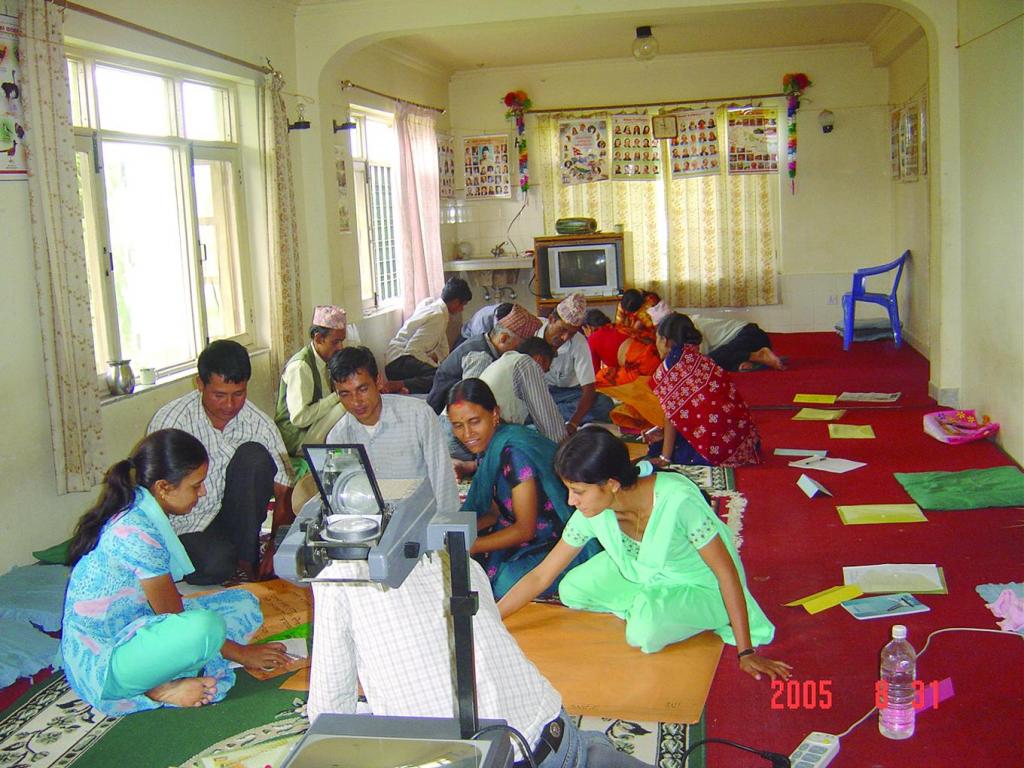
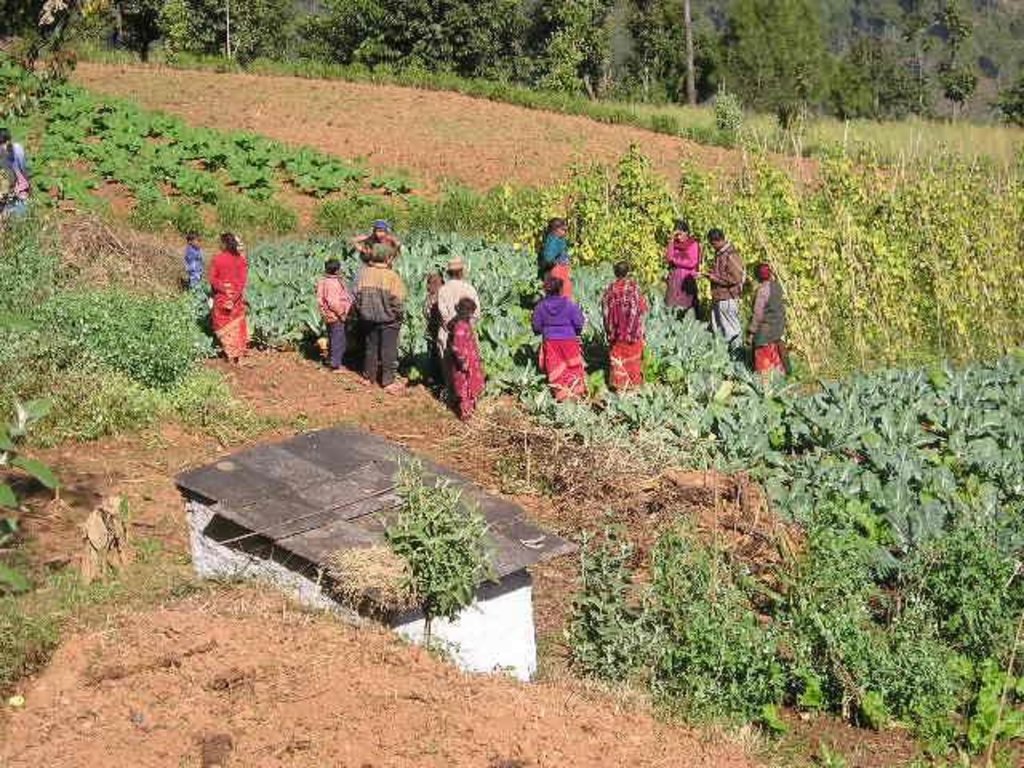
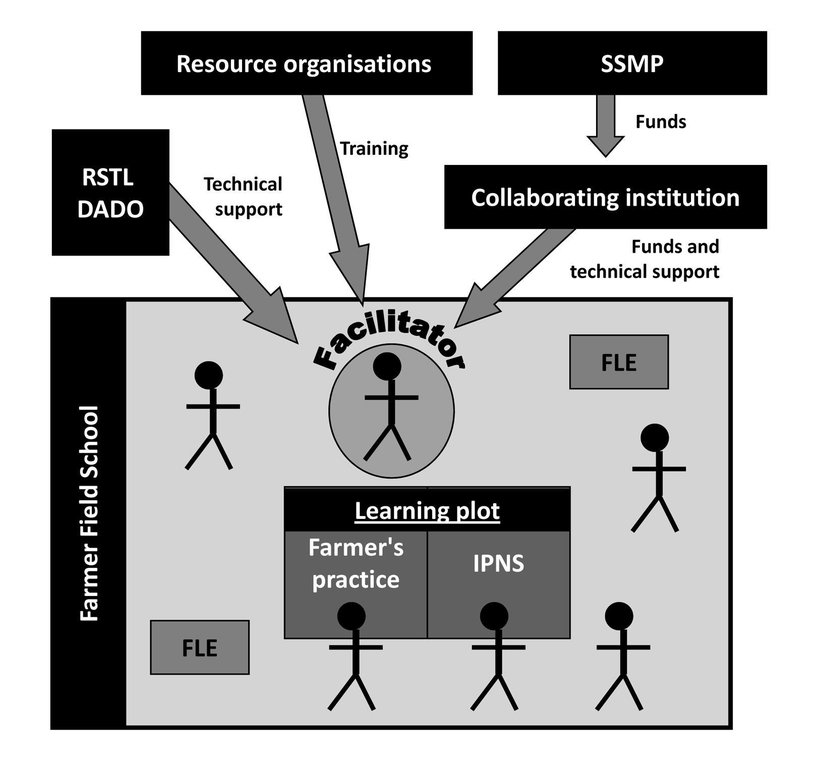
Farmer field schools on integrated plant nutrient systems [Nepal]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: Richard Allen
- Editor: –
- Revisor: Laura Ebneter
Krishak Pathsala (Nepali)
approaches_2351 - Nepal
1. Información general
2. Descripción del Enfoque MST
3. Participación y roles de las partes interesadas involucradas
4. Apoyo técnico, fortalecimiento institucional y gestión del conocimiento
5. Financiamiento y apoyo material externo
6. Análisis de impacto y comentarios de conclusión
7. Referencias y vínculos
Vínculos y módulos
Colapsar todosVínculos
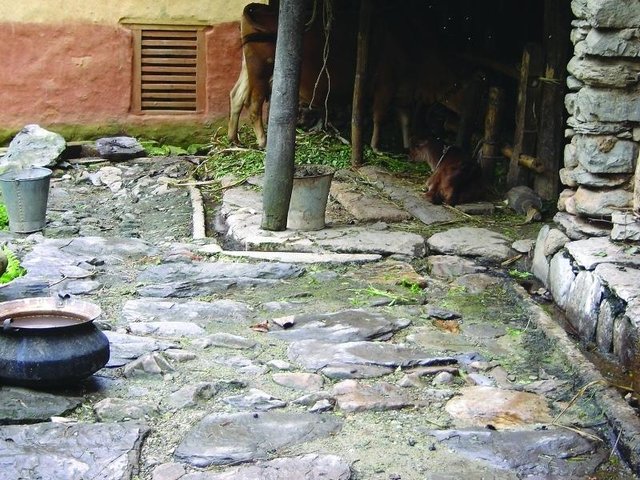

Improved cattleshed for urine collection [Nepal]
Collection of cattle urine in improved cattle sheds for use as liquid manure and organic pesticide
- Compilador: Richard Allen
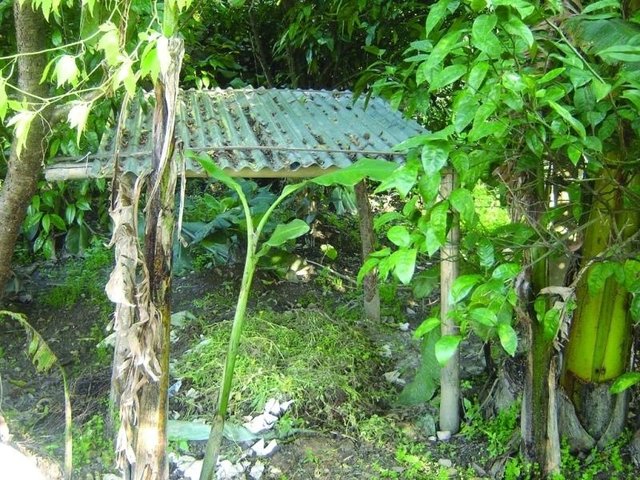

Improved compost preparation [Nepal]
Improved compost preparation using a range of biomass and waste to produce high value fertiliser
- Compilador: Richard Allen
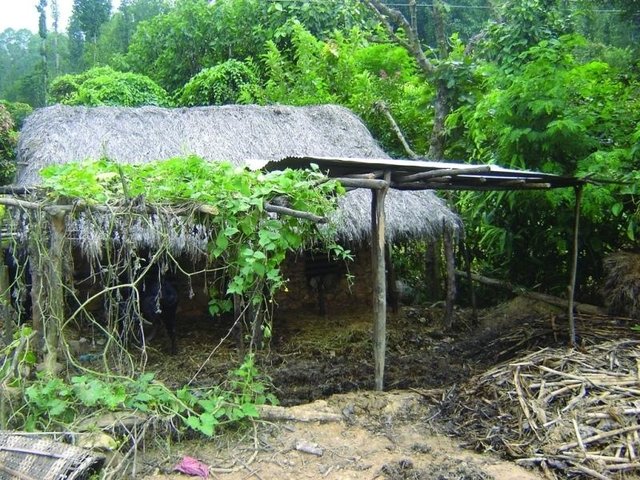

Improved farmyard manure through sunlight, rain and runoff … [Nepal]
Improving farmyard manure by protecting it from direct sunlight, rainfall, and runoff to reduce volatilisation and leaching
- Compilador: Richard Allen
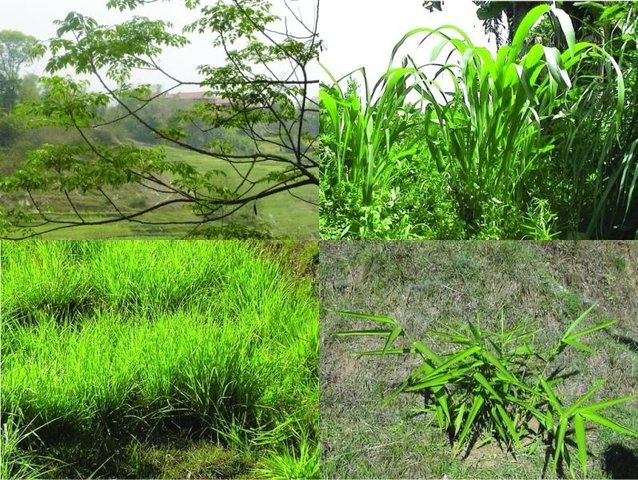

Cultivation of fodder and grasses [Nepal]
Cultivation of fodder crops on marginal lands and terrace risers
- Compilador: Richard Allen
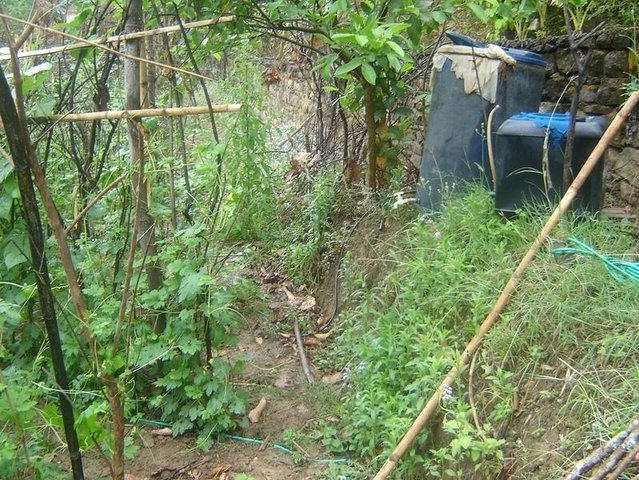

Urine application through drip irrigation for bitter gourd … [Nepal]
Application of cattle urine through drip irrigation technology to provide constant flow of fertiliser to bitter gourd
- Compilador: Richard Allen
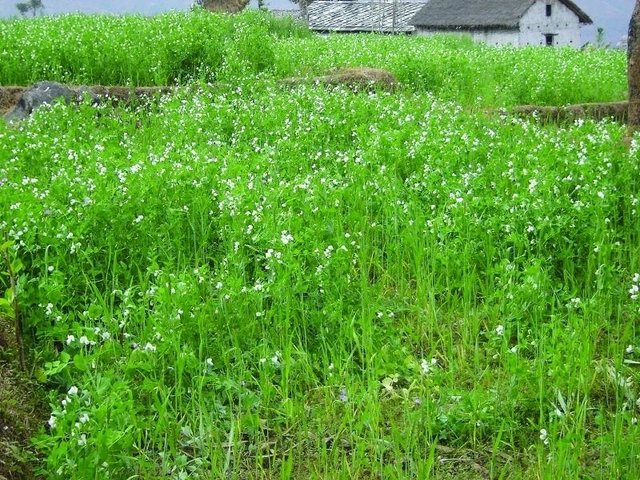

Legume integration [Nepal]
Integration of leguminous crops as intercrops on terrace risers or as relay crops
- Compilador: Richard Allen

Organic pest management [Nepal]
Promotion of botanical pesticides for organic pest management and liquid manure
- Compilador: Richard Allen
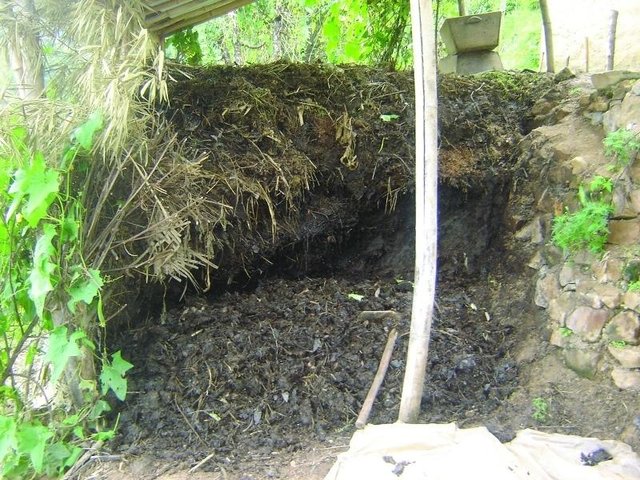

Better quality farmyard manure through improved decomposition [Nepal]
Collection and proper storage of farmyard manure in heaps or pits
- Compilador: Richard Allen
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos