Planting pits for soil fertilisation and moisture improvement [ยูกันดา]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Wilson Bamwerinde
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
EBISANIYA (Runyankore language)
technologies_1587 - ยูกันดา
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
The Transboundary Agro-ecosystem Management Project for the Kagera River Basin (GEF-FAO / Kagera TAMP )ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) - อิตาลี1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
Planting pits in banana plantation filled with a mixture of manure, organic material and soil, to improve soil moisture and fertility and to enhance crop production and famer's income.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
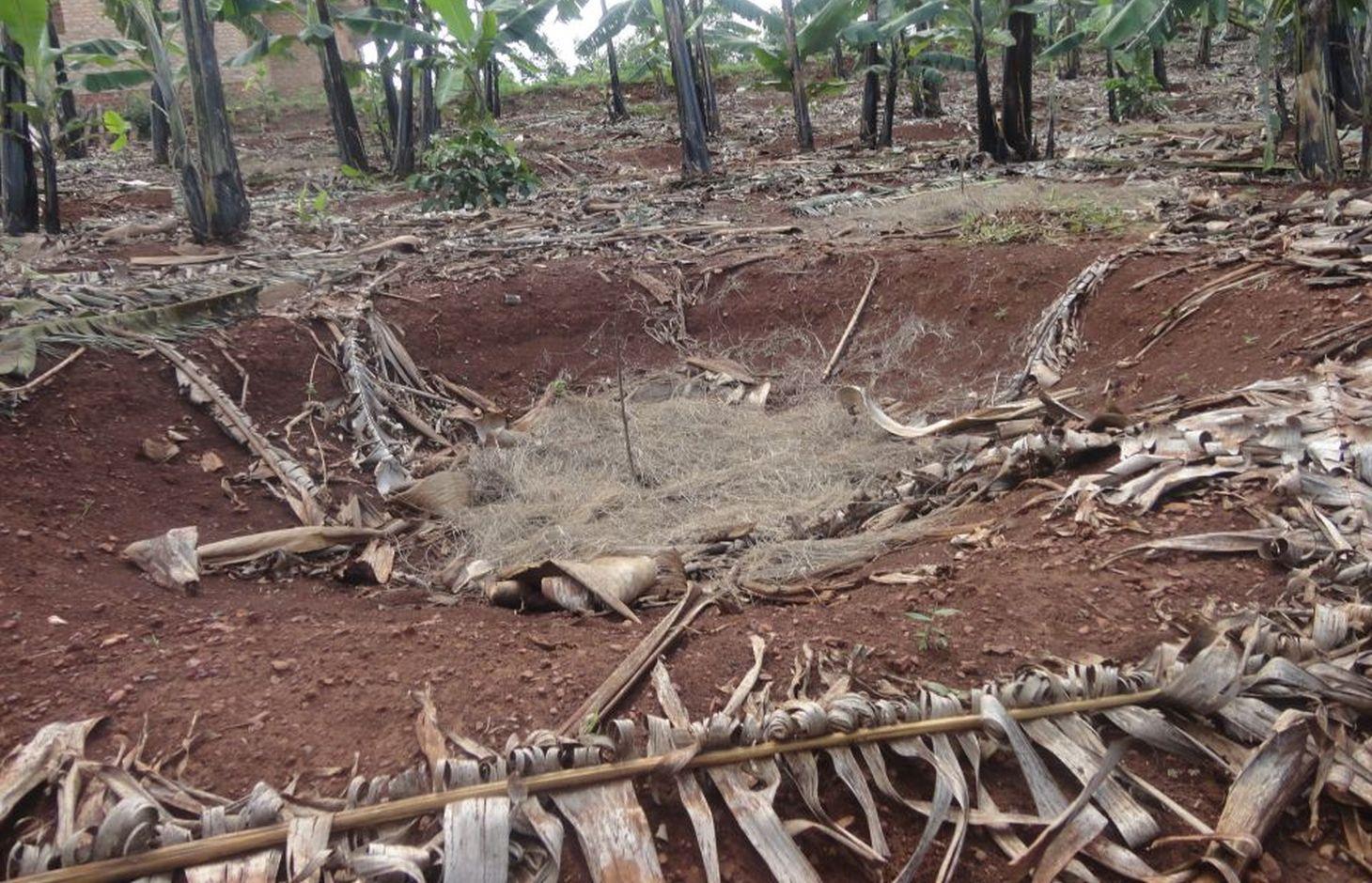
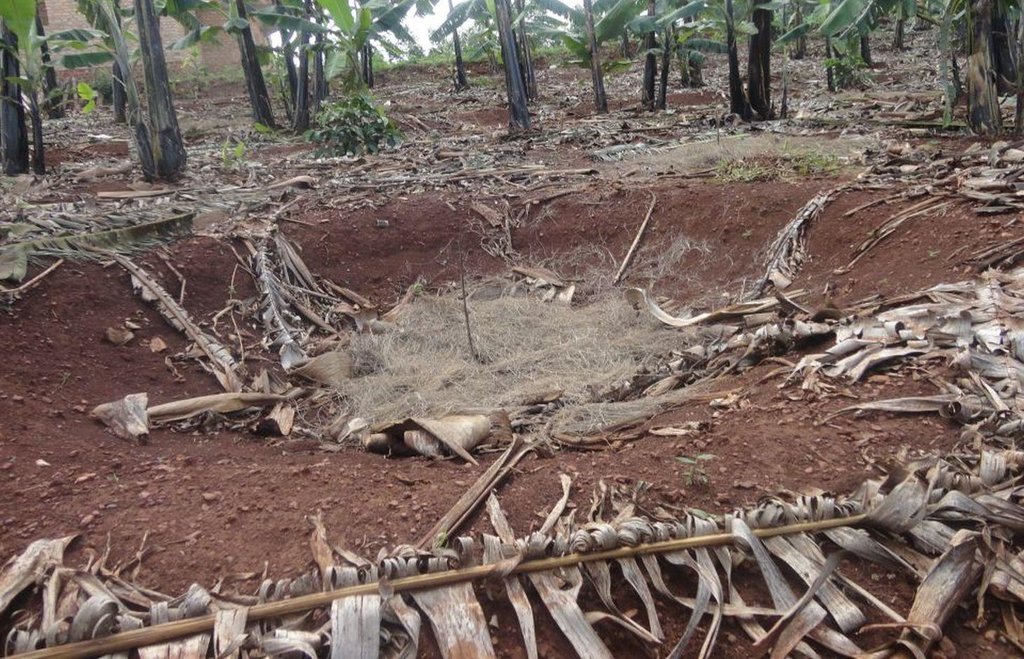
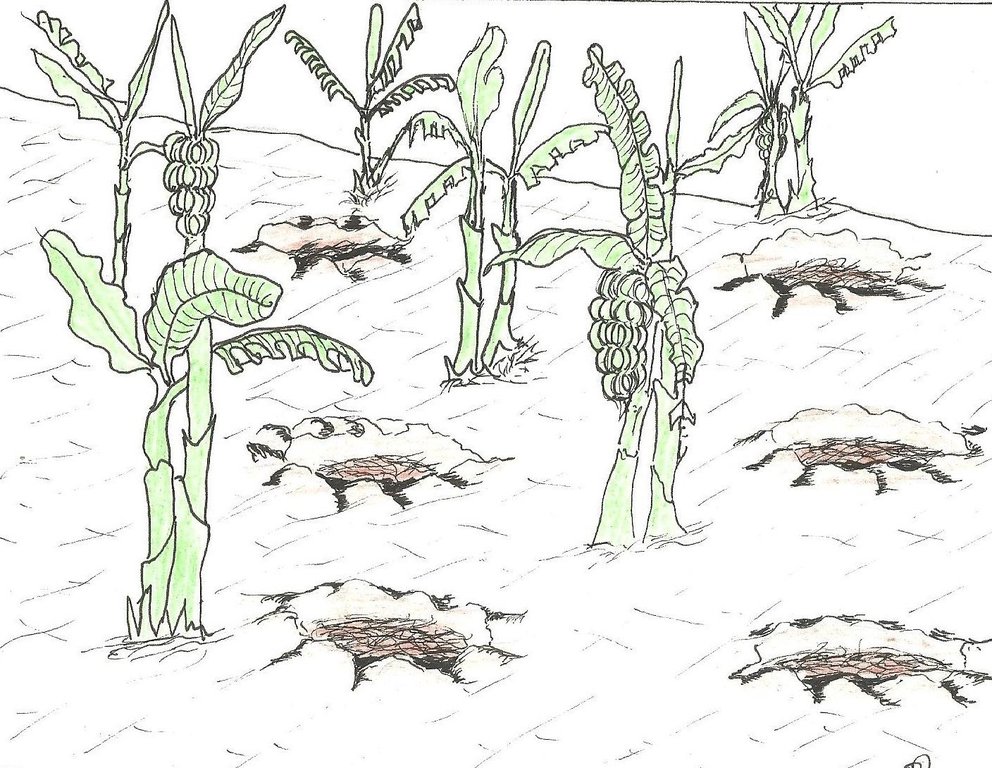
The planting pits are established between banana stems and filled with organic vegetative material mixed with decomposing manure to form a reservoir of nutrients for a long run. On gentle slopes covered with extensive banana plantations, the planting pits are dug at the center of banana stands. Before estbalishment of this technology, only the composting process was available for the conversion of organic domestic waste into manure. However, compost manure takes slightly longer to produce and is more bulky than conservation troughs making the latter easier to adopt. The technology can be applied to annual cropland as well. Application of the technology improves banana bunch size and plantation yield by over 300%.
Purpose of the Technology: The main objective is to improve soil fertility. The planting pits also check runoff thereby reducing soil erosion, improving moisture infiltration and retention, and enabling the plantation to withstand the dry months. Cabbages, beans and other high value vegetables can be grown directly on top of the trough.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The planting pits are established using simple tools such as the hand hoe, spade, panga and wheelbarrow. The hoe is used to dig up the soil and soften it. The soil is then scooped out using a spade, to create a bowl-shaped trough. The panga is used to chop the remains of harvested bananas (stems and leaves) which are then, carried to the troughs using a wheel barrow. The planting pit is 0.45 m to 0.60 m deep depending on the amount of manure available and 0.6 m wide. Each trough is about 0.60 m from the nearest banana stand. It is filled with chopped banana stems, followed by a layer of manure and then covered with mulch to prevent excessive evaporation of moisture. The planting pit is then covered with soil. After 3 to 4 months, the vigor of the banana stems improves. If the trough is opened by digging, roots are observed to have grown through the walls of the planting pit from all directions.
During the rainy season, the trough slowly fills with sediment from surface erosion. Weeding at the trough is done by uprooting the weeds using hands or a hand hoe.
Natural / human environment: Over time, the banana stands grow towards the trough. To maintain the distance between the stands, the suckers nearest to the trough are pruned.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
ยูกันดา
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Uganda
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Mbarara
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Boundary points of the Technology area: -0.86269 30.62587; -0.86275 30.62622; -0.86279 30.62631; -0.86405 30.62522; -0.86393 30.62539, -0.86387 30.62503
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.04 km2.
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- น้อยกว่า 10 ปี (ไม่นานนี้)
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ด้วยการริเริ่มของผู้ใช้ที่ดินเอง
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
In 2012, Kagera TAMP introduced the Farmer Field School methodology. The members of these schools have been experimenting on several SLM technologies since then and the troughs are one of the successful innovations
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ปรับปรุงการผลิตให้ดีขึ้น
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- สร้างผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจที่เป็นประโยชน์
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
- การปลูกพืชยืนต้นที่ไม่มีเนื้อไม้
Annual cropping - Specify crops:
- cereals - maize
- legumes and pulses - beans
- legumes and pulses - peas
- root/tuber crops - potatoes
Perennial (non-woody) cropping - Specify crops:
- banana/plantain/abaca
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 2
ระบุ:
Longest growing period in days: 120 Longest growing period from month to month: February to May Second longest growing period in days: 90 Second longest growing period from month to month: September to November
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): The light, sandy loam soil on a hilly slope has very little capacity to hold water. The soils are dry a few days after it rains. The banana plantation therefore suffers two problems: inadequate soil water for plant growth and low nutrient retention. The problem of soil erosion is critical in the area but is addressed more adequately by fanya ju retention trenches stabilized with Napier grass strips.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Low productivity of the land compared to past seasons.
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การจัดการความอุดมสมบรูณ์ของดินแบบผสมผสาน
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการจัดการพืช
- A7: Others

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยโครงสร้าง
- S4: คูน้ำแนวระดับ หลุม
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main measures: structural measures
Specification of other agronomic measures: Manure application (supp.
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านเคมี
- Cn (Fertility decline): ความอุดมสมบูรณ์และปริมาณอินทรียวัตถุในดินถูกทำให้ลดลงไป (ไม่ได้เกิดจากสาเหตุการกัดกร่อน)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main type of degradation addressed: Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
Main causes of degradation: soil management (No manure was being applied to replenish nutrients inspite of continuous banana harvesting)
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ป้องกันความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
Conservation troughs (0.4-0.6 m deep) are partially filled with a mixture of manure, undecomposed banana stems and other organic matter to add organic matter into the soil. They also capture rainfall runoff and help to maintain suitable soil moisture. The conservation trough should be dug about 0.6 m from banana plant so that the heat produced during decay does not affect the plant.
Location: Rubagano, Mwizi, Mbarara district. Uganda
Date: 29-Nov-2013
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low (Self explanatory)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (Basic training required on the construction methodology e.g. location selection, recommended dimentions of the trough (depth))
Main technical functions: increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, water harvesting / increase water supply
Secondary technical functions: improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), improvement of subsoil structure (hardpan)
Retention/infiltration ditch/pit, sediment/sand trap
Vertical interval between structures (m): n/a
Spacing between structures (m): 3
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 2
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 2
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): n/a
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): n/a
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): n/a
Reshaping surface
Vertical interval between structures (m): n/a
Spacing between structures (m): n/a
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 3
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 2
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 2
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): n/a
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): n/a
Construction material (earth): Troughs are developed by excavating soil; soil mixed with manure is used to fill the pit partially.
Construction material (stone): n/a
Construction material (wood): n/a
Construction material (concrete): n/a
Construction material (other): n/a
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): n/a%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: n/a%
Lateral gradient along the structure: n/a%
Specification of dams/ pans/ ponds: Capacity n/am3
Catchment area: n/am2
Beneficial area: n/am2
Slope of dam wall inside: n/a%;
Slope of dam wall outside: n/a%
Dimensions of spillways: n/am
Other specifications: n/a
For water harvesting: the ratio between the area where the harvested water is applied and the total area from which water is collected is: 1:n/a
ผู้เขียน:
Byonabye Proscovia, Kagera TAMP, Kabale District
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
UGX
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
2500.0
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
4.00
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Measuring and marking pit positions | Wet season |
| 2. | Excavating pits | Wet season |
| 3. | Mixing top soil with animal manure, filling mixture into pits, putting domestic and field organic residues into pits, covering pits | Wet season |
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 44.0 | 44.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Tools | ha | 1.0 | 7.0 | 7.0 | |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Compost/manure | ha | 1.0 | 40.0 | 40.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 91.0 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 0.04 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Duration of establishment phase: 2 month(s)
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Weeding by hand | Wet season |
| 2. | Addition of manure and residues | Once a year |
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 10.0 | 10.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Tools | ha | 1.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 100.0 |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Compost/manure | ha | 1.0 | 20.0 | 20.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 34.0 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 0.01 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Machinery/ tools: hand hoe, wheel barrow
The calculations were made for the rainy season of September to November, 2013.
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
Availability of labour and animal manure are the most important factors affecting cost of the establishment activities. To reduce cost of labour it is recommended to apply Farmer Field Schools approach. To reduce cost of manure farmers can produce their own farmyard manure, e.g. by implementing zero-grazing technology.
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ข้อมูลจำเพาะ/ความคิดเห็นเรื่องปริมาณน้ำฝน:
1400 mm spread over 2 seasons
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งชุ่มชื้น
Thermal climate class: tropics. Located at the Equator. A good supply of rain much of the year, but plenty of sunshine too
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ให้ระบุถ้าเทคโนโลยีได้ถูกนำไปใช้:
- ไม่เกี่ยวข้อง
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องสภาพภูมิประเทศ:
Altitudinal zone: 1501-2000 m a.s.l. (1715 to 1740 m a.s.l.)
Landforms: Hill slopes (ranked 1, concave) and ridges (ranked 2, convex)
Slopes on average: Hilly (Where the technology has been applied so far is on hilly slopes (< 30%) but the adjacent slopes where the technology is planned next is quite steep (> 45%))
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- หยาบ/เบา (ดินทราย)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ปานกลาง (1-3%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
Soil depth on average: Shallow (The soils are generally shallow)
Soil fertility: Low
Topsoil organic matter: Medium (Mulching had already introduced topsoil organic matter)
Soil drainage/infiltration: Good
Soil water storage capacity: Medium
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
> 50 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ไม่ดีหรือไม่มีเลย
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำเพื่อการดื่มที่ไม่ดี (จำเป็นต้องได้รับการบำบัด)
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องคุณภาพและปริมาณน้ำ:
Ground water table: >50 m (Boreholes have been sank before to great lengths but have invariably dried up)
Availability of surface water: Poor/none (Available only as trapped runoff behind rocky formations, but soon dries up)
Water quality (untreated): Poor drinking water (treatment required, runoff)
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ปานกลาง
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- < 10% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- พอมีพอกิน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
เพศ:
- หญิง
- ชาย
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: n/a
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 3% - 4%
and own 20% of the land.
and own 30% of the land.
40% of the land users are average wealthy and own 40% of the land.
and own 10% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: There has been an improvement in yields which translate into money generated per hectare. However, the farmers applying the technology have not yet diversified into other enterprises.
Level of mechanization: Manual work (Hand hoe, spade, wheel barrow)
Market orientation: Mixed (Surplus has grown to such a level that the commercial component has become inevitable)
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดเล็ก
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล ไม่ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- เข้าถึงได้แบบเปิด (ไม่ได้จัดระเบียบ)
- รายบุคคล
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Individual access to water rights is relatively new with the introduction of water harvesting.
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
8 Kg
หลังจาก SLM:
25 Kg
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Bunch of bananas is bigger and heavier at harvest
การเสี่ยงต่อความล้มเหลวในการผลิต
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
20%
หลังจาก SLM:
67%
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
During the dry season or extended drought periods, only about 20% of the banana stands would have a fruiting stem; now well over two thirds of the stands do.
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
ค่าใช่จ่ายของปัจจัยการผลิตทางการเกษตร
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
80 US$
หลังจาก SLM:
200 US$
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Monthly harvests for sale have increased from 20 to over 50 bunches
ภาระงาน
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
ความมั่นคงด้านอาหาร / พึ่งตนเองได้
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
50%
หลังจาก SLM:
100%
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Whereas extended drought posed food insecurity, this is no longer the case
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The earning power has increased greatly. Children are going to school because tuition fees are no longer burdensome and health needs are easily met. The farmers practicing the technology report making some savings from their incomes unlike before.
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
การระเหย
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
การหมุนเวียนและการเติมของธาตุอาหาร
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ต่ำกว่าดินชั้น C
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | increase or decrease | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| อุณหภูมิประจำปี | เพิ่มขึ้น | ดี |
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติทางอุตุนิยมวิทยา
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| พายุฝนประจำท้องถิ่น | ดี |
| พายุลมประจำท้องถิ่น | ดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากสภาพภูมิอากาศ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ภัยจากฝนแล้ง | ดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากน้ำ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| น้ำท่วมตามปกติ (แม่น้ำ) | ไม่ทราบ |
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ช่วงการปลูกพืชที่ลดลงมา | ดี |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The advantages of the technology to cropland are to be found underground. Therefore the technology is protected against most natural adversities above ground.
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Costs at establishment are the only ones involved. There are no maintenance costs involved though pits need to be re-established every 2-3 years
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
ถ้ามีข้อมูลให้บอกปริมาณด้วย (จำนวนของครัวเรือนหรือครอบคลุมพื้นที่):
22
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 91-100%
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Comments on acceptance with external material support: It is a farmer initiative and no support has been received for the adoption of this technology.
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
22 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: This is a farmer field school initiative and the district facilitator for Kagera TAMP (and also an Agricultural officer of the local government) provided guidance on positioning the pits for maximum utility.
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Noticing the results in only 3 seasons, the other farmers (not members of farmer field school) are also adopting the technology.
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
|
The technology requires the use of only the simplest of farm tools such as a hand hoe, a spade and a wheel barrow. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Dissemination of the the technology through regular community meetings and a local language newsletter |
|
Demonstration of benefits is achieved quite quickly and therefore adoption by farmers is good. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Emphasize technology at farmer field school demonstration plots |
|
Technology bears similar benefits to composting but with a shorter list of activities How can they be sustained / enhanced? Encourage adoption through demonstration |
|
Since the technology utilizes stem cuttings, whole stems are harvested reducing the risk of pests and diseases especially banana bacteria, that would be harbored by exposed rotting stems How can they be sustained / enhanced? Knowledge dissemination through regular community meetings and local language newsletter |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| The technology is labor intensive | Farmer Field Schools bring farmers together in a community level effort |
| The technology requires livestock manure in a predominantly cultivator community | Introduce zero-grazing livestock for manure production |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Kagera TAMP project website
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
http://www.fao.org/nr/kagera/en/
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล