Assisted natural regeneration [Niger]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Dieter Nill
- Editor: –
- Reviewers: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Régénération naturelle assistée (French)
technologies_1626 - Niger
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
SLM specialist:
Dorlöchter-Sulser Sabine
Misereor
Germany
SLM specialist:
Mamadou Abdou Gaoh Sani
Programme d’Appui à l’agriculture Productive
Niger
Name of project which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Programme d’Appui à l’agriculture Productive (GIZ / PROMAP)Name of project which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Good Practices in Soil and Water Conservation - A contribution to adaptation and farmers ́ resilience towards climate change in the Sahel (GIZ)Name of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH (GIZ) - GermanyName of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Misereor - Germany1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Yes
1.5 Reference to Questionnaire(s) on SLM Approaches (documented using WOCAT)
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
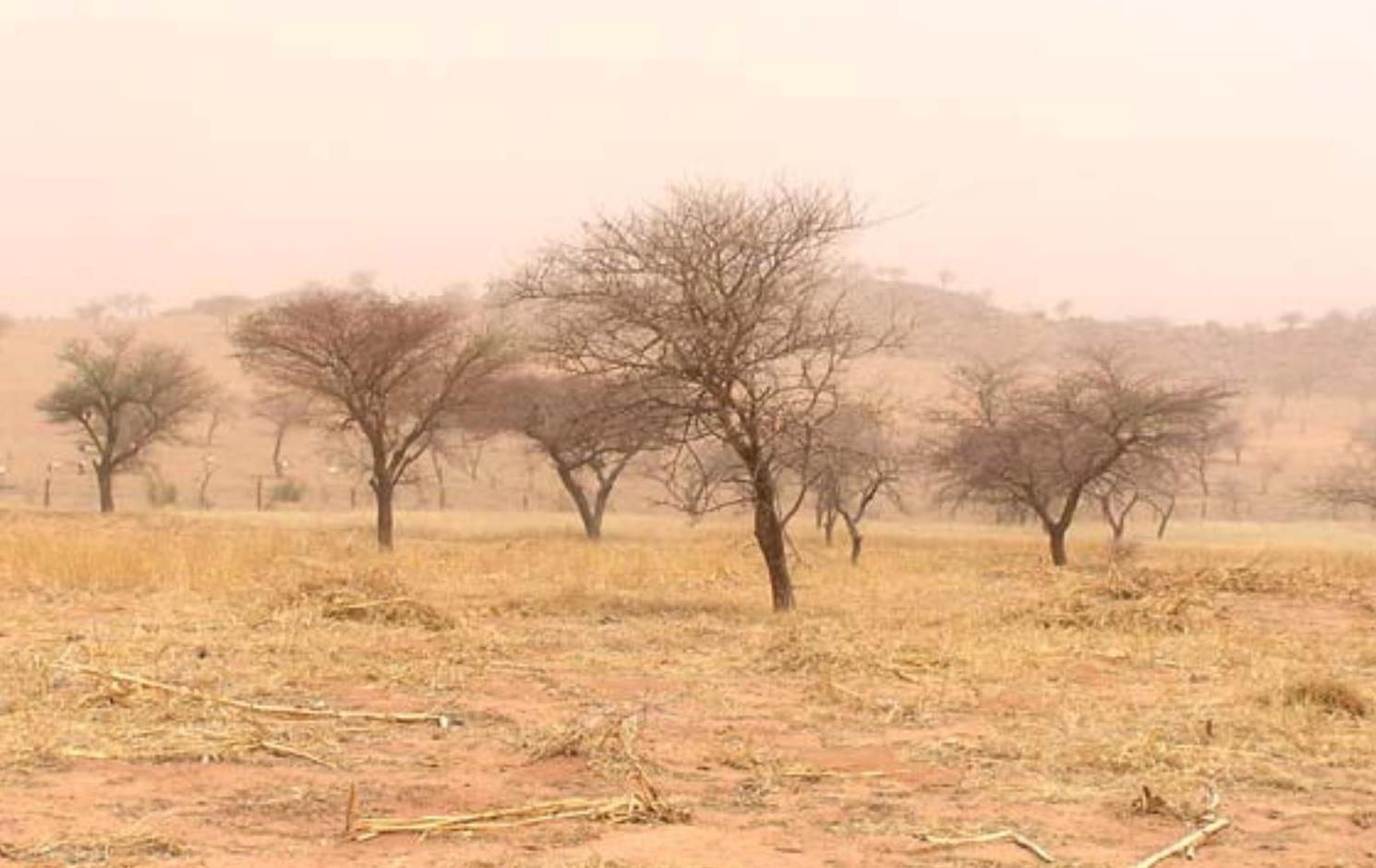
Assisted natural regeneration (ANR) is an agroforestry technique, which consists in protecting and preserving tree seedlings growing naturally on cropland or forest/rangeland.
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
It involves selecting which natural tree seedlings to leave and placing a stake next to them to identify them. The recommended density on cropland is between 60 and 80 trees per hectare. ANR is carried out mainly on individual plots where monitoring and upkeep are easier.
Purpose of the Technology: Tree roots and fallen leaves help to stabilise the soil and thereby reduce water erosion. Some tree species have a fertilising effect on the soil. Legume species (for example, Faidherbia albida) enrich the soil with nitrogen. Other species circulate nutrients from the subsoil into the topsoil thanks to leaf fall. The shade provided by trees lowers soil temperature and reduces the evapotranspiration and thus water stress of plants. They also act as a windbreak and provide protection against wind erosion.
The environmental effect of ANR depends to a large extent on tree density. The reintegration of trees and shrubs into any ecosystem has positive ecological effects and improves and protects the soil. The vegetation provides shelter and forage for animals and contributes to biodiversity. Trees have positive effects on crop yields, when they do not compete with the crops for water. They also provide products and byproducts, such as wood, fruits, leaves, forage, ingredients for medicinal products, etc. Faidherbia albida, for example, has no leaves in the rainy season, which is beneficial for crops. In the dry season, it is green and provides sheltered places for animals to rest. Leaves that fall from this type of tree fertilise the soil. The wood, leaves, pods and fruits provided by trees in crop fields help the owners to meet their family’s needs during the lean season.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: In order to implement this technique, there must be a very clear legal framework governing land tenure.
In order to ensure the success of this measure, it is important to protect the tree seedlings and saplings from browsing animals during the first few years. The young trees are pruned regularly to stimulate growth, so that they quickly achieve the height required to make them safe from browsing animals. The choice of tree species depends on the intentions of the farmers (browse for animals, sale of fruits or byproducts such as shea butter, dawa-dawa, medicinal products, etc.). The technique requires no investment, apart from the work involved, and can be implemented by any land owner.
Natural / human environment: The Sahel is a region where the population has always faced a high degree of climate variability, manifested both in terms of time (unexpected dry spells can occur during the rainy season) and in terms of space (rainfall can vary greatly from one area to another). The population is mainly composed of small farmers and livestock keepers.
Over the last two decades, the effects of climate change have exacerbated the already difficult conditions. Accord¬ing to projections made by climatologists, the Sahel will experience a rise in temperatures combined with highly variable rainfall and an increase in extreme weather events.
The Soil and Water conservation and rehabilitation techniques have helped people in the Sahel to manage their ecosystems more effectively and improve their productive land. As a result, communities are better prepared to cope with environmental changes (changes in the climate, land degradation, etc.) and the im¬pact of shocks, particularly droughts.
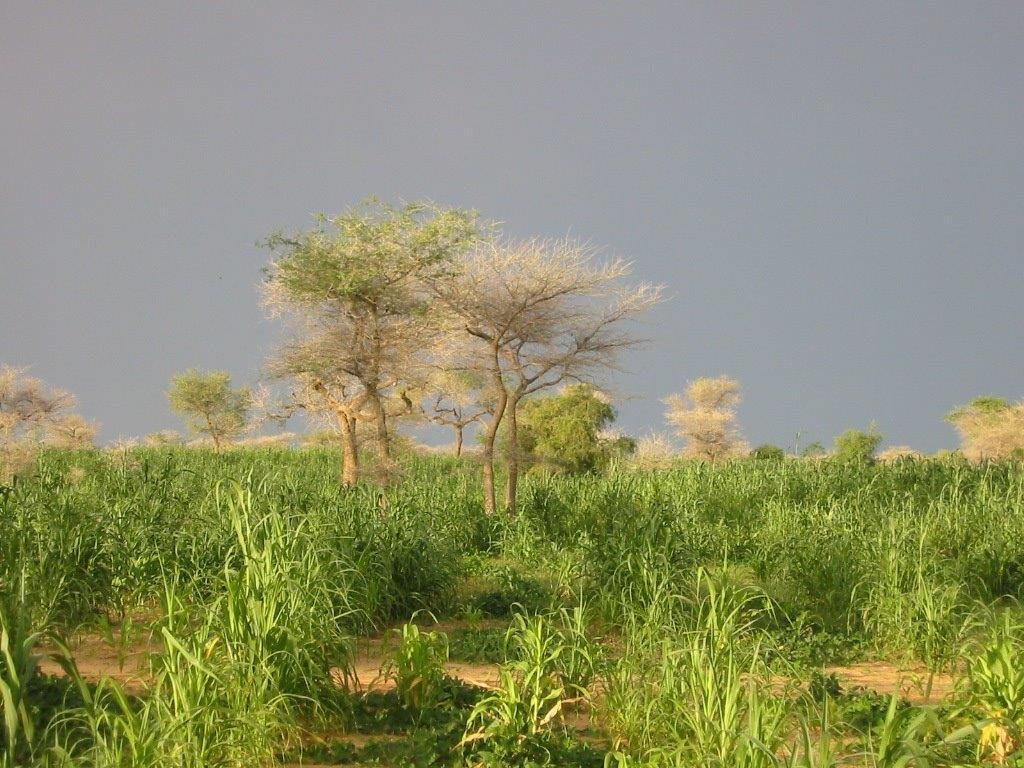
2.3 Photos of the Technology
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
Niger
Region/ State/ Province:
Niger
Further specification of location:
Regions of Tillabéri, Filingué, Ouallam, Téra and Tahuoa
Specify the spread of the Technology:
- evenly spread over an area
If precise area is not known, indicate approximate area covered:
- 1,000-10,000 km2
Comments:
Assisted Regeneration has been applied in farmers' fields in combination with stone bunds and planting holes (tassa).
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
If precise year is not known, indicate approximate date:
- 10-50 years ago
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- through projects/ external interventions
Comments (type of project, etc.):
Developed, implemented and disseminated as part of projects and programmes undertaken from the 1980s onwards to combat desertification and improve natural resource management. Implemented by German Development Cooperation (GIZ/KfW): PDRT (Projet de développement rural de Tahoua - Tahoua Rural Development Project), PASP (Projet de protection intégrée des ressources agro-sylvo-pastorales Tillabéri-Nord - Project for the Integrated Protection of Agricultural, Forest and Rangeland Resources in Tillabéri-Nord)
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- reduce, prevent, restore land degradation
- preserve/ improve biodiversity
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
Yes
Specify mixed land use (crops/ grazing/ trees):
- Agro-silvopastoralism

Cropland
- Annual cropping
- Tree and shrub cropping
Annual cropping - Specify crops:
- oilseed crops - groundnuts
- cereals - millet
- cereals - sorghum
- legumes and pulses - peas
Tree and shrub cropping - Specify crops:
- mango, mangosteen, guava
Number of growing seasons per year:
- 1
Specify:
Longest growing period in days: 120; Longest growing period from month to month: August to October

Grazing land
Extensive grazing:
- Nomadism
- Semi-nomadic pastoralism
Intensive grazing/ fodder production:
- Cut-and-carry/ zero grazing
- Improved pastures

Forest/ woodlands
- (Semi-)natural forests/ woodlands
(Semi-)natural forests/ woodlands: Specify management type:
- Selective felling
Products and services:
- Timber
- Fuelwood
- Fruits and nuts
- Other forest products
- Grazing/ browsing
Comments:
major cash crop: Ground nut
major food crop: Millet
other: Sorghum, cow pea and mangoes
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): water and wind erosion, fertility decline
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): increasing pressure on land, mostly small farmers, traditional land rights, fields are individually managed, grazing land are commons
Nomadism: Yes
Semi-nomadism / pastoralism: Yes
Cut-and-carry/ zero grazing: Yes
Improved pasture: Yes
Other grazingland: agropastoralism
Selective felling of (semi-) natural forests: Yes
Forest products and services: timber, fuelwood, fruits and nuts, grazing / browsing, other forest products / uses (honey, medical, etc.)
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Mixed: Mf: Agroforestry
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: farmers are mainly agropastoralists with some communities specialised on pure pastoralism
Constraints of common grazing land
Constraints of forested government-owned land or commons
Livestock density: 1-10 LU /km2
3.3 Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
- Yes (Please fill out the questions below with regard to the land use before implementation of the Technology)

Cropland
- Annual cropping
3.4 Water supply
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- rainfed
Comments:
Water supply: Also mixed rainfed - irrigated and post-flooding
3.5 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- natural and semi-natural forest management
- agroforestry
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

agronomic measures
- A1: Vegetation/ soil cover

vegetative measures
- V1: Tree and shrub cover
Comments:
Type of vegetative measures: scattered / dispersed
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

soil erosion by water
- Wt: loss of topsoil/ surface erosion

soil erosion by wind
- Et: loss of topsoil

chemical soil deterioration
- Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content (not caused by erosion)

biological degradation
- Bc: reduction of vegetation cover
Comments:
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Unadapted landuse methods, reduced or abandoned fallow periods), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Neglect of crop rotation, clearing of trees in fields), droughts (severe droughts of the 70ies and 80ies), population pressure (rapidly growing population increasing pressure on land), land tenure (insecure access to land and collectively managed communal land), poverty / wealth (very poor population), governance / institutional (no clear landuse regulation on common lands)
Secondary causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (deforestation through overgrazing and fire wood collection), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (firewood collection), overgrazing (cattle, sheep and goats), change in temperature (Climate change: heat waves), change of seasonal rainfall (more variable onset of rain), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (more variable and intensive rains), wind storms / dust storms (frequent storms), floods (due to intensive rain storms), education, access to knowledge and support services (high level of illiteracy)
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- prevent land degradation
- reduce land degradation
Comments:
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
Technical specifications (related to technical drawing):
Not applicable
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, improvement of ground cover, stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), reduction in wind speed, increase of biomass (quantity), promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Secondary technical functions: improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), increase in organic matter, increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 60-80
Trees/ shrubs species: e.g. Faidherbia albida
4.2 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
Specify currency used for cost calculations:
- USD
4.3 Establishment activities
| Activity | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | selecting which natural tree seedlings to leave: the choice of tree species depends on the intentions of the farmers (browse for animals, sale of fruits or byproducts such as shea butter, dawa-dawa, medicinal products, etc.). |
4.5 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
| Activity | Timing/ frequency | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | protect the tree seedlings and saplings from browsing animals during the first few years | |
| 2. | The young trees are pruned regularly |
4.7 Most important factors affecting the costs
Describe the most determinate factors affecting the costs:
Labour: 5 man-days per ha.
• Cost of awareness raising, training and dissemination.
• Shears for pruning.
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Agro-climatic zone
- semi-arid
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
Comments and further specifications on topography:
Landforms: Foot slopes and valley floors
Altitudinal zone: 200 m a.s.l.
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- medium (loamy, silty)
- fine/ heavy (clay)
Topsoil organic matter:
- low (<1%)
If available, attach full soil description or specify the available information, e.g. soil type, soil PH/ acidity, Cation Exchange Capacity, nitrogen, salinity etc.
Soil texture (topsoil): Fine to medium (sandy to clayey loams)
Soil fertility is very low - medium
5.4 Water availability and quality
Ground water table:
5-50 m
Availability of surface water:
medium
Water quality (untreated):
for agricultural use only (irrigation)
Comments and further specifications on water quality and quantity:
Ground water table: > 10 m
Availability of surface water: Surface runoff generated by limited but intense rainfalls
5.5 Biodiversity
Species diversity:
- low
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Off-farm income:
- 10-50% of all income
Relative level of wealth:
- very poor
- poor
Level of mechanization:
- manual work
- animal traction
Gender:
- men
Indicate other relevant characteristics of the land users:
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 3% - 4%
(mostly poor households below poverty line).
Off-farm income specification: men migrate temporarily or permanently to cities for off-farm income, women and men seasonally carry out paid farm work
Market orientation of production system: Most households crop for subsistence (mainly for small agropastoralists) and surplus is sold on market (medium agropastoralists). Commercial markets: Some vegetable growing and pastoralists.
Level of mechanization: Ox and donkey used for animal traction
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
Is this considered small-, medium- or large-scale (referring to local context)?
- small-scale
Comments:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology: Also 1-2 ha
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- state
- communal/ village
Land use rights:
- communal (organized)
- individual
Comments:
traditional land use rights prevail. On fields individual land use rights, communal rights on pasture and forest land (collection of wood and other products (fruits, medicinal plants))
Land ownership: Also individual, not titled
5.9 Access to services and infrastructure
health:
- poor
- moderate
- good
education:
- poor
- moderate
- good
technical assistance:
- poor
- moderate
- good
employment (e.g. off-farm):
- poor
- moderate
- good
markets:
- poor
- moderate
- good
energy:
- poor
- moderate
- good
roads and transport:
- poor
- moderate
- good
drinking water and sanitation:
- poor
- moderate
- good
financial services:
- poor
- moderate
- good
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-economic impacts
Production
crop production
fodder production
animal production
wood production
risk of production failure
product diversity
Socio-cultural impacts
food security/ self-sufficiency
SLM/ land degradation knowledge
conflict mitigation
livelihood and human well-being
Comments/ specify:
The wood, leaves, pods and fruits provided by trees in crop fields help the owners to meet their family’s needs during the lean season. The trees help to improve soil fertility and protect against erosion
Ecological impacts
Water cycle/ runoff
harvesting/ collection of water
surface runoff
evaporation
Soil
soil moisture
soil cover
soil loss
nutrient cycling/ recharge
soil organic matter/ below ground C
Biodiversity: vegetation, animals
plant diversity
beneficial species
Climate and disaster risk reduction
wind velocity
Other ecological impacts
competition with crops for water
stray animals often wipe out ANR efforts
6.2 Off-site impacts the Technology has shown
damage on neighbours' fields
6.3 Exposure and sensitivity of the Technology to gradual climate change and climate-related extremes/ disasters (as perceived by land users)
Gradual climate change
Gradual climate change
| Season | increase or decrease | How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| annual temperature | increase | well |
Climate-related extremes (disasters)
Meteorological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| local rainstorm | well |
| local windstorm | well |
Climatological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| drought | well |
Hydrological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| general (river) flood | not well |
Other climate-related consequences
Other climate-related consequences
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| reduced growing period | well |
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
neutral/ balanced
Long-term returns:
positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
neutral/ balanced
Long-term returns:
positive
Comments:
The naturally growing trees are maintained during field preparation, some of the side branches may be pruned on the bigger trees, sometimes the Young trees are protected with some thorny branches. No other maintenance needed.
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 91-100%
Comments:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: Farmers only received information and training. No external material support needed.
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities of the Technology
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
| Tree roots and fallen leaves help to stabilise the soil and thereby reduce water erosion. Some tree species have a fertilising effect on the soil. |
| The shade provided by trees lowers soil temperature and reduces the evapotranspiration and thus water stress of plants. They also act as a windbreak and provide protection against wind erosion. |
|
ANR contributes to sustainable farming. It is one of the most widely accepted of the land improvement techniques promoted by development projects. The vegetation provides shelter and forage for animals and contributes to biodiversity. Trees have positive effects on crop yields. They also provide products and byproducts, such as wood, fruits, leaves, forage, ingredients for medicinal products. The wood, leaves, pods and fruits provided by trees in crop fields help the owners to meet their family’s needs during the lean season. How can they be sustained / enhanced? In order to implement this technique, there must be a very clear legal framework governing land tenure. It is important to protect the tree seedlings and saplings from browsing animals during the first few years. |
| It does not require a high level of organisation to implement it and it is not costly. |
6.8 Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks of the Technology and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| During the dry season stray animals often wipe out ANR efforts made by farmers on their land. | |
| In some places, anyone can collect fruits, leaves and pods from trees, and this discourages farmers from investing in ANR. | |
| In some places, only the owner of the land is allowed to establish trees on cropland. |
7. References and links
7.1 Methods/ sources of information
7.3 Links to relevant online information
Title/ description:
Good Practices in Soil and Water Conservation. A contribution to adaptation and farmers resilience towards climate change in the Sahel. Published by GIZ in 2012.
URL:
http://agriwaterpedia.info/wiki/Main_Page
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks
No links