Improved farmyard manure through sunlight, rain and runoff protection [Nepal]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: Richard Allen
- Editor: –
- Revisores: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Gham, bhalpani ra baleni bata bachai nirman gariyeko ramro gnastar ko gothemal (Nepali)
technologies_1756 - Nepal
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación de la Tecnología
Especialista MST:
Director
Soil Management Directorate, Department of Agriculture
Nepal
Especialista MST:
Team Leader
Sustainable Soil Management Programme
Nepal
Nombre del proyecto que financió la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Sustainable Soil Management Programme, Nepal (SSMP)Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Department of Agriculture, Soil Management Directorate, Hariharbhawan Lalitpur (doasoil) - NepalNombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
HELVETAS (Swiss Intercooperation)1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT:
Sí
1.5 Referencia al (los) Cuestionario(s) de Enfoques MST (documentados usando WOCAT)

Farmer field schools on integrated plant nutrient systems [Nepal]
Participatory and collaborative learning through the farmer field school approach
- Compilador: Richard Allen

Farmer-to-farmer diffusion [Nepal]
Wider diffusion of sustainable soil management technologies through a demand responsive farmer-to-farmer diffusion approach
- Compilador: Richard Allen
2. Descripción de la Tecnología MST
2.1 Breve descripción de la Tecnología
Definición de la Tecnología:
Improving farmyard manure by protecting it from direct sunlight, rainfall, and runoff to reduce volatilisation and leaching
2.2 Descripción detallada de la Tecnología
Descripción:
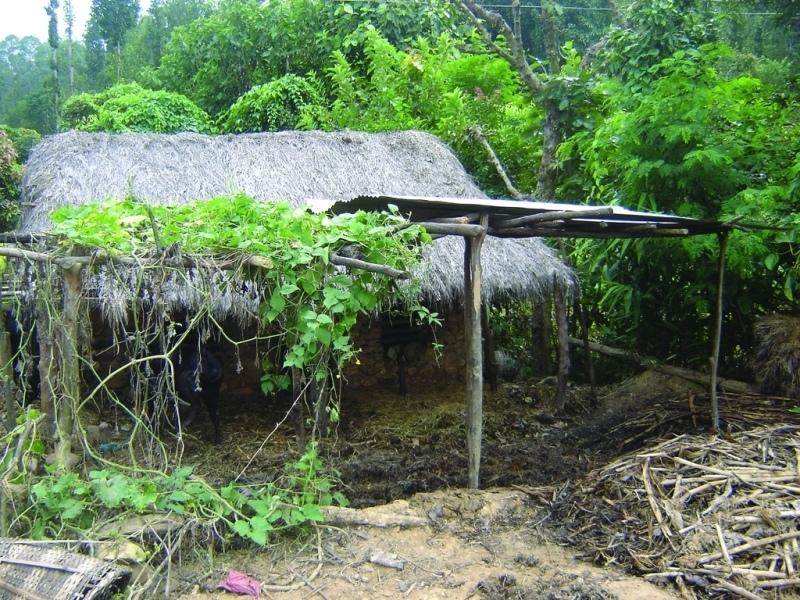
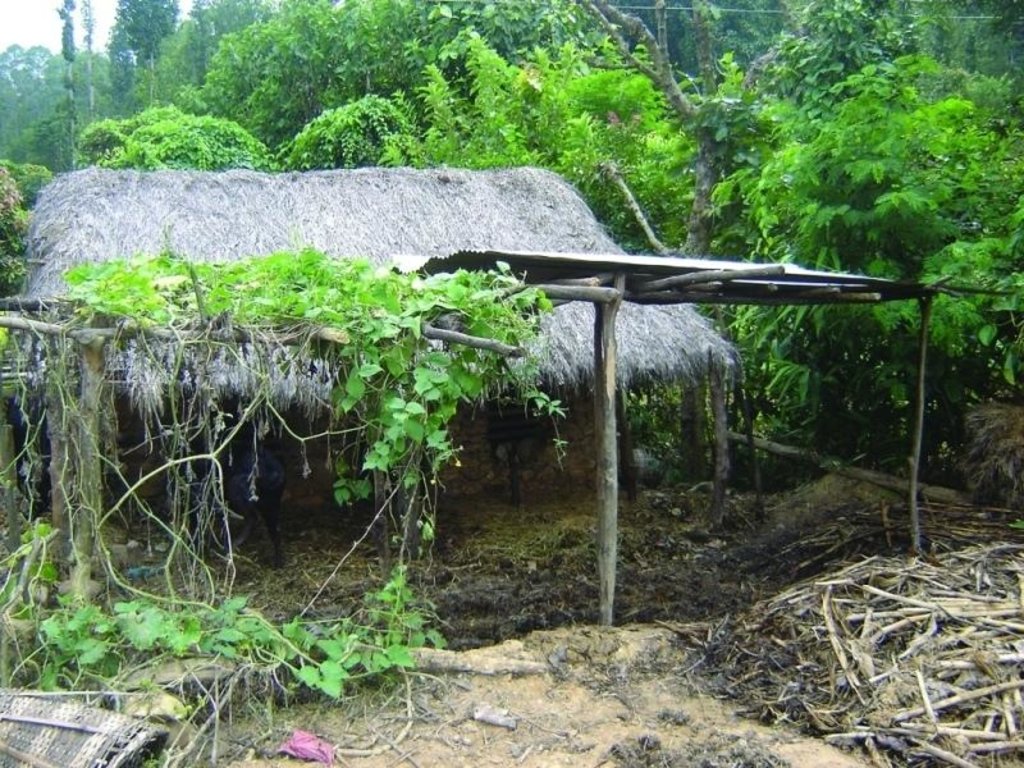
Farmyard manure is the most common form of organic fertiliser applied to crops in the midhills of Nepal. Farmyard manure has a high proportion of organic material which nurtures soil organisms and is essential for maintaining an active soil life. Typically, only about half of the nutrient content of farmyard manure becomes available for crop growth during the first year after it is applied to the soil. The rest of the nutrients are channelled through soil biotic processes and are released in the following years. The high organic matter content and the more active soil life improve or maintain a friable soil structure, increase the cation exchange capacity, the water holding capacity, and the infiltration rate, and reducing the risk of soil pests.
Indigenous methods of preparing and using farmyard manure vary depending on the ecological zone, access to bedding material from crop or forest land and to crop residues and fodder, the availability of labour, and other factors. Traditionally, Nepali farmers take the manure out of their sheds to dry it for 2-3 days and then carry it to the field where it is left in small heaps for a number of days before being spread and incorporated into the soil.
Farmers rate the quality of manure according to which livestock species it comes from. These ratings have been confirmed by nutrient analysis as cattle manure (NPK%: 0.6, 0.13, 0.66) is considered to be better than buffalo manure (0.33, 0.25, 0.10), and horse manure; while pig (0.5, 0.18, 0.42), goat (0.6, 0.13, 0.99), and sheep manure (0.6, 0.13, 0.99) are considered better than cattle manure. Chicken manure (1.46, 0.51, 0.51) is considered the best of all.
It has however been shown that considerable nutrient losses occur if the manure is inappropriately handled or stored. Drying of the manure leads to loss of nutrients through volatilisation, and rainfall and runoff leads to leaching or washing out of nutrients. In addition, the common disposal of urine - the part of the excreta with the highest nutrient concentration - further reduces the level of nutrients in manure.
To reduce nutrient losses farmyard manure needs to be protected from direct sunlight; protected from rainfall or run-on; and protected from runoff. This can be achieved in a variety of ways using a variety of inputs. It is most important to protect the manure during storage and just before it is applied in the field to make the best use of this valuable local resource.
2.3 Fotografías de la Tecnología
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde la Tecnología fue aplicada y que se hallan comprendidos por esta evaluación
País:
Nepal
Especifique más el lugar :
Midhills districts of Nepal
Especifique la difusión de la Tecnología:
- aplicada en puntos específicos/ concentrada en un área pequeña
Map
×3. Clasificación de la Tecnología MST
3.1 Propósito(s) principal(es) de la Tecnología MST
- Improve manure
3.2 Tipo(s) actuales de uso de la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología

Tierras cultivadas
- Cosecha anual
Comentarios:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Intensifying cultivation practices with either 1) inadequate application of fertilisers leading to a decline in soil fertility and the mining of soil nutrients or 2) application of too much fertiliser causing environmental problems through excessive leaching, and losses of fertiliser in surface runoff and consequent eutrophication or nitrification of streams, ponds or groundwater
3.5 Grupo MST al que pertenece la Tecnología
- manejo integrado de la fertilidad del suelo
3.6 Medidas MST que componen la Tecnología

medidas de manejo
- M2: Cambio de gestión/ nivel de intensidad
3.7 Principales tipos de degradación del suelo encarados con la Tecnología

deterioro químico del suelo
- Cn: reducción de la fertilidad y contenido reducido de la materia orgánica del suelo (no ocasionados por la erosión)
3.8 Prevención, reducción o restauración de la degradación del suelo
Especifique la meta de la Tecnología con relación a la degradación de la tierra:
- reducir la degradación del suelo
4. Especificaciones técnicas, actividades de implementación, insumos y costos
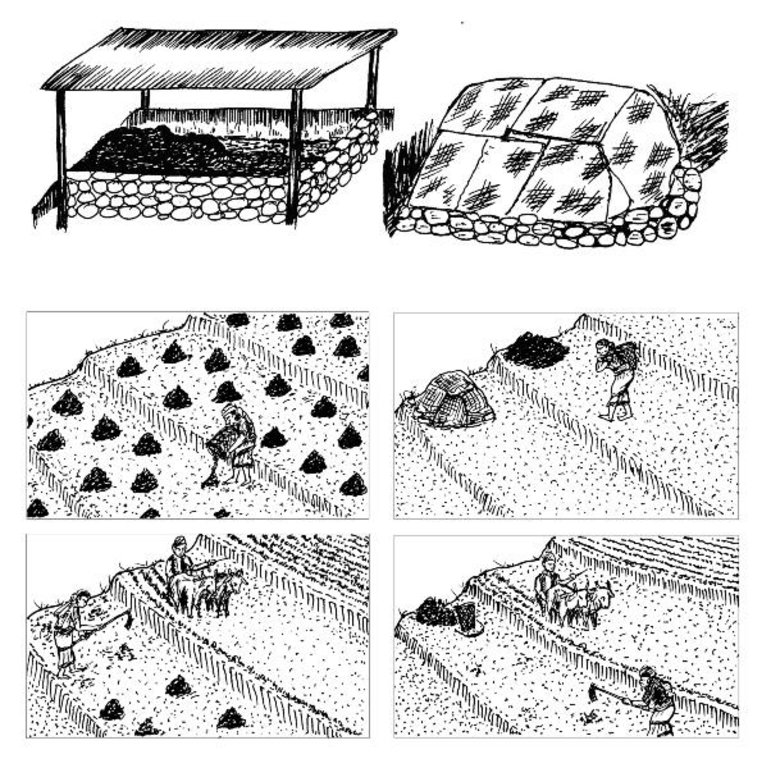
4.1 Dibujo técnico de la Tecnología
Especificaciones técnicas (relacionadas al dibujo técnico):
a) Covering the farmyard manure with a roof made of tin sheet or plastic sheets. Cheaper alternatives are:
- a thatched roof
- shading with creepers like cucurbits
- planting broadleaf mustard on the heap
- applying a covering of crop residues or forest material
b) Farmyard manure is traditionally carried to the fi elds in doko baskets and left there in unprotected heaps to be incorporated often weeks and sometimes several months later (top and bottom left). It is much better to incorporate it on the day of transport as the longer it is left out on the fi elds in heaps the greater are the nutrient losses from the heaps (bottom right). Alternatively it can be stored in a corner of the fi eld covered with plastic sheets, crop residues, or in some other way (top right).
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: increase in organic matter, increase in soil fertility, increase in soil productivity
Secondary technical functions: increased infiltration rate and water holding capacity, improved soil physical properties (friability,easier soil preparation)
Layout change according to natural and human environment: protect farmyard manure; change application
4.2 Información general sobre el cálculo de insumos y costos
Especifique la moneda usada para calcular costos:
- USD
Indique el costo promedio del salario de trabajo contratado por día:
2.00
4.3 Actividades de establecimiento
| Actividad | Momento (estación) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Cover the farmyard manure heap or pit with any available material (crop residues, forest material, plastic sheet, thatched roof, zinc sheet, etc.) |
4.4 Costos e insumos necesarios para el establecimiento
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Building manure pit and shelter | Persons/day | 1,0 | 2,0 | 2,0 | 100,0 |
| Material de construcción | Material | unit | 1,0 | 25,0 | 25,0 | 100,0 |
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 27,0 | |||||
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología en USD | 27,0 | |||||
4.5 Actividades de establecimiento/ recurrentes
| Actividad | Momento/ frequencia | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Pour household wastewater onto the heap or pit to keep the farmyard |
4.6 Costos e insumos necesarios para actividades de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (por año)
Comentarios:
Cost as in January 2007
5. Entorno natural y humano
5.1 Clima
Lluvia anual
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Especificaciones/ comentarios sobre la cantidad de lluvia:
Annual rainfall: Also 2000-3000 mm
Zona agroclimática
- húmeda
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 Topografía
Pendientes en promedio:
- plana (0-2 %)
- ligera (3-5%)
- moderada (6-10%)
- ondulada (11-15%)
- accidentada (16-30%)
- empinada (31-60%)
- muy empinada (>60%)
Formaciones telúricas:
- meseta/ planicies
- cordilleras
- laderas montañosas
- laderas de cerro
- pies de monte
- fondo del valle
Zona altitudinal:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1,000 m s.n.m
- 1,001-1,500 m s.n.m
- 1,501-2,000 m s.n.m
- 2,001-2,500 m s.n.m
- 2,501-3,000 m s.n.m
- 3,001-4,000 m s.n.m
- > 4,000 m s.n.m
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre topografía :
Slopes on average: Also moderate (6-10%), rolling (11-15%) and hilly (16-30%)
Landforms: Also footslopes
Altitudinal zone: Also 1000-1500 m a.s.l., 1500-2000 m a.s.l. and 2000-2500 m a.s.l.
5.6 Las características de los usuarios de la tierra que aplican la Tecnología
Orientación del mercado del sistema de producción:
- subsistencia (autoprovisionamiento)
- mixta (subsistencia/ comercial)
Individuos o grupos:
- individual/ doméstico
Indique otras características relevantes de los usuarios de las tierras:
Off-farm income specification: In most farm households, off-farm income plays at least a minor and increasingly a major role. Occasional opportunities for off-farm income present themselves in the form of daily labour wages. Some households’ members receive regular salaries, whilst an increasing number of Nepalis are working in India, the Middle East, Malaysia, and elsewhere and sending remittance incomes home.
Market orientation of production system: Also commercial/ market
5.7 Área promedio de la tierra usada por usuarios de tierra que aplican la Tecnología
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
5.8 Tenencia de tierra, uso de tierra y derechos de uso de agua
Tenencia de tierra:
- individual, sin título
- individual, con título
Derechos de uso de tierra:
- arrendamiento
- individual
Comentarios:
Sharecropping between owner and tenant
6. Impactos y comentarios para concluir
6.1 Impactos in situ demostrados por la Tecnología
Impactos socioeconómicos
Producción
producción de cultivo
Ingreso y costos
gastos en insumos agrícolas
Comentarios/ especifique:
Reduced expenditure on mineral fertilisers
Impactos ecológicos
Otros impactos ecológicos
Soil characteristics
6.2 Impactos fuera del sitio demostrados por la Tecnología
contaminación de aguas subterráneas/ de ríos
Comentarios/ especifique:
Reduction of nutrient influx into water bodies
Dependence on outside inputs
6.4 Análisis costo-beneficio
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de establecimiento (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
positivo
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
positivo
Comentarios:
Large short- and long-term benefits due to need to use less of the costly mineral fertilisers. The only extra ‘cost’ is the extra labor needed.
6.5 Adopción de la Tecnología
Comentarios:
Comments on acceptance with external material support: An independent assessment found that 95% of the farmers participating in SSMP’s farmyard improvement activities were accepted the technology.
Comments on adoption trend: About 70% of non-participant farmers who had come into contact with the technologies had also adopted them.
6.7 Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades de la Tecnología
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
|
The use of improved farmyard manure reduced the need for mineral fertiliser thereby reducing production costs and outside dependency How can they be sustained / enhanced? Further promotion of the technology will increase this impact |
| A simple technology affordable by poor farmers in remote areas far from a roadhead |
| The increased use of organic fertiliser improves the physical characteristics of soil making ploughing easier and increasing water holding capacity of the soil |
6.8 Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos de la Tecnología y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| Cost of a permanent roof for the manure heap may hinder adoption of the technology | Promote simple alternatives to high cost roofs such as straw cover, cover with broad leaf mustard, thatch, and waste plastic |
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.1 Métodos/ fuentes de información
7.2 Vínculos a las publicaciones disponibles
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
STSS; SSMP (2001) Farmyard Manure and Compost Management (in Nepali) Kathmandu: Soil Testing Services Section, Department of Agriculture and Sustainable Soil Management Programme
¿Dónde se halla disponible? ¿Costo?
SSMP
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos

Farmer field schools on integrated plant nutrient systems [Nepal]
Participatory and collaborative learning through the farmer field school approach
- Compilador: Richard Allen

Farmer-to-farmer diffusion [Nepal]
Wider diffusion of sustainable soil management technologies through a demand responsive farmer-to-farmer diffusion approach
- Compilador: Richard Allen
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos