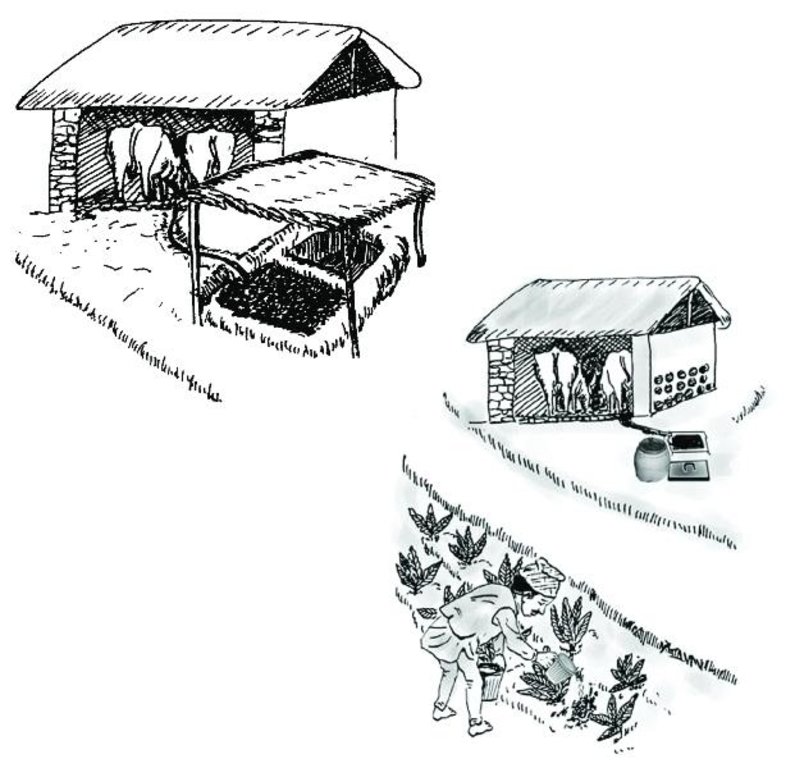
Improved cattleshed for urine collection [Nepal]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: Richard Allen
- Editor: –
- Revisores: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Mutra sankalan ka lagi sudhariyeko goth (Nepali)
technologies_1752 - Nepal
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación de la Tecnología
Especialista MST:
Director
Soil Management Directorate, Department of Agriculture
Nepal
Especialista MST:
Team Leader
Sustainable Soil Management Programme
Nepal
Nombre del proyecto que financió la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Sustainable Soil Management Programme, Nepal (SSMP)Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
HELVETAS (Swiss Intercooperation)Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Department of Agriculture, Soil Management Directorate, Hariharbhawan Lalitpur (doasoil) - Nepal1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT:
Sí
1.5 Referencia al (los) Cuestionario(s) de Enfoques MST (documentados usando WOCAT)

Farmer field schools on integrated plant nutrient systems [Nepal]
Participatory and collaborative learning through the farmer field school approach
- Compilador: Richard Allen

Farmer-led experimentation [Nepal]
Participatory technology testing and adaptation through farmer-led experiments
- Compilador: Richard Allen

Farmer-to-farmer diffusion [Nepal]
Wider diffusion of sustainable soil management technologies through a demand responsive farmer-to-farmer diffusion approach
- Compilador: Richard Allen
2. Descripción de la Tecnología MST
2.1 Breve descripción de la Tecnología
Definición de la Tecnología:
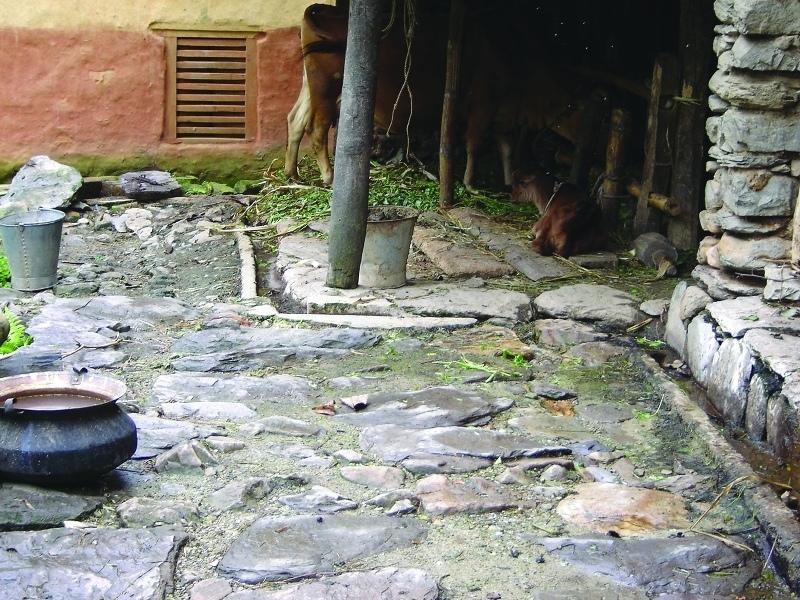
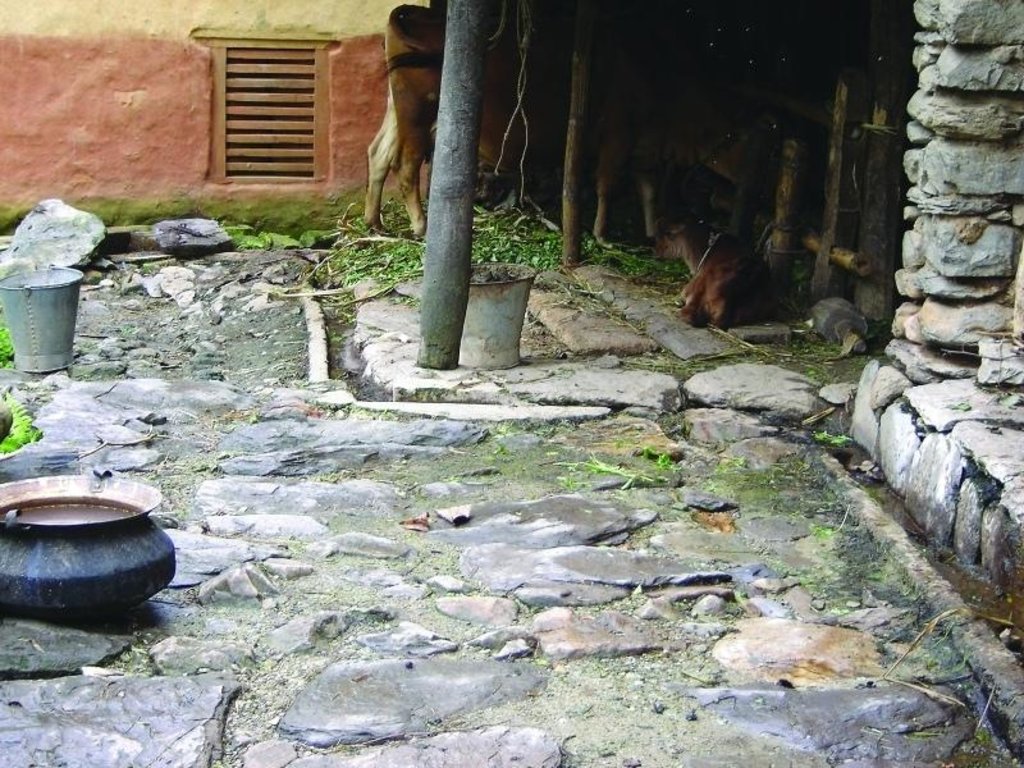
Collection of cattle urine in improved cattle sheds for use as liquid manure and organic pesticide
2.2 Descripción detallada de la Tecnología
Descripción:
Nitrogen is the most important macronutrient for plants, and high crop productivity can only be achieved by making sufficient nitrogen available to crops. Nitrogen is also the most limiting nutrient in farms across Nepal’s midhills. Traditionally farmers applied farmyard manure to fertilise their needs. In many places this is being supplemented or even entirely replaced by inorganic fertiliser - mainly urea. The price of inorganic fertiliser has increased continuously in recent years and it is only available in limited quantities in areas far from the roadheads. On the other hand, cultivation practices are intensifying with increased cropping intensities and more nutrient-demanding crops as, for example, local varieties are replaced by hybrids and new crops are grown. This can easily lead to declining soil fertility and nutrient mining if it is not compensated for by an equivalent increase in organic or mineral fertilisation.
Cattle urine is a viable alternative to mineral fertiliser. Of the nitrogen excreted by cattle, 60% is found in the urine and only 40% in dung. In traditional sheds, urine is left to be absorbed in the bedding material, while excess urine is channelled out of the shed and disposed of. The technology described here - improved cattle sheds- are designed for collecting the urine in a pit or drum. This pit is generally located in the shed itself or just outside connected to the drainage channel through a pipe and protected from rain and runoff. Where urine is collected for incorporation in farmyard manure, the pit may be directly connected to the manure pit or heap. Urine that is going to be used as liquid manure or organic pesticide has to be stored in a drum for fermentation.
A household with two cattle can save the equivalent of purchasing about 100 kg of urea over one year by applying urine either directly as liquid fertiliser or as a component in improved farmyard manure.
2.3 Fotografías de la Tecnología
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde la Tecnología fue aplicada y que se hallan comprendidos por esta evaluación
País:
Nepal
Especifique más el lugar :
Midhill districts of Nepal
Map
×3. Clasificación de la Tecnología MST
3.1 Propósito(s) principal(es) de la Tecnología MST
- Collect fertilizer
3.2 Tipo(s) actuales de uso de la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología

Tierras cultivadas
- Cosecha anual
Comentarios:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Intensifying cultivation practices with either 1) inadequate application of fertilisers leading to a decline in soil fertility and the mining of soil nutrients or 2) application of too much fertiliser causing environmental problems through excessive leaching, and losses of fertiliser in surface runoff and consequent eutrophication or nitrification of streams, ponds, or groundwater.
3.5 Grupo MST al que pertenece la Tecnología
- manejo integrado de la fertilidad del suelo
3.6 Medidas MST que componen la Tecnología

medidas de manejo
- M6: Manejo de desperdicios (reciclado, reutilización o reducción)
Comentarios:
Main measures: management measures
3.7 Principales tipos de degradación de la tierra encarados con la Tecnología

deterioro químico del suelo
- Cn: reducción de la fertilidad y contenido reducido de la materia orgánica del suelo (no ocasionados por la erosión)
3.8 Prevención, reducción o restauración de la degradación de la tierra
Especifique la meta de la Tecnología con relación a la degradación de la tierra:
- no aplica
4. Especificaciones técnicas, actividades de implementación, insumos y costos
4.1 Dibujo técnico de la Tecnología
Especificaciones técnicas (relacionadas al dibujo técnico):
a) Urine collection and direct incorporation in covered farmyard manure pit.
b) Urine collection for later application as liquid manure or organic pesticide.
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: increase in organic matter, increase in soil fertility, increase in soil productivity, pest control
Secondary technical functions: supplementary irrigation
4.2 Información general sobre el cálculo de insumos y costos
Especifique cómo se calcularon los costos e insumos:
- por unidad de Tecnología
Especifique unidad:
Urine collection system
Especifique la moneda usada para calcular costos:
- USD
Indique el costo promedio del salario de trabajo contratado por día:
2.00
4.3 Actividades de establecimiento
| Actividad | Momento (estación) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Provide slight slope to the cattle shed floor | |
| 2. | Dig a draining ditch and a collection pit, if possible at the lowest point inside the shed. If this is not possible, an outside pit should be dug, protected from rain and runoff, and connected with the draining ditch through a pipe or a channel. | |
| 3. | Make the floor as impermeable as possible; e.g. with cement (expensive and durable), stone slabs, soil compaction, or clay (cheap but not durable). The more impermeable the floor, the more urine can be collected. | |
| 4. | Provide a jug/’decapitated’ plastic bottle/cup/etc. to scoop the urine out of the collection pit into the fermentation drum. |
4.4 Costos e insumos necesarios para el establecimiento
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Labour | per unit | 1,0 | 6,0 | 6,0 | 100,0 |
| Material de construcción | Plastic drum | per unit | 6,0 | 1,0 | 6,0 | 100,0 |
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 12,0 | |||||
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología en USD | 12,0 | |||||
Comentarios:
Duration of establishment phase: 0.25 month(s)
4.5 Actividades de establecimiento/ recurrentes
| Actividad | Momento/ frequencia | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | When the collection pit is full, the collected urine has to be removed from the pit and stored in a plastic drum for fermentation. | |
| 2. | The urine is applied as liquid fertiliser by jug or through drip irrigation. |
4.6 Costos e insumos necesarios para actividades de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (por año)
Comentarios:
It is clear that cattle or buffaloes are required for urine production. To help farmers to use their own resources, it is suggested to start with the cheapest and simplest form of urine collection and a compacted sloping floor and a collection pit within the shed. This allows the farmer to see the benefits of collecting the urine and will encourage them to invest in more expensive materials to improve the efficiency of urine collection. Cost as in January 2007
5. Entorno natural y humano
5.1 Clima
Lluvia anual
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Especificaciones/ comentarios sobre la cantidad de lluvia:
Annual rainfall: Also 2000-3000 mm
Zona agroclimática
- húmeda
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 Topografía
Pendientes en promedio:
- plana (0-2 %)
- ligera (3-5%)
- moderada (6-10%)
- ondulada (11-15%)
- accidentada (16-30%)
- empinada (31-60%)
- muy empinada (>60%)
Formaciones telúricas:
- meseta/ planicies
- cordilleras
- laderas montañosas
- laderas de cerro
- pies de monte
- fondo del valle
Zona altitudinal:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1,000 m s.n.m
- 1,001-1,500 m s.n.m
- 1,501-2,000 m s.n.m
- 2,001-2,500 m s.n.m
- 2,501-3,000 m s.n.m
- 3,001-4,000 m s.n.m
- > 4,000 m s.n.m
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre topografía :
Slopes on average: Also moderate (6-10%), rolling (11-15%) and hilly (16-30%)
Landforms: Also footslopes
Altitudinal zone: Also 1000-1500 m a.s.l. and 1500-2000 m a.s.l.
5.6 Las características de los usuarios de la tierra que aplican la Tecnología
Orientación del mercado del sistema de producción:
- subsistencia (autoprovisionamiento)
- comercial/ mercado
Individuos o grupos:
- individual/ doméstico
Indique otras características relevantes de los usuarios de las tierras:
Off-farm income specification: In most farm households, off-farm income plays at least a minor and increasingly a major role. Occasional opportunities for off-farm income present themselves in the form of daily labour wages. Some households’ members receive regular salaries, whilst an increasing number of Nepalis are working in India, the Middle East, Malaysia, and elsewhere and sending remittance incomes home.
5.7 Área promedio de la tierra usada por usuarios de tierra que aplican la Tecnología
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
5.8 Tenencia de tierra, uso de tierra y derechos de uso de agua
Tenencia de tierra:
- individual, sin título
- individual, con título
Derechos de uso de tierra:
- arrendamiento
- individual
6. Impactos y comentarios para concluir
6.1 Impactos in situ demostrados por la Tecnología
Impactos socioeconómicos
Ingreso y costos
gastos en insumos agrícolas
Comentarios/ especifique:
Reduced expenses for agrochemicals
Otros impactos socioeconómicos
Shed management and cleaning
Organic crop production
Animal health
Establishment costs if cement is used
Impactos socioculturales
Social prestige as seen as progressive farmer
Handling of dung and urine
Impactos ecológicos
Otros impactos ecológicos
Eutrophication and nitrification of waterbodies due to controlled outflow of urine
6.2 Impactos fuera del sitio demostrados por la Tecnología
contaminación de aguas subterráneas/ de ríos
Comentarios/ especifique:
Reduction of nutrient influx into water bodies
Dependence on outside inputs
6.4 Análisis costo-beneficio
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de establecimiento (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
positivo
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
positivo
Comentarios:
The high cost of mineral fertiliser means that the establishment costs are soon recovered. In the long-term, the major reduction in fertiliser cost leads to increased benefits.
6.5 Adopción de la Tecnología
Comentarios:
Comments on spontaneous adoption: Approximately 30% of SSMP supported farmers groups and about 15% none members of SSMP supported groups adopted the tehnology.
6.7 Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades de la Tecnología
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
|
The use of urine collected on-farm reduced the requirement for mineral fertiliser which reduced production costs and outside dependency How can they be sustained / enhanced? Further promotion of the technology will increase this impact |
|
Human urine can also be used to fertilise crops, but needs to be fermented longer and may be socially less accepted How can they be sustained / enhanced? Promote the use of urine further and show there is no problem with using human urine |
|
Applying urine as a liquid manure also irrigates the crops (fertigation) How can they be sustained / enhanced? The link between urine application and drip irrigation, or other forms of smallscale irrigation, should be promoted. It has been tested and applied successfully by farmers related to SSMP in Syangja and Surkhet in western Nepal |
6.8 Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos de la Tecnología y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| The initial costs incurred whilst improving a durable shed using cement may hinder adoption | Simpler methods such as using clay soil, compacting the fl oor, and using stone slates may, however lead to less urine being collected |
| Project incentives (cement, plastic drum) have hindered adoption in some places |
No incentives should be provided, rather very simple methods should be demonstrated and adapted to local conditions |
| Urine collection is feasible for subsistence farm households or small scale commercial producers. It may, however, not be applicable for larger scale commercial vegetable producers as a balance between area needed for livestock and growing the crops is needed | Urine could become a tradeable commodity which would see large-scale livestock producers selling their urine to large-scale vegetable producers. |
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.1 Métodos/ fuentes de información
7.2 Vínculos a las publicaciones disponibles
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
STSS; SSMP (2001) Farmyard Manure and Compost Management (in Nepali). Kathmandu: Soil Testing Services Section, Department of Agriculture and Sustainable Soil Management Programme
¿Dónde se halla disponible? ¿Costo?
SSMP
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos

Farmer field schools on integrated plant nutrient systems [Nepal]
Participatory and collaborative learning through the farmer field school approach
- Compilador: Richard Allen

Farmer-led experimentation [Nepal]
Participatory technology testing and adaptation through farmer-led experiments
- Compilador: Richard Allen

Farmer-to-farmer diffusion [Nepal]
Wider diffusion of sustainable soil management technologies through a demand responsive farmer-to-farmer diffusion approach
- Compilador: Richard Allen
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos