Indigenous water collecting pond and livestock watering trough [ຕານຊາເນຍ]
- ການສ້າງ:
- ປັບປູງ:
- ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ: ALLAN BUBELWA
- ບັນນາທິການ: –
- ຜູ້ທົບທວນຄືນ: Donia Mühlematter, Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
elyeshero ne elyato (Haya tribe)
technologies_1157 - ຕານຊາເນຍ
- ສະຫຼຸບສັງລວມຢ່າງທັງໝົດທີ່ເປັນ PDF
- ສັງລວມເປັນບົດ PDF ເພື່ອສັ່ງພິມ
- ສັງລວມເປັນບົດ ຢູ່ໃນ browser
- ບົດສະຫຼຸບ ສະບັບເຕັມ (ບໍ່ມີແບບຟອມ)
- Indigenous water collecting pond and livestock watering trough: Dec. 29, 2016 (inactive)
- Indigenous water collecting pond and livestock watering trough: June 5, 2017 (inactive)
- Indigenous water collecting pond and livestock watering trough: June 28, 2018 (inactive)
- Indigenous water collecting pond and livestock watering trough: Aug. 6, 2019 (public)
ເບິ່ງພາກສ່ວນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດ1. ຂໍ້ມູນທົ່ວໄປ
1.2 ຂໍ້ມູນ ການຕິດຕໍ່ພົວພັນ ຂອງບຸກຄົນທີ່ສໍາຄັນ ແລະ ສະຖາບັນ ທີ່ມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ໃນການປະເມີນເອກກະສານ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ບັນດາຜູ້ຕອບແບບສອບຖາມທີ່ສໍາຄັນ ()
government:
Kagaruki Annagrace
Misseny District Council
ຜຸ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
government:
ຊື່ສະຖາບັນ (ຫຼາຍສະຖາບັນ) ທີ່ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກ ໃນການສ້າງເອກກະສານ / ປະເມີນ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ)
Missenyi District Council (Missenyi District Council) - ຕານຊາເນຍຊື່ສະຖາບັນ (ຫຼາຍສະຖາບັນ) ທີ່ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກ ໃນການສ້າງເອກກະສານ / ປະເມີນ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ)
FAO Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO Food and Agriculture Organization) - ອີຕາລີ1.3 ເງື່ອນໄຂ ກ່ຽວກັບ ການນໍາໃຊ້ຂໍ້ມູນເອກະສານ ທີ່ສ້າງຂື້ນ ໂດຍຜ່ານ ອົງການພາບລວມຂອງໂລກ ທາງດ້ານແນວທາງ ແລະ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຂອງການອານຸລັກ ທໍາມະຊາດ (WOCAT)
ຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ແລະ ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ ທີ່ໃຫ້ຂໍ້ມູນ (ຫຼາຍ) ຍິນຍອມ ຕາມເງື່ອນໄຂ ໃນການນຳໃຊ້ຂໍ້ມູນ ເພື່ອສ້າງເປັນເອກກະສານຂອງ WOCAT:
ແມ່ນ
2. ການອະທິບາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຂອງການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
2.1 ຄໍາອະທິບາຍສັ້ນຂອງ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການກຳໜົດຄວາມໝາຍ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
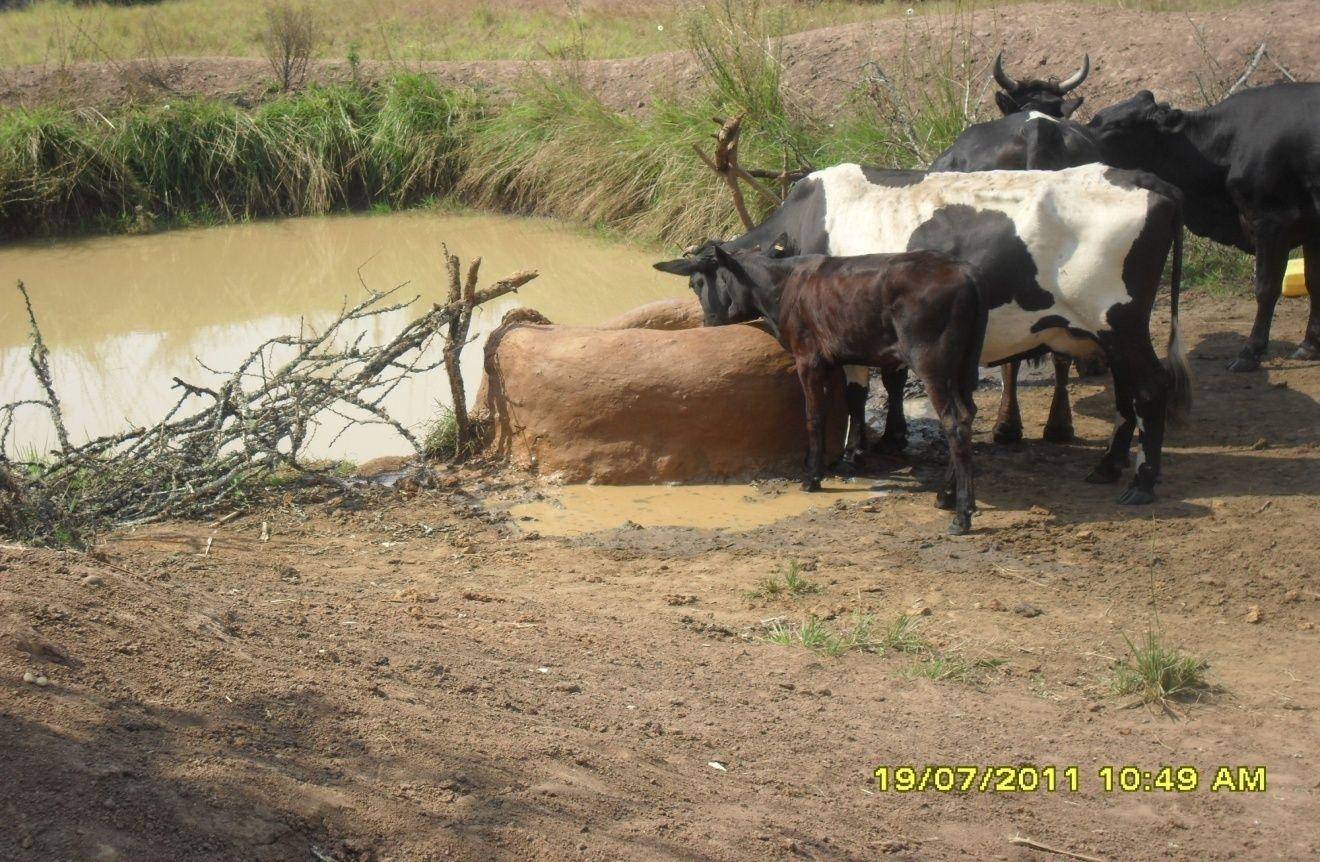
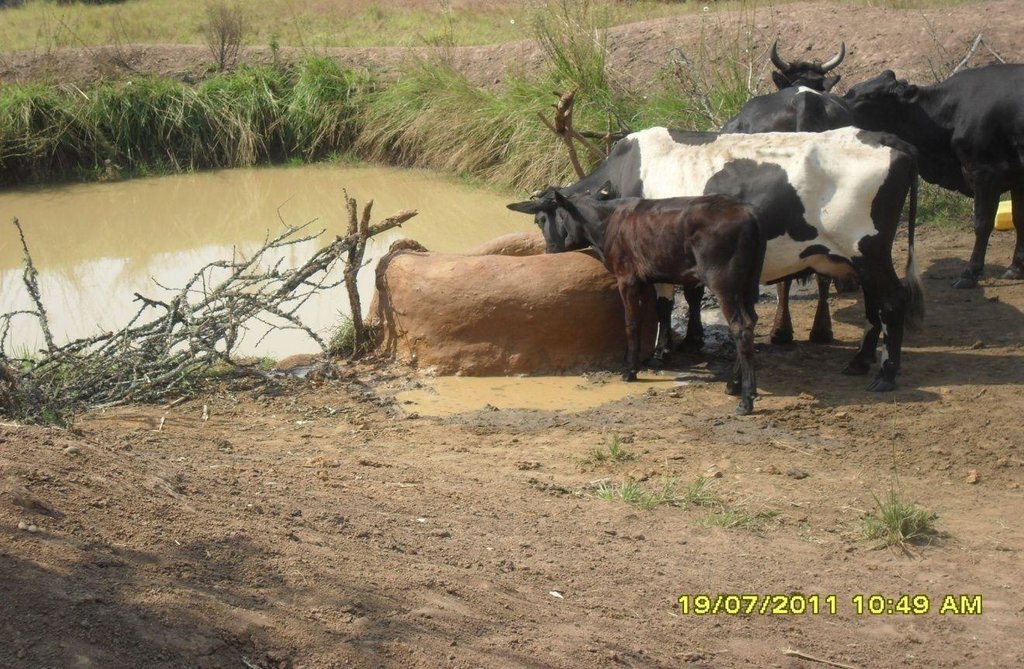
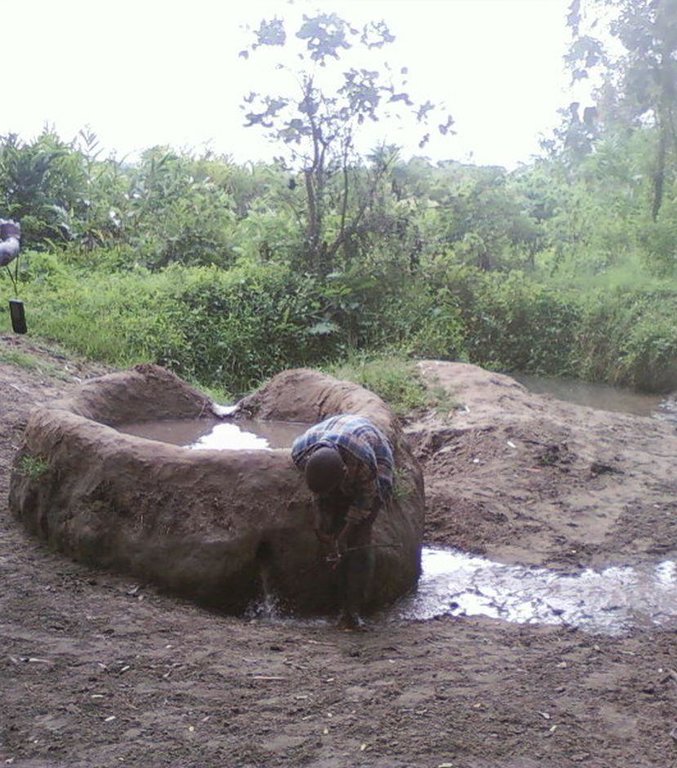
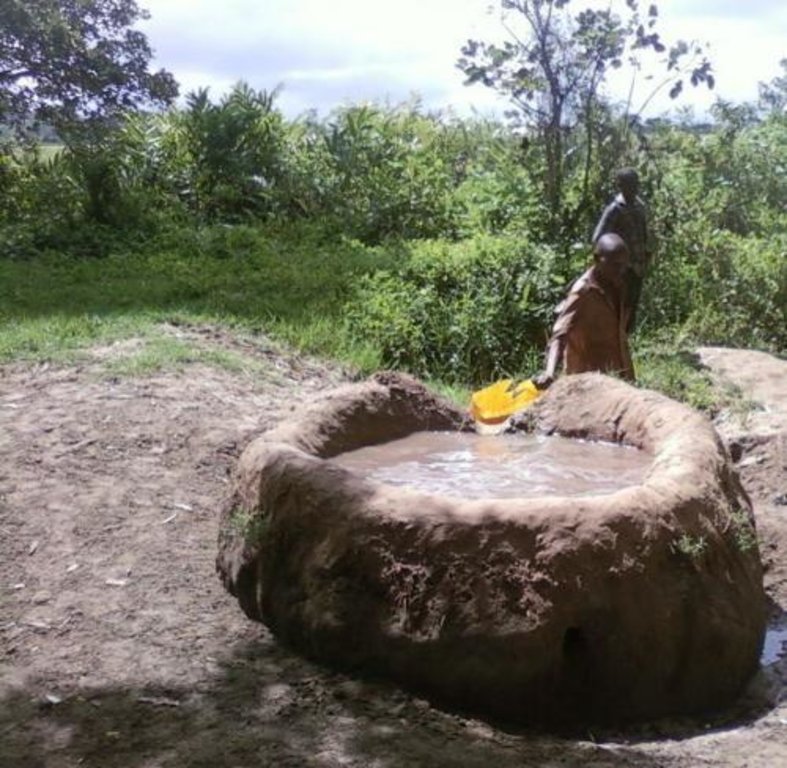
Construction of indigenous water pond and a livestock watering trough along an underground water source.
2.2 ການອະທິບາຍ ລາຍລະອຽດ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການພັນລະນາ:
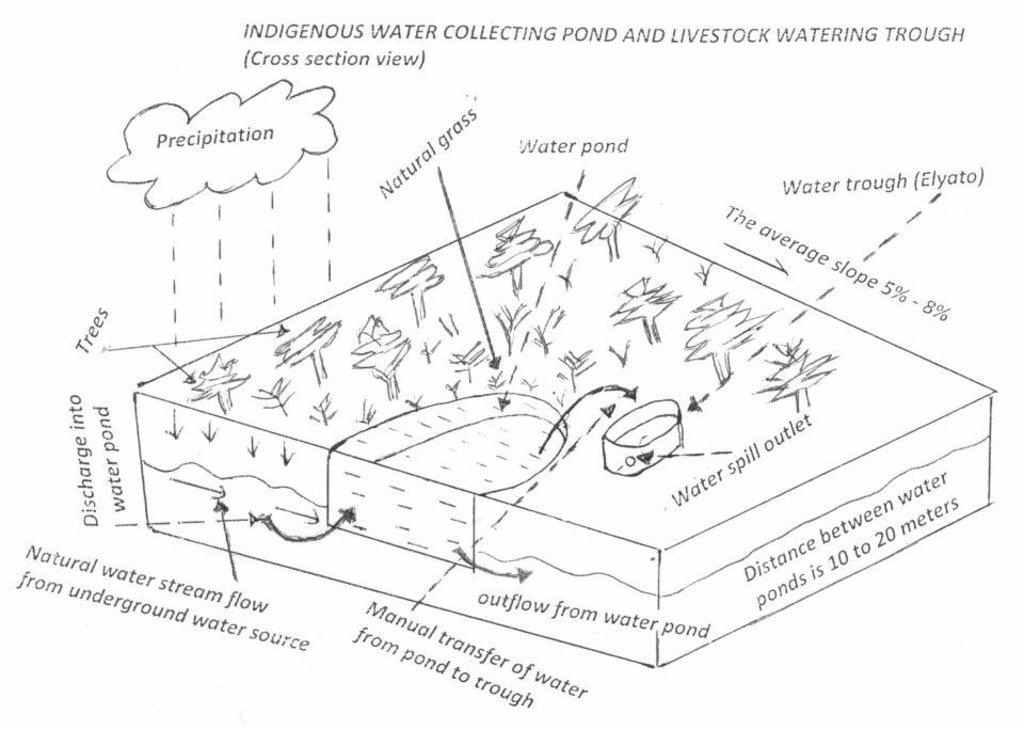
This technology is used during the dry seasons and where ground water level is high and there is natural water stream flowing from underground water source. Water pond is excavated along the naturally flowing water stream and is recharged by natural ground water. The size of the pond will vary depending on the area available, groundwater table, slope and soil characteristic. Groundwater collection ponds described in this technology on average are 4m long, 3m wide and 1m deep of 12m3 (12 000 liter) capacity and the slope is moderate 5% to 8% and soil characteristics is clay loam with deep soil. Water troughs (Elyato by local name) are constructed adjacent to the water pond to allow livestock to access clean drinking water. The number of troughs per pond is usually 1 to 2. Materials used in construction of water trough include clay, red termite mound soil, grass and wooden poles. The number of ponds needed usually depends on the expected number of animals and are arranged at irregular intervals ranging from 10 to 20 meters apart. The average size of a water trough is 0.14 m3 and can cater for 5 cattle at a time. The Pond is stabilized by naturally growing grass on its banks. Common pond stabilizer species are Leodicatiar digitalia and Hyperrhenia rufa. Management of the natural water source is through preventive village/customary by-laws which prohibit tree and grass cutting around the water source. The dominant indicator tree species normally found are Erythrina abysinica, Ficus thorgii and Phoenix recrinata. The animal watering troughs are usually used in the dry period. Before watering the troughs are coated (smeared) with red termite mound soil (normally hand carried by herders) to provide a good taste which is attractive to animals. Water is transferred from the pond to the water trough manually using cans or buckets. Animals drink directly from the troughs. This water from the trough is rich in iron (Fe) from red termite mound soil. The troughs are constructed with outlets used to spill out water immediately after drinking in order to prevent their damage through excessive water saturation.
Purpose of the Technology: This technology is preferred by livestock keepers as it provides for animals to drink clean and mineralized water and for health improvement. User fee payed to land owners also enable them to expand and diversify there income sources.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Establishment: Land clearing, excavation and shaping of water pond and construction of animal watering trough.
Maintenance: repair of water pond and water trough (de-siltation, grass slashing and gap refilling).
Inputs: labour, implements (machete, spade, hand hoe, sickle), clay, red termite mound soil, wooden poles, buckets, grass and tying rope. Average establishment cost for one pond and its water trough is 41.27 American dollars. Average annual maintenance and recurrent costs (filling and emptying of water trough) for one pond and its water trough stands at 458.76 dollars and labour is a core cost determinant factor.
Natural / human environment: Natural environment: Extensive grazing land. The technology is largely structural (excavation and shaping of water ponds and construction of water troughs) supported by the use of by-laws which prohibit destruction of the protective natural and indicative trees and grasses around. The technology is common in sub-humid climatic zone.
Social economic environment: Level of mechanization is handy tools with subsistence production systems on individual fields.
2.3 ຮູບພາບຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
2.5 ປະເທດ / ເຂດ / ສະຖານທີ່ບ່ອນທີ່ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຮັບການນໍາໃຊ້ ແລະ ທີ່ຖືກປົກຄຸມດ້ວຍການປະເມີນຜົນ
ປະເທດ:
ຕານຊາເນຍ
ພາກພື້ນ / ລັດ / ແຂວງ:
Tanzania
ຂໍ້ມູນເພີ່ມເຕີມຂອງສະຖານທີ່:
Missenyi District (Minziro)
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ການແຜ່ຂະຫຍາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
- ແຜ່ຂະຫຍາຍຢ່າງໄວວາໃນພື້ນທີ່
ຖ້າຫາກບໍ່ຮູ້ເນື້ອທີ່ທີ່ແນ່ນອນ, ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເນື້ອທີ່ໂດຍປະມານ ທີ່ໃກ້ຄຽງ:
- < 0.1 ກິໂລແມັດ2 (10 ເຮັກຕາ)
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Boundary points of the Technology area: -1.11472, 31.655 ; -1,09972, 31.70194
The area is owned by individual farmer. The area is found adjacent to extensive grazing land. Water table is high and there is a permanent underground natural water flows.
Map
×2.6 ວັນທີໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ
ຖ້າຫາກວ່າ ບໍ່ຮູ້ຈັກ ປີທີ່ຊັດເຈນ ແມ່ນໃຫ້ປະມານ ວັນທີເອົາ:
- ຫຼາຍກ່ອນ 50 ປີຜ່ານມາ (ແບບພື້ນບ້ານ)
2.7 ການນໍາສະເໜີ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຖືກຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດຄືແນວໃດ?
- ເປັນສ່ວນໜື່ງຂອງລະບົບພື້ນເມືອງ (>50 ປີ)
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ (ປະເພດ ໂຄງການ ແລະ ອື່ນໆ):
the technology has been in use for about 80 years ago
3. ການໃຈ້ແຍກ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໃນການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
3.2 ປະເພດການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃນປະຈຸບັນ() ທີ່ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຖືກນໍາໃຊ້
ການນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ປະສົມພາຍໃນພື້ນທີ່ດຽວກັນ:
ແມ່ນ
ລະບຸການນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນແບບປະສົມ (ຜົນລະປູກ / ທົ່ງຫຍ້າລ້ຽງສັດ / ຕົ້ນໄມ້):
- ກະສິກໍາແບບປະສົມປະສານ (ລວມທັງ ການລ້ຽງສັດ-ປຸກຝັງ)

ດິນທີ່ປູກພືດ
ຈໍານວນ ລະດູການ ປູກໃນປີໜຶ່ງ:
- 2
ລະບຸ ຊະນິດ:
Longest growing period in days: 120Longest growing period from month to month: September to DecemberSecond longest growing period in days: 90Second longest growing period from month to month: March to May

ທົ່ງຫຍ້າລ້ຽງສັດ
ການລ້ຽງສັດແບບປ່ອຍ ຕາມທຳມະຊາດ:
- ການລ້ຽງສັດແບບເຄີ່ງປ່ອຍ
ປະເພດສັດ:
- ສັດໃຫ່ຍ-ງົວພັນນົມ
- ແບ້
- ແກະ

ປ່າໄມ້ / ປ່າ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Livestock density (if relevant):
10-25 LU /km2
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Eutrophication, siltation, water shortage, deforestation and wildfire outbreaks
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Drying of the underground water source.
Constraints of mines and extractive industries
Constraints of settlement / urban
Constraints of infrastructure network (roads, railways, pipe lines, power lines)
Constraints of wastelands / deserts / glaciers / swamps
Constraints of recreation
3.4 ການສະໜອງນ້ຳ
ການສະໜອງນໍ້າ ໃນພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
- ນໍ້າຝົນ
3.6 ມາດຕະການ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ ປະກອບດ້ວຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ

ມາດຕະການ ທາງດ້ານພືດພັນ
- V1: ເປັນໄມ້ຢືນຕົ້ນ ແລະ ການປົກຫຸ້ມຂອງໄມ້ພຸ່ມ
- V2: ຫຍ້າ ແລະ ພືດສະໝູນໄພທີ່ເປັນໄມ້ຢືນຕົ້ນ

ມາດຕະການໂຄງສ້າງ
- S11: ອື່ນໆ

ມາດຕະການ ທາງດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ
- M7: ອື່ນໆ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Specification of other structural measures: water collection pond and animal watering trough
Specification of other management measures: protect water source enclosure by naturally regenerating vegetation
3.7 ປະເພດດິນເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ຫຼັກທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ

ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ຂອງດິນ ທາງກາຍະພາບ
- Pc: ການອັດແໜ້ນ

ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ທາງຊີວະພາບ
- Bc: ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນການປົກຫຸ້ມຂອງພືດ

ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ຂອງນໍ້າ
- Hp: ຄຸນນະພາບ ຂອງນ້ຳຊັ້ນໜ້າດິນຫຼຸດລົງ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (cutting of natural tree and removal of grass along the natural water flow way), overgrazing (Compaction by trampling animals, rainfall runoff, siltation of water collection point and disapearence of vegatative cover.), discharges (point contamination of water) (spoilage and contamination of surface water by human and livestock feaces.), population pressure (Overstocking due to increase in the number of livestock), poverty / wealth (low capacity to invest in enviromental friendly energy sources), inputs and infrastructure: (roads, markets, distribution of water points, other, …) (Unavailable improved and reliable water ponds and animal watering troughs), education, access to knowledge and support services (limited knowledge on sustainable use of natural water sources), governance / institutional (limited enforcement of existing environmental regulatory systems.)
Secondary causes of degradation: soil management (excavation and layout that contradict the natural environment), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (fire wood collection from the natural water source), industrial activities and mining, urbanisation and infrastructure development, release of airborne pollutants (urban/industry…), disturbance of water cycle (infiltration / runoff), over abstraction / excessive withdrawal of water (for irrigation, industry, etc.), other human induced causes (specify), change in temperature, change of seasonal rainfall, Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts), wind storms / dust storms, floods, droughts, other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify, land tenure, labour availability, war and conflicts
3.8 ການປ້ອງກັນ, ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ, ຫຼືການຟື້ນຟູຂອງການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເປົ້າໝາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ພົວພັນ ກັບຄວາມເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ:
- ປ້ອງກັນການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
- ການຟື້ນຟູ / ຟື້ນຟູດິນທີ່ຊຸດໂຊມ
4. ຂໍ້ກໍາໜົດ, ກິດຈະກໍາການປະຕິບັດ, ວັດຖຸດິບ, ແລະຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
4.1 ເຕັກນິກ ໃນການແຕ້ມແຜນວາດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງເຕັກນິກ (ທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ ກັບການແຕ້ມແຜນວາດ ທາງດ້ານເຕັກນີກ):
Water pond and water trough cross section view.
The water pond has an average internal capacity of size of 12m3 (4m length, 3m width and 1m depth).
Water troughs are constructed on the side of the water ponds. The water trough outside height is 0.2 - 0.4m above ground, inner depth is 0.5m, and diameter varies from 0.6 to 1m. It is made of cylindrical walls whose average width is 0.1m.
The average slope of the water catchment is 5% to 8%.
Location: Minziro village, Minziro ward, Missenyi division. Missenyi Dist, Kagera Reg, United Rep of Tanzania
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (At least primary school leaver with the basic indigenous technical knowledge.)
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, water harvesting / increase water supply, improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water
Secondary technical functions: improvement of ground cover, improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase / maintain water stored in soil, increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater, water spreading, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting, increase of biomass (quantity), control of fires, spatial arrangement and diversification of land use
Dam/ pan/ pond
Vertical interval between structures (m): 0
Spacing between structures (m): 10 to 20
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 3
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 4
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.3
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.3
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 4
Structural measure: water trough
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.5
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6 to 1
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6 to 1
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.2
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.1
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.6
Construction material (earth): mostry used clay soil and red termite mound soil.
Construction material (wood): for water pond and trough stabilization
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 8%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 8%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 5%
Specification of dams/ pans/ ponds: Capacity 10.6m3
Catchment area: 4 acresm2
For water harvesting: the ratio between the area where the harvested water is applied and the total area from which water is collected is: 1:4
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
ຜູ້ຂຽນ:
Allan Bubelwa, Box 38 Kyaka Missenyi
ວັນທີ:
28/8/2012
4.2 ຂໍ້ມູນທົ່ວໄປກ່ຽວກັບການຄິດໄລ່ປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າໃນການຜະລິດ ແລະ ມູນຄ່າອື່ນໆ
ສະກຸນເງິນອື່ນໆ / ປະເທດອື່ນໆ (ລະບຸ):
Tanzanian shillings
ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ, ໃຫ້ລະບຸອັດຕາແລກປ່ຽນຈາກ USD ເປັນສະກຸນເງິນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ (ເຊັ່ນ: 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
1600.0
ລະບຸ ຄ່າຈ້າງ ຄ່າແຮງງານສະເລ່ຍ ຕໍ່ ວັນ:
3.13
4.3 ການສ້າງຕັ້ງກິດຈະກໍາ
| ກິດຈະກໍາ | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Land preparation for pond excavation | During dry season |
| 2. | Construction of pond | During dry period |
| 3. | Construction of water trough | During dry season |
4.4 ຕົ້ນທຶນ ແລະ ປັດໄຈຂາເຂົ້າທີ່ຈໍາເປັນໃນຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ
| ລະບຸ ປັດໃຈ ນໍາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລີດ | ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ປະລິມານ | ຕົ້ນທຶນ ຕໍ່ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ຂອງປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດ | % ຂອງຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ຈ່າຍເອງ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ແຮງງານ | Land preparation for pond excavation | person/day | 1.0 | 1.25 | 1.25 | 100.0 |
| ແຮງງານ | Construction of pond | person/day | 1.0 | 21.88 | 21.88 | 100.0 |
| ແຮງງານ | Construction of water trough | person/day | 1.0 | 3.13 | 3.13 | 100.0 |
| ອຸປະກອນ | Tools | piece | 1.0 | 3.13 | 3.13 | 100.0 |
| ອຸປະກອນ | Tools | piece | 3.0 | 9.38 | 28.14 | 100.0 |
| ວັດສະດຸກໍ່ສ້າງ | Wood | pieces | 2.0 | 1.25 | 2.5 | 100.0 |
| ວັດສະດຸກໍ່ສ້າງ | Earth | kg | 20.0 | 1.25 | 25.0 | 100.0 |
| ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ | 85.03 | |||||
| ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍທັງໝົດ ສຳລັບການສ້າງຕັ້ງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ເປັນສະກຸນເງີນໂດລາ | 0.05 | |||||
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Duration of establishment phase: 1 month(s)
4.5 ບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ / ແຜນຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ກິດຈະກໍາ
| ກິດຈະກໍາ | ໄລຍະເວລາ / ຄວາມຖີ່ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Desiltation | During dry season |
| 2. | Wall and bank strengthening and repair (reshaping and grass slashing/gap filling) | During dry season |
| 3. | Water trough repairing | dry season |
| 4. | Filling to and emptying water from water trough and collection and application of red termite mound soil. |
4.6 ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ ແລະ ປັດໄຈນໍາເຂົ້າທີ່ຈໍາເປັນສໍາລັບການບໍາລຸງຮັກສາກິດຈະກໍາ / ແຜນປະຕິບັດ (ຕໍ່ປີ)
| ລະບຸ ປັດໃຈ ນໍາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລີດ | ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ປະລິມານ | ຕົ້ນທຶນ ຕໍ່ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ຂອງປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດ | % ຂອງຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ຈ່າຍເອງ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ແຮງງານ | Desiltation | person days | 5.0 | 6.25 | 31.25 | 100.0 |
| ແຮງງານ | Wall and bank strengthening and repair (reshaping and grass slashing/gap filling) | person days | 5.0 | 6.25 | 31.25 | 100.0 |
| ແຮງງານ | Water trough repairing | person days | 8.0 | 10.0 | 80.0 | 100.0 |
| ແຮງງານ | Filling to and emptying water from water trough and collection and application of red termite mound soil. | person days | 450.0 | 1.25 | 562.5 | 100.0 |
| ອຸປະກອນ | Tools | pieces | 2.0 | 5.0 | 10.0 | 100.0 |
| ອຸປະກອນ | Water can | pieces | 2.0 | 1.88 | 3.76 | 100.0 |
| ວັດສະດຸກໍ່ສ້າງ | Wood | pieces | 6.0 | 3.75 | 22.5 | 100.0 |
| ວັດສະດຸກໍ່ສ້າງ | Earth | kg | 60.0 | 3.75 | 225.0 | 100.0 |
| ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ໃຊ້ໃນການບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ | 966.26 | |||||
| ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍທັງໝົດ ສຳລັບການບົວລະບັດຮກສາເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ເປັນສະກຸນເງີນໂດລາ | 0.6 | |||||
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
The cost is calculated per one water pond and its one trough and as per 28 August 2012
4.7 ປັດໄຈ ທີ່ສໍາຄັນ ທີ່ສົ່ງຜົນກະທົບ ຕໍ່ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
ໃຫ້ອະທິບາຍ ປັດໃຈ ທີ່ສົ່ງຜົນກະທົບ ຕໍ່ຕົ້ນທຶນ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ:
Labour is the most determinant factor affecting the costs
5. ສະພາບແວດລ້ອມທໍາມະຊາດ ແລະ ມະນຸດ
5.1 ອາກາດ
ປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນປະຈໍາປີ
- < 250 ມີລິແມັດ
- 251-500 ມີລິແມັດ
- 501-750 ມີລິແມັດ
- 751-1,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 1,001-1,500 ມີລິແມັດ
- 1,501-2,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 2,001-3,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 3,001-4,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- > 4,000 ມີລິແມັດ
ເຂດສະພາບອາກາດກະສິກໍາ
- ຄວາມຊຸ່ມ
- ເຄີ່ງຄວາມຊຸ່ມ
Thermal climate class: tropics. all months temperature is above 18
Thermal climate class: subtropics
Thermal climate class: temperate
Thermal climate class: boreal
Thermal climate class: polar/arctic
5.2 ພູມິປະເທດ
ຄ່າສະເລ່ຍ ຄວາມຄ້ອຍຊັນ:
- ພື້ນທີ່ຮາບພຽງ (0-2%)
- ອ່ອນ (3-5 %)
- ປານກາງ (6-10 %)
- ມ້ວນ (11-15 %)
- ເນີນ(16-30%)
- ໍຊັນ (31-60%)
- ຊັນຫຼາຍ (>60%)
ຮູບແບບຂອງດິນ:
- ພູພຽງ / ທົ່ງພຽງ
- ສັນພູ
- ເປີ້ນພູ
- ເນີນພູ
- ຕີນພູ
- ຮ່ອມພູ
ເຂດລະດັບສູງ:
- 0-100 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 101-500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- > 4,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
5.3 ດິນ
ຄວາມເລິກ ຂອງດິນສະເລ່ຍ:
- ຕື້ນຫຼາຍ (0-20 ຊັງຕີແມັດ)
- ຕື້ນ (21-50 ຊຕມ)
- ເລີກປານກາງ (51-80 ຊຕມ)
- ເລິກ (81-120 ຊມ)
- ເລິກຫຼາຍ (> 120 cm)
ເນື້ອດິນ (ໜ້າດິນ):
- ບາງລະອຽດ / ໜັກ (ໜຽວ)
ຊັ້ນອິນຊີວັດຖຸ ເທິງໜ້າດິນ:
- ປານກາງ (1-3 %)
- ຕໍາ່ (<1 %)
5.4 ມີນໍ້າ ແລະ ຄຸນນະພາບ
ລະດັບ ນໍ້າໃຕ້ດິນ:
ເທິງຊັ້ນໜ້າດິນ
ການມີນໍ້າ ເທິງໜ້າດິນ:
ດີ
ຄຸນນະພາບນໍ້າ (ບໍ່ມີການບໍາບັດ):
ມີນໍ້າດື່ມ
5.6 ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ລະບົບ ການຕະຫຼາດ ແລະ ຜົນຜະລິດ:
- ປະສົມປົນເປ( ກຸ້ມຕົນເອງ/ເປັນສິນຄ້າ)
ລະດັບຄວາມຮັ່ງມີ:
- ສະເລ່ຍ
ບຸກຄົນ ຫຼື ກຸ່ມ:
- ບຸກຄົນ / ຄົວເຮືອນ
ເພດ:
- ຜູ້ຍິງ
- ຜູ້ຊາຍ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
Difference in the involvement of women and men: little involvement of women because at large/traditionally livestock rearing is done by men.
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
5% of the land users are rich and own 5% of the land.
10% of the land users are average wealthy and own 35% of the land (the techology is used by rich and average livestock keepers who have the animal).
75% of the land users are poor and own 40% of the land (the village poors usually do not have the animals though most of them are cattle herders).
10% of the land users are poor and own 20% of the land.
5.7 ເນື້ອທີ່ສະເລ່ຍຂອງດິນ ທີ່ຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ເຮັດເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
- <0.5 ເຮັກຕາ
- 0.5-1 ເຮັກຕາ
- 1-2 ເຮັກຕາ
- 2-5 ເຮັກຕາ
- 5-15 ເຮັກຕາ
- 15-50 ເຮັກຕາ
- 50-100 ເຮັກຕາ
- 100-500 ເຮັກຕາ
- 500-1,000 ເຮັກຕາ
- 1,000-10,000 ເຮັກຕາ
- > 10,000 ເຮັກຕາ
ຖືໄດ້ວ່າ ເປັນຂະໜາດນ້ອຍ, ກາງ ຫຼື ໃຫຍ່ (ອີງຕາມເງື່ອນໄຂ ສະພາບຄວາມເປັນຈິງ ຂອງທ້ອງຖີ່ນ)? :
- ຂະໜາດນ້ອຍ
5.8 ເຈົ້າຂອງທີ່ດິນ, ສິດໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ, ແລະ ສິດທິການນໍາໃຊ້ນໍ້າ
ເຈົ້າຂອງດິນ:
- ຊຸມຊົນ / ບ້ານ
- ບຸກຄົນ, ບໍ່ມີຕໍາແໜ່ງ
ສິດທິ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
- ບຸກຄົນ
ສິດທິ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ນໍ້າ:
- ຊຸມຊົນ (ທີ່ມີການຈັດຕັ້ງ)
- ບຸກຄົນ
5.9 ການເຂົ້າເຖິງການບໍລິການ ແລະ ພື້ນຖານໂຄງລ່າງ
ສຸຂະພາບ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການສຶກສາ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອ ດ້ານວິຊາການ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການຈ້າງງານ (ຕົວຢ່າງ, ການເຮັດກິດຈະກໍາອື່ນ ທີ່ບໍ່ແມ່ນ ການຜະລິດກະສິກໍາ):
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ຕະຫຼາດ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ຖະໜົນຫົນທາງ ແລະ ການຂົນສົ່ງ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການດື່ມນໍ້າ ແລະ ສຸຂາພິບານ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
6. ຜົນກະທົບ ແລະ ລາຍງານສະຫຼຸບ
6.1 ການສະແດງຜົນກະທົບ ພາຍໃນພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໄດ້ຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຜົນກະທົບທາງເສດຖະກິດສັງຄົມ
ການຜະລິດ
ຜົນຜະລິດຂອງສັດ
ຄວາມໜາແໜ້ນ ຂອງຜົນຜະລິດ
ການຜະລິດພະລັງງານ
ມີນໍ້າ ແລະ ຄຸນນະພາບ
ມີນໍ້າດື່ມ
ລາຍໄດ້ ແລະ ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍ ຂອງແຫຼ່ງລາຍຮັບ
ຄວາມແຕກຕ່າງ ທາງດ້ານເສດຖະກິດ
ຜົນກະທົບດ້ານວັດທະນາທໍາສັງຄົມ
ສະຖາບັນ ການຈັດຕັ້ງຊຸມຊົນ
ສະຖາບັນແຫ່ງຊາດ
ຄວາມຮູ້ກ່ຽວກັບ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ / ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
ຜົນກະທົບຕໍ່ລະບົບນິເວດ
ວົງຈອນນໍ້າ / ນໍ້າ
ປະລິມານນໍ້າ
ຄຸນນະພາບນໍ້າ
ການຂຸດຄົ້ນ / ການເກັບກັກນໍ້າ
ການໄຫຼ ຂອງນໍ້າໜ້າດິນ
ຊັ້ນນໍ້າໄຕ້ດິນ / ນໍ້າ
ການລະເຫີຍອາຍ
ດິນ
ຄວາມຊຸ່ມຂອງດິນ
ວົງຈອນ ຂອງສານອາຫານໃນດິນ
ຊີວະນານາພັນ: ສັດ, ພືດ
ມວນຊີວະພາບ / ຢູ່ເທິງຊັ້ນດິນ C
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍ ທາງດ້ານທີ່ຢູ່ອາໃສ ຂອງສິ່ງທີ່ມີຊີວິດ
ການຄວບຄຸມສັດຕູພືດ / ພະຍາດ
ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ຈາກໄພພິບັດ ແລະ ອາກາດປ່ຽນແປງ
ການລະເຫີຍອາຍກາກບອນ ແລະ ອາຍຜິດເຮືອນແກ້ວ
ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ຈາກໄຟໄໝ້
ຄວາມຮູນແຮງ ຂອງລົມ
6.2 ຜົນກະທົບທາງອ້ອມ ຈາກການນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການໄຫຼຂອງນໍ້າໃນລະດູແລ້ງ
ນໍ້າຖ້ວມຢູ່ເຂດລຸ່ມນໍ້າ
ການປ້ອງກັນ / ຄວາມອາດສາມາດ ການກັ່ນຕອງ
ພື້ນທີ່ທໍາການຜະລິດ ຂອງເພື່ອນບ້ານທີ່ຢູ່ໃກ້ຄຽງ ໄດ້ຮັບຜົນກະທົບ
6.3 ການປ້ອງກັນ ແລະ ຄວາມບອບບາງ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢິ ໃນການປ່ຽນແປງສະພາບດິນຟ້າອາກາດ ແລະ ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງກັບອາກາດທີ່ມີການປ່ຽນແປງທີ່ຮຸນແຮງ / ໄພພິບັດທາງທໍາມະຊາດ (ຮັບຮູ້ໄດ້ໂດຍຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ)
ການປ່ຽນແປງດິນຟ້າອາກາດ ເທື່ອລະກ້າວ
ການປ່ຽນແປງດິນຟ້າອາກາດ ເທື່ອລະກ້າວ
| ລະດູການ | ເພີ່ມຂື້ນ ຫຼື ຫຼຸດລົງ | ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ສາມາດ ຮັບມື ໄດ້ຄືແນວໃດ? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ອຸນຫະພູມປະຈໍາປີ | ເພີ່ມຂື້ນ | ດີ |
ອາກາດ ທີ່ກ່ຽວພັນກັບຄວາມຮຸນແຮງ (ໄພພິບັດທາງທໍາມະຊາດ)
ໄພພິບັດທາງອຸຕຸນິຍົມ
| ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ສາມາດ ຮັບມື ໄດ້ຄືແນວໃດ? | |
|---|---|
| ພະຍຸຝົນ | ບໍ່ດີ |
| ພາຍຸລົມທ້ອງຖິ່ນ | ດີ |
ໄພພິບັດທາງພູມອາກາດ
| ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ສາມາດ ຮັບມື ໄດ້ຄືແນວໃດ? | |
|---|---|
| ແຫ້ງແລ້ງ | ດີ |
ໄພພິບັດທາງອຸທົກກະສາກ
| ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ສາມາດ ຮັບມື ໄດ້ຄືແນວໃດ? | |
|---|---|
| ໂດຍທົ່ວໄປ (ແມ່ນໍ້າ) ນໍ້າຖ້ວມ | ບໍ່ດີ |
ຜົນສະທ້ອນສະພາບອາກາດອື່ນໆທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ
ຜົນສະທ້ອນສະພາບອາກາດອື່ນໆທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ
| ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ສາມາດ ຮັບມື ໄດ້ຄືແນວໃດ? | |
|---|---|
| ໄລຍະເວລາການຂະຫຍາຍຕົວຫຼຸດລົງ | ບໍ່ຮູ້ |
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Improving structure on the pond (use impermeable materials to prevent seepage, use concrete as a building material)
6.4 ການວິເຄາະຕົ້ນທຶນ ແລະ ຜົນປະໂຫຍດ
ຈະເຮັດປະໂຫຍດເພື່ອປຽບທຽບກັບຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍກັບສິ່ງກໍ່ສ້າງ (ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ) ໄດ້ແນວໃດ?
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະສັ້ນ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກ
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະຍາວ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກ
ຈະໄດ້ຮັບຜົນປະໂຫຍດເມື່ອປຽບທຽບກັບ / ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍໃນການບຳລຸງຮັກສາທີເ່ກີດຂື້ນອິກ (ຈາກທັດສະນະຄະຕິຂອງຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ) ໄດ້ແນວໃດ?
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະສັ້ນ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກ
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະຍາວ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
The technology requires low establishment and maintenance cost and benefit surpass the costs.
6.5 ການປັບຕົວຮັບເອົາເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ທັງໝົດນັ້ນ ແມ່ນໃຜ ໄດ້ປັບຕົວເຂົ້າ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ, ມີຈັກຄົນ ທີ່ສາມາດເຮັດເອງໄດ້, ຕົວຢ່າງ, ປາດສະຈາກ ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອ ທາງດ້ານອຸປະກອນ / ການຈ່າຍເປັນເງິນ?
- 11-50%
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
12% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
250 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
All livestock keepers use the technology to water their animals voluntary and through self mobilization.
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
The technology is cheap and requires low investment costs.
6.7 ຈຸດແຂງ / ຂໍ້ດີ / ໂອກາດ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
| ຈຸດແຂງ / ຂໍ້ດີ / ໂອກາດໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ |
|---|
|
Income generation due to water use fee. How can they be sustained / enhanced? improve service to water users. . |
| ຈຸດແຂງ / ຈຸດດີ / ໂອກາດ ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ |
|---|
|
Reduce conflict between livestock keepers and domestic water users. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Bylaws reinforcement, Area enclosure and Demarcation |
|
Improve accessibility of water to animals (improved animal water intake) How can they be sustained / enhanced? sensitization on regular maintenance. |
6.8 ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍ / ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ແລະ ວິທີການແກ້ໄຂບັນຫາ
| ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍ / ຄວາມສ່ຽງໃນມຸມມອງຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ | ມີວິທີການແກ້ໄຂຄືແນວໃດ? |
|---|---|
| Not durable and requires frequent and regular maintenance | Sensitize on regular maintenance. |
| ຈຸດອ່ອນ/ຂໍ້ບົກຜ່ອງ/ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ | ມີວິທີການແກ້ໄຂຄືແນວໃດ? |
|---|---|
| not durable | Sensitize on regular maintenance. |
| high labor demand to fill the troughs | Use simple leverage pump |
7. ເອກະສານອ້າງອີງ ແລະ ການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
7.1 ວິທີການ / ແຫຼ່ງຂໍ້ມູນ
7.2 ເອກກະສານອ້າງອີງທີ່ເປັນບົດລາຍງານ
ຫົວຂໍ້, ຜູ້ຂຽນ, ປີ, ISBN:
Kagera TAMP project website
ມີຢູ່ໃສ?ມູນຄ່າເທົ່າໃດ?
http://www.fao.org/nr/kagera/en/
ຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່ ແລະ ເນື້ອໃນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
ບໍ່ມີຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
ເນື້ອໃນ
ບໍ່ມີເນື້ອໃນ