Push-Pull Integrated Pest and Soil Fertility Management [Kenya]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Unknown User
- Editor: –
- Reviewers: David Streiff, Julie Zähringer, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_958 - Kenya
- Full summary as PDF
- Full summary as PDF for print
- Full summary in the browser
- Full summary (unformatted)
- Push-Pull Integrated Pest and Soil Fertility Management: Dec. 22, 2016 (inactive)
- Push-Pull Integrated Pest and Soil Fertility Management: March 28, 2017 (inactive)
- Push-Pull Integrated Pest and Soil Fertility Management: May 12, 2017 (inactive)
- Push-Pull Integrated Pest and Soil Fertility Management: April 25, 2019 (public)
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
Key resource person(s)
SLM specialist:
Khan Zeyaur
International Centre of Insect Physiology & Ecology (ICIPE)
Kenya
SLM specialist:
Pittchar Jimmy
International Centre of Insect Physiology & Ecology (ICIPE)
Kenya
SLM specialist:
Wartmann Flurina
Biovision Foundation for ecological development
Switzerland
1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Yes
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
“Push-Pull” is a technology to efficiently control pests and progressively improves soil fertility.
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
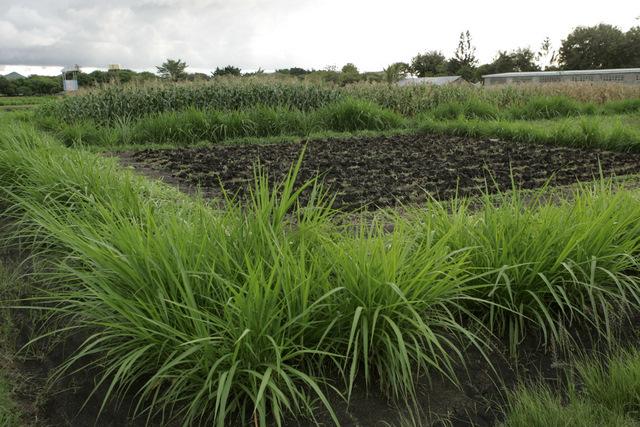
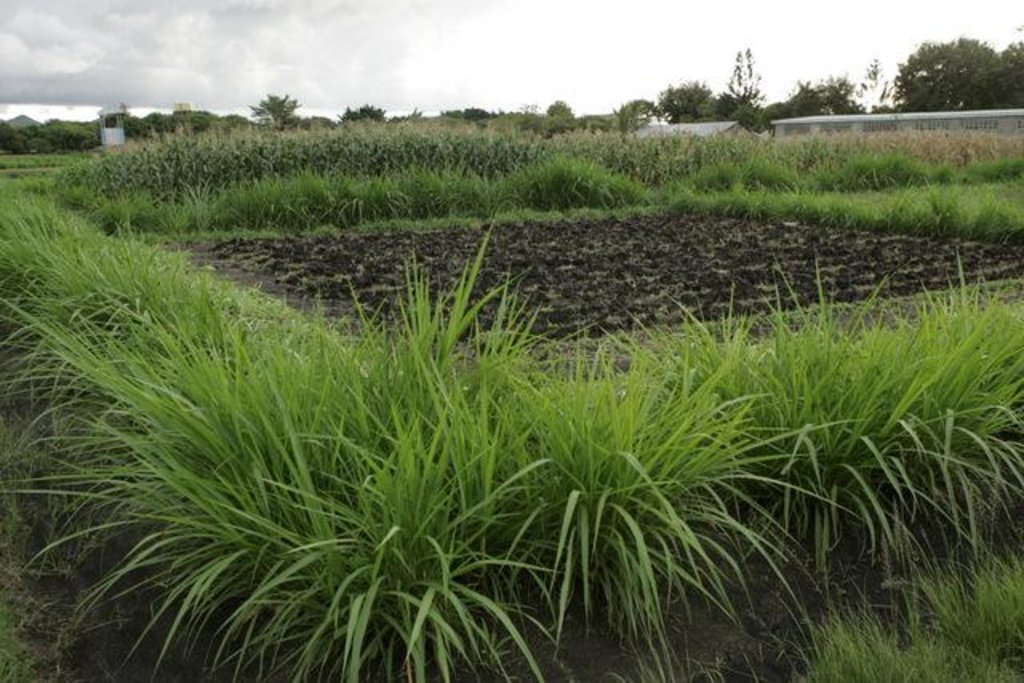
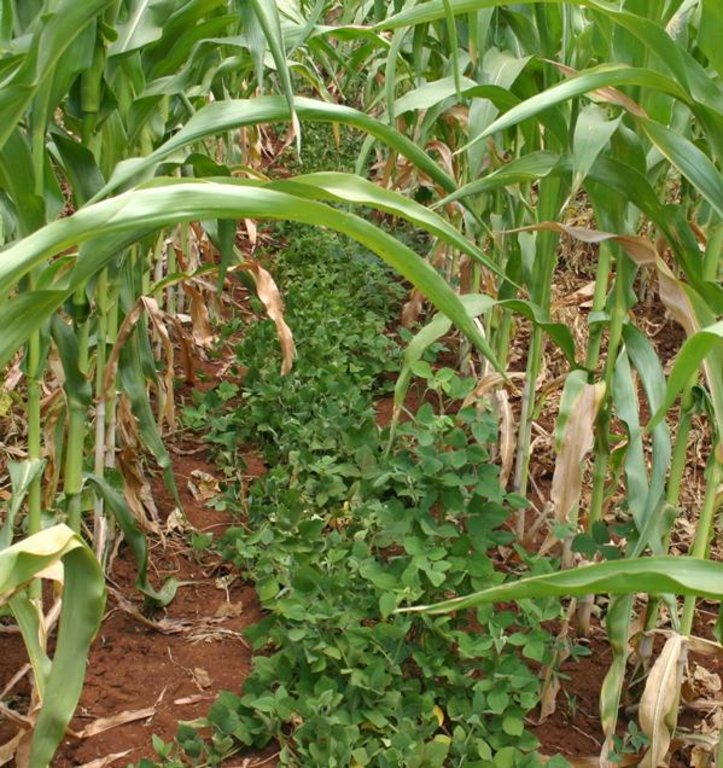
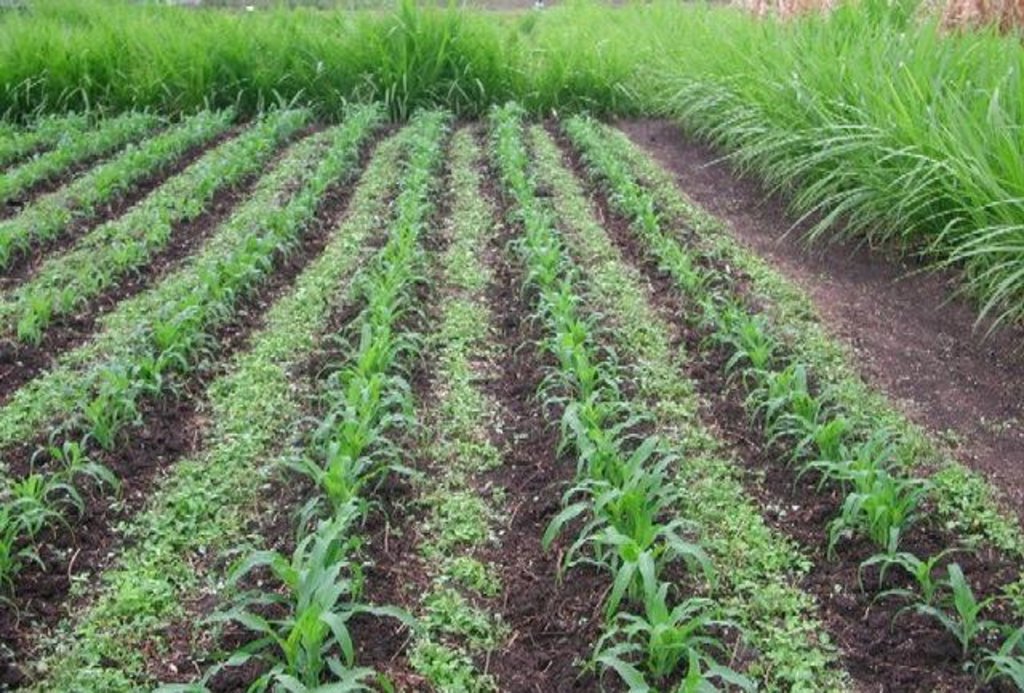
In the Lake Victoria region - like in many other parts of sub-Saharan Africa – stemborer pests, striga weeds and poor soil fertility are the main constraints to efficient production of cereals. In combination they often lead to complete crop failure. The “Push-Pull” technology efficiently controls the pests and progressively improves soil fertility. It involves intercropping maize with a repellent plant, such as desmodium (“push”); an attractant trap plant, such as napier grass (Pennisetum purpureum) is planted as a border crop around this intercrop (“pull”). The stemborer moths are attracted to volatile compounds emitted by the napier grass which at the same time serves as a haven for the borers' natural enemies. When moths lay eggs on napier grass a sticky substance secreted by the grass physically traps the moths’ larvae. Napier is also an important carbohydrate-rich fodder grass. Desmodium, a perennial cover crop, produces repellent volatile chemicals that push away the moths, and the plant effectively suppresses striga weeds through its root exudates. Furthermore, desmodium fixes nitrogen, conserves soil moisture, enhances arthropod abundance and diversity and improves soil organic matter, thereby making cereal cropping systems more resilient and adaptable to climate change. Being a low-growing plant it does not interfere with the crops' growth. Push-pull simultaneously improves cereal productivity; enables production of year-round quality fodder - thereby allowing for integration with livestock husbandry; diversifies income streams and enables smallholders to enter into the cash economy. It also improves soil fertility; protects fragile soils from erosion and enables a minimum tillage system. The technology is appropriate to resource-poor smallholder farmers as it is based on locally available plants, affordable external inputs, and fits well with traditional mixed cropping systems practiced in SSA.
2.3 Photos of the Technology
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
Kenya
Region/ State/ Province:
Lake Victoria region
Comments:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 76000 km2.
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
If precise year is not known, indicate approximate date:
- 10-50 years ago
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- during experiments/ research
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- adapt to climate change/ extremes and its impacts
- create beneficial economic impact
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied

Cropland
- Annual cropping
- Perennial (non-woody) cropping
Annual cropping - Specify crops:
- fodder crops - grasses
- cereals - maize
Perennial (non-woody) cropping - Specify crops:
- medicinal, aromatic, pesticidal plants - perennial
Is intercropping practiced?
Yes
Comments:
Main cash crop (CA): Maiz
Others (CP): Desmodium (fodder) and Pennisetum purpureum
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Cereal pests and diseases, decline of soil organic matter and fertility
3.4 Water supply
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- rainfed
3.5 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- integrated soil fertility management
- improved plant varieties/ animal breeds
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

agronomic measures
- A1: Vegetation/ soil cover

vegetative measures
- V2: Grasses and perennial herbaceous plants
Comments:
Main measures: vegetative measures
Type of agronomic measures: mixed cropping / intercropping, contour planting / strip cropping, retaining more vegetation cover
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -along boundary, aligned: -linear
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

chemical soil deterioration
- Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content (not caused by erosion)

biological degradation
- Bh: loss of habitats
- Bp: increase of pests/ diseases, loss of predators
Comments:
Main type of degradation addressed: Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, Bh: loss of habitats, Bp: increase of pests / diseases, loss of predators
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- prevent land degradation
- reduce land degradation
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
Technical specifications (related to technical drawing):
Layout of push-pull plot with1 m spacing between napier border and maize field
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder), pest control
Mixed cropping / intercropping
Material/ species: Desmodium as a perennial intercrop
Remarks: Desmodium is drilled in between maize rows at 75 cm row to row distance
Contour planting / strip cropping
Material/ species: napier grass (Pennisetum purpureum)
Remarks: Spacing of napier plants should be 75 cm between rows and 50 cm between plants within a row
Aligned: -along boundary
Vegetative material: G : grass
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 75.00
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 50.00
Aligned: -linear
Vegetative material: C : perennial crops
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 75.00
Perennial crops species: Desmodium
Grass species: Napier grass (Pennisetum purpureum)
Author:
ICIPE
4.2 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
Specify currency used for cost calculations:
- USD
Indicate average wage cost of hired labour per day:
1.2
4.3 Establishment activities
| Activity | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Plant 3 consecutive rows of napier grass (Bana variety) around the plot: make planting holes, apply fertilizer (or manure), place 3-node canes or root splits, cover with soil (before rains) | |
| 2. | Land preparation for desmodium: plough and harrow the land (to get fine soil), make furrows between the rows where the maize will be planted (using strong pointed stick; before rains) | |
| 3. | Mix desmodium seed with super phosphate fertilizer (ratio 1:2), or alternatively with fine soil. Sow into the furrows and cover with soil (onset of rains) | |
| 4. | Plant maize./ Weeding of maize, desmodium and Napier grass | 3 and 5-6 weeks after planting maize |
| 5. | Manage napier grass: 1st harvest after 3 months (plants are 1-1,5 m high), leave stem height of 10 cm for quick regrow, start with inner row | 1st harvest after 3 months |
4.4 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | Plant 3 consecutive rows of napier grass | Persons/day | 8.0 | 1.25 | 10.0 | |
| Plant material | Napier | pieces | 1200.0 | 0.1666666 | 200.0 | |
| Plant material | Desmodium seeds | kg | 0.5 | 18.9 | 9.45 | |
| Fertilizers and biocides | Fertilizer | kg | 47.0 | 0.6808 | 32.0 | |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 251.45 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 251.45 | |||||
4.5 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
| Activity | Timing/ frequency | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Land preparation for maize: carefully dig/plough between desmodium lines not to disturb / uproot the desmodium (it is a perennial crop!) | |
| 2. | Plant maize | |
| 3. | Trim the desmodium so that it does not overgrow in between the maize plants | after 3 and 6 weeks |
| 4. | Repeat activities 5.-7. listed under establishment |
4.6 Costs and inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | Land preparation for maize | Persons/day | 6.0 | 1.166666 | 7.0 | 100.0 |
| Fertilizers and biocides | Fertilizer for maiz | kg | 47.0 | 0.6808 | 32.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 39.0 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 39.0 | |||||
Comments:
Machinery/ tools: planting stick / hoe
Size of push-pull plot for the cost calculations above = 0.25 ha.
4.7 Most important factors affecting the costs
Describe the most determinate factors affecting the costs:
Input prices (in US$):
1 Person-day = 1.2 US$.
1 napier root split / cane = 0.14 US$.;
1 kg desmodium seeds = 18.9 US$.;
1 kg superphosphate fertilizer = 0.68US$
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Agro-climatic zone
- sub-humid
Thermal climate class: tropics
Mainly sub-humid; bi-modal rainfall pattern, with main rainy season March-May; short rainy season Oct.-Nov.
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
Comments and further specifications on topography:
Slopes on average: Also flat (0-2%)
Landforms: Also plateau / plains
Altitudinal zone: 1200-1250 m.a.s.l.
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- medium (loamy, silty)
- fine/ heavy (clay)
Topsoil organic matter:
- low (<1%)
If available, attach full soil description or specify the available information, e.g. soil type, soil PH/ acidity, Cation Exchange Capacity, nitrogen, salinity etc.
Soil texture: Also coasre/light but texture is mostly loamy clay, partly sandy
Soil fertility is low
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Market orientation of production system:
- subsistence (self-supply)
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
Relative level of wealth:
- very poor
- poor
Individuals or groups:
- individual/ household
Level of mechanization:
- manual work
- animal traction
Indicate other relevant characteristics of the land users:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly disadvantaged land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: some organized in informal groups
Population density: > 500 persons/km2
Market orientation of production system: commercialization is just starting
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
Is this considered small-, medium- or large-scale (referring to local context)?
- small-scale
Comments:
2ha, production area 0.9 ha
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- communal/ village
- individual, not titled
Comments:
Land ownership: state, communal / village, individual, not titled, individual, titled
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-economic impacts
Production
crop production
Comments/ specify:
Maize yields increase by 25-50% where stemborer is the only problem and by 300% in areas affected by stemborer and striga weed
fodder production
Comments/ specify:
All-year round quality fodder for cattle (napier grass and desmodium)
Income and costs
expenses on agricultural inputs
Comments/ specify:
Reduced fertilizer inputs thanks to nitrogen-fixing by desmodium
farm income
Comments/ specify:
Selling cereal grains, desmodium seed, napier grass (if not fed to own livestock), and milk
workload
Comments/ specify:
Weeding is minimized
Socio-cultural impacts
Social capital generated through common learning and implementing agricultural “best practices”
Ecological impacts
Soil
soil moisture
Comments/ specify:
Cover crop, live mulch
soil cover
Comments/ specify:
Cover crop, live mulch
soil loss
Comments/ specify:
Soil protected from erosion through desmodium (cover crop) and napier grass (barrier)
nutrient cycling/ recharge
soil organic matter/ below ground C
Climate and disaster risk reduction
wind velocity
Comments/ specify:
Reduced wind impacts due to napier barriers
6.3 Exposure and sensitivity of the Technology to gradual climate change and climate-related extremes/ disasters (as perceived by land users)
Comments:
Technology is tolerant to climatic extremes.
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
positive
Long-term returns:
very positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
positive
Long-term returns:
very positive
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 0-10%
Comments:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: To date it has been adopted by over 29,000 smallholder farmers in East Africa, mostly without incentives. Where the technology is being introduced for the first time, farmers only need demonstration and technology information
6.7 Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities of the Technology
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
| Improves cereal productivity |
| Enables production of year-round quality fodder - thereby allowing for integration with livestock husbandry |
| Diversifies income streams and enables smallholders to enter into the cash economy |
| Improves soil fertility; protects fragile soils from erosion and enables a minimum tillage system |
| The technology is appropriate to resource-poor smallholder farmers as it is based on locally available plants, affordable external inputs, and fits well with traditional mixed cropping systems practiced in SSA. |
6.8 Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks of the Technology and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the land user’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| Napier grass is an aggressive plant that spreads through rhizomes under the ground | regular control and weeding. |
| The older napier stems and leaves are less palatable for livestock | regularly cut young, tender leaves and stems. |
| Minor adjustment of the smallholder farming system to introduce desmodium in traditional maize-bean intercrops | desmodium (fodder crop) and beans (food crop, important protein source) can both be intercropped with maize. In areas where striga weed is not a problem, farmers can plant desmodium after every 3 or 5 rows of maize, and use the other rows for beans. Stemborers will still be repelled |
7. References and links
7.2 References to available publications
Title, author, year, ISBN:
Prof. Zeyaur R. Khan (Principal Scientist and Programme Leader) and Jimmy Pittchar, Push-pull Programme, International Centre of Insect Physiology & Ecology (ICIPE), Mbita Point, Kenya; zkhan@mbita.mimcom.net; jpittchar@mbita.mimcom.net; jpittchar@icipe.org
Title, author, year, ISBN:
Prof. Zeyaur R. Khan (Principal Scientist and Programme Leader) and Jimmy Pittchar, Push-pull Programme, International Centre of Insect Physiology & Ecology (ICIPE), Mbita Point, Kenya; zkhan@mbita.mimcom.net; jpittchar@mbita.mimcom.net; jpittchar@icipe.org
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks
No links
Modules
No modules