Indigenous water collecting pond and livestock watering trough [Tanzania, República Unida de]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: ALLAN BUBELWA
- Editor: –
- Revisores: Donia Mühlematter, Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
elyeshero ne elyato (Haya tribe)
technologies_1157 - Tanzania, República Unida de
- Resumen completo en PDF
- Resumen completo en PDF para imprimir
- Resumen completo en el navegador
- Resumen completo (sin formato)
- Indigenous water collecting pond and livestock watering trough: 29 de diciembre de 2016 (inactive)
- Indigenous water collecting pond and livestock watering trough: 5 de junio de 2017 (inactive)
- Indigenous water collecting pond and livestock watering trough: 28 de junio de 2018 (inactive)
- Indigenous water collecting pond and livestock watering trough: 6 de agosto de 2019 (public)
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación de la Tecnología
Persona(s) de referencia clave
government:
Kagaruki Annagrace
Misseny District Council
Especialista MST:
government:
Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Missenyi District Council (Missenyi District Council) - Tanzania, República Unida deNombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
FAO Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO Food and Agriculture Organization) - Italia1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT:
Sí
2. Descripción de la Tecnología MST
2.1 Breve descripción de la Tecnología
Definición de la Tecnología:
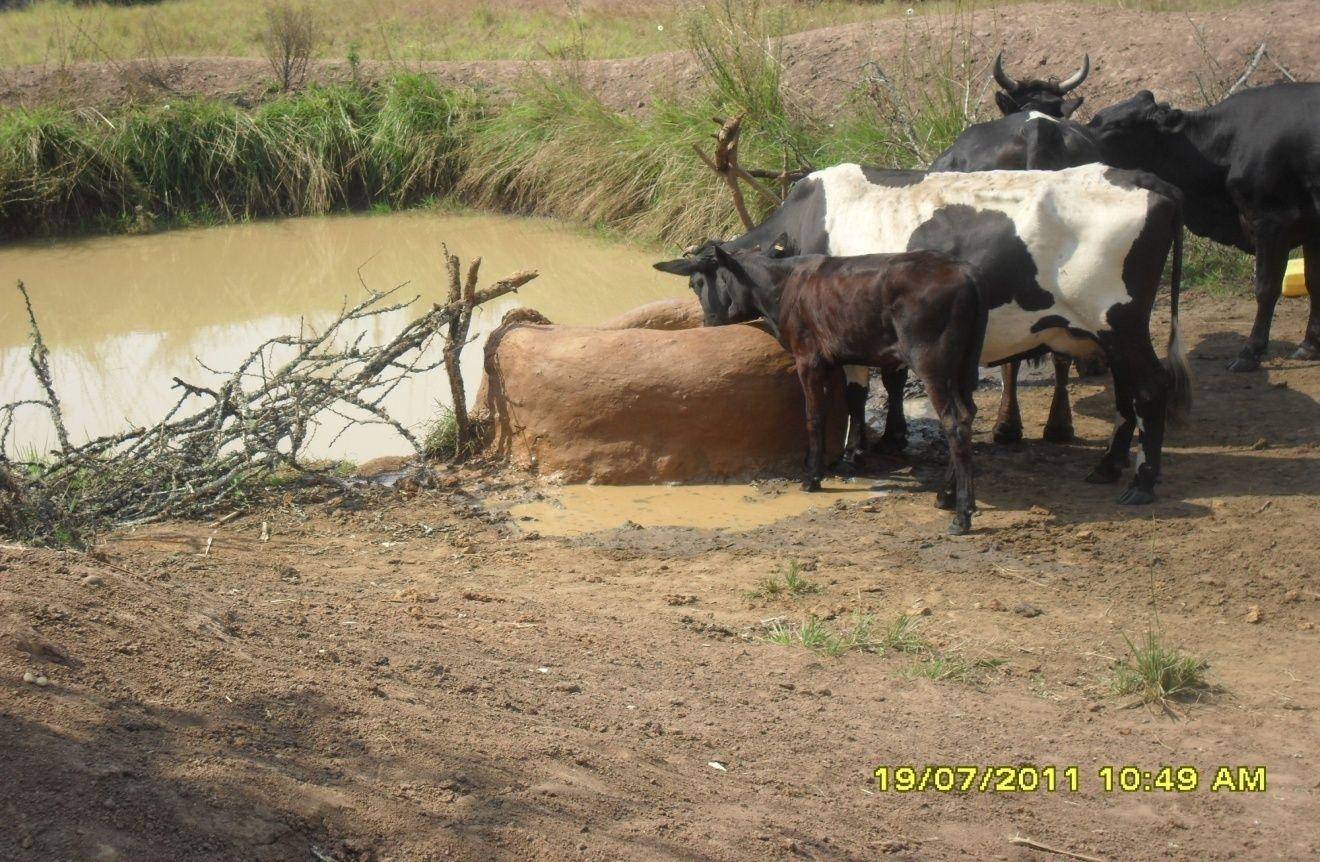
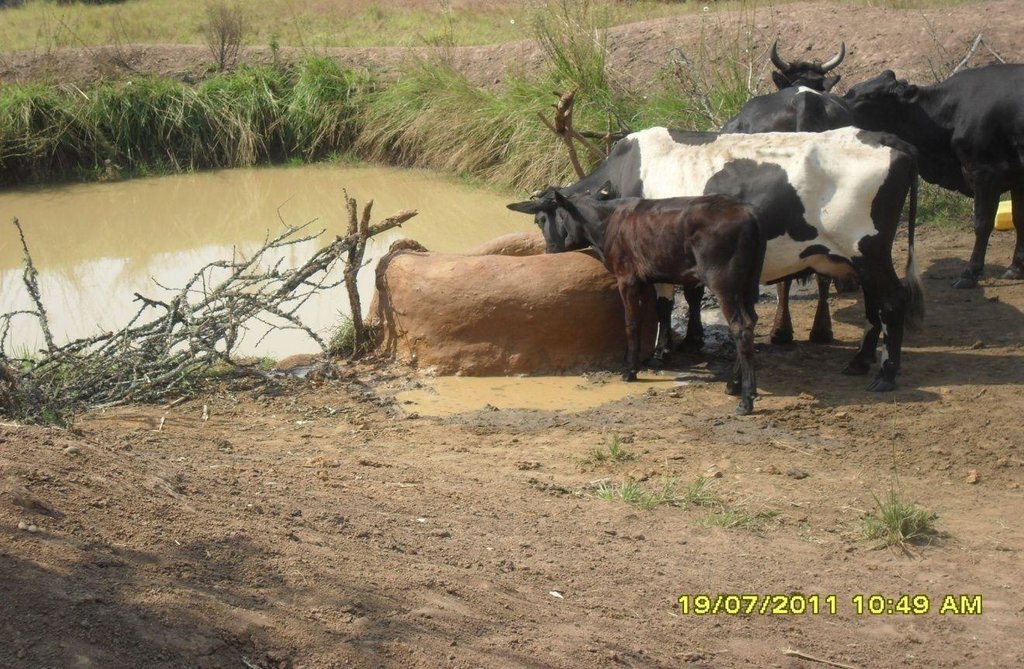
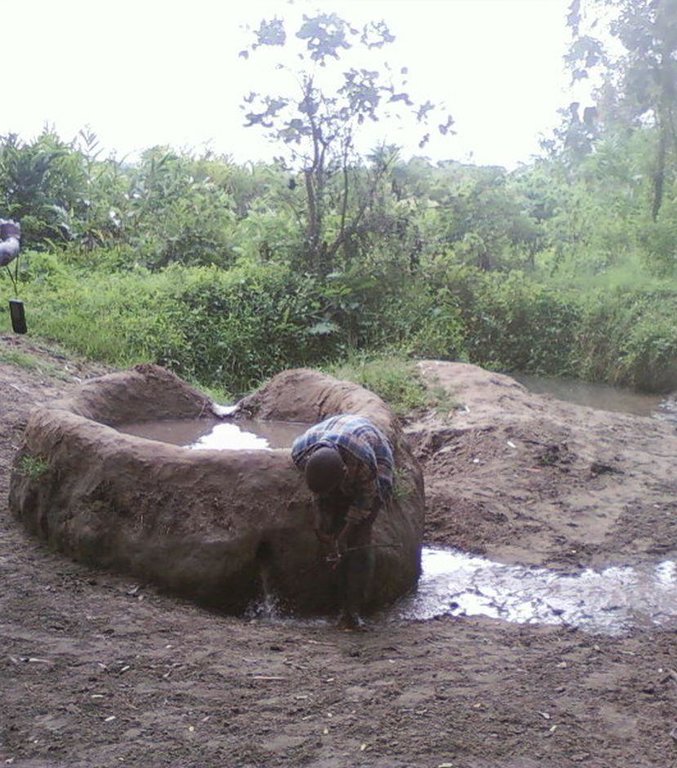
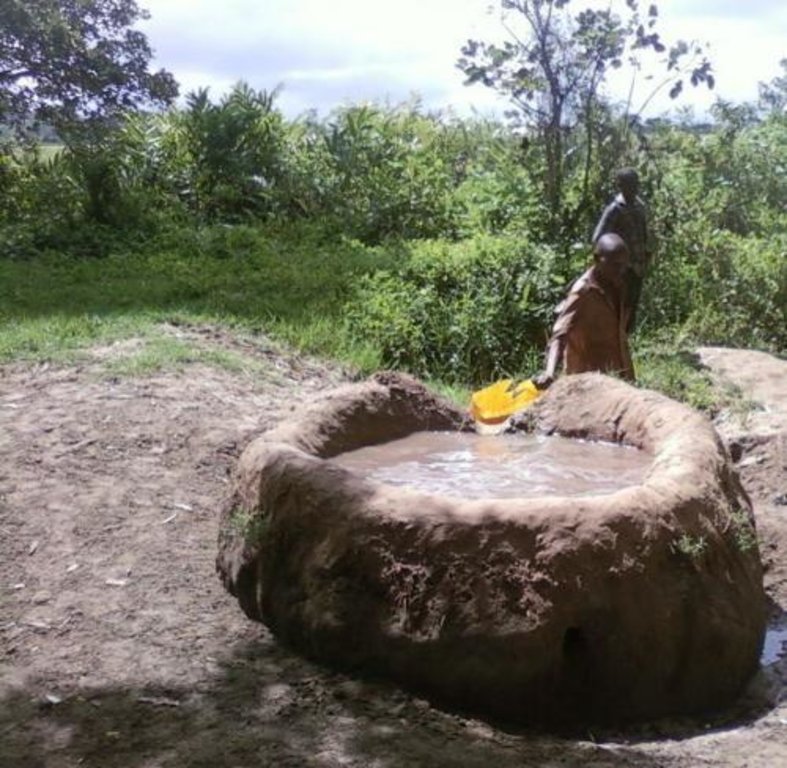
Construction of indigenous water pond and a livestock watering trough along an underground water source.
2.2 Descripción detallada de la Tecnología
Descripción:
This technology is used during the dry seasons and where ground water level is high and there is natural water stream flowing from underground water source. Water pond is excavated along the naturally flowing water stream and is recharged by natural ground water. The size of the pond will vary depending on the area available, groundwater table, slope and soil characteristic. Groundwater collection ponds described in this technology on average are 4m long, 3m wide and 1m deep of 12m3 (12 000 liter) capacity and the slope is moderate 5% to 8% and soil characteristics is clay loam with deep soil. Water troughs (Elyato by local name) are constructed adjacent to the water pond to allow livestock to access clean drinking water. The number of troughs per pond is usually 1 to 2. Materials used in construction of water trough include clay, red termite mound soil, grass and wooden poles. The number of ponds needed usually depends on the expected number of animals and are arranged at irregular intervals ranging from 10 to 20 meters apart. The average size of a water trough is 0.14 m3 and can cater for 5 cattle at a time. The Pond is stabilized by naturally growing grass on its banks. Common pond stabilizer species are Leodicatiar digitalia and Hyperrhenia rufa. Management of the natural water source is through preventive village/customary by-laws which prohibit tree and grass cutting around the water source. The dominant indicator tree species normally found are Erythrina abysinica, Ficus thorgii and Phoenix recrinata. The animal watering troughs are usually used in the dry period. Before watering the troughs are coated (smeared) with red termite mound soil (normally hand carried by herders) to provide a good taste which is attractive to animals. Water is transferred from the pond to the water trough manually using cans or buckets. Animals drink directly from the troughs. This water from the trough is rich in iron (Fe) from red termite mound soil. The troughs are constructed with outlets used to spill out water immediately after drinking in order to prevent their damage through excessive water saturation.
Purpose of the Technology: This technology is preferred by livestock keepers as it provides for animals to drink clean and mineralized water and for health improvement. User fee payed to land owners also enable them to expand and diversify there income sources.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Establishment: Land clearing, excavation and shaping of water pond and construction of animal watering trough.
Maintenance: repair of water pond and water trough (de-siltation, grass slashing and gap refilling).
Inputs: labour, implements (machete, spade, hand hoe, sickle), clay, red termite mound soil, wooden poles, buckets, grass and tying rope. Average establishment cost for one pond and its water trough is 41.27 American dollars. Average annual maintenance and recurrent costs (filling and emptying of water trough) for one pond and its water trough stands at 458.76 dollars and labour is a core cost determinant factor.
Natural / human environment: Natural environment: Extensive grazing land. The technology is largely structural (excavation and shaping of water ponds and construction of water troughs) supported by the use of by-laws which prohibit destruction of the protective natural and indicative trees and grasses around. The technology is common in sub-humid climatic zone.
Social economic environment: Level of mechanization is handy tools with subsistence production systems on individual fields.
2.3 Fotografías de la Tecnología
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde la Tecnología fue aplicada y que se hallan comprendidos por esta evaluación
País:
Tanzania, República Unida de
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
Tanzania
Especifique más el lugar :
Missenyi District (Minziro)
Especifique la difusión de la Tecnología:
- distribuida parejamente sobre un área
Si se desconoce el área precisa, indique el área aproximada cubierta:
- < 0.1 km2 (10 ha)
Comentarios:
Boundary points of the Technology area: -1.11472, 31.655 ; -1,09972, 31.70194
The area is owned by individual farmer. The area is found adjacent to extensive grazing land. Water table is high and there is a permanent underground natural water flows.
Map
×2.6 Fecha de la implementación
Si no se conoce el año preciso, indique la fecha aproximada:
- hace más de 50 años atrás (tradicional)
2.7 Introducción de la Tecnología
Especifique cómo se introdujo la Tecnología:
- como parte de un sistema tradicional (> 50 años)
Comentarios (tipo de proyecto, etc.):
the technology has been in use for about 80 years ago
3. Clasificación de la Tecnología MST
3.2 Tipo(s) actuales de uso de la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología
Mezcla de tipos de uso de tierras dentro de la misma unidad de tierras: :
Sí
Especifique el uso combinado de tierras (cultivos/ pastoreo/ árboles):
- Agropastoralismo (incluyendo cultivo-ganado integrados)

Tierras cultivadas
Número de temporadas de cultivo por año:
- 2
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 120Longest growing period from month to month: September to DecemberSecond longest growing period in days: 90Second longest growing period from month to month: March to May

Tierra de pastoreo
Pastoreo extenso:
- Pastoralismo semi-nómada
Tipo de animal:
- ganado - lechero
- cabras
- ovejas

Bosques
Comentarios:
Livestock density (if relevant):
10-25 LU /km2
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Eutrophication, siltation, water shortage, deforestation and wildfire outbreaks
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Drying of the underground water source.
Constraints of mines and extractive industries
Constraints of settlement / urban
Constraints of infrastructure network (roads, railways, pipe lines, power lines)
Constraints of wastelands / deserts / glaciers / swamps
Constraints of recreation
3.4 Provisión de agua
Provisión de agua para la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología:
- de secano
3.6 Medidas MST que componen la Tecnología

medidas vegetativas
- V1: Cubierta de árboles y arbustos
- V2: Pastos y plantas herbáceas perennes

medidas estructurales
- S11: Otros

medidas de manejo
- M7: Otros
Comentarios:
Specification of other structural measures: water collection pond and animal watering trough
Specification of other management measures: protect water source enclosure by naturally regenerating vegetation
3.7 Principales tipos de degradación del suelo encarados con la Tecnología

deterioro físico del suelo
- Pc: compactación

degradación biológica
- Bc: reducción de la cobertura vegetal del suelo

degradación del agua
- Hq: reducción de la calidad de subterráneas
Comentarios:
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (cutting of natural tree and removal of grass along the natural water flow way), overgrazing (Compaction by trampling animals, rainfall runoff, siltation of water collection point and disapearence of vegatative cover.), discharges (point contamination of water) (spoilage and contamination of surface water by human and livestock feaces.), population pressure (Overstocking due to increase in the number of livestock), poverty / wealth (low capacity to invest in enviromental friendly energy sources), inputs and infrastructure: (roads, markets, distribution of water points, other, …) (Unavailable improved and reliable water ponds and animal watering troughs), education, access to knowledge and support services (limited knowledge on sustainable use of natural water sources), governance / institutional (limited enforcement of existing environmental regulatory systems.)
Secondary causes of degradation: soil management (excavation and layout that contradict the natural environment), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (fire wood collection from the natural water source), industrial activities and mining, urbanisation and infrastructure development, release of airborne pollutants (urban/industry…), disturbance of water cycle (infiltration / runoff), over abstraction / excessive withdrawal of water (for irrigation, industry, etc.), other human induced causes (specify), change in temperature, change of seasonal rainfall, Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts), wind storms / dust storms, floods, droughts, other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify, land tenure, labour availability, war and conflicts
3.8 Prevención, reducción o restauración de la degradación del suelo
Especifique la meta de la Tecnología con relación a la degradación de la tierra:
- prevenir la degradación del suelo
- restaurar/ rehabilitar tierra severamente degradada
4. Especificaciones técnicas, actividades de implementación, insumos y costos
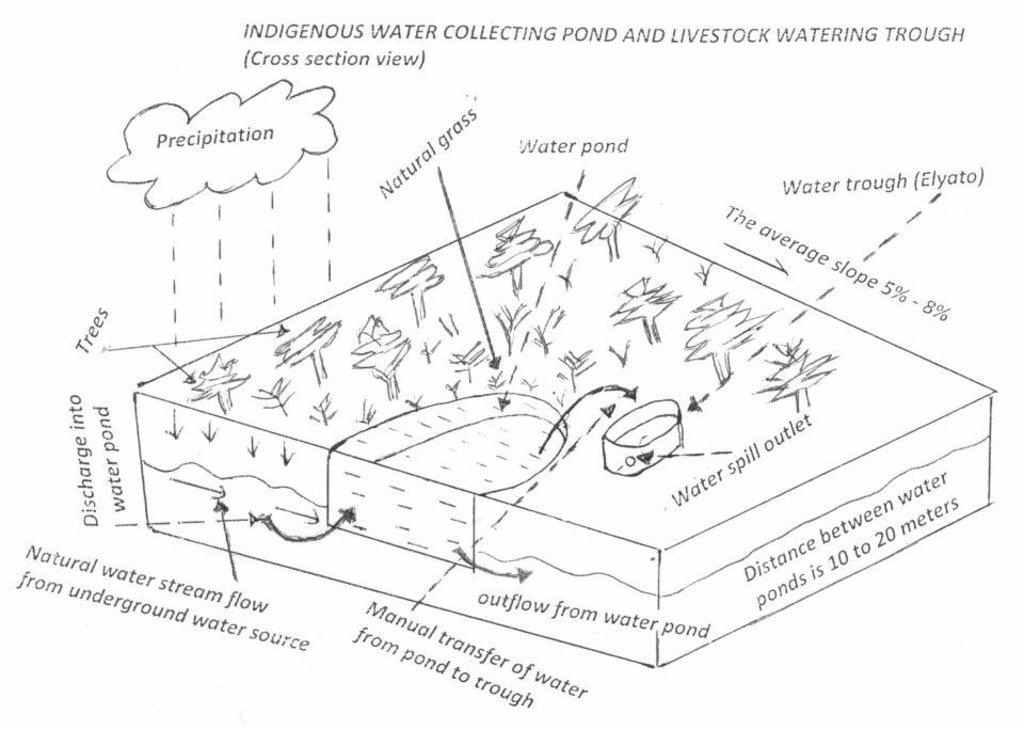
4.1 Dibujo técnico de la Tecnología
Especificaciones técnicas (relacionadas al dibujo técnico):
Water pond and water trough cross section view.
The water pond has an average internal capacity of size of 12m3 (4m length, 3m width and 1m depth).
Water troughs are constructed on the side of the water ponds. The water trough outside height is 0.2 - 0.4m above ground, inner depth is 0.5m, and diameter varies from 0.6 to 1m. It is made of cylindrical walls whose average width is 0.1m.
The average slope of the water catchment is 5% to 8%.
Location: Minziro village, Minziro ward, Missenyi division. Missenyi Dist, Kagera Reg, United Rep of Tanzania
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (At least primary school leaver with the basic indigenous technical knowledge.)
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, water harvesting / increase water supply, improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water
Secondary technical functions: improvement of ground cover, improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase / maintain water stored in soil, increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater, water spreading, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting, increase of biomass (quantity), control of fires, spatial arrangement and diversification of land use
Dam/ pan/ pond
Vertical interval between structures (m): 0
Spacing between structures (m): 10 to 20
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 3
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 4
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.3
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.3
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 4
Structural measure: water trough
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.5
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6 to 1
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6 to 1
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.2
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.1
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.6
Construction material (earth): mostry used clay soil and red termite mound soil.
Construction material (wood): for water pond and trough stabilization
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 8%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 8%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 5%
Specification of dams/ pans/ ponds: Capacity 10.6m3
Catchment area: 4 acresm2
For water harvesting: the ratio between the area where the harvested water is applied and the total area from which water is collected is: 1:4
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
Autor:
Allan Bubelwa, Box 38 Kyaka Missenyi
Fecha:
28/8/2012
4.2 Información general sobre el cálculo de insumos y costos
otra / moneda nacional (especifique):
Tanzanian shillings
Si fuera relevante, indique la tasa de cambio de dólares americanos a la moneda local (ej. 1 U$ = 79.9 Reales Brasileros): 1 U$ =:
1600,0
Indique el costo promedio del salario de trabajo contratado por día:
3.13
4.3 Actividades de establecimiento
| Actividad | Momento (estación) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Land preparation for pond excavation | During dry season |
| 2. | Construction of pond | During dry period |
| 3. | Construction of water trough | During dry season |
4.4 Costos e insumos necesarios para el establecimiento
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Land preparation for pond excavation | person/day | 1,0 | 1,25 | 1,25 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Construction of pond | person/day | 1,0 | 21,88 | 21,88 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Construction of water trough | person/day | 1,0 | 3,13 | 3,13 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | Tools | piece | 1,0 | 3,13 | 3,13 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | Tools | piece | 3,0 | 9,38 | 28,14 | 100,0 |
| Material de construcción | Wood | pieces | 2,0 | 1,25 | 2,5 | 100,0 |
| Material de construcción | Earth | kg | 20,0 | 1,25 | 25,0 | 100,0 |
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 85,03 | |||||
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología en USD | 0,05 | |||||
Comentarios:
Duration of establishment phase: 1 month(s)
4.5 Actividades de establecimiento/ recurrentes
| Actividad | Momento/ frequencia | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Desiltation | During dry season |
| 2. | Wall and bank strengthening and repair (reshaping and grass slashing/gap filling) | During dry season |
| 3. | Water trough repairing | dry season |
| 4. | Filling to and emptying water from water trough and collection and application of red termite mound soil. |
4.6 Costos e insumos necesarios para actividades de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (por año)
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Desiltation | person days | 5,0 | 6,25 | 31,25 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Wall and bank strengthening and repair (reshaping and grass slashing/gap filling) | person days | 5,0 | 6,25 | 31,25 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Water trough repairing | person days | 8,0 | 10,0 | 80,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Filling to and emptying water from water trough and collection and application of red termite mound soil. | person days | 450,0 | 1,25 | 562,5 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | Tools | pieces | 2,0 | 5,0 | 10,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | Water can | pieces | 2,0 | 1,88 | 3,76 | 100,0 |
| Material de construcción | Wood | pieces | 6,0 | 3,75 | 22,5 | 100,0 |
| Material de construcción | Earth | kg | 60,0 | 3,75 | 225,0 | 100,0 |
| Indique los costos totales para mantenecer la Tecnología | 966,26 | |||||
| Costos totales para mantener la Tecnología en USD | 0,6 | |||||
Comentarios:
The cost is calculated per one water pond and its one trough and as per 28 August 2012
4.7 Factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Describa los factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Labour is the most determinant factor affecting the costs
5. Entorno natural y humano
5.1 Clima
Lluvia anual
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Zona agroclimática
- húmeda
- Sub-húmeda
Thermal climate class: tropics. all months temperature is above 18
Thermal climate class: subtropics
Thermal climate class: temperate
Thermal climate class: boreal
Thermal climate class: polar/arctic
5.2 Topografía
Pendientes en promedio:
- plana (0-2 %)
- ligera (3-5%)
- moderada (6-10%)
- ondulada (11-15%)
- accidentada (16-30%)
- empinada (31-60%)
- muy empinada (>60%)
Formaciones telúricas:
- meseta/ planicies
- cordilleras
- laderas montañosas
- laderas de cerro
- pies de monte
- fondo del valle
Zona altitudinal:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1,000 m s.n.m
- 1,001-1,500 m s.n.m
- 1,501-2,000 m s.n.m
- 2,001-2,500 m s.n.m
- 2,501-3,000 m s.n.m
- 3,001-4,000 m s.n.m
- > 4,000 m s.n.m
5.3 Suelos
Profundidad promedio del suelo:
- muy superficial (0-20 cm)
- superficial (21-50 cm)
- moderadamente profunda (51-80 cm)
- profunda (81-120 cm)
- muy profunda (>120 cm)
Textura del suelo (capa arable):
- fina/ pesada (arcilla)
Materia orgánica de capa arable:
- media (1-3%)
- baja (<1%)
5.4 Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
Agua subterránea:
en superficie
Disponibilidad de aguas superficiales:
bueno
Calidad de agua (sin tratar):
agua potable de buena calidad
5.6 Las características de los usuarios de la tierra que aplican la Tecnología
Orientación del mercado del sistema de producción:
- mixta (subsistencia/ comercial)
Nivel relativo de riqueza:
- promedio
Individuos o grupos:
- individual/ doméstico
Género:
- mujeres
- hombres
Indique otras características relevantes de los usuarios de las tierras:
Difference in the involvement of women and men: little involvement of women because at large/traditionally livestock rearing is done by men.
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
5% of the land users are rich and own 5% of the land.
10% of the land users are average wealthy and own 35% of the land (the techology is used by rich and average livestock keepers who have the animal).
75% of the land users are poor and own 40% of the land (the village poors usually do not have the animals though most of them are cattle herders).
10% of the land users are poor and own 20% of the land.
5.7 Área promedio de la tierra usada por usuarios de tierra que aplican la Tecnología
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
¿Esto se considera de pequeña, mediana o gran escala (refiriéndose al contexto local)?
- pequeña escala
5.8 Tenencia de tierra, uso de tierra y derechos de uso de agua
Tenencia de tierra:
- comunitaria/ aldea
- individual, sin título
Derechos de uso de tierra:
- individual
Derechos de uso de agua:
- comunitarios (organizado)
- individual
5.9 Acceso a servicios e infraestructura
salud:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
educación:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
asistencia técnica:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
empleo (ej. fuera de la granja):
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
mercados:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
caminos y transporte:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
agua potable y saneamiento:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
6. Impactos y comentarios para concluir
6.1 Impactos in situ demostrados por la Tecnología
Impactos socioeconómicos
Producción
producción animal
diversidad de producto
generación de energía
Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
disponibilidad de agua potable
Ingreso y costos
diversidad de fuentes de ingreso
disparidades económicas
Impactos socioculturales
instituciones comunitarias
instituciones nacionales
MST/ conocimiento de la degradación del suelo
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo de agua/ escurrimiento de sedimento
cantidad de agua
calidad de agua
cosecha/ recolección de agua
escurrimiento superficial
nivel freático/ acuífero
evaporación
Suelo
humedad del suelo
ciclo/ recarga de nutrientes
Biodiversidad: vegetación, animales
biomasa/ sobre suelo C
diversidad de hábitats
control de pestes/ enfermedades
Reducción de riesgos de desastres y riesgos climáticos
emisión de carbono y gases de invernadero
riesgo de incendio
velocidad de viento
6.2 Impactos fuera del sitio demostrados por la Tecnología
corriente confiable y estable fluye en estación seca
inundaciones río abajo
capacidad de amortiguación/ filtrado
daño a campos de vecinos
6.3 Exposición y sensibilidad de la Tecnología al cambio climático gradual y a extremos relacionados al clima/ desastres (desde la percepción de los usuarios de tierras)
Cambio climático gradual
Cambio climático gradual
| Estación | Incremento o reducción | ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| temperatura anual | incrementó | bien |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados al clima
Desastres climatológicos:
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| tormenta de lluvia local | no muy bien |
| tormenta de viento | bien |
Desastres climatológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| sequía | bien |
Desastres hidrológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| inundación general (río) | no muy bien |
Otras consecuencias relacionadas al clima
Otras consecuencias relacionadas al clima
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| periodo reducido de crecimiento | no se sabe |
Comentarios:
Improving structure on the pond (use impermeable materials to prevent seepage, use concrete as a building material)
6.4 Análisis costo-beneficio
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de establecimiento (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
positivo
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
positivo
Comentarios:
The technology requires low establishment and maintenance cost and benefit surpass the costs.
6.5 Adopción de la Tecnología
De todos quienes adoptaron la Tecnología, ¿cuántos lo hicieron espontáneamente, por ej. sin recibir nada de incentivos/ materiales:
- 11-50%
Comentarios:
12% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
250 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
All livestock keepers use the technology to water their animals voluntary and through self mobilization.
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
The technology is cheap and requires low investment costs.
6.7 Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades de la Tecnología
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra |
|---|
|
Income generation due to water use fee. How can they be sustained / enhanced? improve service to water users. . |
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
|
Reduce conflict between livestock keepers and domestic water users. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Bylaws reinforcement, Area enclosure and Demarcation |
|
Improve accessibility of water to animals (improved animal water intake) How can they be sustained / enhanced? sensitization on regular maintenance. |
6.8 Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos de la Tecnología y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| Not durable and requires frequent and regular maintenance | Sensitize on regular maintenance. |
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| not durable | Sensitize on regular maintenance. |
| high labor demand to fill the troughs | Use simple leverage pump |
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.1 Métodos/ fuentes de información
7.2 Vínculos a las publicaciones disponibles
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
Kagera TAMP project website
¿Dónde se halla disponible? ¿Costo?
http://www.fao.org/nr/kagera/en/
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos
No hay vínculos
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos