Planting poplar forest in the flood plains of high mountain river areas [طاجيكستان]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Gulniso Nekushoeva
- المحرر: –
- المراجعون: Alexandra Gavilano, David Streiff
Буньедкардани чакалакзор дар сохили даръехои баландкух (tajik)
technologies_1515 - طاجيكستان
- Planting poplar forest in the flood plains of high mountain river areas: 15 مارس، 2017 (inactive)
- Planting poplar forest in the flood plains of high mountain river areas: 20 يوليو، 2017 (inactive)
- Planting poplar forest in the flood plains of high mountain river areas: 22 يوليو، 2017 (inactive)
- Planting poplar forest in the flood plains of high mountain river areas: 21 أغسطس، 2019 (public)
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
local community:
Jonbekov Ikbol
طاجيكستان
اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Institute for Environment and Human Security, United Nations University (Institute for Environment and Human Security, United Nations University) - ألمانيااسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
UNEP (UNEP) - كينيااسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
UNDP/GEF Project Uzbekistan (UNDP/GEF Uzbekistan) - أوزبكستاناسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Tajik Soil Insitute (Tajik Soil Institute) - طاجيكستاناسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Tajik Academy of Agricultural Sciences (Tajik Academy of Agricultural Sciences) - طاجيكستان1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
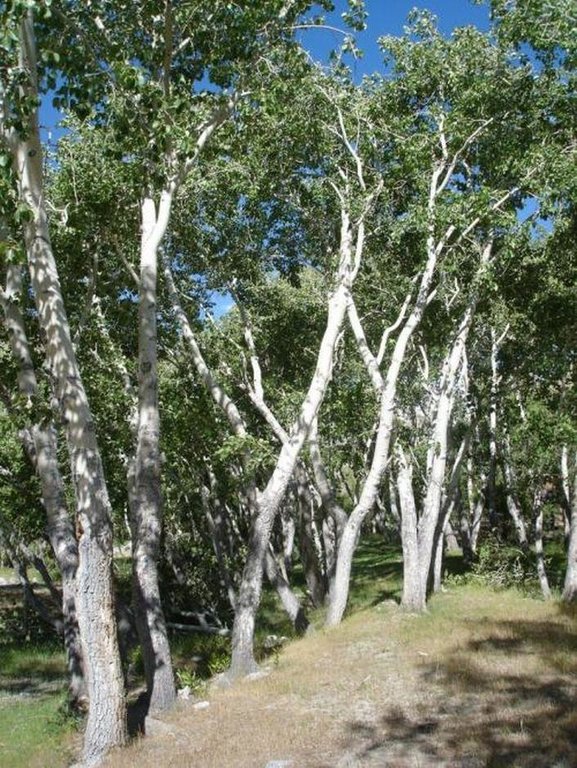
The afforestation of the low productivity sandy lands in the river valley areas of arid highlands with fast growing poplar trees, provides the population with firewood as well as timber and also provides conservation benefits.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
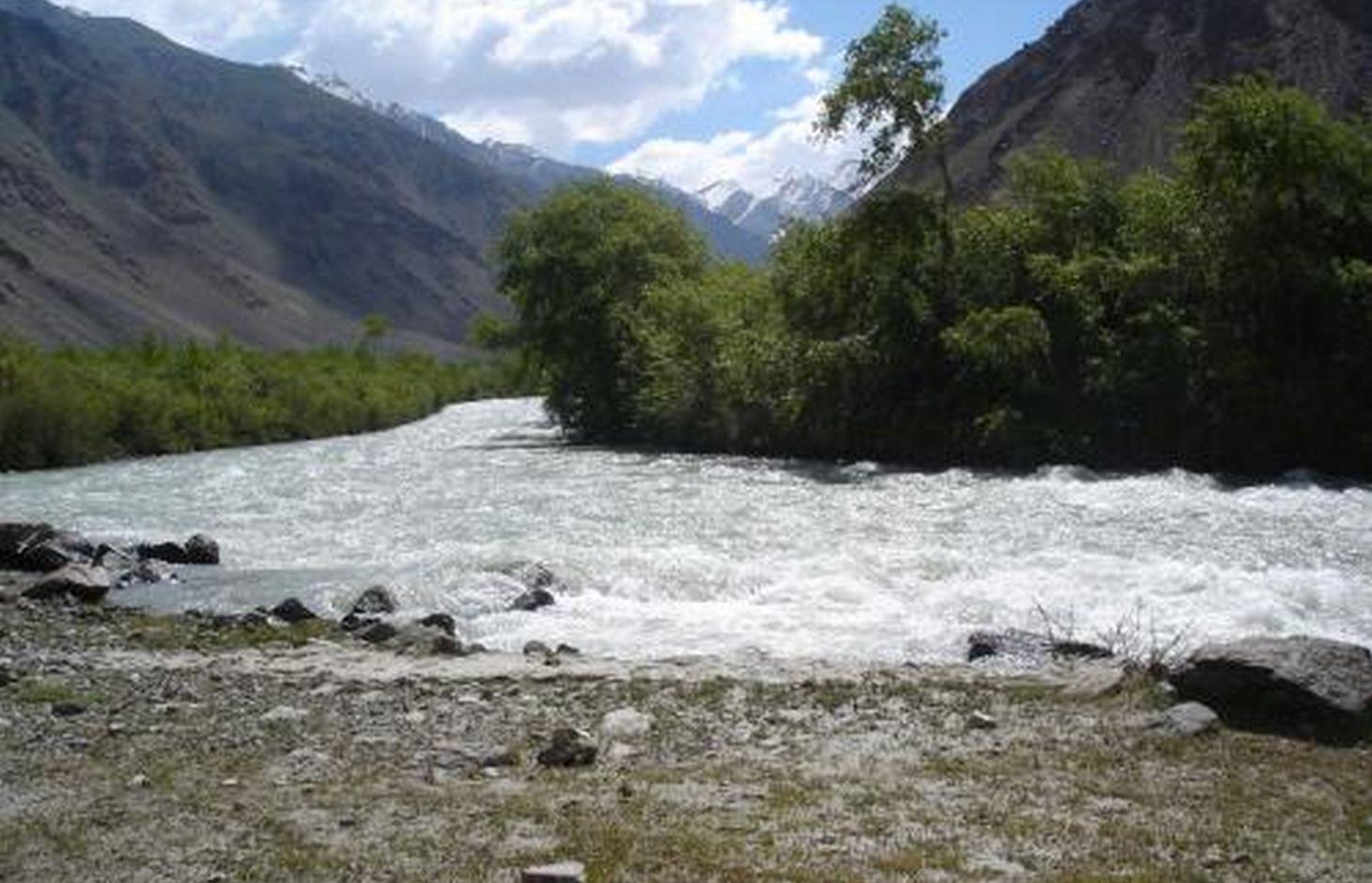
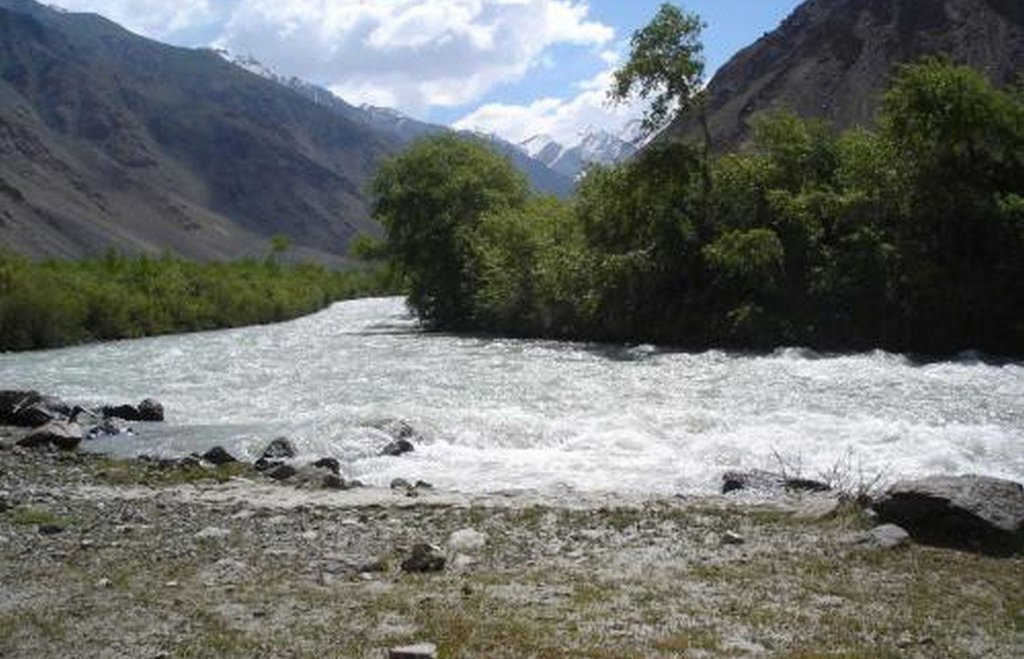
In the Jamoat Vankala area of the Shugnan district in GBAO, low temperatures make it very difficult to grow fruit or trees other than poplar (Populus pamirico) or Salix Schugnanica Coerz.
The natural forest consists mainly of the latter and this grows very slowly. It is very cold for 6-7 months of the year in this region, so the demand for cheap firewood to heat homes is extremely high.
In the 1980s, the sovhoz decided to transform 10ha of a low productivity pasture land into more productive irrigated forest land. After the collapse of the Soviet system, the Jamoat rented this forest land to a farmer, who still remains in charge of this piece of land.
Purpose of the Technology: The creation of a poplar forest on the river shore in this treeless desert alpine zone can go someway towards meeting the local's demand for firewood. It can provide cheap timber and environmental benefits as well as a pleasant environment.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The process of establishing this poplar forest began with the creation of irrigation canals and the planting of seedlings. In the first few years, the seedlings had to be watered frequently due to the thirsty sandy soils.
Other factors that needed to be considered were protecting the area from grazing cattle, watering areas around the forest away from the the river bank, the selective felling of some poplars, the additional planting of trees on barren soil, as well as the protection of the forest from predatory deforestation by the locals (which has increased during the economic crisis). Thanks to natural regeneration processes, farmers can now prepare firewood for the winter and do not have to bring the timber from far away.
Natural / human environment: 88% of the Pamir region is covered by glaciers, snow, and rocks, and is thus completely devoid of soil. Consequently, the area of arable and orchard lands in the GBAO region is only about 2%, with a forest area of 0.4%. Two-thirds of all the Pamir natural forests are located along the river banks of the Vanch, Gunt, Tokuzbulak, and others, at an altitude of 3200m.
In the narrow V-shaped valleys of the Western Pamirs, the lowest points are at an altitude of 1,200m,extending up to the highest points at 7,400m. This explains the climatic differences within the region, because the lower parts in the valleys enjoy a warmer climate than the higher parts. Overall, the annual average air temperature in the region is 9°C, and most rainfall occurs between the winter and spring periods with an average precipitation of 191-227mm.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
طاجيكستان
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Tajikistan / GBAO
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Shugnan / Vankala
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ 10-50 سنة
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- من خلال ابتكار مستخدمي الأراضي
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
During the 1980s much of the low productivity sandy land was converted to poplar forest. This was initiated by a local group who put in many voluntary hours. From 1993 onwards, this forest was part of the local jamoat "Vankala" lands. The local administration rented it to a local farmer- (Jonbekov Ikbol).
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- التخفيف من تغير المناخ وآثاره
- خلق أثر اقتصادي مفيد
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

أراضي الرعي
نوع الحيوان:
- ماشية - الألبان
الصنف:
ماشية - الألبان
العدد:
2

الغابات/ الأراضي الحرجية
- الغابات/الأراضي الحرجية (شبه) الطبيعية
- زراعة الأشجار، التشجير
الغابات/الأراضي الحرجية (شبه) الطبيعية: حدد نوع الإدارة:
- قطع الأشجار الانتقائي
زراعة الأشجار والتشجير: تحديد أصل وتكوين الأنواع:
- زراعة محصول واحد من صنف محلي
- Populus pamirico, Salix Schugnanica Coerz, dog rose
منتجات وخدمات:
- الخشب
- حطب الوقود
- الرعي/ رعي أطراف الأشجار الفتية (الجلح)
- حفظ/حماية الطبيعة
- الترفيه / السياحة
- الحماية من المخاطر الطبيعية
التعليقات:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): The main problems include; Low soil productivity, a short growing season, desertification, low temperatures and a sharp drop in average daily temperatures and an early night frost. Very sparse vegetation of drought-tolerant grass and little shrubs
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): water shortages, low soil fertility, low yields
Selective felling of (semi-) natural forests: Every autumn
Plantation forestry: Every year they plant new seedlings to assist with afforestation
Forest products and services: timber, fuelwood, grazing / browsing, nature conservation / protection, recreation / tourism, protection against natural hazards
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Forests / woodlands: Fp: Plantations, afforestations
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: The farmer owns 1-2 of his own cows which graze in the forest over the smmer. They use these cows for milk. The cows are not allowed to roam free, they are tied up. Someimes the children try to sell milk and dairy products on the roadside, but there is not much passing trade.
Livestock is grazing on crop residues
3.3 هل تغير استخدام الأراضي نتيجة لتنفيذ التقنية؟

أراضي الرعي

الغابات/ الأراضي الحرجية
- الغابات/الأراضي الحرجية (شبه) الطبيعية
- زراعة الأشجار، التشجير
الغابات/الأراضي الحرجية (شبه) الطبيعية: حدد نوع الإدارة:
- قطع الأشجار الانتقائي
3.4 إمدادات المياه
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- ري كامل
التعليقات:
Water supply: Also mixed rainfed
Longest growing period in days: 120 longest growing period from month to month: May- September
3.5 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- تحسين الغطاء الأرضي/النباتي
- الحد من مخاطر الكوارث بالاستناد على النظام البيئي
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير الزراعية
- A1: الغطاء النباتي/التربة

التدابير النباتية
- V1: غطاء من الأشجار والشجيرات

التدابير البنيوية
- S3: الخنادق المتدرجة ،والقنوات، والممرات المائية

التدابير الإدارية
- M1: التغيير في نوع استخدام الأراضي
التعليقات:
Main measures: vegetative measures, management measures
Secondary measures: structural measures
Type of vegetative measures: in blocks
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح

التدهور الكيميائي للتربة
- (Cn): تراجع الخصوبة وانخفاض محتوى المادة العضوية (غير ناتج عن الانجراف)

التدهور البيولوجي
- (Bc): تناقص الغطاء النباتي
- (Bq): انخفاض الكمية/الكتلة الحيوية
التعليقات:
Main type of degradation addressed: Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, Bc: reduction of vegetation cover, Bq: quantity / biomass decline
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (24hr electricity has been available only for the last 2 years. Over the last 16 years the local population have cut down all the surrounding trees.), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (All the trees were cut down for use as animal feed and fire wood.), overgrazing (Livestock were grazed in the areas around the village all year round.), change in temperature (The summeres have become colder in recent years, the summer became more colder, most of crops ripen at low temperatures), poverty / wealth (most of the population are poor, thus placing high pressure on the natural reasources as they are forced to use these for fuel and food.)
Secondary causes of degradation: droughts (Low levels of rain fall, strong сold winds, high insolaton, low soil moisture), war and conflicts (During the civil war the area had high rates of food insecurity.)
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
- اصلاح/إعادة تأهيل الأراضي المتدهورة بشدة
التعليقات:
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
المواصفات الفنية (المتعلقة بالرسم الفني):
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (Needs to use chainsaws so some extra technical knowledge required.)
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, increase in organic matter, increase of biomass (quantity), spatial arrangement and diversification of land use
Secondary technical functions: improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), improvement of subsoil structure (hardpan), stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase / maintain water stored in soil, reduction in wind speed, promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Aligned: -graded strips
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
In blocks
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 400
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 5
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 5
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Trees/ shrubs species: Populus pamirico, Salix Schugnanica Coerz, dog rose
Grass species: different natural grasses
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 5.00%
Structural measure: main irrigation canal along the plot upper border
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.5
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.8
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 2000
Structural measure: irrigation networks inside the forest
Vertical interval between structures (m): 5
Spacing between structures (m): 5
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.2
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.3
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 200000
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 5%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 5%
Change of land use type: low-productivity grasslands have changed to a high productive poplar forest
Change of land use practices / intensity level: Changed from an area of open access to locals, to having controlled access (pasture land, forest land)
4.2 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
عملة أخرى/ عملة وطنية (حدد):
Somoni
إذا كان ذا صلة، وضح سعر الصرف من الدولار الأمريكي إلى العملة المحلية (على سبيل المثال، 1 دولار أمريكي = 79.9 ريال برازيلي): 1 دولار أمريكي =:
4,53
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
30
4.3 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | التوقيت (الموسم) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Growing seedlings in a nursery | one year (5 month irrigation) |
| 2. | Digging holes 50x60cm on 1 ha - 400 on 10 hectares - 4000 holes | During Spring |
| 3. | Manure (dung) | in Spring |
| 4. | Delivering of manure to plot by tractor and truck | in Spring |
| 5. | Prepare a mixture of soil and dung for filling planting holes on 10 ha | in Spring |
| 6. | Planting poplar seedlings and watering them | in Spring |
| 7. | Planting trees along the irrigation canal along the road to Jelondi and the upper boundaries of the site (10m on 1day) | before tree planting in spring |
| 8. | Establishment of irrigation networks from the canal in the garden(7x 1000м per day) | before tree planting in spring |
| 9. | Collection of sea buck thorn stems and branches | before tree planting |
| 10. | Load sea buck thorn stems and branches into the car and unloadthem | before tree planting |
| 11. | Delivering stems and branches using a car | before tree planting |
| 12. | Fencing the area | before trees planting |
4.4 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Growing seedlings in a nursery (irrigation and nursering) | Persons/day | 25,0 | 30,0 | 750,0 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Digging holes | Persons/day | 100,0 | 30,0 | 3000,0 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Prepare a mixture of soil and dung | Persons/day | 40,0 | 30,0 | 1200,0 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Planting poplar seedlings and watering them | Persons/day | 40,0 | 30,0 | 1200,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Tractor for delivering manure | hours | 8,0 | 75,0 | 600,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Labour: Planting trees along the irrigation canal | Persons/day | 200,0 | 30,0 | 6000,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Labour: Establishment of irrigation networks from the canal in the garden | Persons/day | 30,0 | 30,0 | 900,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Car for transporting branches | Trucks/day | 20,0 | 100,0 | 2000,0 | 100,0 |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | Manure (dung) | tons | 40,0 | 50,0 | 2000,0 | 100,0 |
| غير ذلك | Labour: Collection of sea buck thorn stems and branches | Persons/day | 20,0 | 30,0 | 600,0 | 100,0 |
| غير ذلك | Labour: Load sea buck thorn stems and branches into the car and unload them | Persons/day | 10,0 | 30,0 | 300,0 | 100,0 |
| غير ذلك | Labour: Fencing the area | Persons/day | 100,0 | 30,0 | 3000,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 21550,0 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 4757,17 | |||||
4.5 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Watering seedlings 2 times per week first year (40 pers days on 1 month - 10 ha) | 5 months per year |
| 2. | Watering seedlings once per week per year (20 pers days -1 month- 10 ha) | 5 months per year |
| 3. | Protection, avoidance of grazing(5 hour per day) | 5 months per year |
| 4. | Annual harvest of firewood | every year/autumn |
| 5. | Selective felling of trees(Ø=40-50см) | After 10 years / October |
| 6. | Annual haymaking of natural grass | every year/summer |
| 7. | Repairs and cleaning of the main irrigation canal to clear sediment and debris | Before the irrigation season/in spring |
| 8. | Repairs and cleaning of the irrigation network to clear sediment and brancheson 10 ha | Before the irrigation season in spring |
| 9. | Repairing fences | if needed |
4.6 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Watering seedlings (First year and followin year) | Persons/day | 300,0 | 30,0 | 9000,0 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Protection, avoidance of grazing | Persons/day | 87,0 | 30,0 | 2610,0 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Annual harvest of firewood | Persons/day | 10,0 | 30,0 | 300,0 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Selective felling of trees (after 10 years | Persons/day | 15,0 | 30,0 | 450,0 | |
| غير ذلك | Labour: Annual haymaking of natural grass | Persons/day | 40,0 | 30,0 | 1200,0 | |
| غير ذلك | Labour: Repairs and cleaning of the main irrigation canal abd irrigation network | Persons/day | 15,0 | 30,0 | 450,0 | |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 14010,0 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 3092,72 | |||||
التعليقات:
Machinery/ tools: shovel
The costs were calculated for the whole plantation area of 10 ha
4.7 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
Labour is the most determinate factor affecting the costs, however, in this situation, most of it was provided by the land users themselves. Costs reported are those for additional labour that would need to be paid for.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المواصفات/التعليقات على هطول الأمطار:
200-230 mm average rainfall. Main season is during winter to spring period.
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- قاحلة
Thermal climate class: boreal
In general, the Pamirs are is characterised by dry air and low precipitation
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
وضح ما إذا كانت التقنية مطبقة على وجه التحديد في:
- حالات مقعرة
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التضاريس:
Altitudinal zone: 3200 m a.s.l.
Slopes on average: It is a narrow river valley
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- خشن / خفيف (رملي)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- متوسطة (1-3%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Soil depth on average: The soil is sandy-loam, shallow, with low productivity
Soil texture: Sandy-loamy soil
These soils have low natural fertility, and irrigation increases the productivity of this soil
Topsoil organic matter: After irrigation and changing the land use type, organic matter increases
Soil drainage / infiltration is good because this soil is sandy-loam
Soil water storage capacity is low because this soil is sandy-loam
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
< 5 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
جيد
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
مياه شرب جيدة
تعليقات ومواصفات أخرى بشأن نوعية المياه وكميتها:
Ground water table: 2/3 of the forest is close to the river and the ground water level is 2-3m
Availability of surface water: The River Tokuzbulak is in close proximity (somtimes also just medium)
Water quality (untreated): The river can provide clean drinking water
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- مرتفع
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التنوع البيولوجي:
Poplar trees provide a favourable microclimate for growing many bushes and herbaceous plants beneath, and also provides a good natural habitat for birds and some wild animals.
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- الكفاف (الإمداد الذاتي)
- مختلط (كفاف/ تجاري)
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- >50% من إجمالي الدخل
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- ثري
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- فرد/أسرة معيشية
مستوى المكننة:
- عمل يدوي
الجنس:
- نساء
- رجال
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly Leaders / privileged
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
10% of the land users are rich (He has a car, big forest plot, 5 yaks, 2 cows, 20 sheep).
Off-farm income specification: The farmer owns a car, sometimes he works as a tour gide, he sells the timber and firewood, and in autumn he buys meat in Murgab to resell in Khatlon.
Market orientation of production system: subsistence (self-supply), mixed (subsistence/ commercial, mixed (subsistence/ commercial
Market orientation of production system: In the first 7 years subsistence and after 7-10 years some of the trees had reached maturity, the rest he sold (20-30m3). ( In the autumn haymaking and firewood (10m3) for himself and 3 cars (30m3) firewood for sale)
Level of mechanization: Watering, pruning of poplars, haymaking is all manual
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض التي يستخدمها مستخدمو الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق متوسط
التعليقات:
At 1-2 ha: The area of crop land in the Western Pamirs is very small.
At 2-5 ha: This farmer has 3 ha of crop land because there is a small population in this village.
At 0.5-1 ha the population is more dense.
Also 5-15 ha, but it is rare that one individual farmer is rented such a large area of forest.
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- دولة
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- مؤجر
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- وصول مفتوح (غير منظم)
التعليقات:
before 1992-93 it was the Sovhoz forest land, after 1993 the forest was in the Vankala Jamoat. The farmer rents this land.
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج الأعلاف
التعليقات/ حدد:
natural grass under the trees
جودة العلف
التعليقات/ حدد:
More grasses and edible plants grow under the shadow of the trees.
إنتاج حيواني
التعليقات/ حدد:
more furaj more animals
إنتاج الخشب
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
10%
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
100%
توليد الطاقة
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
100%
الدخل والتكاليف
دخل المزرعة
التعليقات/ حدد:
More animals and firewood that he can sell.
تنوع مصادر الدخل
التعليقات/ حدد:
He can sell firewood, meat, dairy products, and can be a touris guide.
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الأمن الغذائي / الاكتفاء الذاتي
الفرص الترفيهية
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
5%
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
100%
التعليقات/ حدد:
The environmnt looks much more pleasant with more green areas.
المعرفة بالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي/تدهور الأراضي
التخفيف من حدة الصراع
التعليقات/ حدد:
The area is too big for one farmer
Livelihood and human well-being
التعليقات/ حدد:
The extra money earned from the sale of timber, firewood and livestock can be spent on health and education for the family
الآثار الايكولوجية
التربة
رطوبة التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Reduces evaporation from the soil surface
غطاء التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
good vegetation cover helps improve the soil cover
فقدان التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
The trees and grass roots stabilise the soil
دورة المغذيات/إعادة الشحن
التعليقات/ حدد:
Matter and roots of the herbaceous plants, improves structure and fertility of the soil
المادة العضوية في التربة/تحت الطبقة c
التعليقات/ حدد:
SOM is increased underneath the poplar forest
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
الكتلة الحيوية/ طبقة الكربون فوق التربة
التنوع النباتي
التعليقات/ حدد:
The diversity of plants is higher than in the surrounding areas
التنوع الحيواني
التعليقات/ حدد:
Provides a habitat for more wild animals.
الأنواع المفيدة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Good microclimate and protection for them
تنوع الموائل
التعليقات/ حدد:
Good microclimate and protection for them
الحد من مخاطر المناخ والكوارث
انبعاث الكربون والغازات المسببة للاحتباس الحراري
التعليقات/ حدد:
carbon sis stored within the high amounts of biomass
سرعة الرياح
التعليقات/ حدد:
tall trees provide wind barrier
الآثار الايكولوجية الأخرى
Bio energy generation
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
الفيضان في اتجاه مجرى النهر
الأضرار التي لحقت بحقول الجيران
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | زيادة أو نقصان | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة السنوية | زيادة | ليس جيدا |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث الجوية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| عاصفة ممطرة محلية | جيدا |
| عاصفة هوائية محلية | ليس جيدا |
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| جفاف | ليس جيدا |
الكوارث الهيدرولوجية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| فيضان عام (نهر) | جيدا |
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| انخفاض فترة النمو | جيدا |
التعليقات:
The use of irrigation has made the technology more sustainable and more tolerant to temperature changes and to droughts.
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
سلبي قليلا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
سلبي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
التعليقات:
In the short term the farmer doesn' have a lot of available firewood, timber or grass.
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
- > 50%
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بتحديد الكمية (عدد الأسر المعيشية و/أو المساحةالمغطاة):
80 household in an area of 1 km^2
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 91-100%
التعليقات:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
80 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Many other farmers planted trees on plots surrounding their own homes, these included poplar and willow trees. This saves a lot of time and money in collecting firewood from far away, and increases the asethics of their home environment.
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
| It gives the land user wood, grass, money, and a beautiful place for rest |
| The land user can graze his cows by rotation in this forest and has dairy production all year. |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
| The micro climate created by the forest increased plant and animal biodiversity. |
|
This technology also provides a provides increased economic benefits, such as firewood, timber, fodder grass, medicinal herbs etc. How can they be sustained / enhanced? It will be good to plant some perennial fodder grasses |
| Poplar and willow are the only trees which can grow in such extreme conditions in these highlands areas. They do need a good water supply hich can be provided by the rivers or by irrigation systems when planted next to houses. |
| The soil became more productive. Carbon sequestration is much higher when compared to the surrounding arid desert landscape. |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| No money available for fencing | If the forest is protected by fencing this will mean less work for the farmers in protecting the area of land from grazing and tree cutting. |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| No fencing in situ, maybe the farmer is not sure of the length of the land rental period. | If the forest is protected by fencing this will mean less work for the farmers in protecting the area of land from grazing and tree cutting. |
| The farmer could use stones to construct a fence which are plentiful in this area. |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
1. Справочник по климату СССР, вып. 31, Таджикская ССР, частьII. гидрометеорологическое издательство, Ленинград, 1966,228с.
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
in libraries
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
2. Справочник по климату СССР, вып. 31, Таджикская ССР, частьIV, гидрометеорологическое, Ленинград, 1966, 212с.
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية