Water run-off control plan on cultivated land [South Africa]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Carin Pretorius
- Editor: –
- Reviewer: Alexandra Gavilano
Watercourses and contours
technologies_956 - South Africa
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
When were the data compiled (in the field)?
01/06/1999
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Yes
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
Artificially built watercourses with contour banks with a specific gradient
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
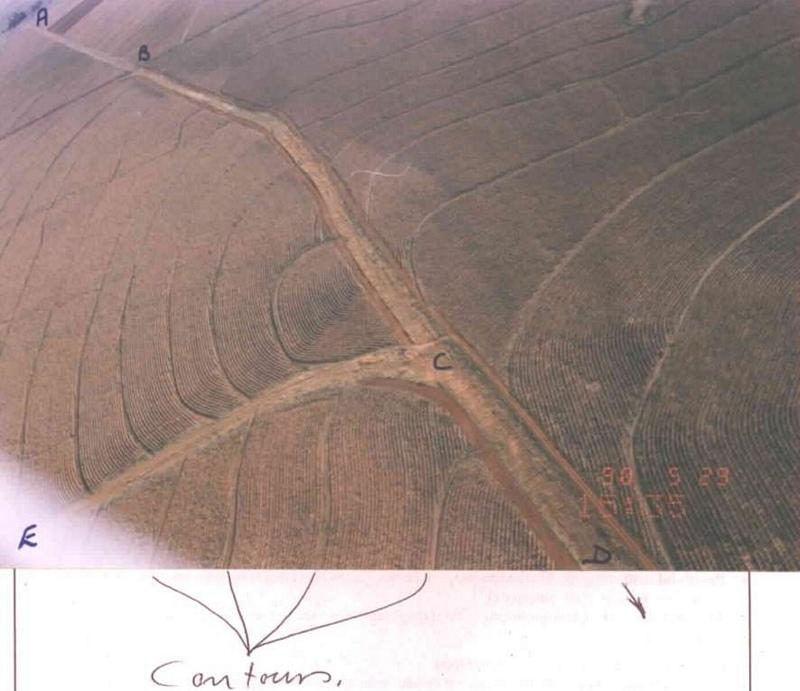
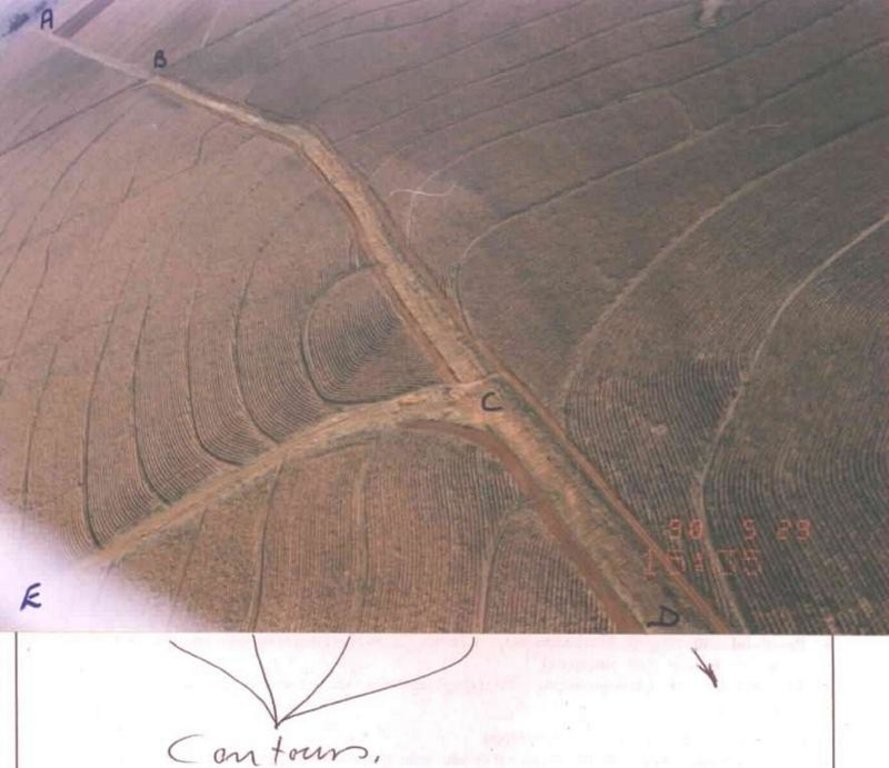
Watercourse: According to the topography, one or two watercourses are needed to drain any excess run-off water during high rainfall intensities. A watercourse is built directly downhill. A perennial grass adapted to the specific environment is established in the watercourses. Maintenance requires that the grass must be fertilised according to the climate of the area. Regular (once or twice a year) cutting of the grass is very important to maintain a good grass cover, through which soil erosion in the watercourse can be prevented.
Contour banks: These are built with a gradient to spill the excess water into the watercourse. The purpose of contour banks is to shorten the slope so as to reduce the speed of the water and prevent soil erosion. The maintenance requires keeping the canal in good shape and maintaining the height of the banks.
2.3 Photos of the Technology
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
South Africa
Region/ State/ Province:
North West Province
Further specification of location:
Lichtenburg
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
If precise year is not known, indicate approximate date:
- 10-50 years ago
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- through projects/ external interventions
Comments (type of project, etc.):
The contour part came mainly form the USA.
The watercourse part was developed in South Africa.
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied

Cropland
- Annual cropping
Comments:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Cultivating lands without the necessary soil conservation works to prevent soil erosion.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Cultivating the lands preventing soil erosion through plant directions
3.3 Further information about land use
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- rainfed
Number of growing seasons per year:
- 1
Specify:
Longest growing period in days: 180
Longest growing period from month to month: Oct - Mar
3.5 Spread of the Technology
Specify the spread of the Technology:
- evenly spread over an area
If the Technology is evenly spread over an area, indicate approximate area covered:
- 1-10 km2
Comments:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 3 m2.
Although the total extent of the farm is 584 ha, only 250 ha plus 50 ha adjacent land was addressed through this technology.
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

soil erosion by water
- Wg: gully erosion/ gullying
- Wt: loss of topsoil/ surface erosion

water degradation
- Ha: aridification

chemical soil deterioration
- Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content (not caused by erosion)
Comments:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Ha: aridification
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
Main causes of degradation: other human induced causes (specify) (Agricultural causes - Cultivating land on a step slope without proper conservation practices.), education, access to knowledge and support services (Lack of knowledge - How to solve the problem)
Secondary causes of degradation: other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (Topography; concentrating water in valleys causing soil erosion (steep slopes).), Poor conservation ethic
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- reduce land degradation
- prevent land degradation
Comments:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation, mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
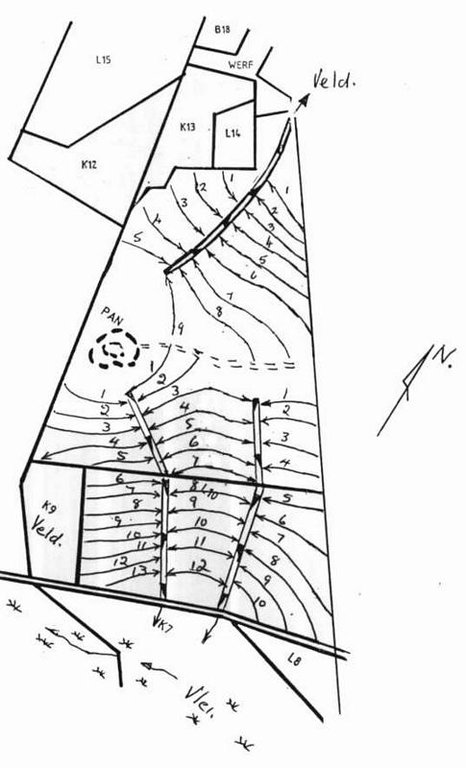
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
4.2 Technical specifications/ explanations of technical drawing
Water run-off control plan
Location: Lichtenburg. North West
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert, reduction of slope length
Secondary technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, Maintain soil fertility as less fertilizer are lost by water run-off
Vegetative measure: watercourses
Vegetative material: C : perennial crops, G : grass
Number of plants per (ha): seeds 6-8kg/ha
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: C : perennial crops, G : grass
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: C : perennial crops, G : grass
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: C : perennial crops, G : grass
Grass species: Digitaria Smuts, Eragrostis curvula, Cynodom dactylon
Structural measure: bunds/banks: contour
Vertical interval between structures (m): 1.3-1.75
Spacing between structures (m): 72-33
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.4
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 2
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.3
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 4
Construction material (earth): Construction contour banks with soil form the ditches
Lateral gradient along the structure: 0.3%
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
4.3 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
other/ national currency (specify):
rand
Indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (if relevant): 1 USD =:
6.00
4.4 Establishment activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Established grass in the watercourses | Vegetative | After construction according to design specifications |
| 2. | Surveying | Structural | Dry season |
| 3. | Construction of contours | Structural | Any time depending on soil moisture |
| 4. | Construction of watercourse | Structural | Before growing season |
4.5 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
Comments:
Duration of establishment phase: 24 month(s)
4.6 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing/ frequency | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Building contours and watercourses | Agronomic | Any time / Before planting of crops |
| 2. | Building contours and watercourses | Agronomic | Depending on soil moisture / |
| 3. | Maintenance | Agronomic | Before planting of crops / Annually |
| 4. | Cultivation between contours | Agronomic | Depending on the crop / Annually |
| 5. | Maintaining a good grass cover | Vegetative | Rainy season /Once or more times a year depending on the grass |
| 6. | Fertilisation of the grass in the watercourse | Vegetative | Rainy season /Once or twice in the rainy season |
| 7. | Watercourse, cutting the grass | Structural | Beginning of rainy season/Annual |
| 8. | Contours repairing flood damage | Structural | Dry season/After heavy rains |
| 9. | Contour opening ditches | Structural | Before planting of cops/Annual |
4.7 Costs and inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
Comments:
Machinery/ tools: Tractor & plough or a grader
Contours per kilometre. NB currant tariff for subsidy. Watercourse construction per volume soil moved and grass establishing per ha above the current tariff for subsidy from April 1998
4.8 Most important factors affecting the costs
Describe the most determinate factors affecting the costs:
Soil moisture and clay contents
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Agro-climatic zone
- semi-arid
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- medium (loamy, silty)
Topsoil organic matter:
- low (<1%)
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Market orientation of production system:
- commercial/ market
Off-farm income:
- less than 10% of all income
Relative level of wealth:
- average
Level of mechanization:
- mechanized/ motorized
Indicate other relevant characteristics of the land users:
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
10% of the land users are very rich and own 100% of the land.
90% of the land users are average wealthy and own 100% of the land (If management is good).
Off-farm income specification: Farmers are dedicated to make a living out of farming, although there are some farmers with an off-farm income such as transport.
5.7 Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- individual, titled
Land use rights:
- individual
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-economic impacts
Production
crop production
production area
land management
Socio-cultural impacts
conflict mitigation
Ecological impacts
Water cycle/ runoff
surface runoff
Quantity before SLM:
60
Quantity after SLM:
20
excess water drainage
Soil
soil moisture
soil loss
Quantity before SLM:
25
Quantity after SLM:
4
6.2 Off-site impacts the Technology has shown
downstream siltation
groundwater/ river pollution
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
neutral/ balanced
Long-term returns:
neutral/ balanced
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
neutral/ balanced
Long-term returns:
neutral/ balanced
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
Comments:
15% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: estimates
1% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: So little, almost none. The lack in technicians from government promoting this technology and to deliver technical services are the main reasons expect for the poor conservation ethic of the farmers.
6.7 Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities of the Technology
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the land user’s view |
|---|
|
Prevent soil erosion How can they be sustained / enhanced? Good regular maintenance |
| Building up a good layer of topsoil |
| Effective run-off control of excess rainwater |
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
|
Effective erosion control How can they be sustained / enhanced? Regular maintenance |
|
Improve water infiltration How can they be sustained / enhanced? Good cultivation practices and maintenance of contours |
|
Increase crop yield How can they be sustained / enhanced? Good cultivation practices and maintenance of contours |
|
Prevent off-site siltation How can they be sustained / enhanced? Good maintenance |
6.8 Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks of the Technology and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the land user’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| Hampers cultivation | Adapt change in cultivation practises |
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| Cannot think of any |
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks
No links
Modules
No modules