Non-inversion deep cultivation [比利时]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Unknown User
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: David Streiff
Diepe, niet-kerende bodembewerking
technologies_967 - 比利时
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
SLM专业人员:
Gillijns Katleen
Catholic University of Leuven
比利时
SLM专业人员:
Govers Gerard
Catholic University of Leuven
比利时
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Soil and water protection (EU-SOWAP)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Catholic University of Leuven (KU Leuven) - 比利时1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
08/11/2010
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.5 请参阅有关SLM方法的问卷

Introduction of conservation agriculture in a highly mechanised … [比利时]
Combination of 'dissemination of the SWC technology 'non-inversion tillage'' and research.
- 编制者: Unknown User
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
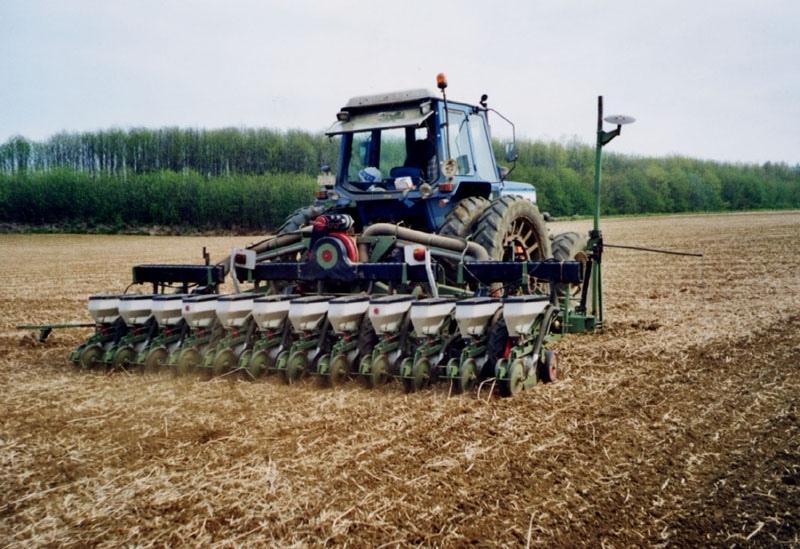
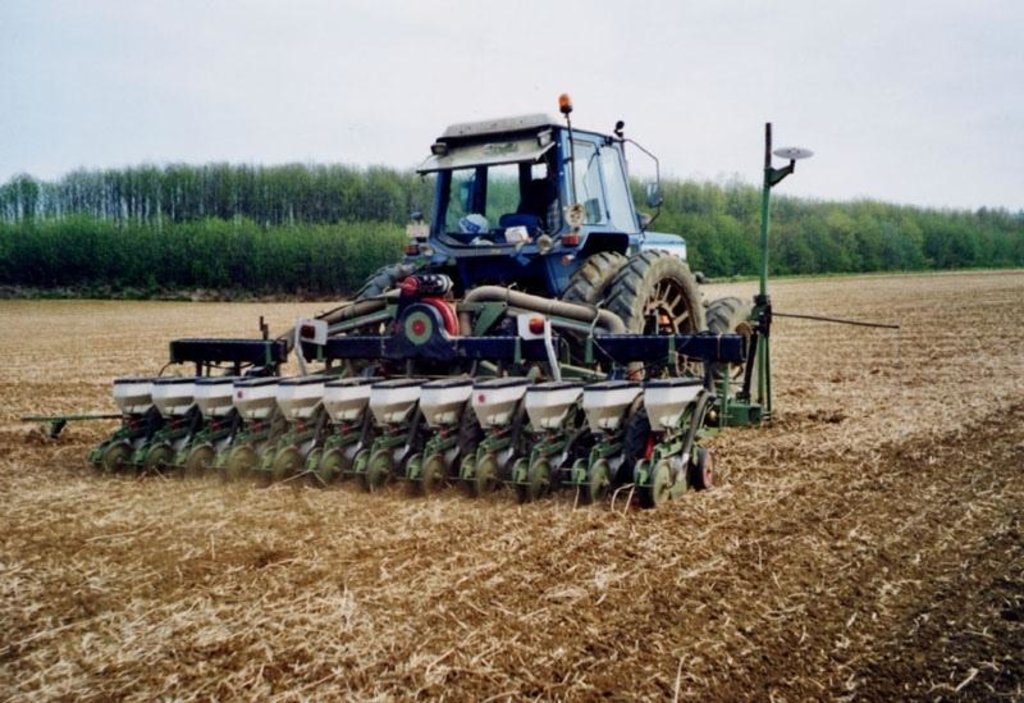
技术定义:
The technology consists of the use of cover crops and of a non-inversion seedbed preparation.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
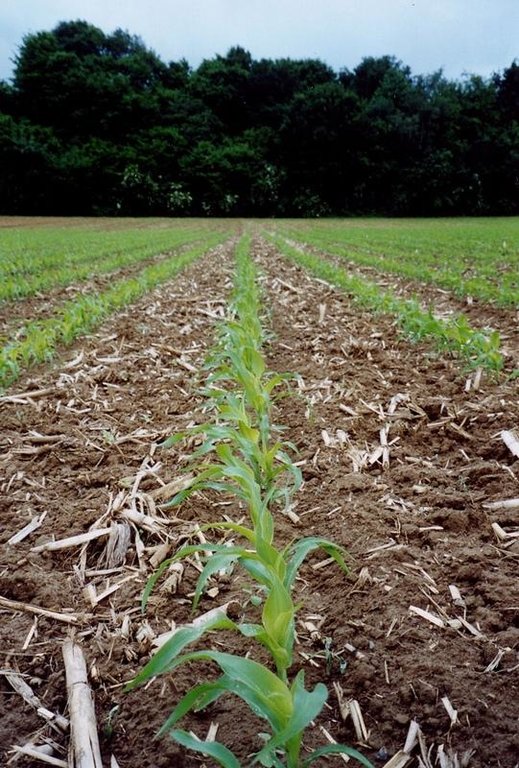
The technology consists of agronomic measures. The most important thing is that the farmers are not allowed to invert the soil by ploughing. Farmers may only cultivate their fields at plough depths. Farmers also have to use a cover crop, if possible. In this way the soil is always covered with residues of a previous crop or with residues of the cover crop. The improvement of the ground cover protects the soil against different kinds of water erosion. In the long term period, the soil structure will improve (more organic matter in top soil) and more earthworm activity will be determined. The infiltration will increase.
Purpose of the Technology: Protecting the soil against erosion and increasing infiltration.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The farmer may never plough.
Natural / human environment: The technology is applied on cropland with annual crops.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
比利时
区域/州/省:
Flanders
有关地点的进一步说明:
Vlaams-Brabant
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 在实验/研究期间
注释(项目类型等):
In the Walloon part of Belgium and in the surrounding countries (France, Germany), farmers are already applying this technology for a long time. In Flanders, the technology was introduced in the 1970' by professor De Ploey of our Faculty. Farmers didn't see the benefits of the technology and decided not to implement the technology. Now, time has changed: farmers know that they have to do something against the erosion problem.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
主要农作物(经济作物及粮食作物):
major cash crop: Sugar beet

牧场
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Soil loss by water erosion. Soil erosion related environmental problems 'muddy floods, retention pond sedimentation, declining water quality due to sediment and sediment - fixed contaminants)
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Strong nitrogen regulations and EU rules are hindering the farmer.
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: normal sequence of crops at the farm: sugar beet - wheat - potatoes - maize. Crop rotation at the experimental field: maize - wheat -sugar beet
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Longest growing period from month to month: Mar - Oct; Second longest growing period from month to month: Apr - Nov
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 改良的地面/植被覆盖
- 最小的土壤扰动
3.5 技术传播
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.0046 km2.
It's a field trial with 3 treatments. Every treatment is 4620 m² (see map). The 3 treatments are: non-inversion shallow cultivation, non inversion deep cultivation and conventional ploughing. In the region of this field, other farmers are also experimenting with the technology on their own fields.
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A2:有机质/土壤肥力
- A3:土壤表面处理
- A4:地表下处理
注释:
Type of agronomic measures: cover cropping, manure / compost / residues, mineral (inorganic) fertilizers, breaking compacted topsoil, minimum tillage
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wg:冲沟侵蚀/沟蚀
- Wo:场外劣化效应

物理性土壤退化
- Pk:熟化和结壳
- Pi:覆土
注释:
Main causes of degradation: other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (soil erosion), lack of knowledge
Secondary causes of degradation: other human induced causes (specify) (agricultural causes, hevay machinery)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: high
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, increase of infiltration, improvement of soil structure
Secondary technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, increase in organic matter
Cover cropping
Material/ species: maize 2004
Agronomic measure: cover cropping
Material/ species: winter wheat 2004-2005
Agronomic measure: cover cropping
Material/ species: oats 2005-2006
Agronomic measure: removing less vegetation cover
Remarks: by not ploughing, every year.
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: injection of slurry 2004
Quantity/ density: 40000l/ha
Mineral (inorganic) fertilizers
Material/ species: spraying N with seed 2004
Quantity/ density: 200 kg/ha
Remarks: 26%
Agronomic measure: mineral (inorganic) fertilizers
Material/ species: spraying N 2005
Quantity/ density: 120 kg/ha
Remarks: 38%
Agronomic measure: mineral (inorganic) fertilizers
Material/ species: spraying N 2005
Quantity/ density: 175 kg/ha
Remarks: 39%
Agronomic measure: manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: broadcast N 2005
Quantity/ density: 45 kg/ha
Remarks: 27%
Agronomic measure: mineral (inorganic) fertilizers
Material/ species: 30 % K
Quantity/ density: 800 kg/ha
Breaking compacted topsoil
Remarks: every year
Minimum tillage
Remarks: every year
4.6 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | injection of slurry, spraying paraquat (to kill previous crop) | 农业学的 | mar 04 |
| 2. | sowing maize, nitrogen fertiliser | 农业学的 | apr 04 |
| 3. | herbicides | 农业学的 | may 05 |
| 4. | harvesting maize, sowing winter wheat | 农业学的 | nov 04 |
| 5. | nitrogen fertiliser | 农业学的 | mar 05 / apr 05 |
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
注释:
Comparing to ordinary field operations, there are normally no additional costs if applying the new technique. The farmer will not plough anymore, this is an economic benefit. In some cases and for some crops the farmer will use another machine, for example: the farmer will need a direct drilling machine for sowing sugar beets in stead of a normal sowing machine. In Flanders, always agricultural contractors are sowing beets (not the farmers). The agricultural contractor will ask the same price for the normal sowing machine as for the direct drilling machine. Although farmers have no additional costs, they get subsidies (80€/ha.year for shallow cultivation, 200€/ha.year for no tillage) from the Flemish Government for practicing the new technique - subsidies are mainly given to encourage the farmers.
Additional info: herbicides - apr 05 / 2 herbicides - may 05 / 2 nitrogen fertiliser - jun 05 herbicides - jun 05 harvesting winter wheat - aug 05 fertiliser (manure) - sep 05 fertiliser K - sep 05 sowing oats - sep 05
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
780.10
农业气候带
- 半湿润
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Slopes on average: 10 %
Landforms: The main topographgy is a plateau (100 above sea level) in which rivers are incised. The technology is applied at fields situated on the slopes between the plateau and the valley.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil depth on average: The loess deposits, which vary in thickness between a few dm to several m cover Terti
Soil texture (topsoil): 60 % loam, 30% sand and 10% clay.
Topsoil organic matter: 1,2% (experimental field)
Soil fertility is high
Soil drainage / infiltration
Soil water storage capacity is medium and sometimes very high
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 商业/市场
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 丰富
机械化水平:
- 机械化/电动
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Population density: 200-500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 0.5% - 1%
70% of the land users are rich and own 80% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: The farmer is only working at his own farm.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
收入和成本
农业收入
注释/具体说明:
Because of reduced working time and lower fuel consumption
其它社会经济效应
special equipement
社会文化影响
SLM/土地退化知识
farmers opinion of a non-ploughed field
生态影响
水循环/径流
地表径流
SLM之前的数量:
34
SLM之后的数量:
18
注释/具体说明:
Also 21 before, 18 after
土壤
土壤覆盖层
注释/具体说明:
More residues
土壤流失
SLM之前的数量:
28.26
SLM之后的数量:
1
注释/具体说明:
Significant reduction in soil loss
其它生态影响
biodiversity
注释/具体说明:
More earthworms
use of herbicides
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
下游洪水
注释/具体说明:
Because of less runoff
地下水/河流污染
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
轻度消极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
非常积极
长期回报:
非常积极
6.5 技术采用
- 单例/实验
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发地采用该技术,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 90-100%
注释:
Comments on acceptance with external material support: survey results
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
1 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: survey results
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Nowadays about 49% of the farmers in the region are practicing conservation tillage, whereas only 33% was doing it in 2001. At the beginning of the project 63% of the farmers intend to cultivate their fields in a conservative way into 3 years. (based on e
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| less soil erosion |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| The technology clearly reduces the erosion risk while maintaining profitability. |
| The new technology also ha other benefits on soil structure and biodiversity. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| high investment costs for buying new agricultural machinery | |
| more attention to crop damages caused by slugs and mice should be given. | |
| practising the new technology requires a relative dry soil |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Practising the new technology requires a greater skill of the farmers | education, training |
7. 参考和链接
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
SOWAP Project. 2003-2006www. Sowap.org.
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Introduction of conservation agriculture in a highly mechanised … [比利时]
Combination of 'dissemination of the SWC technology 'non-inversion tillage'' and research.
- 编制者: Unknown User
模块
无模块