Planting pits for soil fertilisation and moisture improvement [Uganda]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: Wilson Bamwerinde
- Editor: –
- Revisores: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
EBISANIYA (Runyankore language)
technologies_1587 - Uganda
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación de la Tecnología
Especialista MST:
Especialista MST:
Especialista MST:
Nombre del proyecto que financió la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
The Transboundary Agro-ecosystem Management Project for the Kagera River Basin (GEF-FAO / Kagera TAMP )Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) - Italia1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT:
Sí
2. Descripción de la Tecnología MST
2.1 Breve descripción de la Tecnología
Definición de la Tecnología:
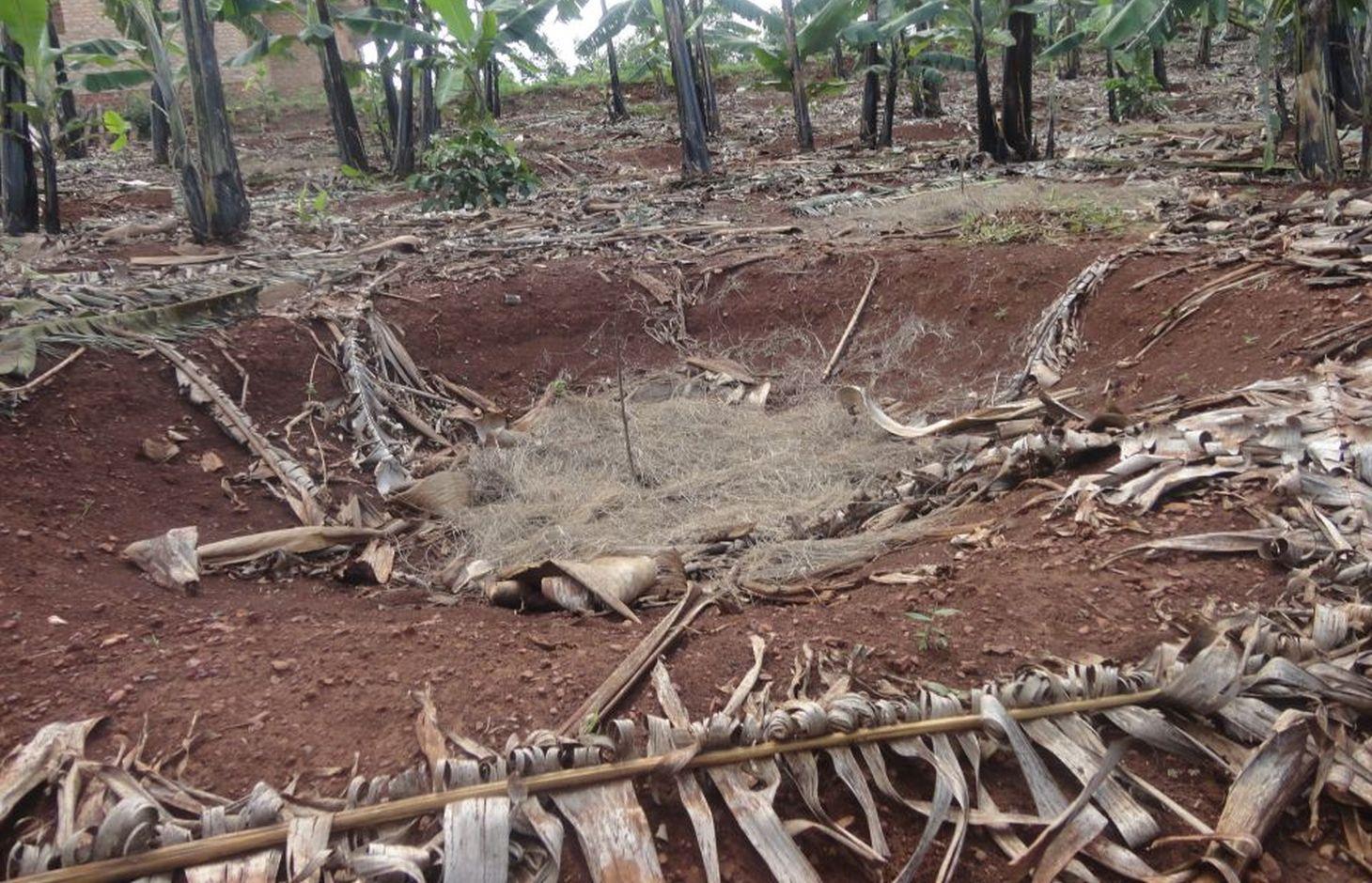
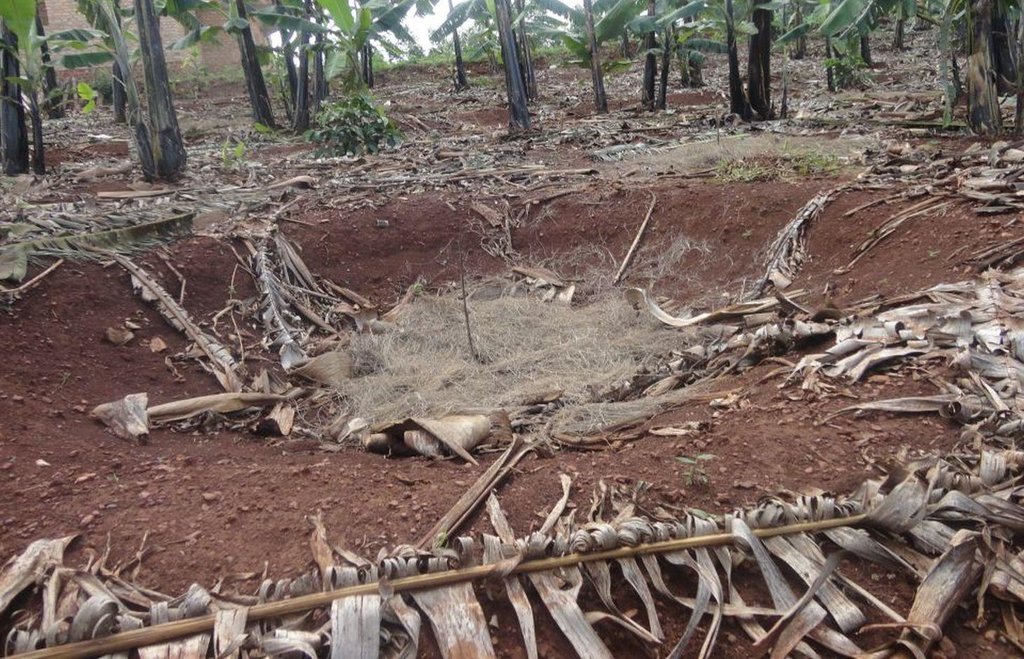
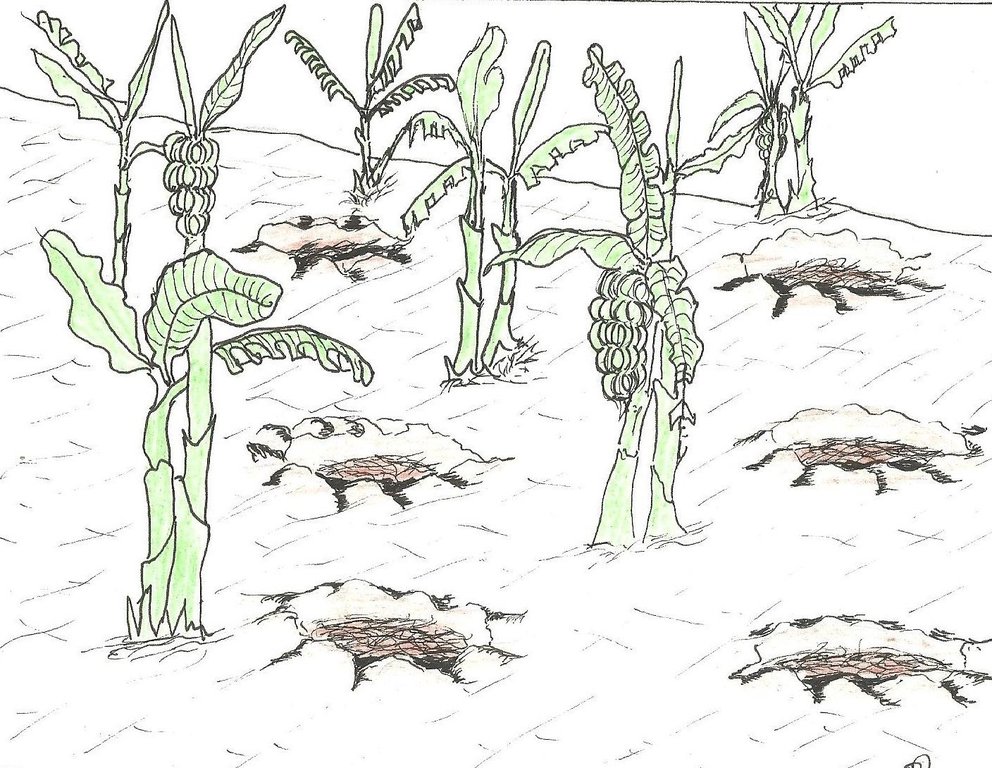
Planting pits in banana plantation filled with a mixture of manure, organic material and soil, to improve soil moisture and fertility and to enhance crop production and famer's income.
2.2 Descripción detallada de la Tecnología
Descripción:
The planting pits are established between banana stems and filled with organic vegetative material mixed with decomposing manure to form a reservoir of nutrients for a long run. On gentle slopes covered with extensive banana plantations, the planting pits are dug at the center of banana stands. Before estbalishment of this technology, only the composting process was available for the conversion of organic domestic waste into manure. However, compost manure takes slightly longer to produce and is more bulky than conservation troughs making the latter easier to adopt. The technology can be applied to annual cropland as well. Application of the technology improves banana bunch size and plantation yield by over 300%.
Purpose of the Technology: The main objective is to improve soil fertility. The planting pits also check runoff thereby reducing soil erosion, improving moisture infiltration and retention, and enabling the plantation to withstand the dry months. Cabbages, beans and other high value vegetables can be grown directly on top of the trough.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The planting pits are established using simple tools such as the hand hoe, spade, panga and wheelbarrow. The hoe is used to dig up the soil and soften it. The soil is then scooped out using a spade, to create a bowl-shaped trough. The panga is used to chop the remains of harvested bananas (stems and leaves) which are then, carried to the troughs using a wheel barrow. The planting pit is 0.45 m to 0.60 m deep depending on the amount of manure available and 0.6 m wide. Each trough is about 0.60 m from the nearest banana stand. It is filled with chopped banana stems, followed by a layer of manure and then covered with mulch to prevent excessive evaporation of moisture. The planting pit is then covered with soil. After 3 to 4 months, the vigor of the banana stems improves. If the trough is opened by digging, roots are observed to have grown through the walls of the planting pit from all directions.
During the rainy season, the trough slowly fills with sediment from surface erosion. Weeding at the trough is done by uprooting the weeds using hands or a hand hoe.
Natural / human environment: Over time, the banana stands grow towards the trough. To maintain the distance between the stands, the suckers nearest to the trough are pruned.
2.3 Fotografías de la Tecnología
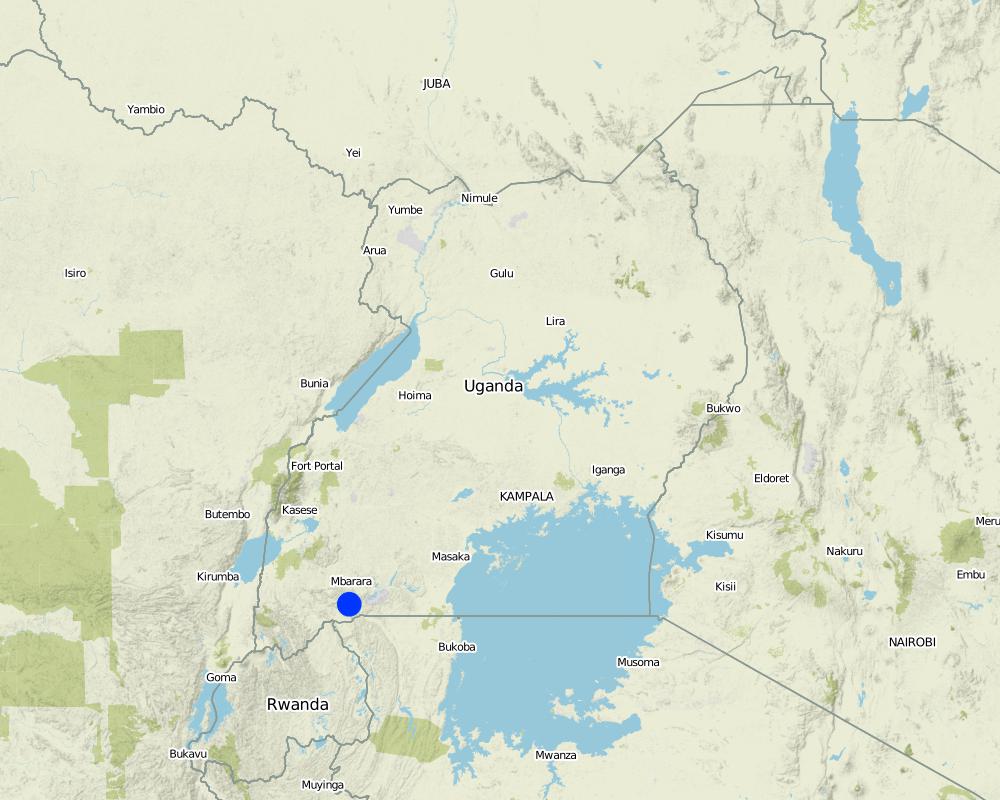
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde la Tecnología fue aplicada y que se hallan comprendidos por esta evaluación
País:
Uganda
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
Uganda
Especifique más el lugar :
Mbarara
Comentarios:
Boundary points of the Technology area: -0.86269 30.62587; -0.86275 30.62622; -0.86279 30.62631; -0.86405 30.62522; -0.86393 30.62539, -0.86387 30.62503
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.04 km2.
Map
×2.6 Fecha de la implementación
Si no se conoce el año preciso, indique la fecha aproximada:
- hace menos de 10 años (recientemente)
2.7 Introducción de la Tecnología
Especifique cómo se introdujo la Tecnología:
- mediante la innovación de usuarios de tierras
Comentarios (tipo de proyecto, etc.):
In 2012, Kagera TAMP introduced the Farmer Field School methodology. The members of these schools have been experimenting on several SLM technologies since then and the troughs are one of the successful innovations
3. Clasificación de la Tecnología MST
3.1 Propósito(s) principal(es) de la Tecnología MST
- mejorar la producción
- reducir, prevenir, restaurar la degradación de la tierra
- crear impacto económico benéfico
3.2 Tipo(s) actuales de uso de la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología

Tierras cultivadas
- Cosecha anual
- Cultivos perennes (no leñosos)
Cosechas anuales - Especifique cultivos:
- cereales - maíz
- leguminosas y legumbres - frijoles
- leguminosas y legumbres - arvejas
- cultivos de raíces/ tubérculos - patatas
Cultivos perennes (no maderables) - Especifique cultivos:
- banana/plátano/abacá
Número de temporadas de cultivo por año:
- 2
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 120 Longest growing period from month to month: February to May Second longest growing period in days: 90 Second longest growing period from month to month: September to November
Comentarios:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): The light, sandy loam soil on a hilly slope has very little capacity to hold water. The soils are dry a few days after it rains. The banana plantation therefore suffers two problems: inadequate soil water for plant growth and low nutrient retention. The problem of soil erosion is critical in the area but is addressed more adequately by fanya ju retention trenches stabilized with Napier grass strips.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Low productivity of the land compared to past seasons.
3.4 Provisión de agua
Provisión de agua para la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología:
- de secano
3.5 Grupo MST al que pertenece la Tecnología
- manejo integrado de la fertilidad del suelo
3.6 Medidas MST que componen la Tecnología

medidas agronómicas
- A7: Otros

medidas estructurales
- S4: Acequias niveladas, fosas
Comentarios:
Main measures: structural measures
Specification of other agronomic measures: Manure application (supp.
3.7 Principales tipos de degradación de la tierra encarados con la Tecnología

deterioro químico del suelo
- Cn: reducción de la fertilidad y contenido reducido de la materia orgánica del suelo (no ocasionados por la erosión)
Comentarios:
Main type of degradation addressed: Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
Main causes of degradation: soil management (No manure was being applied to replenish nutrients inspite of continuous banana harvesting)
3.8 Prevención, reducción o restauración de la degradación de la tierra
Especifique la meta de la Tecnología con relación a la degradación de la tierra:
- prevenir la degradación de la tierra
- reducir la degradación de la tierra
Comentarios:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation
4. Especificaciones técnicas, actividades de implementación, insumos y costos
4.1 Dibujo técnico de la Tecnología
Especificaciones técnicas (relacionadas al dibujo técnico):
Conservation troughs (0.4-0.6 m deep) are partially filled with a mixture of manure, undecomposed banana stems and other organic matter to add organic matter into the soil. They also capture rainfall runoff and help to maintain suitable soil moisture. The conservation trough should be dug about 0.6 m from banana plant so that the heat produced during decay does not affect the plant.
Location: Rubagano, Mwizi, Mbarara district. Uganda
Date: 29-Nov-2013
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low (Self explanatory)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (Basic training required on the construction methodology e.g. location selection, recommended dimentions of the trough (depth))
Main technical functions: increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, water harvesting / increase water supply
Secondary technical functions: improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), improvement of subsoil structure (hardpan)
Retention/infiltration ditch/pit, sediment/sand trap
Vertical interval between structures (m): n/a
Spacing between structures (m): 3
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 2
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 2
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): n/a
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): n/a
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): n/a
Reshaping surface
Vertical interval between structures (m): n/a
Spacing between structures (m): n/a
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 3
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 2
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 2
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): n/a
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): n/a
Construction material (earth): Troughs are developed by excavating soil; soil mixed with manure is used to fill the pit partially.
Construction material (stone): n/a
Construction material (wood): n/a
Construction material (concrete): n/a
Construction material (other): n/a
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): n/a%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: n/a%
Lateral gradient along the structure: n/a%
Specification of dams/ pans/ ponds: Capacity n/am3
Catchment area: n/am2
Beneficial area: n/am2
Slope of dam wall inside: n/a%;
Slope of dam wall outside: n/a%
Dimensions of spillways: n/am
Other specifications: n/a
For water harvesting: the ratio between the area where the harvested water is applied and the total area from which water is collected is: 1:n/a
Autor:
Byonabye Proscovia, Kagera TAMP, Kabale District
4.2 Información general sobre el cálculo de insumos y costos
otra / moneda nacional (especifique):
UGX
Si fuera relevante, indique la tasa de cambio de dólares americanos a la moneda local (ej. 1 U$ = 79.9 Reales Brasileros): 1 U$ =:
2500,0
Indique el costo promedio del salario de trabajo contratado por día:
4.00
4.3 Actividades de establecimiento
| Actividad | Momento (estación) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Measuring and marking pit positions | Wet season |
| 2. | Excavating pits | Wet season |
| 3. | Mixing top soil with animal manure, filling mixture into pits, putting domestic and field organic residues into pits, covering pits | Wet season |
4.4 Costos e insumos necesarios para el establecimiento
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 44,0 | 44,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | Tools | ha | 1,0 | 7,0 | 7,0 | |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | Compost/manure | ha | 1,0 | 40,0 | 40,0 | 100,0 |
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 91,0 | |||||
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología en USD | 0,04 | |||||
Comentarios:
Duration of establishment phase: 2 month(s)
4.5 Actividades de establecimiento/ recurrentes
| Actividad | Momento/ frequencia | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Weeding by hand | Wet season |
| 2. | Addition of manure and residues | Once a year |
4.6 Costos e insumos necesarios para actividades de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (por año)
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 10,0 | 10,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | Tools | ha | 1,0 | 4,0 | 4,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | Compost/manure | ha | 1,0 | 20,0 | 20,0 | 100,0 |
| Indique los costos totales para mantenecer la Tecnología | 34,0 | |||||
| Costos totales para mantener la Tecnología en USD | 0,01 | |||||
Comentarios:
Machinery/ tools: hand hoe, wheel barrow
The calculations were made for the rainy season of September to November, 2013.
4.7 Factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Describa los factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Availability of labour and animal manure are the most important factors affecting cost of the establishment activities. To reduce cost of labour it is recommended to apply Farmer Field Schools approach. To reduce cost of manure farmers can produce their own farmyard manure, e.g. by implementing zero-grazing technology.
5. Entorno natural y humano
5.1 Clima
Lluvia anual
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Especificaciones/ comentarios sobre la cantidad de lluvia:
1400 mm spread over 2 seasons
Zona agroclimática
- Sub-húmeda
Thermal climate class: tropics. Located at the Equator. A good supply of rain much of the year, but plenty of sunshine too
5.2 Topografía
Pendientes en promedio:
- plana (0-2 %)
- ligera (3-5%)
- moderada (6-10%)
- ondulada (11-15%)
- accidentada (16-30%)
- empinada (31-60%)
- muy empinada (>60%)
Formaciones telúricas:
- meseta/ planicies
- cordilleras
- laderas montañosas
- laderas de cerro
- pies de monte
- fondo del valle
Zona altitudinal:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1,000 m s.n.m
- 1,001-1,500 m s.n.m
- 1,501-2,000 m s.n.m
- 2,001-2,500 m s.n.m
- 2,501-3,000 m s.n.m
- 3,001-4,000 m s.n.m
- > 4,000 m s.n.m
Indique si la Tecnología se aplica específicamente en:
- no relevante
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre topografía :
Altitudinal zone: 1501-2000 m a.s.l. (1715 to 1740 m a.s.l.)
Landforms: Hill slopes (ranked 1, concave) and ridges (ranked 2, convex)
Slopes on average: Hilly (Where the technology has been applied so far is on hilly slopes (< 30%) but the adjacent slopes where the technology is planned next is quite steep (> 45%))
5.3 Suelos
Profundidad promedio del suelo:
- muy superficial (0-20 cm)
- superficial (21-50 cm)
- moderadamente profunda (51-80 cm)
- profunda (81-120 cm)
- muy profunda (>120 cm)
Textura del suelo (capa arable):
- áspera/ ligera (arenosa)
Materia orgánica de capa arable:
- media (1-3%)
Si se halla disponible, adjunte una descripción completa de los suelos o especifique la información disponible, por ej., tipo de suelo, pH/ acidez de suelo, capacidad de intercambio catiónico, nitrógeno, salinidad, etc. :
Soil depth on average: Shallow (The soils are generally shallow)
Soil fertility: Low
Topsoil organic matter: Medium (Mulching had already introduced topsoil organic matter)
Soil drainage/infiltration: Good
Soil water storage capacity: Medium
5.4 Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
Agua subterránea:
> 50 m
Disponibilidad de aguas superficiales:
pobre/ ninguna
Calidad de agua (sin tratar):
agua potable de mala calidad (requiere tratamiento)
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre calidad y cantidad de agua:
Ground water table: >50 m (Boreholes have been sank before to great lengths but have invariably dried up)
Availability of surface water: Poor/none (Available only as trapped runoff behind rocky formations, but soon dries up)
Water quality (untreated): Poor drinking water (treatment required, runoff)
5.5 Biodiversidad
Diversidad de especies:
- mediana
5.6 Las características de los usuarios de la tierra que aplican la Tecnología
Orientación del mercado del sistema de producción:
- mixta (subsistencia/ comercial)
Ingresos no agrarios:
- menos del 10% de todos los ingresos
Nivel relativo de riqueza:
- promedio
Individuos o grupos:
- individual/ doméstico
Nivel de mecanización:
- trabajo manual
Género:
- mujeres
- hombres
Indique otras características relevantes de los usuarios de las tierras:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: n/a
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 3% - 4%
and own 20% of the land.
and own 30% of the land.
40% of the land users are average wealthy and own 40% of the land.
and own 10% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: There has been an improvement in yields which translate into money generated per hectare. However, the farmers applying the technology have not yet diversified into other enterprises.
Level of mechanization: Manual work (Hand hoe, spade, wheel barrow)
Market orientation: Mixed (Surplus has grown to such a level that the commercial component has become inevitable)
5.7 Área promedio de la tierra usada por usuarios de tierra que aplican la Tecnología
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
¿Esto se considera de pequeña, mediana o gran escala (refiriéndose al contexto local)?
- pequeña escala
5.8 Tenencia de tierra, uso de tierra y derechos de uso de agua
Tenencia de tierra:
- individual, sin título
Derechos de uso de tierra:
- individual
Derechos de uso de agua:
- acceso abierto (no organizado)
- individual
Comentarios:
Individual access to water rights is relatively new with the introduction of water harvesting.
5.9 Acceso a servicios e infraestructura
salud:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
educación:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
asistencia técnica:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
empleo (ej. fuera de la granja):
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
mercados:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
energía:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
caminos y transporte:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
agua potable y saneamiento:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
servicios financieros:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
6. Impactos y comentarios para concluir
6.1 Impactos in situ demostrados por la Tecnología
Impactos socioeconómicos
Producción
producción de cultivo
Cantidad antes de MST:
8 Kg
Cantidad luego de MST:
25 Kg
Comentarios/ especifique:
Bunch of bananas is bigger and heavier at harvest
riesgo de fracaso de producción
Cantidad antes de MST:
20%
Cantidad luego de MST:
67%
Comentarios/ especifique:
During the dry season or extended drought periods, only about 20% of the banana stands would have a fruiting stem; now well over two thirds of the stands do.
Ingreso y costos
gastos en insumos agrícolas
ingreso agrario
Cantidad antes de MST:
80 US$
Cantidad luego de MST:
200 US$
Comentarios/ especifique:
Monthly harvests for sale have increased from 20 to over 50 bunches
carga de trabajo
Impactos socioculturales
seguridad alimentaria/ autosuficiencia
Cantidad antes de MST:
50%
Cantidad luego de MST:
100%
Comentarios/ especifique:
Whereas extended drought posed food insecurity, this is no longer the case
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
Comentarios/ especifique:
The earning power has increased greatly. Children are going to school because tuition fees are no longer burdensome and health needs are easily met. The farmers practicing the technology report making some savings from their incomes unlike before.
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo de agua/ escurrimiento de sedimento
evaporación
Suelo
humedad del suelo
ciclo/ recarga de nutrientes
materia orgánica debajo del suelo C
6.3 Exposición y sensibilidad de la Tecnología al cambio climático gradual y a extremos relacionados al clima/ desastres (desde la percepción de los usuarios de tierras)
Cambio climático gradual
Cambio climático gradual
| Estación | Incremento o reducción | ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| temperatura anual | incrementó | bien |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados al clima
Desastres climatológicos:
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| tormenta de lluvia local | bien |
| tormenta de viento | bien |
Desastres climatológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| sequía | bien |
Desastres hidrológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| inundación general (río) | no se sabe |
Otras consecuencias relacionadas al clima
Otras consecuencias relacionadas al clima
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| periodo reducido de crecimiento | bien |
Comentarios:
The advantages of the technology to cropland are to be found underground. Therefore the technology is protected against most natural adversities above ground.
6.4 Análisis costo-beneficio
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de establecimiento (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
muy positivo
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
muy positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
muy positivo
Comentarios:
Costs at establishment are the only ones involved. There are no maintenance costs involved though pits need to be re-established every 2-3 years
6.5 Adopción de la Tecnología
Si tiene la información disponible, cuantifique (número de hogares y/o área cubierta):
22
De todos quienes adoptaron la Tecnología, ¿cuántos lo hicieron espontáneamente, por ej. sin recibir nada de incentivos/ materiales:
- 91-100%
Comentarios:
Comments on acceptance with external material support: It is a farmer initiative and no support has been received for the adoption of this technology.
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
22 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: This is a farmer field school initiative and the district facilitator for Kagera TAMP (and also an Agricultural officer of the local government) provided guidance on positioning the pits for maximum utility.
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Noticing the results in only 3 seasons, the other farmers (not members of farmer field school) are also adopting the technology.
6.7 Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades de la Tecnología
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
|
The technology requires the use of only the simplest of farm tools such as a hand hoe, a spade and a wheel barrow. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Dissemination of the the technology through regular community meetings and a local language newsletter |
|
Demonstration of benefits is achieved quite quickly and therefore adoption by farmers is good. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Emphasize technology at farmer field school demonstration plots |
|
Technology bears similar benefits to composting but with a shorter list of activities How can they be sustained / enhanced? Encourage adoption through demonstration |
|
Since the technology utilizes stem cuttings, whole stems are harvested reducing the risk of pests and diseases especially banana bacteria, that would be harbored by exposed rotting stems How can they be sustained / enhanced? Knowledge dissemination through regular community meetings and local language newsletter |
6.8 Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos de la Tecnología y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| The technology is labor intensive | Farmer Field Schools bring farmers together in a community level effort |
| The technology requires livestock manure in a predominantly cultivator community | Introduce zero-grazing livestock for manure production |
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.1 Métodos/ fuentes de información
7.2 Vínculos a las publicaciones disponibles
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
Kagera TAMP project website
¿Dónde se halla disponible? ¿Costo?
http://www.fao.org/nr/kagera/en/
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos
No hay vínculos
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos