Integrated Soil and Water Conservation Approach in Improving Biophysical Condition of Mt. Kitanglad Agri-Development Corporation (MKADC) Pineapple Production
(Philippines)
Description
Integration of soil and water conservation technologies primarily aim to protect the area from loss of biodiversity and land degradation.
Aims: (1) To improve biodiversity in the area; (2) To prevent on-site erosion; and (3) To minimize off-site impacts like siltation of natural water bodies.
MKADC is internationally renowned producer of export quality fresh pineapples. They cater different countries in Asia as a proof of their excellent service in pineapple production. Along with this success in MKADC, environmental management system is incorporated in their production area which gives additional merit in the protection of our ecology. This system includes various soil and water conservation technologies namely: 1) buffer zones; 2) sediment traps, brush dams and catch basins; 3) contour straight block lay-out technology; 4) natural vegetative strip; 5) pineapple as erosion control commodity; and 6) relay cropping which aim to minimize soil erosion and improve biodiversity in the area.
Stages of implementation: (a) Site development for 4 to 6 months; (b) Land preparation for 3 months; (c) Planting and replanting; (d) Plant care and crop management which include fertilization and weed control when the pineapple is at 2 to 11 months; (e) Flower induction, fruit development, fruit care and fruit estimates when pineapple is at 12 to 17 months; (f) Degreening and harvesting at 18 months; (g) Ratooning; and (h) Maintenance i.e manual weeding (as needs arises).
The primary stakeholders are the land owners of the leased lands and MKADC.The approach of MKADC ensures that at the end of the contract between the company and the land owners, the land is still productive.
Location
Location: Brgy. Lurugan, Valencia City, Bukidnon, Philippines
Geo-reference of selected sites
Initiation date: n.a.
Year of termination: n.a.
Type of Approach
-
traditional/ indigenous
-
recent local initiative/ innovative
-
project/ programme based

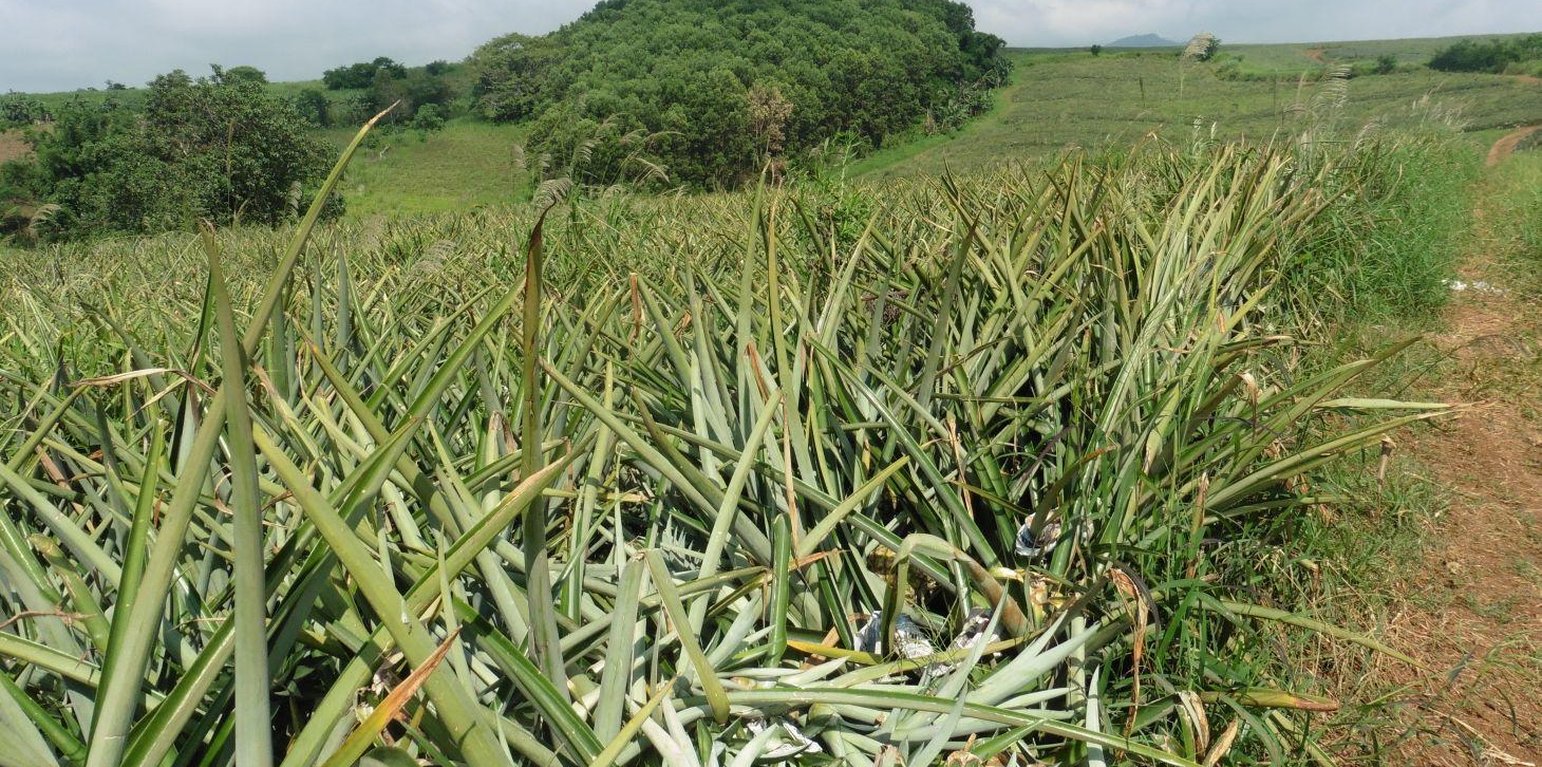
Pineapple plant serves as silt traps along trenches (Baldwin M. Pine, Bureau of Soils and Water Management)
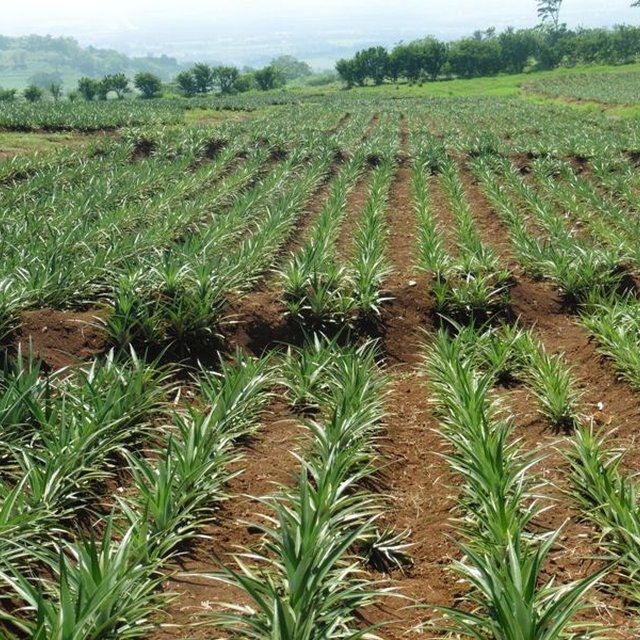

Pineapple plantation of MKADC (Engr. Djolly Ma. P. Dinamling (Bureau of Soils and Water Management))
Approach aims and enabling environment
Main aims / objectives of the approach
The main objectives of the approach are to prevent soil erosion and improve biodiversity.
Conditions enabling the implementation of the Technology/ ies applied under the Approach
-
Legal framework (land tenure, land and water use rights): Contract leasing minimum of ten years. After ten years and the owner wish to have its land back, the company is obliged to return the land to its original state/ or productivity. They conduct before and after fertility sampling to ensure the area is productive for cultivation.
-
Workload, availability of manpower: Compliment labor needs from field operations thru internal environmental management services. Filling up the labor requirement thru reassignment of regular labor from other areas.
-
Other: Fences were built along boundaries to prevent the entry of stray animals and assignment of watchmen in critical areas.
Conditions hindering the implementation of the Technology/ ies applied under the Approach
Participation and roles of stakeholders involved
Stakeholders involved in the Approach and their roles
| What stakeholders / implementing bodies were involved in the Approach? |
Specify stakeholders |
Describe roles of stakeholders |
| local land users/ local communities |
|
|
Involvement of local land users/ local communities in the different phases of the Approach
none
passive
external support
interactive
self-mobilization
initiation/ motivation
Sustainability of pineapple production inspite of identical issues on soil erosion, slope protection, and soil fertility loss.
planning
Yearly review and modification of farm field layout to correct deficiencies and to enhance control measures.
implementation
Integrated in the pineapple field production approaches.
monitoring/ evaluation
Internal audits / self-monitoring during high rainfall.
research
Benchmarking on new approaches to address identified issues.
Decision-making on the selection of SLM Technology
Decisions were taken by
-
land users alone (self-initiative)
-
mainly land users, supported by SLM specialists
-
all relevant actors, as part of a participatory approach
-
mainly SLM specialists, following consultation with land users
-
SLM specialists alone
-
politicians/ leaders
Decisions were made based on
-
evaluation of well-documented SLM knowledge (evidence-based decision-making)
-
research findings
-
personal experience and opinions (undocumented)
Technical support, capacity building, and knowledge management
The following activities or services have been part of the approach
-
Capacity building/ training
-
Advisory service
-
Institution strengthening (organizational development)
-
Monitoring and evaluation
-
Research
Capacity building/ training
Training was provided to the following stakeholders
-
land users
-
field staff/ advisers
Form of training
-
on-the-job
-
farmer-to-farmer
-
demonstration areas
-
public meetings
-
courses
Monitoring and evaluation
Research
Research treated the following topics
-
sociology
-
economics / marketing
-
ecology
-
technology
Collection of sediment/ silt from sediment traps and catch basins. Attempt to conduct research by third party, however cost constraints are foremost. In-house are conducted thru practical approaches and benchmarking.
Financing and external material support
Annual budget in USD for the SLM component
-
< 2,000
-
2,000-10,000
-
10,000-100,000
-
100,000-1,000,000
-
> 1,000,000
Precise annual budget: n.a.
MKADC (land owner,company) 100%
The following services or incentives have been provided to land users
-
Financial/ material support provided to land users
-
Subsidies for specific inputs
-
Credit
-
Other incentives or instruments
Impact analysis and concluding statements
Impacts of the Approach
No
Yes, little
Yes, moderately
Yes, greatly
Did the Approach help land users to implement and maintain SLM Technologies?
Retention of soil fertility since eroded soils are trapped in the catchment canals, embankments and other structures to prevent the further movement of the soil downstream.
Did the Approach empower socially and economically disadvantaged groups?
It provided additional source of income for laborers to support their families.
Did the Approach improve issues of land tenure/ user rights that hindered implementation of SLM Technologies?
The land used for the pineapple production are leased from private owners. If the owner decided not to renew the lease of contract then the company needs to revert back the state of the land before returning to the owner.For this, soil fertility analysis is being practiced.Water rights use is exclusive under National Irrigation Administration (NIA). Need for water are arrange thru fees.
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
Some private companies are starting to adopt the approach. Small-scale farmers nearby the plantation are also encouraged in establishing SWC structures but most of them did not adopt the technology as it lessened the production area and would entail additional cost for them.
Main motivation of land users to implement SLM
-
increased production
-
increased profit(ability), improved cost-benefit-ratio
-
reduced land degradation
-
reduced risk of disasters
-
reduced workload
-
payments/ subsidies
-
rules and regulations (fines)/ enforcement
-
prestige, social pressure/ social cohesion
-
affiliation to movement/ project/ group/ networks
-
environmental consciousness
-
customs and beliefs, morals
-
enhanced SLM knowledge and skills
-
aesthetic improvement
-
conflict mitigation
Sustainability of Approach activities
Can the land users sustain what hat been implemented through the Approach (without external support)?
The company has the financial capabilities to sustain the program since it is part of their workplan.
Conclusions and lessons learnt
Strengths: land user's view
-
Pineapple produced are exported in Japan, Korea, Middle East and China.
-
Physical environment is favorable for pineapple production.
Strengths: compiler’s or other key resource person’s view
-
Improves livelihood of farmers/ land-users without compromising the productivity of the land since it is ecologically viable.
-
Financial capabilities of the company to implement and sustain the program.
Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks: land user's viewhow to overcome
-
Physical destruction of field planted with trees providing additional environmental depletion by outside parties (eg. charcoal making, firewood, others).
Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks: compiler’s or other key resource person’s viewhow to overcome
-
High input and labour requirements.
References
Compiler
-
Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
Reviewer
-
Eduardo Alberto
-
Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Date of documentation: March 20, 2017
Last update: March 29, 2017
Resource persons
-
Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies (philcatsecretariat@gmail.com) - SLM specialist
-
Baldwin Pine (baldwinmp@gmail.com) - SLM specialist
-
Djolly Ma. P. Dinamling - SLM specialist
-
Teodoro M. Bersabe - SLM specialist
-
Gloria L. Betonio - SLM specialist
-
Jerry M. Manubag (manubagjerry@gmail.com) - SLM specialist
Full description in the WOCAT database
Documentation was faciliated by
Institution
- Department of Agriculture-Region VIII (DA-8) - Philippines
Project
- Decision Support for Mainstreaming and Scaling out Sustainable Land Management (GEF-FAO / DS-SLM)






