Improved cattleshed for urine collection [Népal]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Richard Allen
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateurs : David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Mutra sankalan ka lagi sudhariyeko goth (Nepali)
technologies_1752 - Népal
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Spécialiste GDT:
Director
Soil Management Directorate, Department of Agriculture
Népal
Spécialiste GDT:
Team Leader
Sustainable Soil Management Programme
Népal
Nom du projet qui a facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Sustainable Soil Management Programme, Nepal (SSMP)Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
HELVETAS (Swiss Intercooperation)Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Department of Agriculture, Soil Management Directorate, Hariharbhawan Lalitpur (doasoil) - Népal1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.5 Référence au(x) Questionnaires sur les Approches de GDT (documentées au moyen de WOCAT)

Farmer field schools on integrated plant nutrient systems [Népal]
Participatory and collaborative learning through the farmer field school approach
- Compilateur : Richard Allen

Farmer-led experimentation [Népal]
Participatory technology testing and adaptation through farmer-led experiments
- Compilateur : Richard Allen

Farmer-to-farmer diffusion [Népal]
Wider diffusion of sustainable soil management technologies through a demand responsive farmer-to-farmer diffusion approach
- Compilateur : Richard Allen
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
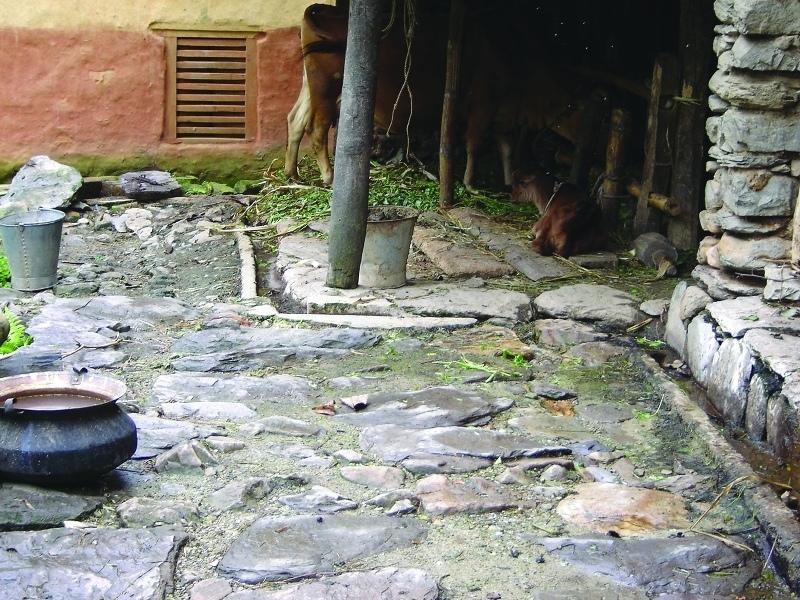
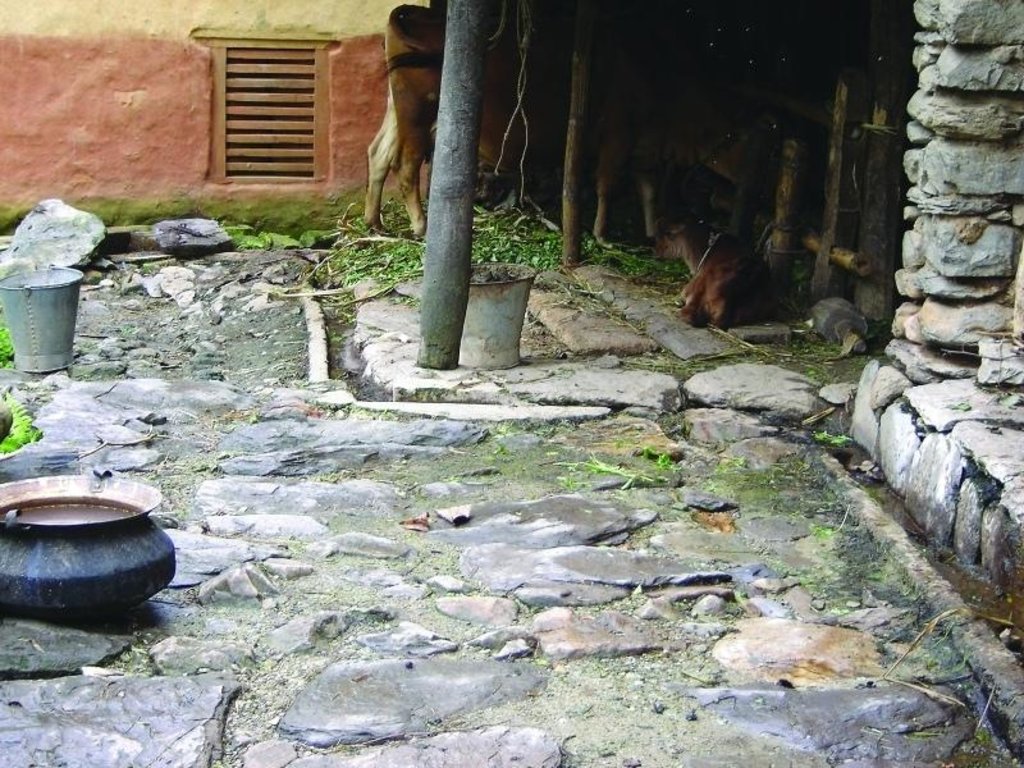
Collection of cattle urine in improved cattle sheds for use as liquid manure and organic pesticide
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
Nitrogen is the most important macronutrient for plants, and high crop productivity can only be achieved by making sufficient nitrogen available to crops. Nitrogen is also the most limiting nutrient in farms across Nepal’s midhills. Traditionally farmers applied farmyard manure to fertilise their needs. In many places this is being supplemented or even entirely replaced by inorganic fertiliser - mainly urea. The price of inorganic fertiliser has increased continuously in recent years and it is only available in limited quantities in areas far from the roadheads. On the other hand, cultivation practices are intensifying with increased cropping intensities and more nutrient-demanding crops as, for example, local varieties are replaced by hybrids and new crops are grown. This can easily lead to declining soil fertility and nutrient mining if it is not compensated for by an equivalent increase in organic or mineral fertilisation.
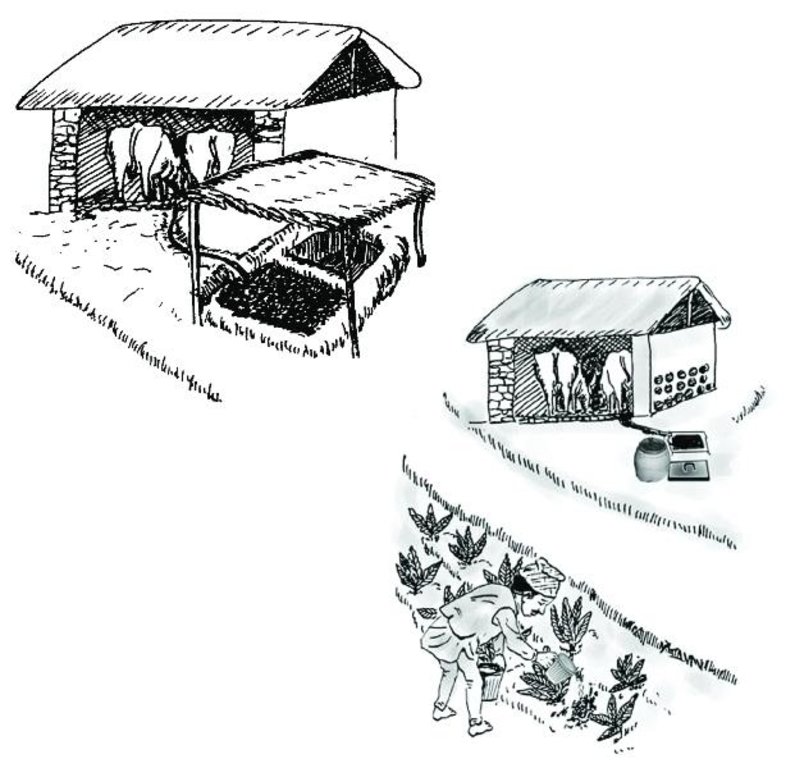
Cattle urine is a viable alternative to mineral fertiliser. Of the nitrogen excreted by cattle, 60% is found in the urine and only 40% in dung. In traditional sheds, urine is left to be absorbed in the bedding material, while excess urine is channelled out of the shed and disposed of. The technology described here - improved cattle sheds- are designed for collecting the urine in a pit or drum. This pit is generally located in the shed itself or just outside connected to the drainage channel through a pipe and protected from rain and runoff. Where urine is collected for incorporation in farmyard manure, the pit may be directly connected to the manure pit or heap. Urine that is going to be used as liquid manure or organic pesticide has to be stored in a drum for fermentation.
A household with two cattle can save the equivalent of purchasing about 100 kg of urea over one year by applying urine either directly as liquid fertiliser or as a component in improved farmyard manure.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Népal
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Midhill districts of Nepal
Map
×3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- Collect fertilizer
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

Terres cultivées
- Cultures annuelles
Commentaires:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Intensifying cultivation practices with either 1) inadequate application of fertilisers leading to a decline in soil fertility and the mining of soil nutrients or 2) application of too much fertiliser causing environmental problems through excessive leaching, and losses of fertiliser in surface runoff and consequent eutrophication or nitrification of streams, ponds, or groundwater.
3.5 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- gestion intégrée de la fertilité des sols
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

modes de gestion
- M6: Gestion des déchets (recyclage, réutilisation ou réduction)
Commentaires:
Main measures: management measures
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

dégradation chimique des sols
- Cn: baisse de la fertilité des sols et réduction du niveau de matière organique (non causée par l’érosion)
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- non applicable
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
Spécifications techniques (associées au dessin technique):
a) Urine collection and direct incorporation in covered farmyard manure pit.
b) Urine collection for later application as liquid manure or organic pesticide.
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: increase in organic matter, increase in soil fertility, increase in soil productivity, pest control
Secondary technical functions: supplementary irrigation
4.2 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
Spécifiez la manière dont les coûts et les intrants ont été calculés:
- par entité de la Technologie
Précisez l'unité:
Urine collection system
Indiquez la monnaie utilisée pour le calcul des coûts:
- dollars américains
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
2.00
4.3 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Calendrier des activités (saisonnier) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Provide slight slope to the cattle shed floor | |
| 2. | Dig a draining ditch and a collection pit, if possible at the lowest point inside the shed. If this is not possible, an outside pit should be dug, protected from rain and runoff, and connected with the draining ditch through a pipe or a channel. | |
| 3. | Make the floor as impermeable as possible; e.g. with cement (expensive and durable), stone slabs, soil compaction, or clay (cheap but not durable). The more impermeable the floor, the more urine can be collected. | |
| 4. | Provide a jug/’decapitated’ plastic bottle/cup/etc. to scoop the urine out of the collection pit into the fermentation drum. |
4.4 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % du coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Labour | per unit | 1,0 | 6,0 | 6,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériaux de construction | Plastic drum | per unit | 6,0 | 1,0 | 6,0 | 100,0 |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 12,0 | |||||
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 12,0 | |||||
Commentaires:
Duration of establishment phase: 0.25 month(s)
4.5 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | When the collection pit is full, the collected urine has to be removed from the pit and stored in a plastic drum for fermentation. | |
| 2. | The urine is applied as liquid fertiliser by jug or through drip irrigation. |
4.6 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
Commentaires:
It is clear that cattle or buffaloes are required for urine production. To help farmers to use their own resources, it is suggested to start with the cheapest and simplest form of urine collection and a compacted sloping floor and a collection pit within the shed. This allows the farmer to see the benefits of collecting the urine and will encourage them to invest in more expensive materials to improve the efficiency of urine collection. Cost as in January 2007
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifications/ commentaires sur les précipitations:
Annual rainfall: Also 2000-3000 mm
Zone agro-climatique
- humide
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la topographie:
Slopes on average: Also moderate (6-10%), rolling (11-15%) and hilly (16-30%)
Landforms: Also footslopes
Altitudinal zone: Also 1000-1500 m a.s.l. and 1500-2000 m a.s.l.
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Orientation du système de production:
- subsistance (auto-approvisionnement)
- commercial/ de marché
Individus ou groupes:
- individu/ ménage
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Off-farm income specification: In most farm households, off-farm income plays at least a minor and increasingly a major role. Occasional opportunities for off-farm income present themselves in the form of daily labour wages. Some households’ members receive regular salaries, whilst an increasing number of Nepalis are working in India, the Middle East, Malaysia, and elsewhere and sending remittance incomes home.
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres utilisées par les exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- individu, sans titre de propriété
- individu, avec titre de propriété
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- loué
- individuel
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Revenus et coûts
dépenses pour les intrants agricoles
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Reduced expenses for agrochemicals
Autres impacts socio-économiques
Shed management and cleaning
Organic crop production
Animal health
Establishment costs if cement is used
Impacts socioculturels
Social prestige as seen as progressive farmer
Handling of dung and urine
Impacts écologiques
Autres impacts écologiques
Eutrophication and nitrification of waterbodies due to controlled outflow of urine
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
pollution des rivières/ nappes phréatiques
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Reduction of nutrient influx into water bodies
Dependence on outside inputs
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
Commentaires:
The high cost of mineral fertiliser means that the establishment costs are soon recovered. In the long-term, the major reduction in fertiliser cost leads to increased benefits.
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
Commentaires:
Comments on spontaneous adoption: Approximately 30% of SSMP supported farmers groups and about 15% none members of SSMP supported groups adopted the tehnology.
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
|
The use of urine collected on-farm reduced the requirement for mineral fertiliser which reduced production costs and outside dependency How can they be sustained / enhanced? Further promotion of the technology will increase this impact |
|
Human urine can also be used to fertilise crops, but needs to be fermented longer and may be socially less accepted How can they be sustained / enhanced? Promote the use of urine further and show there is no problem with using human urine |
|
Applying urine as a liquid manure also irrigates the crops (fertigation) How can they be sustained / enhanced? The link between urine application and drip irrigation, or other forms of smallscale irrigation, should be promoted. It has been tested and applied successfully by farmers related to SSMP in Syangja and Surkhet in western Nepal |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| The initial costs incurred whilst improving a durable shed using cement may hinder adoption | Simpler methods such as using clay soil, compacting the fl oor, and using stone slates may, however lead to less urine being collected |
| Project incentives (cement, plastic drum) have hindered adoption in some places |
No incentives should be provided, rather very simple methods should be demonstrated and adapted to local conditions |
| Urine collection is feasible for subsistence farm households or small scale commercial producers. It may, however, not be applicable for larger scale commercial vegetable producers as a balance between area needed for livestock and growing the crops is needed | Urine could become a tradeable commodity which would see large-scale livestock producers selling their urine to large-scale vegetable producers. |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
7.2 Références des publications disponibles
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
STSS; SSMP (2001) Farmyard Manure and Compost Management (in Nepali). Kathmandu: Soil Testing Services Section, Department of Agriculture and Sustainable Soil Management Programme
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
SSMP
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens

Farmer field schools on integrated plant nutrient systems [Népal]
Participatory and collaborative learning through the farmer field school approach
- Compilateur : Richard Allen

Farmer-led experimentation [Népal]
Participatory technology testing and adaptation through farmer-led experiments
- Compilateur : Richard Allen

Farmer-to-farmer diffusion [Népal]
Wider diffusion of sustainable soil management technologies through a demand responsive farmer-to-farmer diffusion approach
- Compilateur : Richard Allen
Modules
Aucun module trouvé