Improved farmyard manure through sunlight, rain and runoff protection [尼泊尔]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Richard Allen
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Gham, bhalpani ra baleni bata bachai nirman gariyeko ramro gnastar ko gothemal (Nepali)
technologies_1756 - 尼泊尔
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
Director
Soil Management Directorate, Department of Agriculture
尼泊尔
SLM专业人员:
Team Leader
Sustainable Soil Management Programme
尼泊尔
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Sustainable Soil Management Programme, Nepal (SSMP)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Department of Agriculture, Soil Management Directorate, Hariharbhawan Lalitpur (doasoil) - 尼泊尔有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
HELVETAS (Swiss Intercooperation)1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.5 参考关于SLM方法(使用WOCAT记录的SLM方法)的调查问卷

Farmer field schools on integrated plant nutrient systems [尼泊尔]
Participatory and collaborative learning through the farmer field school approach
- 编制者: Richard Allen

Farmer-to-farmer diffusion [尼泊尔]
Wider diffusion of sustainable soil management technologies through a demand responsive farmer-to-farmer diffusion approach
- 编制者: Richard Allen
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Improving farmyard manure by protecting it from direct sunlight, rainfall, and runoff to reduce volatilisation and leaching
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
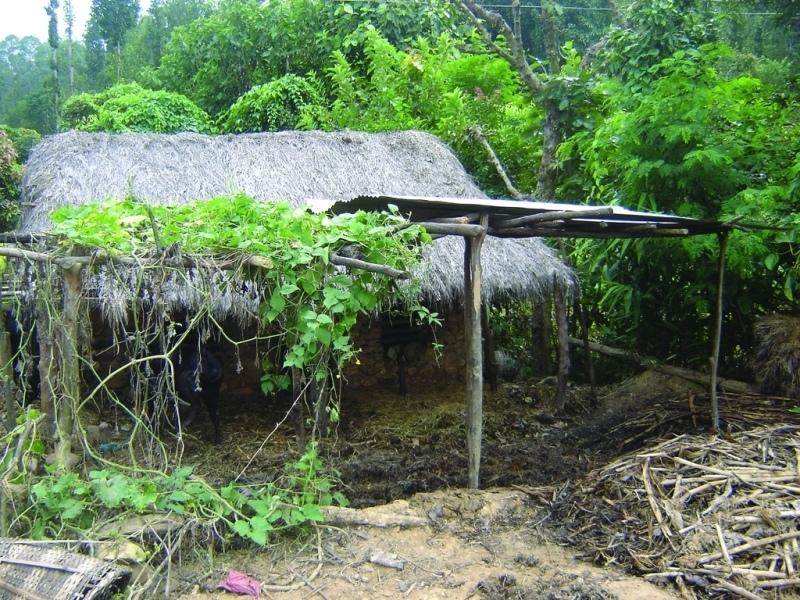
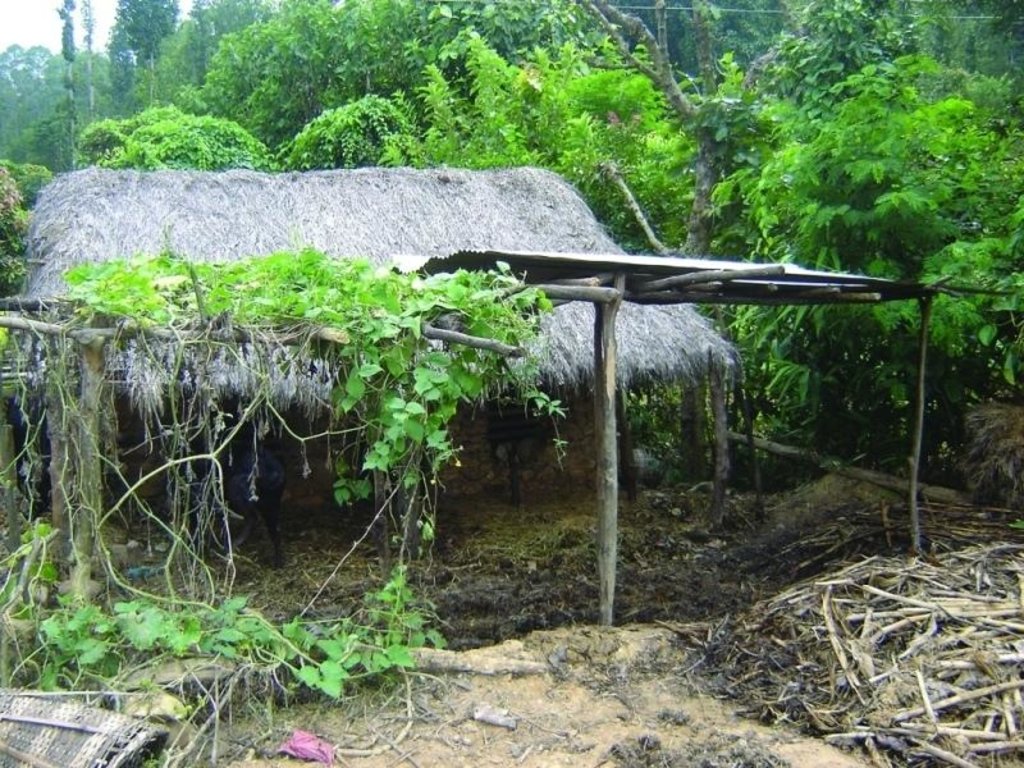
Farmyard manure is the most common form of organic fertiliser applied to crops in the midhills of Nepal. Farmyard manure has a high proportion of organic material which nurtures soil organisms and is essential for maintaining an active soil life. Typically, only about half of the nutrient content of farmyard manure becomes available for crop growth during the first year after it is applied to the soil. The rest of the nutrients are channelled through soil biotic processes and are released in the following years. The high organic matter content and the more active soil life improve or maintain a friable soil structure, increase the cation exchange capacity, the water holding capacity, and the infiltration rate, and reducing the risk of soil pests.
Indigenous methods of preparing and using farmyard manure vary depending on the ecological zone, access to bedding material from crop or forest land and to crop residues and fodder, the availability of labour, and other factors. Traditionally, Nepali farmers take the manure out of their sheds to dry it for 2-3 days and then carry it to the field where it is left in small heaps for a number of days before being spread and incorporated into the soil.
Farmers rate the quality of manure according to which livestock species it comes from. These ratings have been confirmed by nutrient analysis as cattle manure (NPK%: 0.6, 0.13, 0.66) is considered to be better than buffalo manure (0.33, 0.25, 0.10), and horse manure; while pig (0.5, 0.18, 0.42), goat (0.6, 0.13, 0.99), and sheep manure (0.6, 0.13, 0.99) are considered better than cattle manure. Chicken manure (1.46, 0.51, 0.51) is considered the best of all.
It has however been shown that considerable nutrient losses occur if the manure is inappropriately handled or stored. Drying of the manure leads to loss of nutrients through volatilisation, and rainfall and runoff leads to leaching or washing out of nutrients. In addition, the common disposal of urine - the part of the excreta with the highest nutrient concentration - further reduces the level of nutrients in manure.
To reduce nutrient losses farmyard manure needs to be protected from direct sunlight; protected from rainfall or run-on; and protected from runoff. This can be achieved in a variety of ways using a variety of inputs. It is most important to protect the manure during storage and just before it is applied in the field to make the best use of this valuable local resource.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
尼泊尔
有关地点的进一步说明:
Midhills districts of Nepal
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 适用于特定场所/集中在较小区域
Map
×3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- Improve manure
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Intensifying cultivation practices with either 1) inadequate application of fertilisers leading to a decline in soil fertility and the mining of soil nutrients or 2) application of too much fertiliser causing environmental problems through excessive leaching, and losses of fertiliser in surface runoff and consequent eutrophication or nitrification of streams, ponds or groundwater
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 土壤肥力综合管理
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

管理措施
- M2:改变管理/强度级别
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
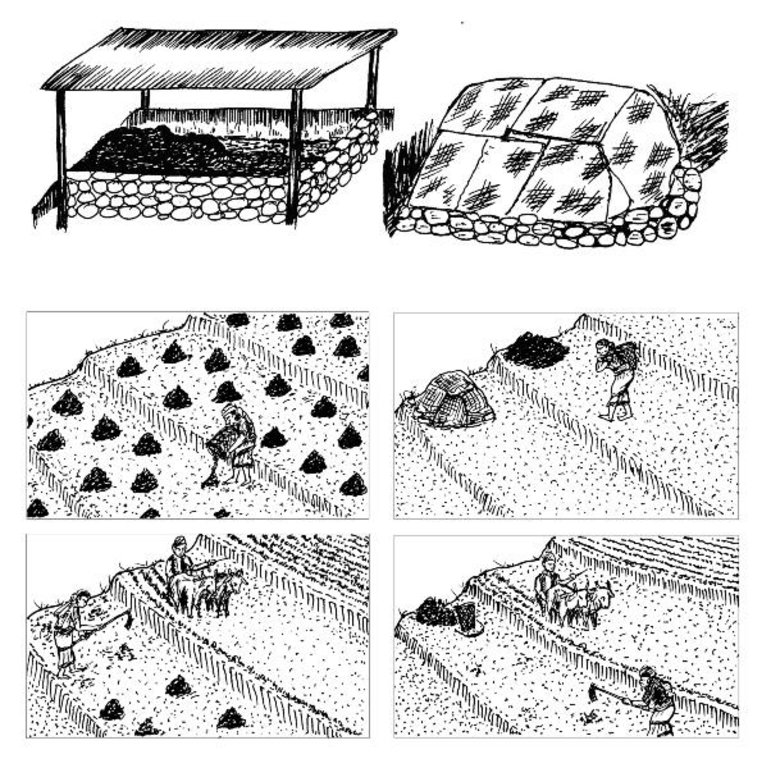
a) Covering the farmyard manure with a roof made of tin sheet or plastic sheets. Cheaper alternatives are:
- a thatched roof
- shading with creepers like cucurbits
- planting broadleaf mustard on the heap
- applying a covering of crop residues or forest material
b) Farmyard manure is traditionally carried to the fi elds in doko baskets and left there in unprotected heaps to be incorporated often weeks and sometimes several months later (top and bottom left). It is much better to incorporate it on the day of transport as the longer it is left out on the fi elds in heaps the greater are the nutrient losses from the heaps (bottom right). Alternatively it can be stored in a corner of the fi eld covered with plastic sheets, crop residues, or in some other way (top right).
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: increase in organic matter, increase in soil fertility, increase in soil productivity
Secondary technical functions: increased infiltration rate and water holding capacity, improved soil physical properties (friability,easier soil preparation)
Layout change according to natural and human environment: protect farmyard manure; change application
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本计算所用货币:
- 美元
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
2.00
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Cover the farmyard manure heap or pit with any available material (crop residues, forest material, plastic sheet, thatched roof, zinc sheet, etc.) |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Building manure pit and shelter | Persons/day | 1.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | Material | unit | 1.0 | 25.0 | 25.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 27.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 27.0 | |||||
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Pour household wastewater onto the heap or pit to keep the farmyard |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
注释:
Cost as in January 2007
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
有关降雨的规范/注释:
Annual rainfall: Also 2000-3000 mm
农业气候带
- 潮湿的
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Slopes on average: Also moderate (6-10%), rolling (11-15%) and hilly (16-30%)
Landforms: Also footslopes
Altitudinal zone: Also 1000-1500 m a.s.l., 1500-2000 m a.s.l. and 2000-2500 m a.s.l.
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 生计(自给)
- 混合(生计/商业)
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Off-farm income specification: In most farm households, off-farm income plays at least a minor and increasingly a major role. Occasional opportunities for off-farm income present themselves in the form of daily labour wages. Some households’ members receive regular salaries, whilst an increasing number of Nepalis are working in India, the Middle East, Malaysia, and elsewhere and sending remittance incomes home.
Market orientation of production system: Also commercial/ market
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,未命名
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 租赁
- 个人
注释:
Sharecropping between owner and tenant
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
收入和成本
农业投入费用
注释/具体说明:
Reduced expenditure on mineral fertilisers
生态影响
其它生态影响
Soil characteristics
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
地下水/河流污染
注释/具体说明:
Reduction of nutrient influx into water bodies
Dependence on outside inputs
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
注释:
Large short- and long-term benefits due to need to use less of the costly mineral fertilisers. The only extra ‘cost’ is the extra labor needed.
6.5 技术采用
注释:
Comments on acceptance with external material support: An independent assessment found that 95% of the farmers participating in SSMP’s farmyard improvement activities were accepted the technology.
Comments on adoption trend: About 70% of non-participant farmers who had come into contact with the technologies had also adopted them.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
The use of improved farmyard manure reduced the need for mineral fertiliser thereby reducing production costs and outside dependency How can they be sustained / enhanced? Further promotion of the technology will increase this impact |
| A simple technology affordable by poor farmers in remote areas far from a roadhead |
| The increased use of organic fertiliser improves the physical characteristics of soil making ploughing easier and increasing water holding capacity of the soil |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Cost of a permanent roof for the manure heap may hinder adoption of the technology | Promote simple alternatives to high cost roofs such as straw cover, cover with broad leaf mustard, thatch, and waste plastic |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
STSS; SSMP (2001) Farmyard Manure and Compost Management (in Nepali) Kathmandu: Soil Testing Services Section, Department of Agriculture and Sustainable Soil Management Programme
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
SSMP
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Farmer field schools on integrated plant nutrient systems [尼泊尔]
Participatory and collaborative learning through the farmer field school approach
- 编制者: Richard Allen

Farmer-to-farmer diffusion [尼泊尔]
Wider diffusion of sustainable soil management technologies through a demand responsive farmer-to-farmer diffusion approach
- 编制者: Richard Allen
模块
无模块