Non-inversion deep cultivation [Belgium]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Unknown User
- Editor: –
- Reviewer: David Streiff
Diepe, niet-kerende bodembewerking
technologies_967 - Belgium
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
Key resource person(s)
SLM specialist:
Gillijns Katleen
Catholic University of Leuven
Belgium
SLM specialist:
Govers Gerard
Catholic University of Leuven
Belgium
Name of project which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Soil and water protection (EU-SOWAP)Name of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Catholic University of Leuven (KU Leuven) - Belgium1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
When were the data compiled (in the field)?
08/11/2010
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Yes
1.5 Reference to Questionnaire(s) on SLM Approaches

Introduction of conservation agriculture in a highly mechanised … [Belgium]
Combination of 'dissemination of the SWC technology 'non-inversion tillage'' and research.
- Compiler: Unknown User
2. Description of the SLM Technology
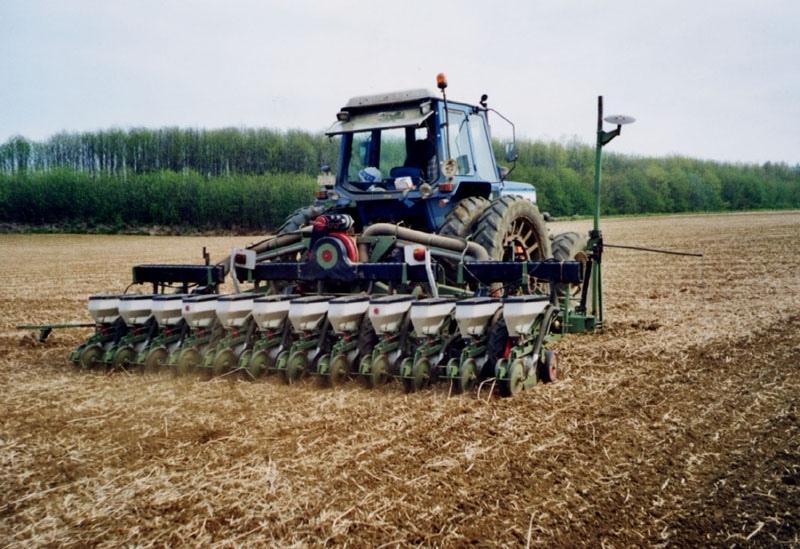
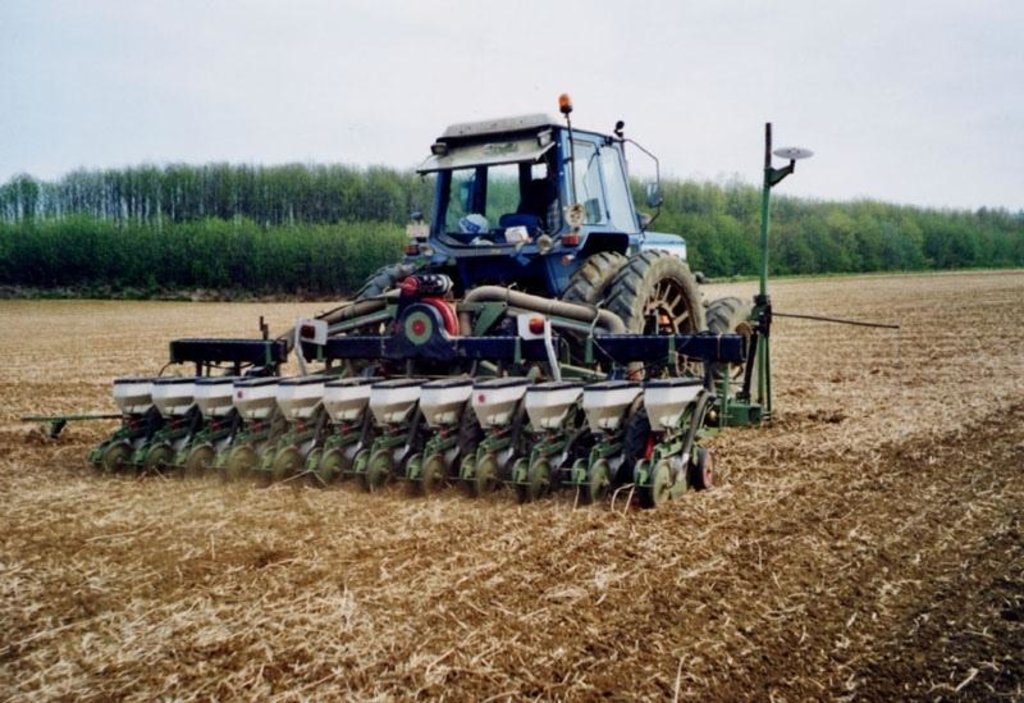
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
The technology consists of the use of cover crops and of a non-inversion seedbed preparation.
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
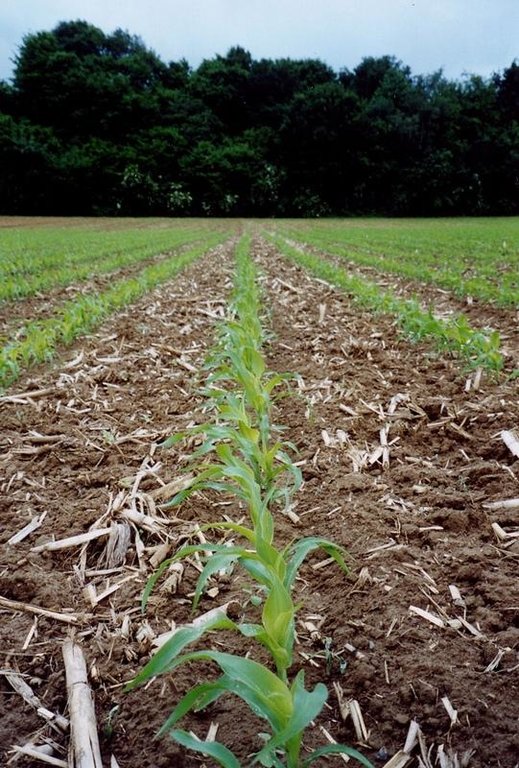
The technology consists of agronomic measures. The most important thing is that the farmers are not allowed to invert the soil by ploughing. Farmers may only cultivate their fields at plough depths. Farmers also have to use a cover crop, if possible. In this way the soil is always covered with residues of a previous crop or with residues of the cover crop. The improvement of the ground cover protects the soil against different kinds of water erosion. In the long term period, the soil structure will improve (more organic matter in top soil) and more earthworm activity will be determined. The infiltration will increase.
Purpose of the Technology: Protecting the soil against erosion and increasing infiltration.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The farmer may never plough.
Natural / human environment: The technology is applied on cropland with annual crops.
2.3 Photos of the Technology
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
Belgium
Region/ State/ Province:
Flanders
Further specification of location:
Vlaams-Brabant
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
If precise year is not known, indicate approximate date:
- less than 10 years ago (recently)
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- during experiments/ research
Comments (type of project, etc.):
In the Walloon part of Belgium and in the surrounding countries (France, Germany), farmers are already applying this technology for a long time. In Flanders, the technology was introduced in the 1970' by professor De Ploey of our Faculty. Farmers didn't see the benefits of the technology and decided not to implement the technology. Now, time has changed: farmers know that they have to do something against the erosion problem.
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- reduce, prevent, restore land degradation
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied

Cropland
- Annual cropping
Main crops (cash and food crops):
major cash crop: Sugar beet

Grazing land
Comments:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Soil loss by water erosion. Soil erosion related environmental problems 'muddy floods, retention pond sedimentation, declining water quality due to sediment and sediment - fixed contaminants)
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Strong nitrogen regulations and EU rules are hindering the farmer.
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: normal sequence of crops at the farm: sugar beet - wheat - potatoes - maize. Crop rotation at the experimental field: maize - wheat -sugar beet
3.3 Further information about land use
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- rainfed
Number of growing seasons per year:
- 1
Specify:
Longest growing period from month to month: Mar - Oct; Second longest growing period from month to month: Apr - Nov
3.4 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- improved ground/ vegetation cover
- minimal soil disturbance
3.5 Spread of the Technology
Specify the spread of the Technology:
- evenly spread over an area
Comments:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.0046 km2.
It's a field trial with 3 treatments. Every treatment is 4620 m² (see map). The 3 treatments are: non-inversion shallow cultivation, non inversion deep cultivation and conventional ploughing. In the region of this field, other farmers are also experimenting with the technology on their own fields.
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

agronomic measures
- A2: Organic matter/ soil fertility
- A3: Soil surface treatment
- A4: Subsurface treatment
Comments:
Type of agronomic measures: cover cropping, manure / compost / residues, mineral (inorganic) fertilizers, breaking compacted topsoil, minimum tillage
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

soil erosion by water
- Wt: loss of topsoil/ surface erosion
- Wg: gully erosion/ gullying
- Wo: offsite degradation effects

physical soil deterioration
- Pk: slaking and crusting
- Pi: soil sealing
Comments:
Main causes of degradation: other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (soil erosion), lack of knowledge
Secondary causes of degradation: other human induced causes (specify) (agricultural causes, hevay machinery)
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- prevent land degradation
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
4.2 Technical specifications/ explanations of technical drawing
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: high
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, increase of infiltration, improvement of soil structure
Secondary technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, increase in organic matter
Cover cropping
Material/ species: maize 2004
Agronomic measure: cover cropping
Material/ species: winter wheat 2004-2005
Agronomic measure: cover cropping
Material/ species: oats 2005-2006
Agronomic measure: removing less vegetation cover
Remarks: by not ploughing, every year.
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: injection of slurry 2004
Quantity/ density: 40000l/ha
Mineral (inorganic) fertilizers
Material/ species: spraying N with seed 2004
Quantity/ density: 200 kg/ha
Remarks: 26%
Agronomic measure: mineral (inorganic) fertilizers
Material/ species: spraying N 2005
Quantity/ density: 120 kg/ha
Remarks: 38%
Agronomic measure: mineral (inorganic) fertilizers
Material/ species: spraying N 2005
Quantity/ density: 175 kg/ha
Remarks: 39%
Agronomic measure: manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: broadcast N 2005
Quantity/ density: 45 kg/ha
Remarks: 27%
Agronomic measure: mineral (inorganic) fertilizers
Material/ species: 30 % K
Quantity/ density: 800 kg/ha
Breaking compacted topsoil
Remarks: every year
Minimum tillage
Remarks: every year
4.6 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing/ frequency | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | injection of slurry, spraying paraquat (to kill previous crop) | Agronomic | mar 04 |
| 2. | sowing maize, nitrogen fertiliser | Agronomic | apr 04 |
| 3. | herbicides | Agronomic | may 05 |
| 4. | harvesting maize, sowing winter wheat | Agronomic | nov 04 |
| 5. | nitrogen fertiliser | Agronomic | mar 05 / apr 05 |
4.7 Costs and inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
Comments:
Comparing to ordinary field operations, there are normally no additional costs if applying the new technique. The farmer will not plough anymore, this is an economic benefit. In some cases and for some crops the farmer will use another machine, for example: the farmer will need a direct drilling machine for sowing sugar beets in stead of a normal sowing machine. In Flanders, always agricultural contractors are sowing beets (not the farmers). The agricultural contractor will ask the same price for the normal sowing machine as for the direct drilling machine. Although farmers have no additional costs, they get subsidies (80€/ha.year for shallow cultivation, 200€/ha.year for no tillage) from the Flemish Government for practicing the new technique - subsidies are mainly given to encourage the farmers.
Additional info: herbicides - apr 05 / 2 herbicides - may 05 / 2 nitrogen fertiliser - jun 05 herbicides - jun 05 harvesting winter wheat - aug 05 fertiliser (manure) - sep 05 fertiliser K - sep 05 sowing oats - sep 05
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Specify average annual rainfall (if known), in mm:
780.10
Agro-climatic zone
- sub-humid
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
Comments and further specifications on topography:
Slopes on average: 10 %
Landforms: The main topographgy is a plateau (100 above sea level) in which rivers are incised. The technology is applied at fields situated on the slopes between the plateau and the valley.
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- medium (loamy, silty)
Topsoil organic matter:
- medium (1-3%)
If available, attach full soil description or specify the available information, e.g. soil type, soil PH/ acidity, Cation Exchange Capacity, nitrogen, salinity etc.
Soil depth on average: The loess deposits, which vary in thickness between a few dm to several m cover Terti
Soil texture (topsoil): 60 % loam, 30% sand and 10% clay.
Topsoil organic matter: 1,2% (experimental field)
Soil fertility is high
Soil drainage / infiltration
Soil water storage capacity is medium and sometimes very high
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Market orientation of production system:
- commercial/ market
Off-farm income:
- less than 10% of all income
Relative level of wealth:
- rich
Level of mechanization:
- mechanized/ motorized
Indicate other relevant characteristics of the land users:
Population density: 200-500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 0.5% - 1%
70% of the land users are rich and own 80% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: The farmer is only working at his own farm.
5.7 Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- individual, titled
Land use rights:
- individual
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-economic impacts
Income and costs
farm income
Comments/ specify:
Because of reduced working time and lower fuel consumption
Other socio-economic impacts
special equipement
Socio-cultural impacts
SLM/ land degradation knowledge
farmers opinion of a non-ploughed field
Ecological impacts
Water cycle/ runoff
surface runoff
Quantity before SLM:
34
Quantity after SLM:
18
Comments/ specify:
Also 21 before, 18 after
Soil
soil cover
Comments/ specify:
More residues
soil loss
Quantity before SLM:
28.26
Quantity after SLM:
1
Comments/ specify:
Significant reduction in soil loss
Other ecological impacts
biodiversity
Comments/ specify:
More earthworms
use of herbicides
6.2 Off-site impacts the Technology has shown
downstream flooding
Comments/ specify:
Because of less runoff
groundwater/ river pollution
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
slightly negative
Long-term returns:
very positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
very positive
Long-term returns:
very positive
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
- single cases/ experimental
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many have did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 90-100%
Comments:
Comments on acceptance with external material support: survey results
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
1 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: survey results
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Nowadays about 49% of the farmers in the region are practicing conservation tillage, whereas only 33% was doing it in 2001. At the beginning of the project 63% of the farmers intend to cultivate their fields in a conservative way into 3 years. (based on e
6.7 Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities of the Technology
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the land user’s view |
|---|
| less soil erosion |
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
| The technology clearly reduces the erosion risk while maintaining profitability. |
| The new technology also ha other benefits on soil structure and biodiversity. |
6.8 Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks of the Technology and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the land user’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| high investment costs for buying new agricultural machinery | |
| more attention to crop damages caused by slugs and mice should be given. | |
| practising the new technology requires a relative dry soil |
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| Practising the new technology requires a greater skill of the farmers | education, training |
7. References and links
7.2 References to available publications
Title, author, year, ISBN:
SOWAP Project. 2003-2006www. Sowap.org.
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks

Introduction of conservation agriculture in a highly mechanised … [Belgium]
Combination of 'dissemination of the SWC technology 'non-inversion tillage'' and research.
- Compiler: Unknown User
Modules
No modules