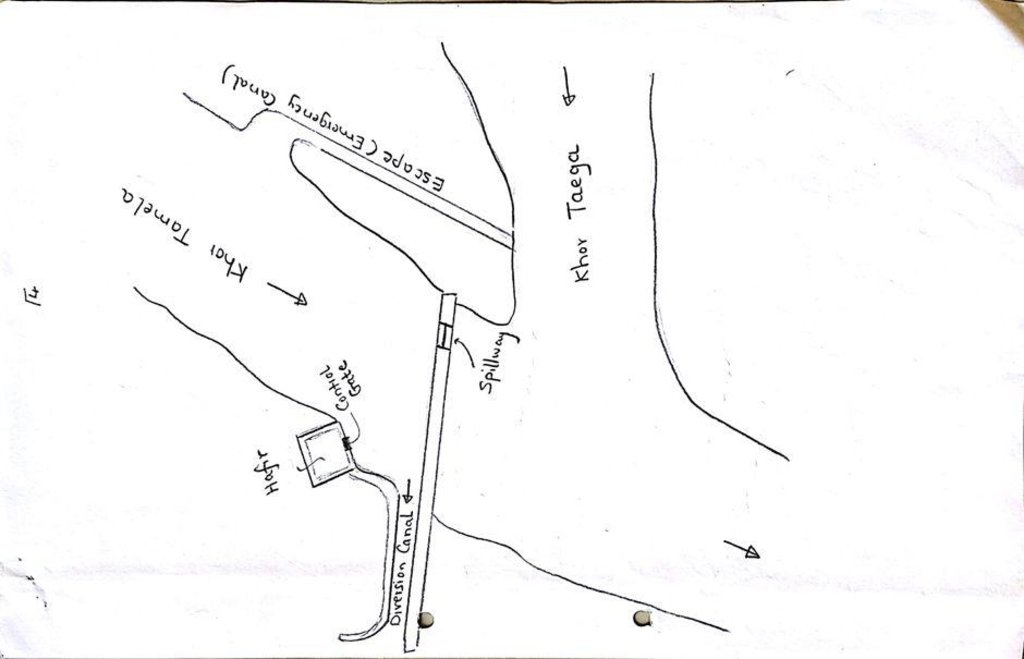
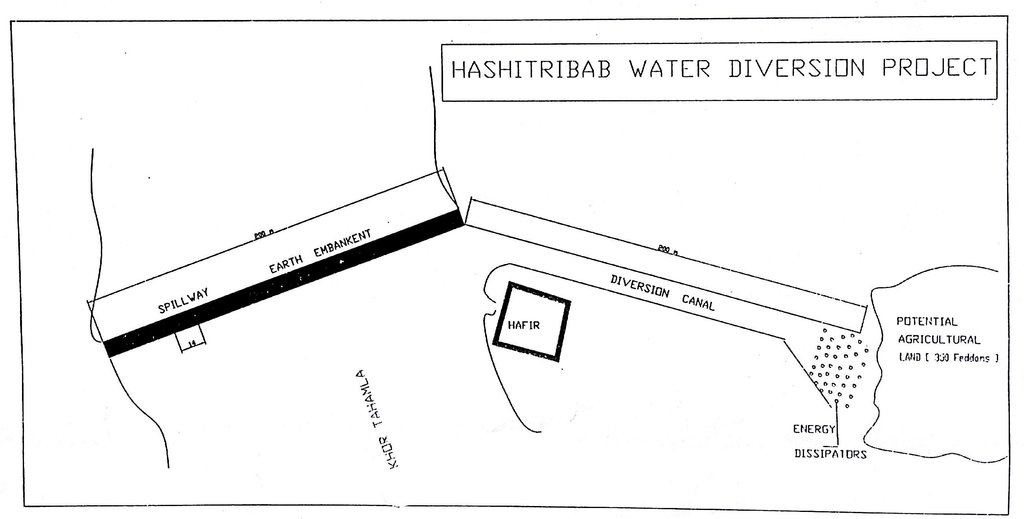
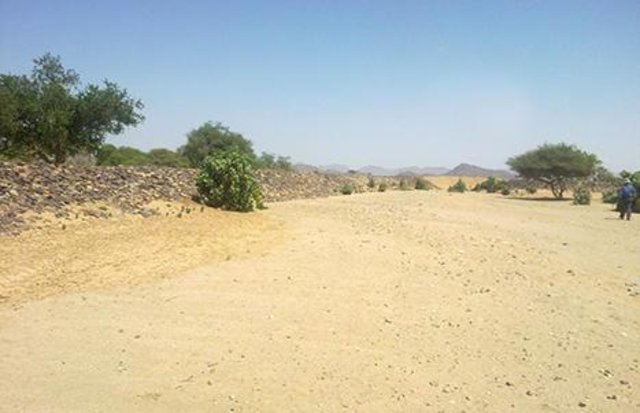
Water Spreading from khors or wadis where channelized runoff/ floodwater is diverted onto plains which are then cultivated on residual moisture. An example of a scheme which was constructed in 1999 is located at Hashitribab, some 7 km from Sinkat on the road towards Kassala. This scheme, comprising a stone-pitched earth diversion barrier across a khor (an ephemeral water course), is documented by using among others the WOCAT Questionnaire and WOCAT’s QA. While the diversion is still intact and provides water to the fields about one kilometre downstream (there were young sorghum plants growing at the time of the visit in November 2011) maintenance will be needed.
There was only a very small input of voluntary labour in its original construction (comprising a contribution in terms of stone pitching).
Construction by the Government, using machinery, with little local contribution might explain why voluntary maintenance of the structures has been negligible. Water spreading schemes have gradually expanded in number over the last 20 years in Red Sea State (according to Sayed Dabloub’s personal comment). Currently it was confirmed that there are new sites under planning and construction.
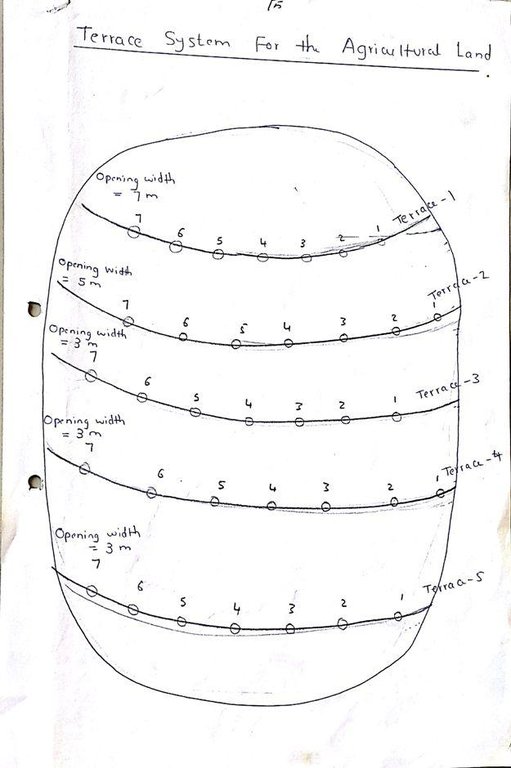
The purposes of diversion dam construction was to divert the main water course to take its way in the crop growing area replacing the old one and being controlled by small diversion dams (terraces to spread water for even water distribution through the original land. These terraces remarkably reduce gully formation.
Most important purpose is to provide water to growing crops in an area which is too dry for rain fed production and where no source for irrigation is available. It secures moisture during the growing season, by allowing more water to penetrate soil and to preserve moisture for a longer period at plant root zone.
The decrease of flood water velocity leads to silt accumulation and other debris materials which increase soil capability in providing moisture, nutrients and maintain soil structure and conservation.
For the earthen/stone-pitched diversion structure with spillway and small haffir alongside machines have been used (mainly loaders provided by the government) which excavated and built the bund. In addition local communities were involved in some aspects of the establishment (mainly stone pitching) supported/subsidized with incentives. The structure/scheme at Hashitribab (close to Sinkat) was built in 1999 (and no maintenance has been done since that time). It helps in watering about 500 feddan (c. 200 hectares) of agricultural area where water is spread by the use of small contour bunds: these were also constructed using subsidies and machines.
Terraces are usually used to control water spreading along the cropped area. Those terraces usually receive the water at low speed velocity. For that reason they are very small in size and volume. Usually they are located in very gentle and uniformed areas. The terraces can be constructed by simple hand tool and tractors accessories. But the prolonged drought makes the maintenance difficult as the dry soil is more susceptible to wind erosion and sand accumulation on both sides of the dam and the bottom of the bund is one of several desertification phenomenon in the region. But the wind-blown sand is one of the most serious one especially in the dry lands of the Red Sea State. Contour survey for land leveling slope identification and location is an important step before implementation.
The study site is located in the arid region of Red Sea State where steep hills from north-south inland mountains are interrupted by arid plains. The population density is low and the population depends on both cropping and livestock with high incidence of poverty. For this reason there should be a clear plan for construction and community extension approach to care about the maintenance of the technology. About 120 families live in Hashitribab area. All the year round they secure their provision by storing food crops in particular sorghum.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
السودان
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Red Sea
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Sinkat Locality
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت المساحة الدقيقة غير معروفة، فيرجى الإشارة إلى المنطقة التقريبية المغطاة:
- 10-1 كم2
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ 10-50 سنة
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- من خلال ابتكار مستخدمي الأراضي
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
This scheme was built – in 1999 - on the site of a smaller traditional diversion
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- تحسين الإنتاج
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي ومنعه وعكسه
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة سنوية
الزراعة السنوية - حدد المحاصيل:
- الحبوب - الذرة الرفيعة
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 1
حدد:
Longest growing period in days: 90
التعليقات:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Soil vulnerability to erosion due to rainfall irregularity and characterized by drought cycles; in some years rainfall recorded complete absence. Bare and and dried soils are easily affected by erosion agents (wind and water erosion) as these soils are weakly tolerant. Soils in plains are very poor, not renewable and are affected more than soils in seasonable rivers which are renewable with high soil water moisture.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Rain fed soils are weak in moisture holding capacity contrast to soils in flush irrigation soils and preferably used for seasonal cultivation by users and producing stable food crops with good productivity besides all underground water for human consumption and livestock through wells at reasonable depths are to be found.
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Cropland: Ca: Annual cropping
3.3 هل تغير استخدام الأراضي نتيجة لتنفيذ التقنية؟

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة سنوية
3.4 إمدادات المياه
أخرى (مثل ما بعد الفيضانات):
- post-flooding
3.5 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- التدابير المتقاطعة للمنحدرات
- تحويل المياه والصرف
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير البنيوية
- الحواجز والضفاف
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح
- (Wg):الانجراف الخلجاني/ الخلجان
- (Wo:) تأثيرات التدهور من مواقع أخرى
التعليقات:
Main causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Clearance of land from resdues to mitigate erosion), overgrazing (Stocking at trees and shrubs continue during the flowering stage preventing seeds production.), industrial activities and mining (To manage mining activities.), change in temperature (Reduced rainfall rate and more affection by wind erosion.), change of seasonal rainfall (More unpredictable and uncertain), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (affect in water erosin), droughts (affect passively on the vegetation cover and disintegration of rural families.), poverty / wealth (Not able to conserve resources)
Secondary causes of degradation: soil management (Breaking and blanking soil clods, and leveling and furrowing to increase soil roughness specially at wet seasons to reduce water erodability.), deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (excessive use of tree products), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (Rising population and thus more resource requirements. This is typically is round growing population at urban at centres unlike to people in rural areas except at rainy season where they are gathered), urbanisation and infrastructure development (Sequence to absence of infrastructures and related problems of drought increased rural migration to urban areas.), wind storms / dust storms (Erosion of top soil by wind blown.), floods (unless controlled), inputs and infrastructure: (roads, markets, distribution of water points, other, …) (Blocking water flow in some areas), education, access to knowledge and support services (Low environmental awareness and preparedness.)
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- منع تدهور الأراضي
- اصلاح/إعادة تأهيل الأراضي المتدهورة بشدة
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
4.3 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | التوقيت (الموسم) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Excavation of foundation trenches. | 1 week |
| 2. | Backfilling with heavy soil | 1 day |
| 3. | Establishment diversion structure | 8 weeks |
| 4. | Stonepitching by hand | 3 weeks |
| 5. | Construction of spillway | 2 weeks |
4.4 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | labour | ha | 1,0 | 57,0 | 57,0 | |
| معدات | machine use | ha | 1,0 | 355,0 | 355,0 | |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 412,0 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 412,0 | |||||
4.5 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Tillage | before fluding period |
4.6 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
التعليقات:
For the diversion structure and spillway at time of construction (1999)
4.7 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
The slope and depth of the wadi/ khor to be diverted
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- قاحلة
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- منخفضة (<1%)
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
< 5 م
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
مياه الشرب سيئة (تتطلب معالجة)
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- الكفاف (الإمداد الذاتي)
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- 10-50% من جميع الإيرادات
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- فرد/أسرة معيشية
مستوى المكننة:
- عمل يدوي
الجنس:
- نساء
- رجال
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly disadvantaged land users
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
100% of the land users are poor.
Off-farm income specification: Other activities include casual labour and livestock raising
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض التي يستخدمها مستخدمو الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق صغير
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- مجتمعي/قروي
- فردية، يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- مجتمعي (منظم)
- فردي
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
التعليقات/ حدد:
Relative to nothing otherwise
إنتاج الأعلاف
خطر فشل الإنتاج
منطقة الإنتاج
توافر المياه ونوعيتها
توافر مياه الشرب
الدخل والتكاليف
دخل المزرعة
تنوع مصادر الدخل
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الأمن الغذائي / الاكتفاء الذاتي
الفرص الثقافية
الفرص الترفيهية
المؤسسات المجتمعية
competition with natural ecosystem
التعليقات/ حدد:
Floodwaters diverted will not reach original destination and those former beneficiaries
contribution to human well-being
التعليقات/ حدد:
Due to more reliable production despite low and variable rainfall
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
كمية المياه
جودة المياه
حصاد / جمع المياه
الجريان السطحي
التبخر
التربة
رطوبة التربة
غطاء التربة
المادة العضوية في التربة/تحت الطبقة c
الآثار الايكولوجية الأخرى
competition with natural ecosystem
التعليقات/ حدد:
Floodwaters diverted will not reach original destination
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
توافر المياه
الفيضان في اتجاه مجرى النهر
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | زيادة أو نقصان | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة السنوية | زيادة | جيدا |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث الهيدرولوجية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| فيضان عام (نهر) | جيدا |
التعليقات:
Construction of water spreading devices serves to preserve water, reduce the waste, increase soil moisture capacity and raise soil fertility (silt accumulation)
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي قليلا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
التعليقات:
no maintenance carried out so not applicable here
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
- > 50%
التعليقات:
75% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
102 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support, scheme construction subsidised by Government
15% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
18 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology. People cannot construct khor/ wadi diversion barriers themselves by hand
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
| Useful and important in the area where floodwater harvesting/ spate irrigation is the only option for crop production. No rain fed irrigation system on the Red Sea State unlike to other Sudan. |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| SLM not falls under the community responsibility. They believe SLM is completely Gos role. | Land users awareness and involvement |
| They don’t think that community plays a role in the ongoing soil and vegetation degradation | Rotational grazing and seed broadcasting |
| They also say no regular concern by the government is given in relation to land reclamation | A location of budget and equipment to reclaim land and natural vegetation conservation. |
| They confirm that the physical conditions played a great role in land degradation e.g. drought aridity and high temperatures . | To ensure water harvesting and without waste. |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| High cost (needs machinery to move earth) | More support from Government and outside |
| Not enough trained personnel | More up-grading skills are required |
| Very little data available (apart from construction details) | Better system of monitoring and evaluation |
| Low technical capacity of the community | Capacity building and training |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
- زيارات ميدانية، مسوحات ميدانية
- مقابلات مع مستخدمي الأراضي
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط

Water Spreading (typical example from Hashatribab) [السودان]
Construction of water spreading system on khor and wadi with machinery jointly government and farmers in dam compaction and pitching.
- جامع المعلومات: Abdalla Osman Eisa
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية