Restoration of degraded lands through participatory land use planning [Sri Lanka]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: Head Soil Science
- Editor: –
- Revisores: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Village-based participatory land use planning
approaches_6237 - Sri Lanka
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación del Enfoque
co-compiler:
co-compiler:
Agrarian Research and Production Assistant:
Karunarachchi Mangalika
+94714955038
Department of Agrarian Development
Agrarian Research and Production Assistant Office, Galayata Kandura, Bindunuwewa, Bandarawela.
Sri Lanka
Usuario de la tierra:
Podimenike W.M.
+94572232842
Galayata Kandura, Bindunuwewa, Bandarawela.
Sri Lanka
Nombre del proyecto que facilitó la documentación/ evaluación del Enfoque (si fuera relevante)
Rehabilitation of Degraded Agricultural Lands in Kandy, Badulla and Nuwara Eliya Districts in the Central Highlands of Sri LankaNombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación del Enfoque si fuera relevante)
Faculty of Agriculture, University of Peradeniya, Sri Lanka (AGRI.PDN) - Sri Lanka1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
¿Cuándo se compilaron los datos (en el campo)?
24/02/2022
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT :
Sí
2. Descripción del Enfoque MST
2.1 Breve descripción del Enfoque
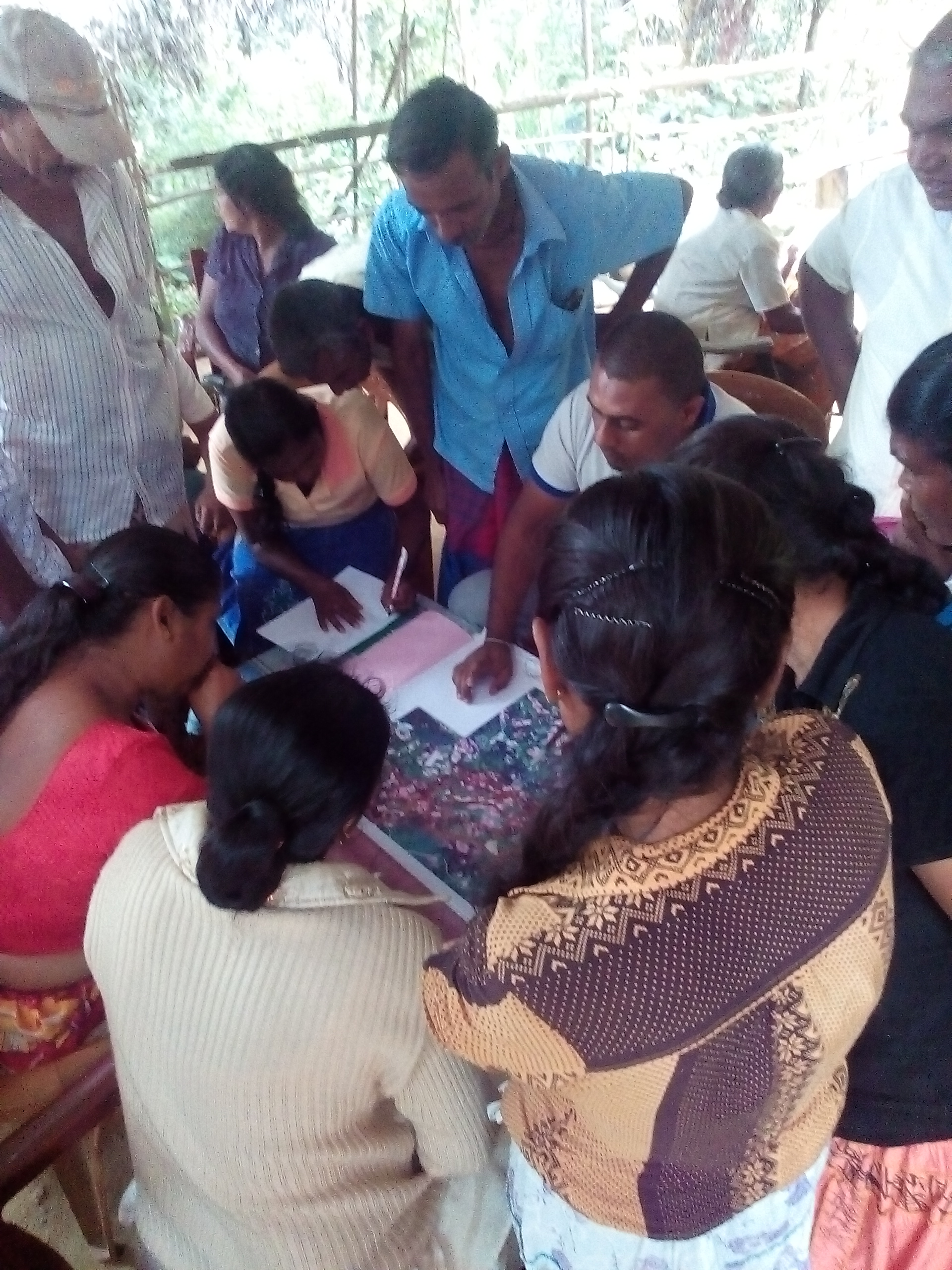
Microwatershed-based participatory land use planning is a systematic and interactive process that primarily focuses on the optimal allocation of village land resources according to needs and demands of the people while promoting sustainable land management. Key features of this approach are multi-sectoral coordination, multi-stakeholder engagement and the active participation of land users throughout the participatory land use planning process.
2.2 Descripción detallada del Enfoque MST
Descripción detallada del Enfoque MST:
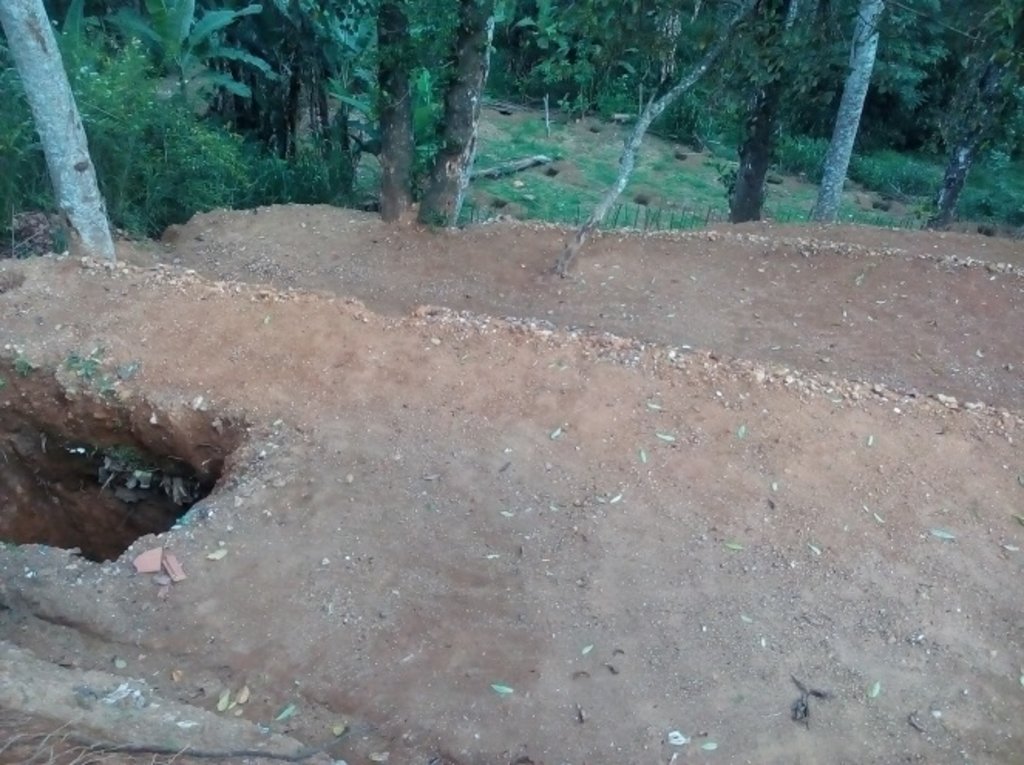
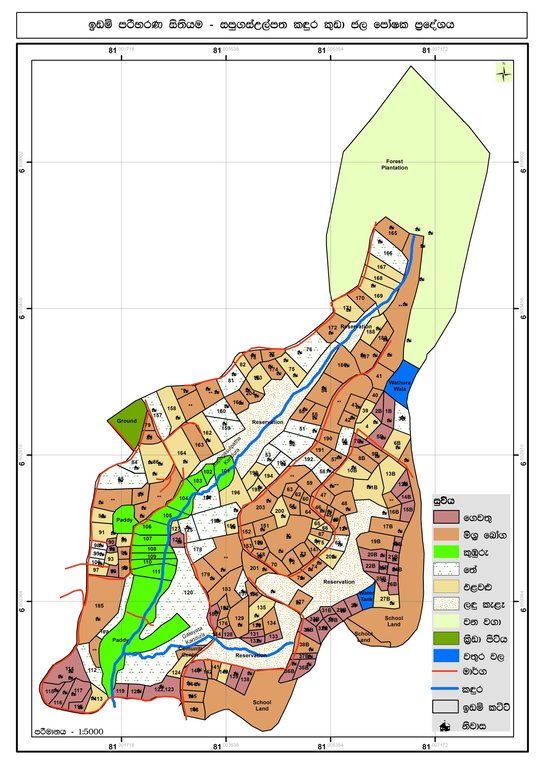
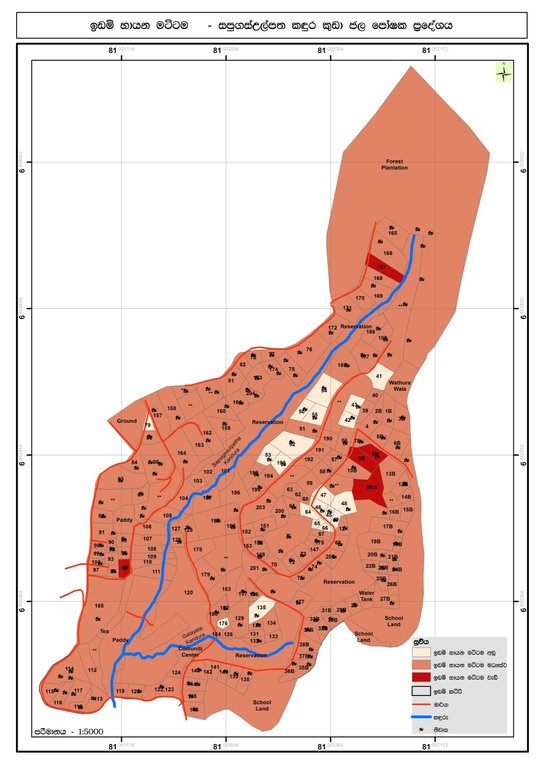
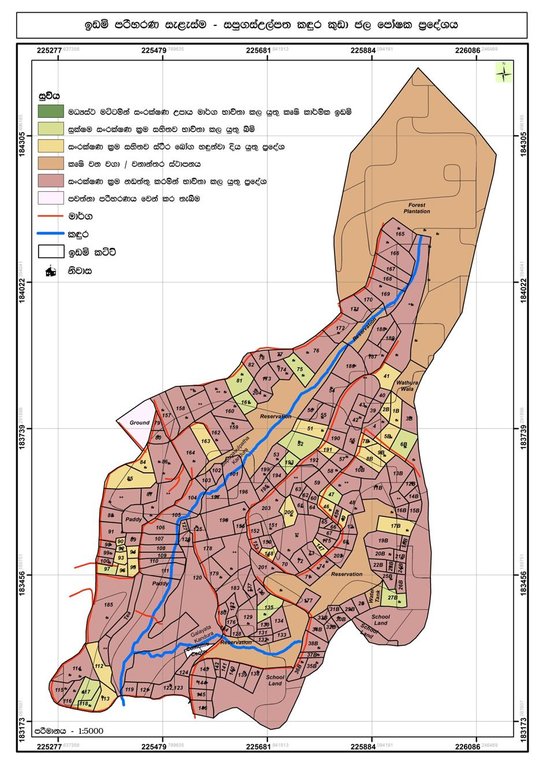
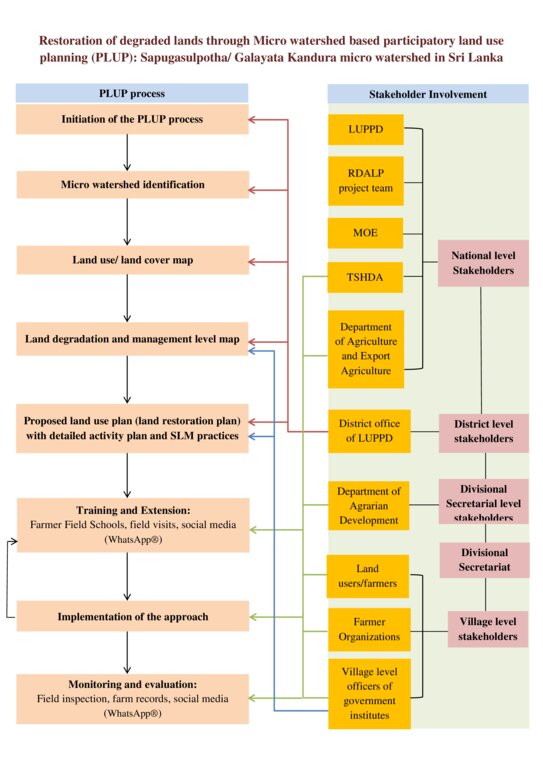
The Sapugasulpatha/ Galayata Kandura microwatershed is located in Bandarawela Divisional Secretariat (DS), Badulla District, Sri Lanka. Unsustainable land management has led to land degradation causing associated challenges. There was a need to identify strategies for restoration of degraded lands while addressing water scarcity. In 2018, the Rehabilitation of Degraded Agricultural Lands Project (RDALP) introduced participatory land use planning (PLUP) for this microwatershed. Previously, stakeholders were dealt with individually. But the PLUP process relies on the active involvement of all stakeholders. Key is microcatchment level planning - embedded in multi-sectoral coordination and multi-stakeholder engagement.
The process is initiated by the district office of the Land Use Policy Planning Department (LUPPD). Firstly, the LUPPD identifies microwatersheds and develops land use/cover maps. It is assisted by the Bandarawela DS, which is the administrative body for lands in the area and has the capacity to coordinate all relevant stakeholders. Then, officers of the LUPPD meet with community leaders, representatives of farmer organizations and field level officers to verify the land use maps through field visits. Demarcation of individual plots on these maps is also carried out. Next, a field visit is conducted with all stakeholders to identify the status of land degradation and the current crop management practices. This is, effectively, “training of trainers”. Subsequently, the community prepares maps of land degradation and management types with the support of LUPPD.
This is followed by a participatory rural appraisal (PRA) process with all stakeholders. In the PRA, issues related to land degradation/use, ownership, conflicts and socio-economic concerns are discussed. Participants come to an initial consensus on solutions. After this, a detailed action plan is prepared and stakeholders identified. The next stage involves the development of land use plans for the entire microwatershed targeting the restoration of degraded and poorly managed lands. The land use plan covers both on-farm and off-farm land, and provides recommendations for SLM practices over the entire microwatershed: it serves as a detailed land restoration plan. Then, detailed discussions are held with specific stakeholders to prepare sector-based plans. This includes detailed plans for individual farms. As an example, officers of Tea Smallholdings Development Authority (TSHDA) provide inputs to develop detailed plans for smallholder tea cultivation - including plans for individual farmers. Subsequently, implementation is performed jointly by stakeholders. If, for example, a farm is identified for tea cultivation intercropped with export crops, officers both from TSHDA and the Department of Export Agriculture extend their support. The approach includes farmer field schools (FFS) conducted by the Department of Agrarian Development officers and project officers of RDALP. Moreover, farmers are encouraged to use social media (WhatsApp®) to share their knowledge and experiences with SLM practices. The local community is also exposed to examples of good SLM through field visits. The final step is evaluation and monitoring. This is performed by the officers of the Agrarian Service Development, RDALP, and also by individuals. A divisional agricultural committee is mandated to perform continuous monitoring of implementation. PLUP provides the stimulus for farmers to continue SLM - since practices are not enforced but identified themselves. Further, firm bonding is established between land users and other stakeholders, including government institutes, strengthening the likelihood of sustainability.
2.3 Fotos del Enfoque
2.4 Videos del Enfoque
Comentarios, descripción breve:
https://youtu.be/uHBRGYVT--M
Participatory Land Use Planning for Sustainable Land Management
Fecha:
03/08/2021
Lugar:
Dambugasagala, Welimada
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde el Enfoque fue aplicado
País:
Sri Lanka
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
Badulla District - Uva province
Especifique más el lugar :
Watagamuwa Grama Niladhari Division, Bandarawela Divisional Secretariat Division
Map
×2.6 Fechas de inicio y conclusión del Enfoque
Indique año del inicio:
2018
Año de conclusión (si el Enfoque ya no se aplica):
2021
Comentarios:
Stakeholders continue to provide extension service for this microwatershed, even though the project was finished.
2.7 Tipo de Enfoque
- proyecto/ basado en un programa
2.8 Propósitos/ objetivos principales del Enfoque
1)Identification and mapping of degraded lands at microwatershed level.
2)Integration of multi-sectoral coordination and multi-stakeholder engagement in participatory land use planning implemented at village micro watershed level.
3)Identification of land management related issues and factors contributing to land degradation and prioritizing sustainable land use/management options through participatory approach.
4)Development and implementation of a land use plan and an action plan to restore and mitigate the degradation within the micro watershed employing PLUP approach.
5)Maintenance and promotion of ecosystem services for the sustainability of rural livelihoods.
6)Reduction of the pressure of competitive land use on natural resources.
2.9 Condiciones que facilitan o impiden la implementación de la/s Tecnología/s aplicadas bajo el Enfoque
normas y valores sociales/ culturales/ religiosos
- facilitan
Greater social capital as local community is well organized with a strong social bonding among villagers. Farmer organization with leaders appointed by villagers further strengthened the bonding between people for agriculture/ land management related activities.
- impiden
Lack of interest of young generation on farming.
disponibilidad/ acceso a recursos y servicios financieros
- facilitan
Having access to a comprehensive land use plan for each land increases access for financial resources such as loan facilities from banks, subsidy schemes of TSHDA, Loan facilities of tea factories. Farmers have the option to come with an agreement with a leading supermarket chain in Sri Lanka to obtain financial services/materials with the promise of supplying the products exclusively to the said supermarket chain.
- impiden
Existing financial wellbeing of farmers and land ownership related issues limits the access.
entorno institucional
- facilitan
National, regional and village level institutional set up is existing. Moreover, farmer organizations have strengthened the collective power of farmers to coordinate with institutes. Female farmers have formed “Sithamu” Women's Farmers' Organization and both female and male farmers in the village have formed “Galayata Kandura” Rural Farmer Organization. Land use plan serves as a common platform for the collaboration between institutes enhancing the overall synergy.
- impiden
Often the lack of coordination between sectoral institutes and top-down approach in decision making. Lack dedicated institutes to coordinate activities at national level.
colaboración/ coordinación de actores
- facilitan
Officers of relevant government institutes namely, DS, LUPPD, Extension service of the Department of Agriculture, Department of Agrarian Development, Department of Export Agriculture and TSHDA are willingly to support farmers. Moreover, RDALP project officers play an important role in coordinating the activity.
marco de trabajo legal (tenencia de tierra, derechos de uso de tierra y agua)
- facilitan
Majority of farmers own their lands (home gardens and tea smallholdings). Legal frameworks of land ownership and land and water usage are well established.
- impiden
Delays and complications in solving legal issues pertaining to land use
políticas
- facilitan
Land use policy, soil conservation act, national action plan (NAP) to combat land degradation
- impiden
Lack of implementation of policies and acts
gobernanza de tierras (toma de decisiones, implementación y aplicación)
- facilitan
Presence of land use committee (at divisional level) and divisional agriculture committee (included all government institutes related to land use) for decision making. The DS is the chairperson of these committee who is also a part of the PLUP process. Farmers have the liberty to take land use decisions within the framework of land use policy and administrative framework. However, field level officers representing government institutes such as LUPPD, Department of Agriculture, Department of Export Agriculture, TSHDA play a supporting role in implementation of these decisions. Absence of Gender biasedness is a very important factor.
- impiden
Land ownerships, conflicts on land ownership, illegal encroachment of sensitive areas of the micro watershed and political interferences
conocimiento de MST, acceso a apoyo técnico
- facilitan
Farmer organizations serve as a platform to share knowledge on SLM. Strong village level extension service is facilitated by the Department of Agriculture, Export Agriculture, TSHDA and other technical services. These officers are available at Agrarian Service Centre and Wednesdays are allocated for meeting with farmers. Moreover, conducting field visits is a part of their duty. Farmer groups have been identified and introduced social media platforms such as WhatsApp® to share SLM knowledge by experts and among themselves. Farmers are capable of operating online interaction facilities such as Zoom® allowing experts to share the knowledge conveniently.
- impiden
Inadequacy of extension officers
mercados (para comprar insumos, vender productos) y precios
- facilitan
Farmers have the choice of marketing their products and enter into the value chain i.e. direct selling at the village vegetable market, private companies those visit to the field for purchasing their products (vegetable, spice crops and tea) and intermediate buyers. Farmers also have the option to come into a contract with a leading supermarket chain to sell their products if they are willing to adopt Good Agricultural Practices (GAP).
- impiden
Lack of transport facilities, low market price offered by intermediate buyers, price fluctuations
carga de trabajo, disponibilidad de mano de obra
- facilitan
Most of the SLM practices which are promoted through this approach are not very labor-intensive. Often, family members are sufficient to establish the majority SLM practices.
- impiden
Lack of labor force due to the labor migration
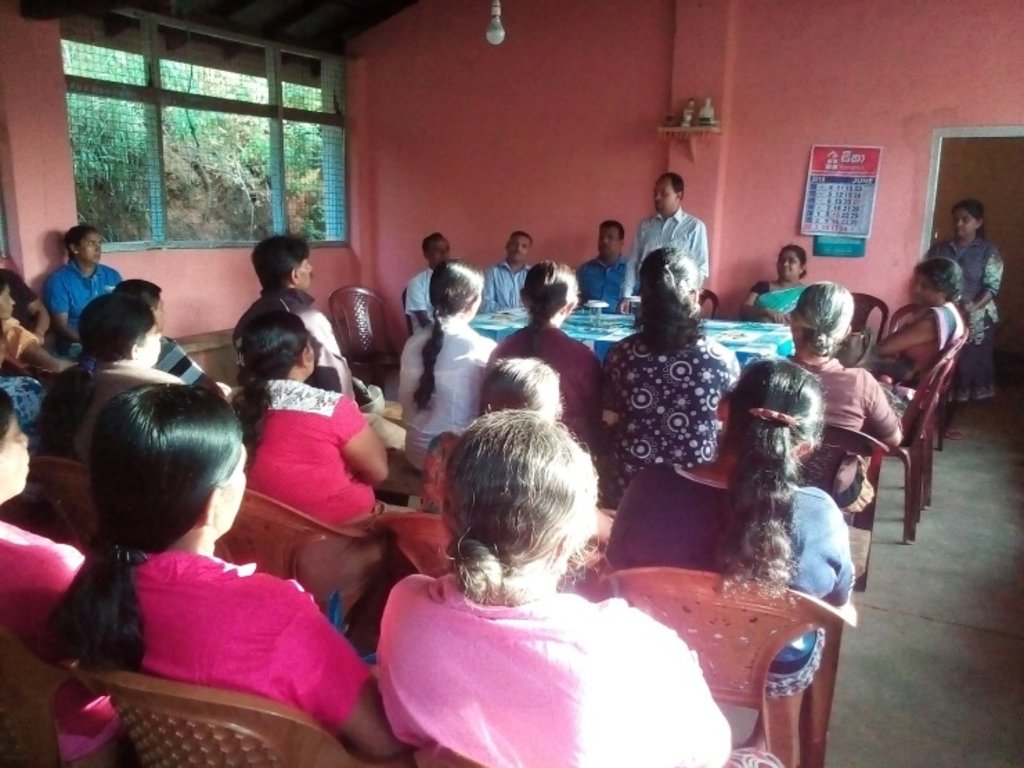
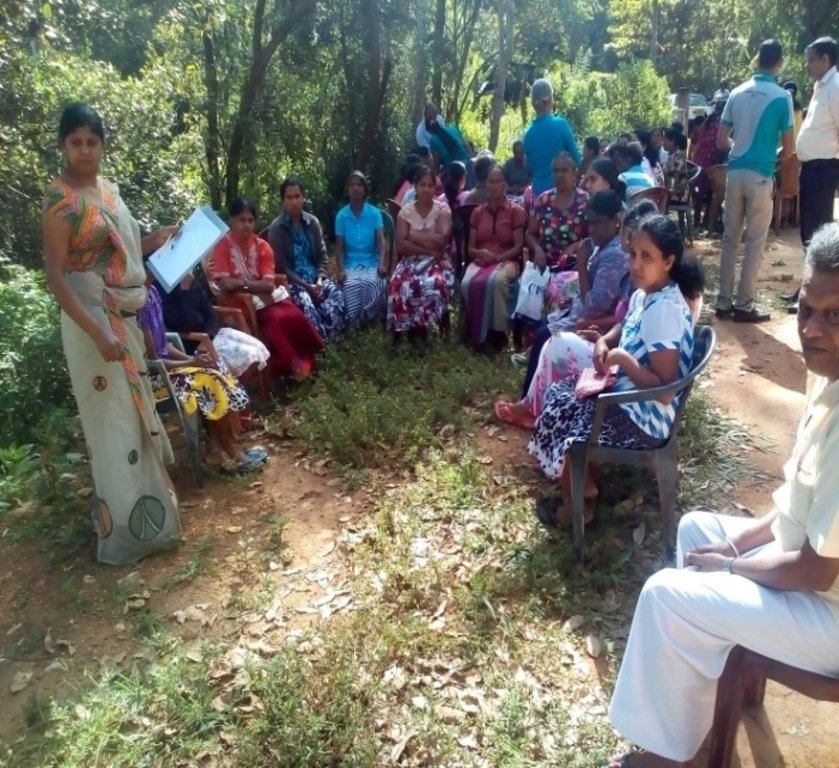
3. Participación y roles de las partes interesadas involucradas
3.1 Partes interesadas involucradas en el Enfoque y sus roles
- usuarios locales de tierras/ comunidades locales
Land users/ village farmers (both men and women)
Express their willingness to involve in PLUP. They are involved in the entire process by actively participating for group discussions and activities with other stakeholders to identify land use related issues, prepare a community land use plan, identify SLM practices and implementation. Further, participation for training programmes and share the knowledge about SLM practices.
- organizaciones comunitarias
“Sithamu” Women's Farmers' Organization and “Galayata Kandura" Rural Farmer Organization
All farmers of the village are members of these community based organizations. These serve as a platform to promote the involvement of farmers in the PLUP process. Moreover, problems/issues arise in the process are discussed within the organization to come up with socially agreed solutions.
- especialistas MST/consejeros agrícolas
LUPPD, Department of Agriculture, Department of Export Agriculture, Department of Agrarian Development, TSHDA
Identification of village level micro-catchments by LUPPD
Introducing SLM technologies
Provision of training
Oversee the implementation and monitoring the success of field adopted SLM technologies
- gobierno local
DS office of Bandarawela, Department of Agrarian Development, TSHDA, Department of Agriculture and Department of Export Agriculture
Involved in the PLUP process as key stakeholders responsible for advisory services, conflict resolution, capacity building and overall implementation and monitoring
- gobierno nacional (planificadores, autoridades)
LUPPD, Ministry of Environment (MOE), Natural Resource Management Centre of the Department of Agriculture
Support the preparation of land use plans within the context of legal frame work of the country
- organización internacional
Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), Global Environment Facility (GEF)
Project coordination, partial financial support, Capacity building
Si varias partes interesadas estuvieron involucradas, indique la agencia principal:
LUPPD
3.2 Involucramiento de los usuarios locales de tierras/ comunidades locales en las distintas fases del Enfoque
| Involucramiento de los usuarios locales de tierras/ comunidades locales | Especifique quién se involucró y describa las actividades | |
|---|---|---|
| iniciación/ motivación | interactivo | Community leaders, LUPPD, DS and RDAL Project officers. The process is initiated by the district office of LUPPD which is the responsible national level authority to prepare sustainable land use plans. The regional office identifies village level micro catchment and develop land use/cover maps. The DS serves as a body that coordinate the activity by linking relevant stakeholders. |
| planificación | interactivo | Community leaders, land users, LUPPD, DS and RDALP officers. Planning of the PLUP process is performed by these parties. |
| implementación | interactivo | Land users, community leaders, Department of Agrarian Development, Department of Agriculture, Department of Export Agriculture, TSHDA, officers of RDALP, other officers representing different agriculture sectors and land users. Implementation of the restoration plan for individual farm is performed jointly by different stake holders. As an example if a farmers` land is identified for tea cultivation intercropped with export agricultural crops, officers both from TSHDA and Department of Export Agriculture extend their support for implementation. |
| monitoreo y evaluación | interactivo | Land users, Department of Agrarian Development, RDALP officers, individual stakeholders, Department of Agriculture, officers of Natural Resource management Centre and divisional agricultural committee. Please note that participatory monitoring mechanism was implemented. |
| Marketing | auto-movilización | Land users (farmers), private companies and intermediate sellers. Farmers have the choice of marketing their products by direct selling at the village vegetable market, through private companies those visit to the field for purchasing their products (vegetable and tea) and intermediate buyers. Moreover, farmers also have the option to come into a contract with a leading supermarket chain to sell their products if they are willing to adopt Good Agricultural Practices (GAP) |
3.3 Flujograma (si estuviera disponible)
Descripción:
The PLUP described above is focused on restoration of degraded lands at microwatershed level. The multi-sectoral coordination and multi-stakeholder engagement throughout the process are key features of this process leading to the preparation of detailed restoration plan at on-farm and off-farm levels promoting sustainable land management.
Autor:
Prof. W.A.U. Vitharana
3.4 La toma de decisiones en la selección de Tecnología(s) MST
Especifique quién decidió la selección de las Tecnología/ Tecnologías a implementarse:
- todos los actores relevantes, como parte de un enfoque participativo
Explique:
This is a participatory approach in which stakeholders make collective decisions on the selection of appropriate technologies. Multi-stakeholder engagement is a prominent characteristic.
Especifique las bases que sustentaron la toma de decisiones:
- la evaluación de conocimiento MST bien documentado (la toma de decisiones se basa en evidencia)
- hallazgos de investigaciones
- la experiencia personal y opiniones (no documentadas)
4. Apoyo técnico, fortalecimiento institucional y gestión del conocimiento
4.1 Construcción de capacidades / capacitación
¿Se proporcionó la capacitación a usuarios de tierras/ otras partes interesadas?
Sí
Especifique quién fue capacitado:
- usuarios de tierras
- personal de campo/ consejeros
Si fuese relevante, también especifique género, edad, estatus, etnicidad, etc.
Training was provided for both men and women farmers of the microwatershed
Forma de capacitación:
- de agricultor a agricultor
- áreas de demostración
- reuniones públicas
Forma de capacitación:
- social media (WhatsApp®) and online meetings via Zoom® platform
Temas avanzados:
Sustainable Land Management practices, compost preparation, liquid fertilizer preparation, water harvesting techniques, soil conservation practices and pruning of fruit trees
Comentarios:
Farmers have shown a great interest on sharing knowledge and experiences through the social media
4.2 Servicio de asesoría
¿Los usuarios de tierras tienen acceso a un servicio de asesoría?
Sí
Especifique si servicio proporcionado se realizó:
- en los campos de los usuarios de tierras
- en centros permanentes
Describa/ comentarios:
Well organized advisory service is available in Sri Lanka which is conducted through the field officers of the Department of Agriculture, Export Agriculture, TSHDA. These officers are available at Agrarian Service Centre and Wednesdays are allocated for meeting with farmers and making field visits is a part of their job. Moreover, members of the project team RDALP also served as trainers. Importantly, community leaders and farmer organization representatives were trained as trainers to assure the sustainability.
4.3 Fortalecimiento institucional (desarrollo institucional)
¿Se establecieron o fortalecieron instituciones mediante el Enfoque?
- sí, moderadamente
Especifique el nivel o los niveles en los que se fortalecieron o establecieron las instituciones:
- local
- regional
Describa la institución, roles y responsabilidades, miembros, etc.
The PLUP process strengthens the institutional coordination and their roles at village level.
Especifique el tipo de apoyo:
- financiero
- construcción de capacidades/ entrenamiento
- equipo
- infrastructure
Proporcione detalles adicionales:
Details are provided in Table 6.3
4.4 Monitoreo y evaluación
¿El monitoreo y la evaluación forman parte del Enfoque?
Sí
Comentarios:
Field level government officers are entrusted with the monitoring process with the participation of land users
Si respondió que sí, ¿la documentación se utilizará para monitoreo y evaluación?
No
4.5 Investigación
¿La investigación formó parte del Enfoque?
No
5. Financiamiento y apoyo material externo
5.1 Presupuesto anual para el componente MST del Enfoque
Si no se conoce el presupuesto anual preciso, indique el rango:
- 10,000-100,000
Comentarios (ej. fuentes principales de financiamiento/ donantes principales):
GEF and local government institutions
5.2 Apoyo financiero/material proporcionado a los usuarios de tierras
¿Los usuarios de tierras recibieron financiamiento/ apoyo material para implementar la Tecnología/ Tecnologías? :
Sí
Si respondió sí, especifique el tipo o los tipos de apoyo, condiciones y proveedor(es) :
Financial support for soil conservation, materials for preparation of nursery sheds (4x4 feet), vegetable seeds and fruit plants for home gardening, tea seedlings for infilling and polythene for rain water harvesting ponds
5.3 Subsidios para insumos específicos (incluyendo mano de obra)
- mano de obra
| En qué grado | Especifique los subsidios |
|---|---|
| parcialmente financiado | Subsidy for establishment of soil conservation structures |
- equipo
| Especifique qué insumos se subsidiaron | En qué grado | Especifique los subsidios |
|---|---|---|
| maquinaria | totalmente financiado | Pruning kits for fruit tree management, Portable hole drilling machine* for establishment of tea plantations, Bush cutters*, selective plucking machines. *Provided for the Village farmer society |
| herramientas | totalmente financiado | Nursery trays |
- agrícola
| Especifique qué insumos se subsidiaron | En qué grado | Especifique los subsidios |
|---|---|---|
| semillas | totalmente financiado | Vegetables seeds |
| Fruit plants, Tea seedlings | totalmente financiado | Fruit plants for home gardening and intercropped with tea, tea seedling for infilling |
- construcción
| Especifique qué insumos se subsidiaron | En qué grado | Especifique los subsidios |
|---|---|---|
| UV treated Polyethene | totalmente financiado | UV treated Polyethene for water harvesting ponds and nursery sheds |
- infraestructura
| Especifique qué insumos se subsidiaron | En qué grado | Especifique los subsidios |
|---|---|---|
| Rainwater storage tank | totalmente financiado | Rainwater storage tank to harness water for micro watershed and the downstream areas as ground water |
Si la mano de obra de usuarios de tierras fue un insumo sustancial, ¿fue:
- voluntario?
Comentarios:
Most of the time family members are engaged with field activities
5.4 Crédito
¿Se proporcionó crédito bajo el Enfoque para actividades MST?
No
5.5 Otros incentivos o instrumentos
¿Se usaron otros incentivos o instrumentos para promover la implementación de Tecnologías MST?
Sí
Si fuera el caso, especifique :
Land use policy and agriculture policy of Sri Lanka are overarching instruments. Moreover, regulations identified in the Soil Conservation Act of Sri Lanka promote SLM technologies.
6. Análisis de impacto y comentarios de conclusión
6.1 Impactos del Enfoque
¿El Enfoque empoderó a los usuarios locales de tierras, mejoró el involucramiento de las partes interesadas?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
All land users are part of the approach which empowered land users on knowledge on land degradation, SLM practices and preparation of detailed restoration plan for degraded/poorly management lands. Moreover, training programs and field visits empowered land users with specific skills.
¿El Enfoque facilitó la toma de decisiones basada en evidencia?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
The participatory approach includes field visits, analysis of field evidences to identify degraded lands and lands those have not been properly managed. These allow land users on evidence based decision making to implement SLM practices.
¿El Enfoque ayudó a los usuarios de tierras a implementar y mantener Tecnologías MST?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
The entire process help land users to understand user specific sustainable land management options and also integrate local knowledge and experience. Since SLM options are identified by land users it enables them to implement based on available resources. Involvement relevant stakeholders (e.g. Agriculture extension officers) and training programs help land users for the implementation and maintenance of SLM technologies. Partial financial support and material support further help farmers to implement and maintain SLM practices.
¿El Enfoque mejoró la coordinación e implementación efectiva en costos de MST?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
Multi-sectoral coordination embedder throughout the process improve coordination among stakeholders. The SLM practices which are identified by land users assured to be cost-effective and manageable.
¿El Enfoque movilizó/mejoró el acceso a recursos financieros para implementar MST?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
Involvement of key institutes in the process and documentary evidence on proposed activities enhance the access to financial resources for SLM implementation.
¿El Enfoque mejoró el conocimiento y capacidades de los usuarios para implementar MST?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
Land users are trained on SLM by providing on-ground hands on experience and through online sessions. Farmers are motivated from others who have already implemented SLM practices.
¿El Enfoque mejoró el conocimiento y capacidades de otras partes interesadas?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
Interaction between stakeholders is a dominant activity throughout the process. This allows knowledge sharing leading to improve capacities of all stakeholders. FAO officers, Extension officers and officers of Department of Agrarian Development visit each land plot and give further instructions
¿El Enfoque construyó/ fortaleció instituciones, colaboración entre partes interesadas?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
Multiple institutions are involved in this approach and they work together in the process of land use planning.
¿El Enfoque resultó en mejor seguridad alimentaria/ mejoró la nutrición?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
Increased production of vegetables and fruits through appropriate land use planning and SLM practices enhance the village level food security
¿El Enfoque llevó a un acceso mejorado a tierra y saneamiento?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
Establishment of rainwater harvesting ponds has been integrated to land use plan. Further, establishment of village level water harvesting tank increase the ground water status. This lead to access for irrigation water during the dry season.
¿El Enfoque mejoró la capacidad de los usuarios de tierras a adaptarse a los cambios climáticos/ extemos y mitigar desastres relacionados al clima?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
Soil conservation practices and SLM practices lead to enhancement of soil organic carbon levels. Further, rainwater harvesting ponds sustain the water supply during extreme drought periods. These will contribute to the enhance climate resilience potential.
¿El Enfoque llevó a oportunidades de empleo, ingresos?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
Increase in farmer income is expected through appropriate land use planning and application of SLM practices. Especially, crop diversification options introduced and increased irrigation water availability through rain water harvesting will enhance income opportunities. E.g. intercropping of spice crops (export agricultural crops) with tea as one of the consequences of this approach
6.2 Motivación principal del usuario de la tierra para implementar MST
- producción incrementada
Increased production from home gardens and tea smallholdings
- incremento de la renta(bilidad), proporción mejorada de costo-beneficio
Increased crop yields, thus profits are expected through proper land allocation and application of SLM practices
- reducción de la degradación del suelo
Reduced land degradation (specially soil erosion) achieved through SLM practices such as application of soil conservation measures (stone bunds, terraces, contour farming) and application of organic fertilizers (compost) produced by farmers.
- reducción del riesgo de desastres naturales
Soil conservation practices reduce the risk of earth slips which are prevalent in the area. Rainwater harvesting ponds reduce the risk of droughts.
- pagos/ subsidios
Subsidies were provided to implement soil conservation practices. Material support was provided for the preparation of rain water harvesting ponds, establishment of nurseries, and operations in tea lands.
- conocimiento y capacidades mejorados de MST
Land users understand the importance of SLM application for their lands through participatory approach and farmer field schools.
- mejoramiento estético
Aesthetic value of home gardens were improved and it is given extra income for the family.
6.3 Sostenibilidad de las actividades del Enfoque
¿Pueden los usuarios de tierras sostener lo que se implementó mediante el Enfoque (sin apoyo externo)?
- sí
Si respondió que sí, describa cómo:
There is a greater potential for farmers to continue SLM practices since such practices are not forcefully enforced but identified by land users themselves through a participatory approach. Therefore, SLM technologies identified by farmers suit to their socio-economic capacity. Further, strong bonding is established with land users and other stakeholders such as government institutes, that will lead to the sustainability of the approach.
6.4 Fortalezas/ ventajas del Enfoque
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra |
|---|
| Multi-sectoral coordination and multi-stakeholder engagement throughout all activities of the approach |
| Land users perceive a sense of ownership of the SLM practice implemented through the approach |
| Training programmes conducted through online platforms motivate farmers to implement SLM on their own land while improving the awareness on SLM practices |
| Greater potential of enhancement of the farmer income through practices such as crop diversification, intercropping etc. |
| Enhanced food security |
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
| Field evidence suggested farmers have willingly embraced the approach to restore their degraded lands |
| The approach has enhanced collaborations with land users and other stakeholders |
| The approach has inculcated ownership of the entire process on land users |
6.5 Debilidades/ desventajas del Enfoque y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| Marketing of Vegetables | Though farmers has access to village vegetable market, if farmers can be incorporated to the Good Agricultural Practices (GAP) program this limitation can be overcome. |
| Lack of financial resources | Formally link a financial supporting institute as a key stakeholder (e.g. Banks, social protection schemes) |
| Lack of labor | Though land users identified less labor intensive SLM practices, the provision of necessary machinery could have substitute such practices with more appropriate ones. |
| Time constraints of land users to participate continuously | Use of ICT tools and scheduling meetings at convenient times for land users |
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| PLUP approach is a time consuming process | Simplify the PLUP process |
| This approach requires a large number of officers to carry out | Simplify the PLUP process |
| Incompatibility of micro-watershed boundaries and administrative boundaries | Use administrative boundaries in planning process |
| Negative attitude of some institutions and some officials towards collective effort | National level stakeholders should be made aware of the project activities and incorporate them into their plans |
| Some stakeholders' involvement exceeds beyond their mandate | Ensuring that each institution executes their mandate and the due respect for their intervention |
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.1 Métodos/ fuentes de información
- visitas de campo, encuestas de campo
One field visit
- entrevistas con usuarios de tierras
Three families were interviewed
- entrevistas con especialistas/ expertos en MST
RDAL project officers, Agriculture Research and Production Assistants
- compilación de informes y otra documentación existente
Healthy Soil Matters (FAO, United Nations Colombo, 2021)
7.2 Referencias a publicaciones disponibles
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
Healthy Soil Matters, The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations Colombo, 2021
¿Dónde se halla disponible? ¿Costo?
SriCAT website
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
Guidelines for participatory land use planning
¿Dónde se halla disponible? ¿Costo?
LUPPD
7.3 Vínculos a la información relevante disponible en línea
Título/ descripción:
Healthy Soil Matters, The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations Colombo, 2021
URL:
https://sricat.net/index.php/en/media-gallery/documents/248-healthy-soil-matters
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos
No hay vínculos
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos