Water Spreading (typical example from Hashatribab) [Soudan]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Abdalla Osman Eisa
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateurs : Deborah Niggli, Alexandra Gavilano
Sidud (Local Arabic) - Tarrit (Beja dialect) for earth dams
technologies_1292 - Soudan
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Spécialiste GDT:
Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Soil Conservation, Land Use and Water Adminstratio (Soil Conservation, Land Use and Water Adminstratio) - Soudan1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.4 Déclaration sur la durabilité de la Technologie décrite
Est-ce que la Technologie décrite ici pose problème par rapport à la dégradation des terres, de telle sorte qu'elle ne peut pas être déclarée comme étant une technologie de gestion durable des terres?
Non
1.5 Référence au(x) Questionnaires sur les Approches de GDT (documentées au moyen de WOCAT)

Water Spreading (typical example from Hashatribab) [Soudan]
Construction of water spreading system on khor and wadi with machinery jointly government and farmers in dam compaction and pitching.
- Compilateur : Abdalla Osman Eisa
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
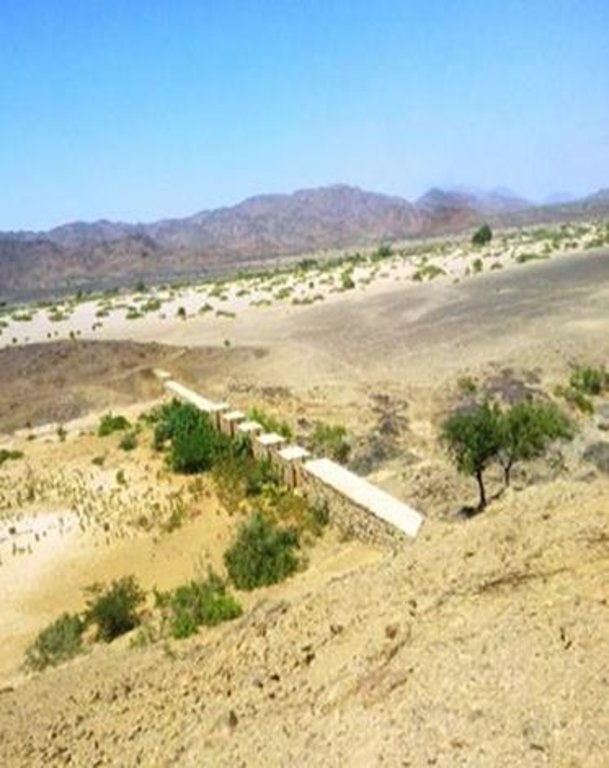
Water Spreading (or Spate Irrigation system) conducted through the construction of earth dam structures at the khor cross section.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
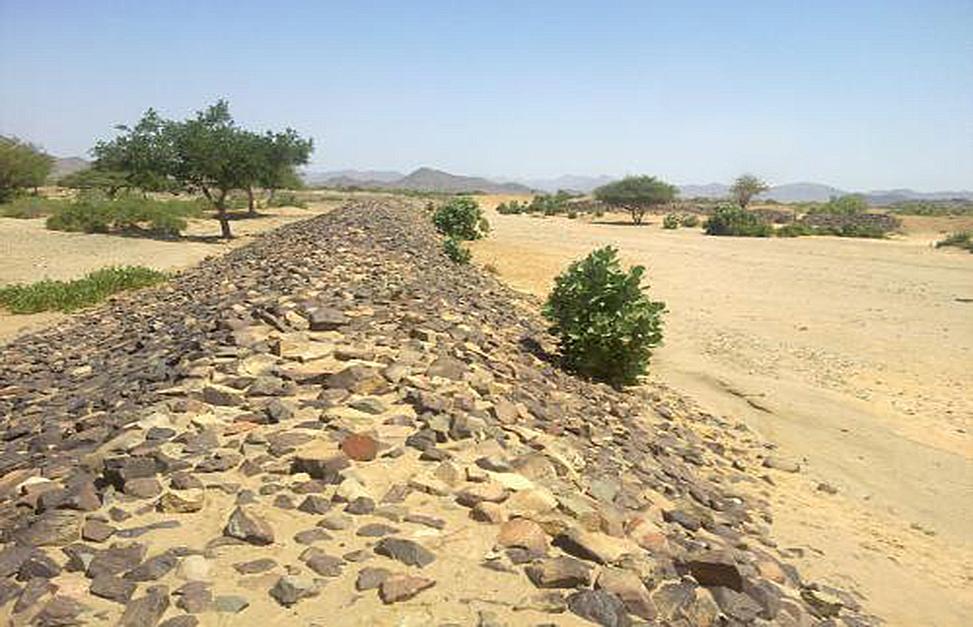
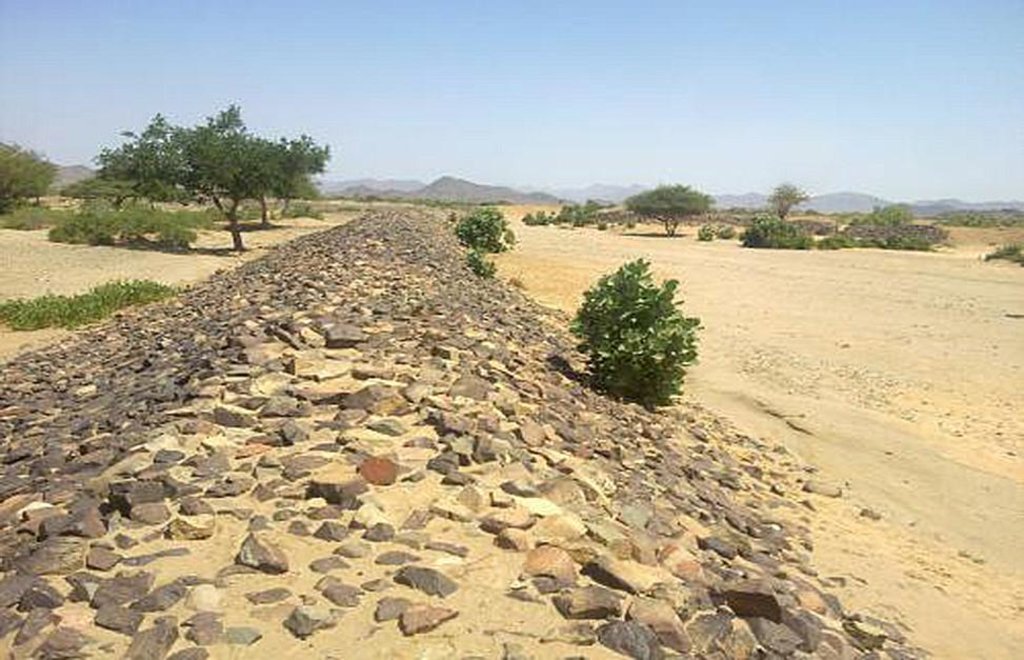
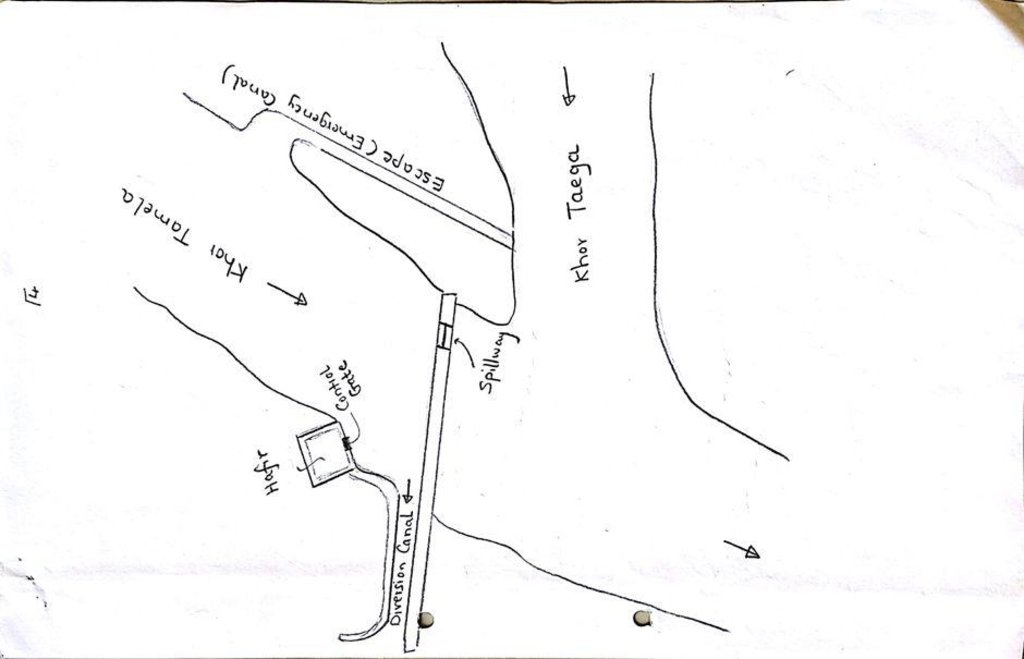
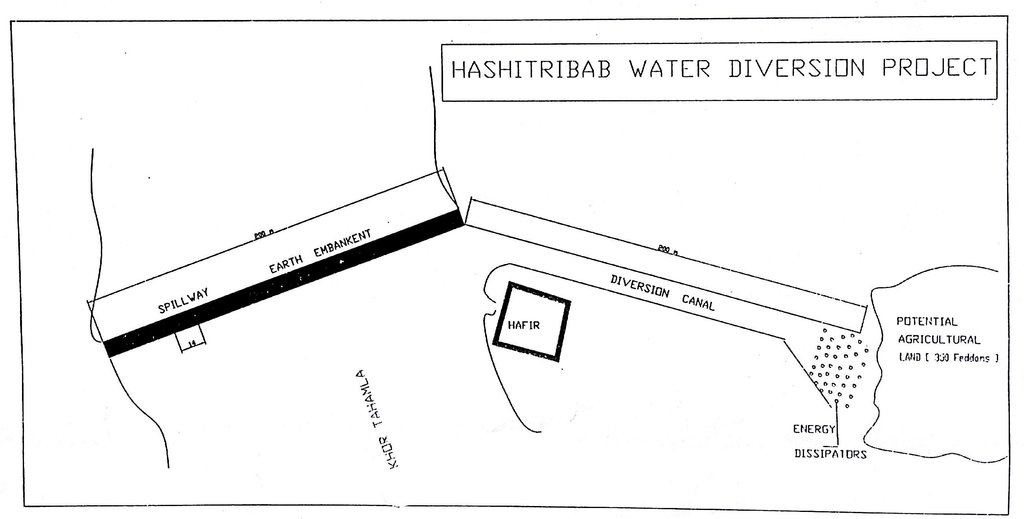
Water Spreading (or Spate Irrigation) can be done through the construction of an angled bank or weir – with a spillway in case of excess flow – to divert a “khor” (ephemeral stream) and spread it (using spaced contour bunds) for crop production.
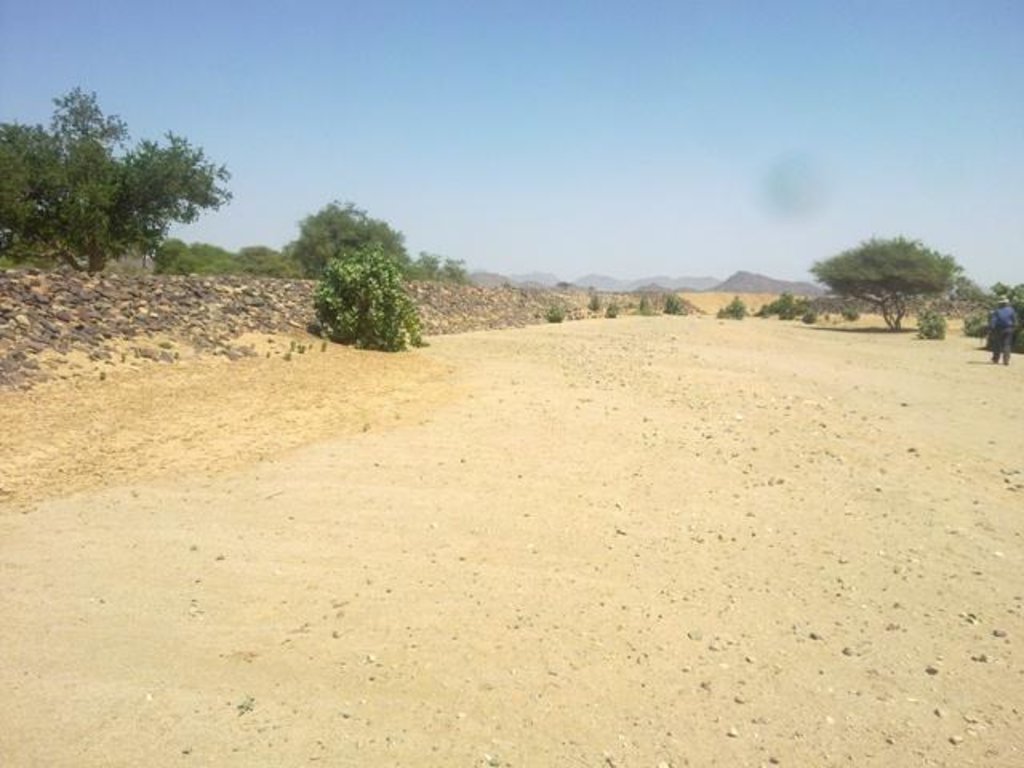
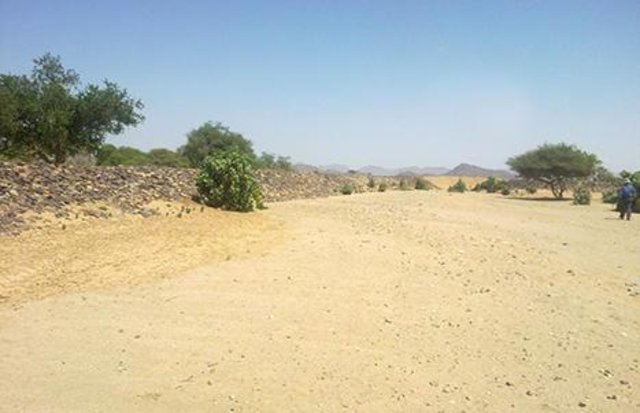
Water Spreading from khors or wadis where channelized runoff/ floodwater is diverted onto plains which are then cultivated on residual moisture. An example of a scheme which was constructed in 1999 is located at Hashitribab, some 7 km from Sinkat on the road towards Kassala. This scheme, comprising a stone-pitched earth diversion barrier across a khor (an ephemeral water course), is documented by using among others the WOCAT Questionnaire and WOCAT’s QA. While the diversion is still intact and provides water to the fields about one kilometre downstream (there were young sorghum plants growing at the time of the visit in November 2011) maintenance will be needed.
There was only a very small input of voluntary labour in its original construction (comprising a contribution in terms of stone pitching).
Construction by the Government, using machinery, with little local contribution might explain why voluntary maintenance of the structures has been negligible. Water spreading schemes have gradually expanded in number over the last 20 years in Red Sea State (according to Sayed Dabloub’s personal comment). Currently it was confirmed that there are new sites under planning and construction.
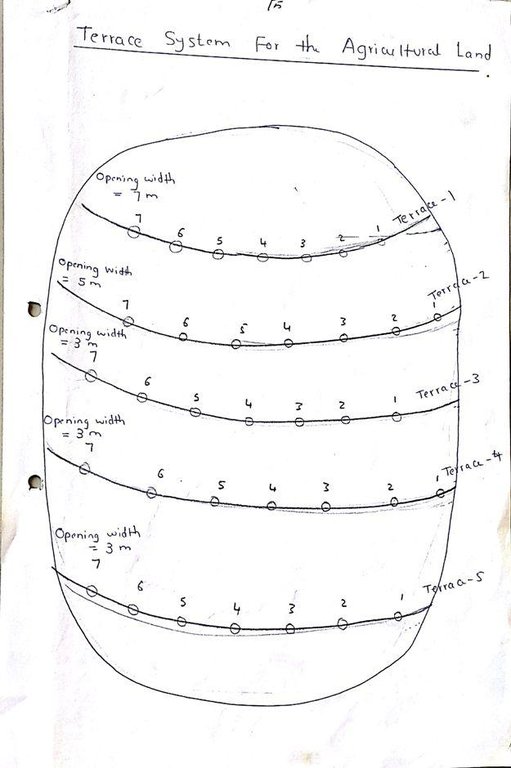
The purposes of diversion dam construction was to divert the main water course to take its way in the crop growing area replacing the old one and being controlled by small diversion dams (terraces to spread water for even water distribution through the original land. These terraces remarkably reduce gully formation.
Most important purpose is to provide water to growing crops in an area which is too dry for rain fed production and where no source for irrigation is available. It secures moisture during the growing season, by allowing more water to penetrate soil and to preserve moisture for a longer period at plant root zone.
The decrease of flood water velocity leads to silt accumulation and other debris materials which increase soil capability in providing moisture, nutrients and maintain soil structure and conservation.
For the earthen/stone-pitched diversion structure with spillway and small haffir alongside machines have been used (mainly loaders provided by the government) which excavated and built the bund. In addition local communities were involved in some aspects of the establishment (mainly stone pitching) supported/subsidized with incentives. The structure/scheme at Hashitribab (close to Sinkat) was built in 1999 (and no maintenance has been done since that time). It helps in watering about 500 feddan (c. 200 hectares) of agricultural area where water is spread by the use of small contour bunds: these were also constructed using subsidies and machines.
Terraces are usually used to control water spreading along the cropped area. Those terraces usually receive the water at low speed velocity. For that reason they are very small in size and volume. Usually they are located in very gentle and uniformed areas. The terraces can be constructed by simple hand tool and tractors accessories. But the prolonged drought makes the maintenance difficult as the dry soil is more susceptible to wind erosion and sand accumulation on both sides of the dam and the bottom of the bund is one of several desertification phenomenon in the region. But the wind-blown sand is one of the most serious one especially in the dry lands of the Red Sea State. Contour survey for land leveling slope identification and location is an important step before implementation.
The study site is located in the arid region of Red Sea State where steep hills from north-south inland mountains are interrupted by arid plains. The population density is low and the population depends on both cropping and livestock with high incidence of poverty. For this reason there should be a clear plan for construction and community extension approach to care about the maintenance of the technology. About 120 families live in Hashitribab area. All the year round they secure their provision by storing food crops in particular sorghum.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Soudan
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Red Sea
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Sinkat Locality
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- répartie uniformément sur une zone
S'il n'existe pas d'informations exactes sur la superficie, indiquez les limites approximatives de la zone couverte:
- 1-10 km2
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a entre 10-50 ans
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- grâce à l'innovation d'exploitants des terres
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
This scheme was built – in 1999 - on the site of a smaller traditional diversion
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- améliorer la production
- réduire, prévenir, restaurer les terres dégradées
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

Terres cultivées
- Cultures annuelles
Cultures annuelles - Précisez les cultures:
- céréales - sorgho
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 1
Précisez:
Longest growing period in days: 90
Commentaires:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Soil vulnerability to erosion due to rainfall irregularity and characterized by drought cycles; in some years rainfall recorded complete absence. Bare and and dried soils are easily affected by erosion agents (wind and water erosion) as these soils are weakly tolerant. Soils in plains are very poor, not renewable and are affected more than soils in seasonable rivers which are renewable with high soil water moisture.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Rain fed soils are weak in moisture holding capacity contrast to soils in flush irrigation soils and preferably used for seasonal cultivation by users and producing stable food crops with good productivity besides all underground water for human consumption and livestock through wells at reasonable depths are to be found.
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Cropland: Ca: Annual cropping
3.3 Est-ce que l’utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie ?

Terres cultivées
- Cultures annuelles
3.4 Approvisionnement en eau
autre (par ex., post-inondation):
- post-flooding
3.5 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- mesures en travers de la pente
- dérivation et drainage de l'eau
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

structures physiques
- S2: Diguettes, digues
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

érosion hydrique des sols
- Wt: perte de la couche superficielle des sols (couche arable)/ érosion de surface
- Wg: ravinement/ érosion en ravines
- Wo: effets hors-site de la dégradation
Commentaires:
Main causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Clearance of land from resdues to mitigate erosion), overgrazing (Stocking at trees and shrubs continue during the flowering stage preventing seeds production.), industrial activities and mining (To manage mining activities.), change in temperature (Reduced rainfall rate and more affection by wind erosion.), change of seasonal rainfall (More unpredictable and uncertain), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (affect in water erosin), droughts (affect passively on the vegetation cover and disintegration of rural families.), poverty / wealth (Not able to conserve resources)
Secondary causes of degradation: soil management (Breaking and blanking soil clods, and leveling and furrowing to increase soil roughness specially at wet seasons to reduce water erodability.), deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (excessive use of tree products), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (Rising population and thus more resource requirements. This is typically is round growing population at urban at centres unlike to people in rural areas except at rainy season where they are gathered), urbanisation and infrastructure development (Sequence to absence of infrastructures and related problems of drought increased rural migration to urban areas.), wind storms / dust storms (Erosion of top soil by wind blown.), floods (unless controlled), inputs and infrastructure: (roads, markets, distribution of water points, other, …) (Blocking water flow in some areas), education, access to knowledge and support services (Low environmental awareness and preparedness.)
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- prévenir la dégradation des terres
- restaurer/ réhabiliter des terres sévèrement dégradées
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
4.3 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Calendrier des activités (saisonnier) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Excavation of foundation trenches. | 1 week |
| 2. | Backfilling with heavy soil | 1 day |
| 3. | Establishment diversion structure | 8 weeks |
| 4. | Stonepitching by hand | 3 weeks |
| 5. | Construction of spillway | 2 weeks |
4.4 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % du coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | labour | ha | 1,0 | 57,0 | 57,0 | |
| Equipements | machine use | ha | 1,0 | 355,0 | 355,0 | |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 412,0 | |||||
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 412,0 | |||||
4.5 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Tillage | before fluding period |
4.6 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
Commentaires:
For the diversion structure and spillway at time of construction (1999)
4.7 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
The slope and depth of the wadi/ khor to be diverted
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Zone agro-climatique
- aride
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- faible (<1%)
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Profondeur estimée de l’eau dans le sol:
< 5 m
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
faiblement potable (traitement nécessaire)
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Orientation du système de production:
- subsistance (auto-approvisionnement)
Revenus hors exploitation:
- 10-50% de tous les revenus
Individus ou groupes:
- individu/ ménage
Niveau de mécanisation:
- travail manuel
Genre:
- femmes
- hommes
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly disadvantaged land users
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
100% of the land users are poor.
Off-farm income specification: Other activities include casual labour and livestock raising
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres utilisées par les exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- petite dimension
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- communauté/ village
- individu, avec titre de propriété
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- communautaire (organisé)
- individuel
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
énergie:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Relative to nothing otherwise
production fourragère
risque d'échec de la production
surface de production
Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
disponibilité de l'eau potable
Revenus et coûts
revenus agricoles
diversité des sources de revenus
Impacts socioculturels
sécurité alimentaire/ autosuffisance
opportunités culturelles
possibilités de loisirs
institutions communautaires
competition with natural ecosystem
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Floodwaters diverted will not reach original destination and those former beneficiaries
contribution to human well-being
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Due to more reliable production despite low and variable rainfall
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
quantité d'eau
qualité de l'eau
récolte/ collecte de l'eau
ruissellement de surface
évaporation
Sols
humidité du sol
couverture du sol
matière organique du sol/ au dessous du sol C
Autres impacts écologiques
competition with natural ecosystem
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Floodwaters diverted will not reach original destination
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
disponibilité de l'eau
inondations en aval
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Changements climatiques progressifs
Changements climatiques progressifs
| Saison | Augmentation ou diminution | Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| températures annuelles | augmente | bien |
Extrêmes climatiques (catastrophes)
Catastrophes hydrologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| inondation générale (rivière) | bien |
Commentaires:
Construction of water spreading devices serves to preserve water, reduce the waste, increase soil moisture capacity and raise soil fertility (silt accumulation)
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
légèrement positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
Commentaires:
no maintenance carried out so not applicable here
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
- > 50%
Commentaires:
75% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
102 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support, scheme construction subsidised by Government
15% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
18 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology. People cannot construct khor/ wadi diversion barriers themselves by hand
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
| Useful and important in the area where floodwater harvesting/ spate irrigation is the only option for crop production. No rain fed irrigation system on the Red Sea State unlike to other Sudan. |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| SLM not falls under the community responsibility. They believe SLM is completely Gos role. | Land users awareness and involvement |
| They don’t think that community plays a role in the ongoing soil and vegetation degradation | Rotational grazing and seed broadcasting |
| They also say no regular concern by the government is given in relation to land reclamation | A location of budget and equipment to reclaim land and natural vegetation conservation. |
| They confirm that the physical conditions played a great role in land degradation e.g. drought aridity and high temperatures . | To ensure water harvesting and without waste. |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| High cost (needs machinery to move earth) | More support from Government and outside |
| Not enough trained personnel | More up-grading skills are required |
| Very little data available (apart from construction details) | Better system of monitoring and evaluation |
| Low technical capacity of the community | Capacity building and training |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
- visites de terrain, enquêtes sur le terrain
- interviews/entretiens avec les exploitants des terres
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens

Water Spreading (typical example from Hashatribab) [Soudan]
Construction of water spreading system on khor and wadi with machinery jointly government and farmers in dam compaction and pitching.
- Compilateur : Abdalla Osman Eisa
Modules
Aucun module trouvé