Shade-grown coffee [Costa Rica]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Olman Quiros Madrigal
- Editor: –
- Reviewers: Deborah Niggli, Alexandra Gavilano
Café arbolado (spanish)
technologies_1044 - Costa Rica
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
Name of project which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Book project: where the land is greener - Case Studies and Analysis of Soil and Water Conservation Initiatives Worldwide (where the land is greener)1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Yes
1.4 Declaration on sustainability of the described Technology
Is the Technology described here problematic with regard to land degradation, so that it cannot be declared a sustainable land management technology?
No
1.5 Reference to Questionnaire(s) on SLM Approaches (documented using WOCAT)

Agroforestry extension [Costa Rica]
Participatory extension of agroforestry systems, especially of shadegrown coffee, to promote sustainable and productive use of natural resources among small and medium scale farmers.
- Compiler: Olman Quiros Madrigal
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
An agroforestry system which combines coffee with shade trees - including fruit, timber and leguminous species - in a systematic fashion.
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
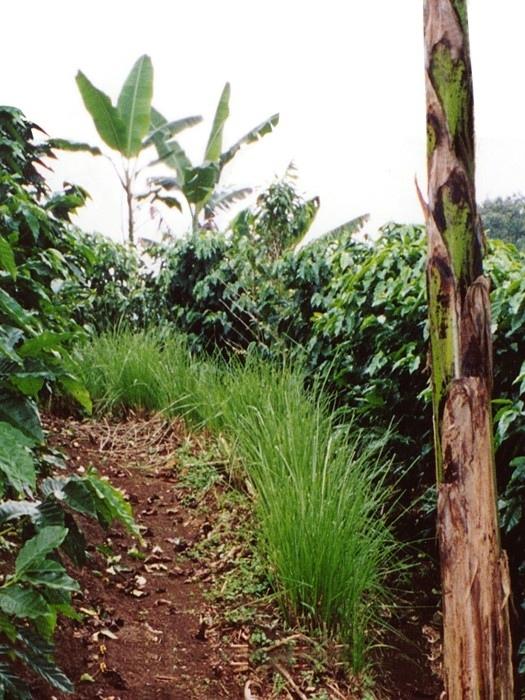
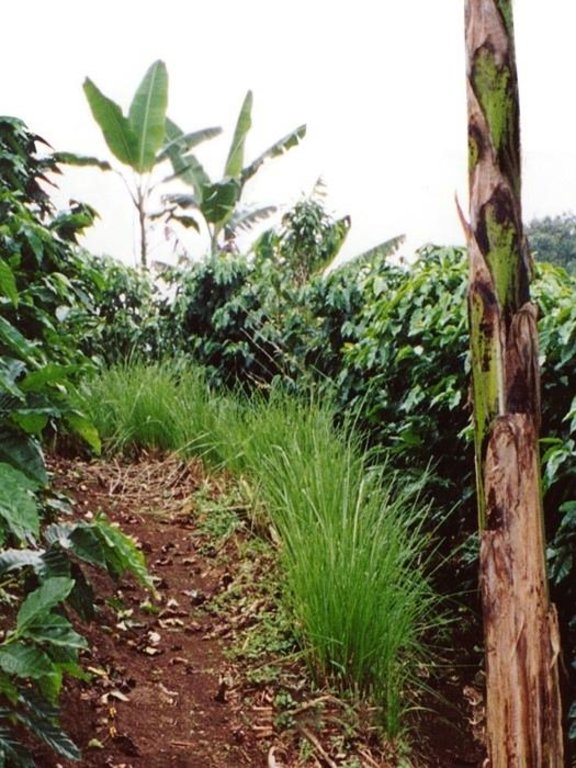
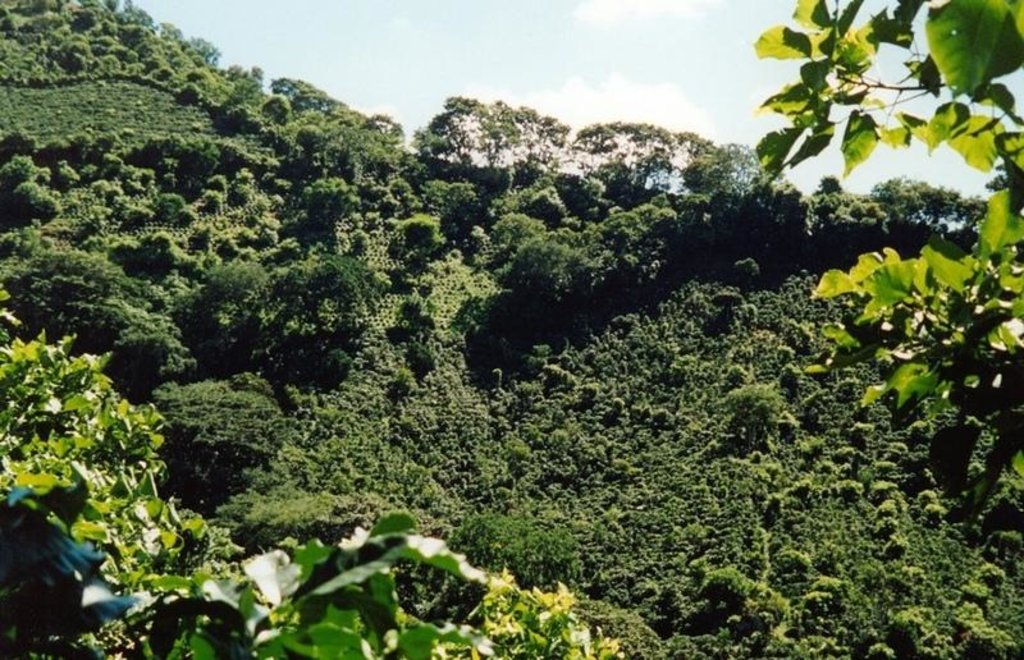
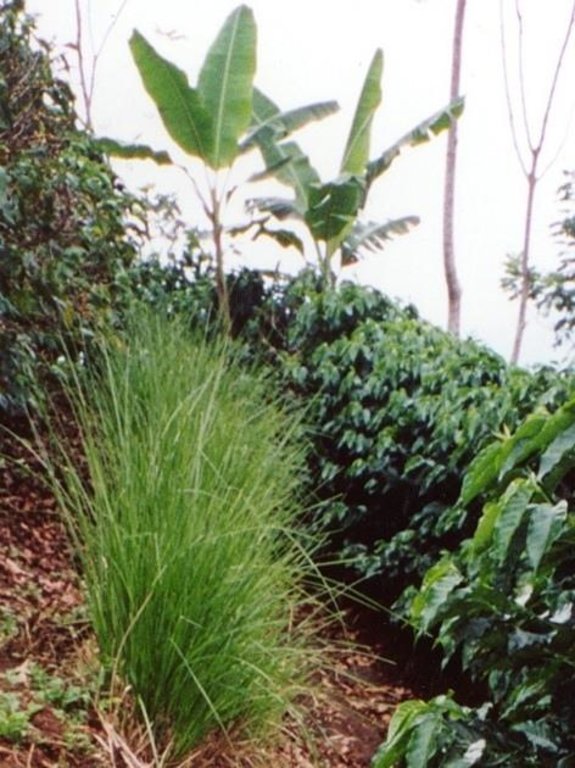
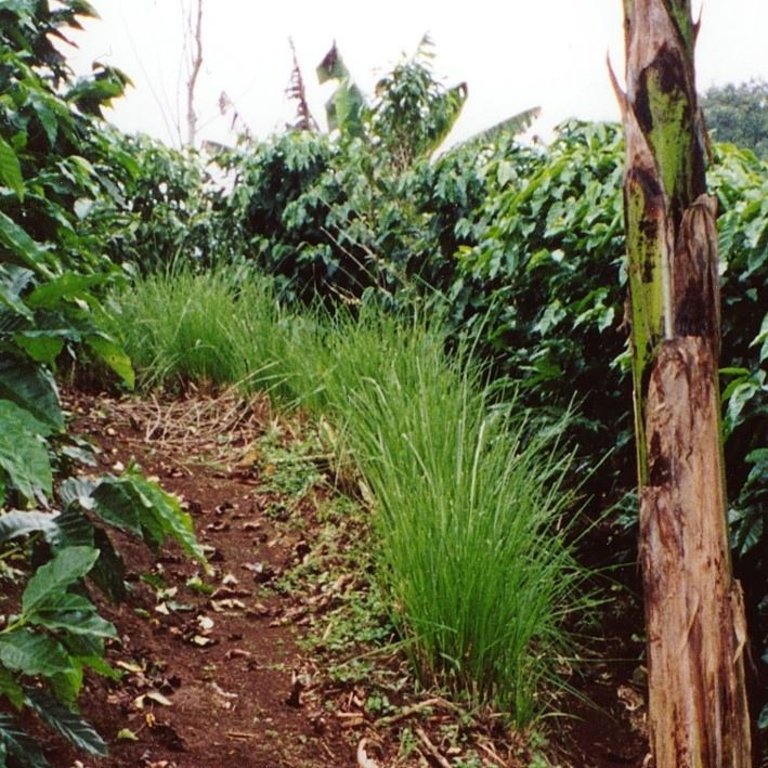
Shade-grown coffee is a traditional and complex agroforestry system where coffee is associated with various other species in different storeys (or ‘levels’). This provides ecologically and economically sustainable use of natural resources. Café arbolado, the example promoted by PRODAF (Programme for Agroforestry Development, see related approach: ‘Agroforestry Extension’) since 1987 is one technical option for shade-grown coffee.
While based on a traditional system the shade-grown coffee technology has a specific layout, and a reduced number of intercropped species. It comprises: (1) Coffee (Coffea arabica) planted on the contour at approximately 5,000 plants per hectare; (2) Associated trees: fruits, most commonly oranges (120 trees/ha), cedar (Cedrela odorata) or caoba (Swietenia macrophylla) for timber (60 trees/ha) and also two legumes, poró (Erythrina poeppigiana) and chalum (Inga sp.) which act as shade trees and at the same time improve the soil by fixing nitrogen (60 trees/ha). Farmers often include bananas in the system. In some cases, orange trees have partly been substituted by avocado (Persea americana), soursop (Anona muricata), and/or jocotes (Spondias purpurea). The latter two command good market prices and do not compete with labour needed for harvesting and other activities; (3) Supportive soil conservation measures on steep slopes to avoid soil erosion, predominantly strips of lemon grass (Cymbopogon citratus) on the contour, retention ditches and soil cover improvement; (4) Fertilizers: both organic and inorganic combined.
Full establishment of a shaded coffee plot can be achieved in two years - after replanting trees which fail to establish. Coffee yields a harvest after two years, but timber from associated trees can be expected after only 25 years. The trees grown in association allow more efficient cycling of nutrients (because of deep rooting and nitrogen fixation) and provide a favourable microclimate for coffee. This production system is well adapted to the local biophysical and socio-economic conditions, characterised by steep erosion-prone mountain slopes, humid climate and small to medium scale agriculture. Based on café arbolado a new, and further developed system of ‘sustainable coffee’ has evolved. This involves certification of the overall process and is attractive to the growing number of environmentally conscious consumers.
2.3 Photos of the Technology
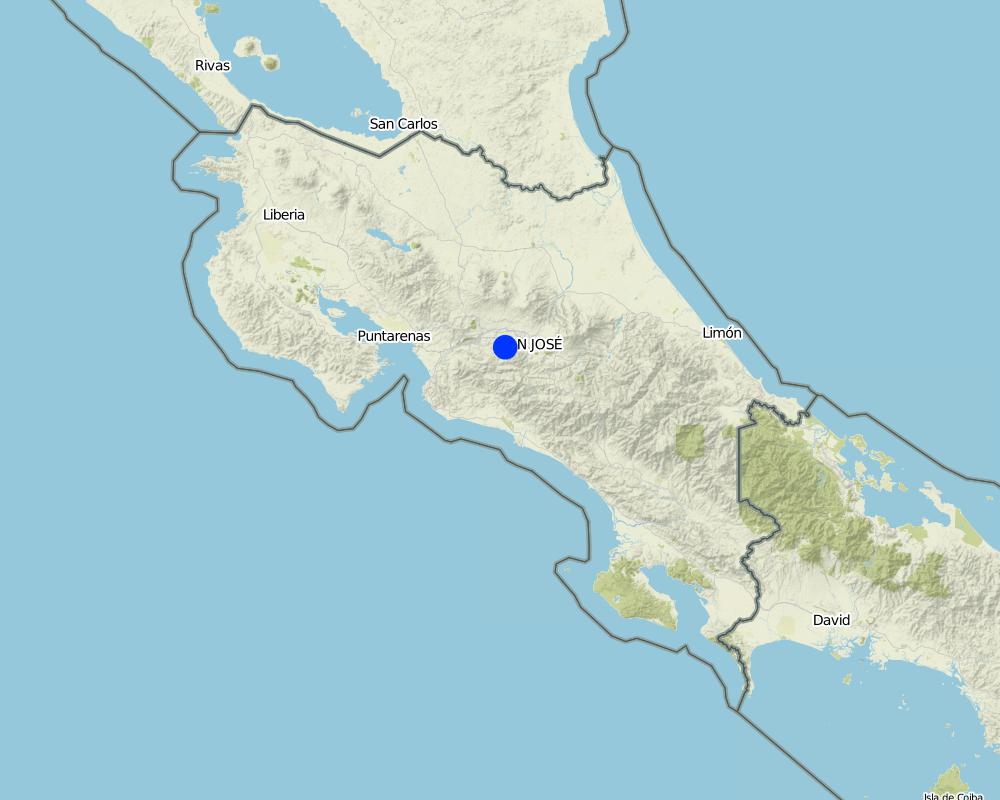
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
Costa Rica
Region/ State/ Province:
San José/Río Parrita
Further specification of location:
Acosta-Puriscal
Specify the spread of the Technology:
- evenly spread over an area
If the Technology is evenly spread over an area, specify area covered (in km2):
400.0
Comments:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 400 km2.
Map
×2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- through projects/ external interventions
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- improve production
- reduce, prevent, restore land degradation
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
Yes
Specify mixed land use (crops/ grazing/ trees):
- Agroforestry

Cropland
- Annual cropping
- Perennial (non-woody) cropping
- Tree and shrub cropping
Annual cropping - Specify crops:
- fodder crops - grasses
- chalum, poró, cedar, caoba, soursop
Perennial (non-woody) cropping - Specify crops:
- banana/plantain/abaca
Tree and shrub cropping - Specify crops:
- cashew
- avocado
- coffee, shade grown
- citrus
Specify:
Longest growing period in days: 270, Longest growing period from month to month: Apr - Dec
Is intercropping practiced?
Yes

Forest/ woodlands
Type of tree:
- Swietenia macrophylla
Products and services:
- Timber
Comments:
(1) Coffee (Coffea arabica) planted on the contour at approximately 5,000 plants per hectare; (2) Associated trees: fruits, most commonly oranges (120 trees/ha), cedar (Cedrela odorata) or caoba (Swietenia macrophylla) for timber (60 trees/ha) and also two legumes, poró (Erythrina poeppigiana) and chalum (Inga sp.) which act as shade trees and at the same time improve the soil by fixing nitrogen (60 trees/ha). Farmers often include bananas in the system. In some cases, orange trees have partly been substituted by avocado (Persea americana), soursop (Anona muricata), and/or jocotes (Spondias purpurea)
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Severe deforestation, inappropriate land management practices (monocultures on steep slopes; lack of conservation measures); resulting in physical (soil erosion) and chemical (fertility decline) degradation of agricultural soils, low productivity and low yields.
3.4 Water supply
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- rainfed
3.5 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- agroforestry
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

agronomic measures
- A1: Vegetation/ soil cover

vegetative measures
- V1: Tree and shrub cover
- V2: Grasses and perennial herbaceous plants
Comments:
Type of agronomic measures: mixed cropping / intercropping
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -contour
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

soil erosion by water
- Wt: loss of topsoil/ surface erosion
- Wm: mass movements/ landslides

chemical soil deterioration
- Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content (not caused by erosion)
Comments:
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use, overgrazing, education, access to knowledge and support services (Falta de conocimientos), Falta de tecnología
Secondary causes of degradation: poverty / wealth (Falta de capital), Falta de fortaleza de legislación / de autoridad
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- prevent land degradation
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
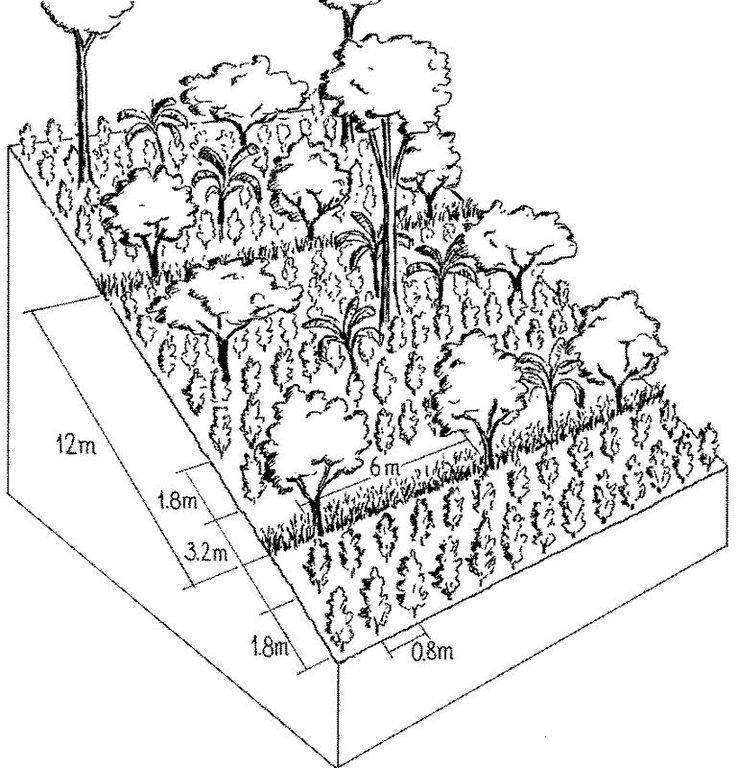
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
Technical specifications (related to technical drawing):
Example layout of coffee grown below shade trees: various species are used for shade, and each has intrinsic value of its own - orange trees (for fruit) are associated with strips of lemon grass, tall cedars (for timber) are planted in rows alternating with Erythrina sp. (for fertility improvement). Optionally, banana trees are interplanted.
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: high
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, increase in organic matter, increase of infiltration, increase in soil fertility
Secondary technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of concentrated runoff, control of dispersed runoff
Agronomic measure: organic/chem. Fertilization
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 60-120
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 12
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 6
Vegetative measure: grass strips
Vegetative material: G : grass
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 12
Vegetative measure: aligned shrubs
Vegetative material: G : grass
Number of plants per (ha): 5000
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1.8
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.8
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: G : grass
Trees/ shrubs species: poró (Erythrina poeppigiana), chalum (Inga spp.)
Fruit trees / shrubs species: Coffee, oranges, cedar or caoba for timber, bananas, oranges or avocado, soursop , and/or jocotes
Grass species: lemon grass (Cymbopogon citratus)
Structural measure: retention ditches (supp.)
Author:
Mats Gurtner
4.3 Establishment activities
| Activity | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Clearing of land. | beginning of rainy season (March/April) |
| 2. | Surveying for contour planting of coffee, grass strips, trees etc. | beginning of rainy season (March/April) |
| 3. | Digging holes, fertilizer application. | beginning of rainy season (March/April) |
| 4. | Planting coffee, trees, grass barriers etc along the contour. | beginning of rainy season (March/April) |
| 5. | Replanting coffee that fails to establish in first year. | beginning of rainy season (March/April) |
4.4 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | labour | ha | 1.0 | 700.0 | 700.0 | 100.0 |
| Plant material | Seedlings: poró/cedar | ha | 1.0 | 15.0 | 15.0 | |
| Plant material | Seedlings: orange trees | ha | 1.0 | 220.0 | 220.0 | |
| Plant material | Seedlings: coffee | ha | 1.0 | 1240.0 | 1240.0 | |
| Fertilizers and biocides | fertilizer | ha | 1.0 | 350.0 | 350.0 | |
| Other | transport | ha | 1.0 | 10.0 | 10.0 | |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 2535.0 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 2535.0 | |||||
Comments:
Duration of establishment phase: 24 month(s)
4.5 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
| Activity | Timing/ frequency | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Fertilization | May, July, November / 1–3 times |
| 2. | Pest control (spraying) | May, September / 1–2 times |
| 3. | Application of lime. | |
| 4. | Pest control (spraying) | May, September / 1–2 times |
| 5. | Application of lime. | |
| 6. | Weed control | Weed control |
| 7. | Pruning coffee | February or March / |
| 8. | Pruning shade trees. |
4.6 Costs and inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | labour | ha | 1.0 | 28.0 | 28.0 | 100.0 |
| Fertilizers and biocides | fertilizer | ha | 1.0 | 175.0 | 175.0 | 100.0 |
| Other | transport | ha | 1.0 | 127.0 | 127.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 330.0 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 330.0 | |||||
Comments:
Machinery/ tools: shovel, machete, knapsack
The costs of planting coffee are included. Shade-grown coffee is an integrated production system, and thus costs for coffee and the agroforestry component cannot be disaggregated.
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Agro-climatic zone
- humid
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- medium (loamy, silty)
- fine/ heavy (clay)
Topsoil organic matter:
- high (>3%)
- medium (1-3%)
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Market orientation of production system:
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
Off-farm income:
- 10-50% of all income
Level of mechanization:
- manual work
Indicate other relevant characteristics of the land users:
Off-farm income specification: subdivision of land (through inheritance), improved communications linking the capital with rural areas, and a better system of education all provide for increased off-farm income earning opportunities
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- individual, not titled
- individual, titled
Land use rights:
- individual
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-economic impacts
Production
crop production
Comments/ specify:
coffee, about 10% less than in conventional systems (per ha per year)
wood production
Income and costs
workload
Socio-cultural impacts
national institutions
Ecological impacts
Soil
soil moisture
soil cover
soil loss
Climate and disaster risk reduction
wind velocity
6.2 Off-site impacts the Technology has shown
downstream flooding
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
negative
Long-term returns:
positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
positive
Long-term returns:
very positive
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
Comments:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology. There is a slight trend towards growing spontaneous adoption - after the end of the programme. However, the crisis triggered by the big drop in coffee prices has had a negative impact on adoption of the technology. Many coffee farms have been abandoned specially those located under 800-900 m a.s.l. where coffee is of a lower quality due to climatic conditions.
6.7 Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities of the Technology
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
| Increased overall crop production and diversity: coffee, fruit, timber, legumes |
| Different crops harvested at different periods, gives better distribution of labour (and income) throughout the year; participation of all family members; increased food security and minimal economic risk |
| Improved profitability. |
| More efficient use of nutrients, nitrogen fixation, lower inputs of fertilizers. |
| Increased pest resistance, lower external inputs of biocides. Coffe plants continue to produce over 25 years due to optimal microclimate (only 15 years in conventional system without trees). Production system adapted to steep erosion prone slopes, thus a productive alternative to simple afforestation. Not labour-intensive compared with structural measures of SWC. High commercial potential of environmentally friendly produced coffee due to new market trends. Price increase for agricultural inputs has favoured a shift from conventional to shade-grown coffee, the latter being a system with a higher ratio of applied inputs/harvested yields although total production is usually lower than in modern coffee plantations. |
6.8 Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks of the Technology and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| Slight decrease in production of coffee per hectare compared to the conventional pure stand | Compensate by additional benefits: wood production, fruit, etc. |
| Short-term negative cost-benefit ratio in the first 4–5 years: Costintensive technology in the establishment phase. | Identify fast growing species or species providing intermediate products. |
| Timber harvest only in the long term (after 25 years) |
7. References and links
7.1 Methods/ sources of information
- field visits, field surveys
- interviews with land users
When were the data compiled (in the field)?
01/08/2001
7.2 References to available publications
Title, author, year, ISBN:
PRODAF . Sistema agroforestal – Café arbolado, Ecología y economía para el progreso, Puriscal, Costa Rica. 1994.
Title, author, year, ISBN:
Neuenschwander E . Agorforstwirtschaftlicher Kaffeeanbau als Lösungsansatz für eine ökologisch nachhaltige Bodennutzung der Hanglagen inCosta Rica: eine Fallstudie im Rahmen des WOCAT Programms, unpublished MSc thesis. 2002.
Available from where? Costs?
Science Faculty, University of Berne, Centre for Developmentand Environment
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks

Agroforestry extension [Costa Rica]
Participatory extension of agroforestry systems, especially of shadegrown coffee, to promote sustainable and productive use of natural resources among small and medium scale farmers.
- Compiler: Olman Quiros Madrigal
Modules
No modules