Integrated Soil Management for Organic Vegetables on the Highland Watershed in the Northern Region [Tailandia]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: Pitayakon Limtong
- Editor: –
- Revisores: Rima Mekdaschi Studer, William Critchley
Organic vegetables in the Royal Project
technologies_4283 - Tailandia
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación de la Tecnología
Persona(s) de referencia clave
co-compiler:
Wattanaprapat Kamalapa
Land Development Department
Tailandia
usuario de la tierra:
Phojanabandit Watcharin
Headman of village
Tailandia
local extension officer:
Kerephuwadon Boontre
Inthanon Royal Agricultural Station, the Royal Project
Tailandia
local LDD officer:
Intha Charun
Royal Project Land Development Center, Land Development Office Region 6, Land Development Department.
Tailandia
Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Land Development Department LDD (Land Development Department LDD) - Tailandia1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT:
Sí
1.4 Declaración de la sostenibilidad de la Tecnología descrita
¿La Tecnología aquí descrita resulta problemática en relación a la degradación de la tierra, de tal forma que no puede considerársela una tecnología sostenible para el manejo de la tierra?
No
Comentarios:
Organic vegetable production is a technology that prevents and restores land degradation due to soil management emphasized in using organic and natural materials to improve soil fertility and productivity, especially in terms of soil organic matter.
2. Descripción de la Tecnología MST
2.1 Breve descripción de la Tecnología
Definición de la Tecnología:
Organic vegetable cultivation on the highland area of the northern region of Thailand has been encouraged by local officers in order to produce safe food on degraded land through building up soil fertility and soil organic matter.
2.2 Descripción detallada de la Tecnología
Descripción:
This case study is of organic vegetable cultivation at Ban Muang Ang Village which is located in Ban Luang Sub-district, Chom Thong District, Chiang Mai Province, covering approx. 25,881 Rai (6.25 rai = 1 ha; 625 rai = 1 sq km). The topography is a complex mountainous area within the Doi Inthanon National Park, at an elevation of 600-800 m asl. The climate is quite cool and humid with average temperature throughout the year being 20⁰C. The average annual rainfall is 2,000-2,100 mm. Most of the population belong to the Pakhayo hilltribe, living in 219 households, with total population of 588 persons (308 males, 280 females). The main purpose of promoting growing organic vegetables in greenhouses is to change their way of life from forest encroachment/ shifting cultivation in the upper watershed, to improving the ecosystem services and environment with better health and higher incomes for villagers.
Since 2002, the government and the Royal Project Foundation have had a policy to change land use to organic farming. At the early stage, yields of organic vegetables were not good. In the year 2010, the Inthanon Royal Agricultural Station brought a number of these land users to visit the Mae Tho Royal Project Development Center in Bo Sali Sub-district, Hot District, Chiang Mai Province. They obtained knowledge about organic cultivation in simple greenhouses made from bamboo poles, covered with plastic sheets and nylon nets. Local officers of the Inthanon Royal Agricultural Station supported with education, offered suggestions and recommended practices, as well as finding markets to sell the organic products; that became the model. It took only 25-30 days for a crop, and they could harvest about 200 kg of vegetables per greenhouse. They could produce 11 crops of vegetables in one year, which means that they could earn 10 times more income than before. At present, Muang Ang Village there are 153 members operating in 270 greenhouses which is the largest organic vegetable production area in the Inthanon Royal Project.
The production of organic vegetables in this area is outstanding. This network has received certification from the Department of Agriculture (DOA) and the Office of Organic Agriculture Certification Thailand (ACT Organic). Farmers or farming enterprises certified by this system are entitled to apply the logos and certification card of ACT Organic and IFOAM Accredited brand on their products. Moreover, the Agri-Food & Veterinary Authority of Singapore (AVA) has approved the production processes. Every production step has been approved through the standard regulation of each agency with tracking to the source of production inputs such as fertilizers, disease, weed and pest control measures, cultivation practices, etc. Now they have nine types of vegetables that constitute the main production: Choy, Baby Emperor, Cos Salad, Green Oak, Red Oak, Fille Iceberg, String Bean, Kale Hong Kong and Baby Carrot.
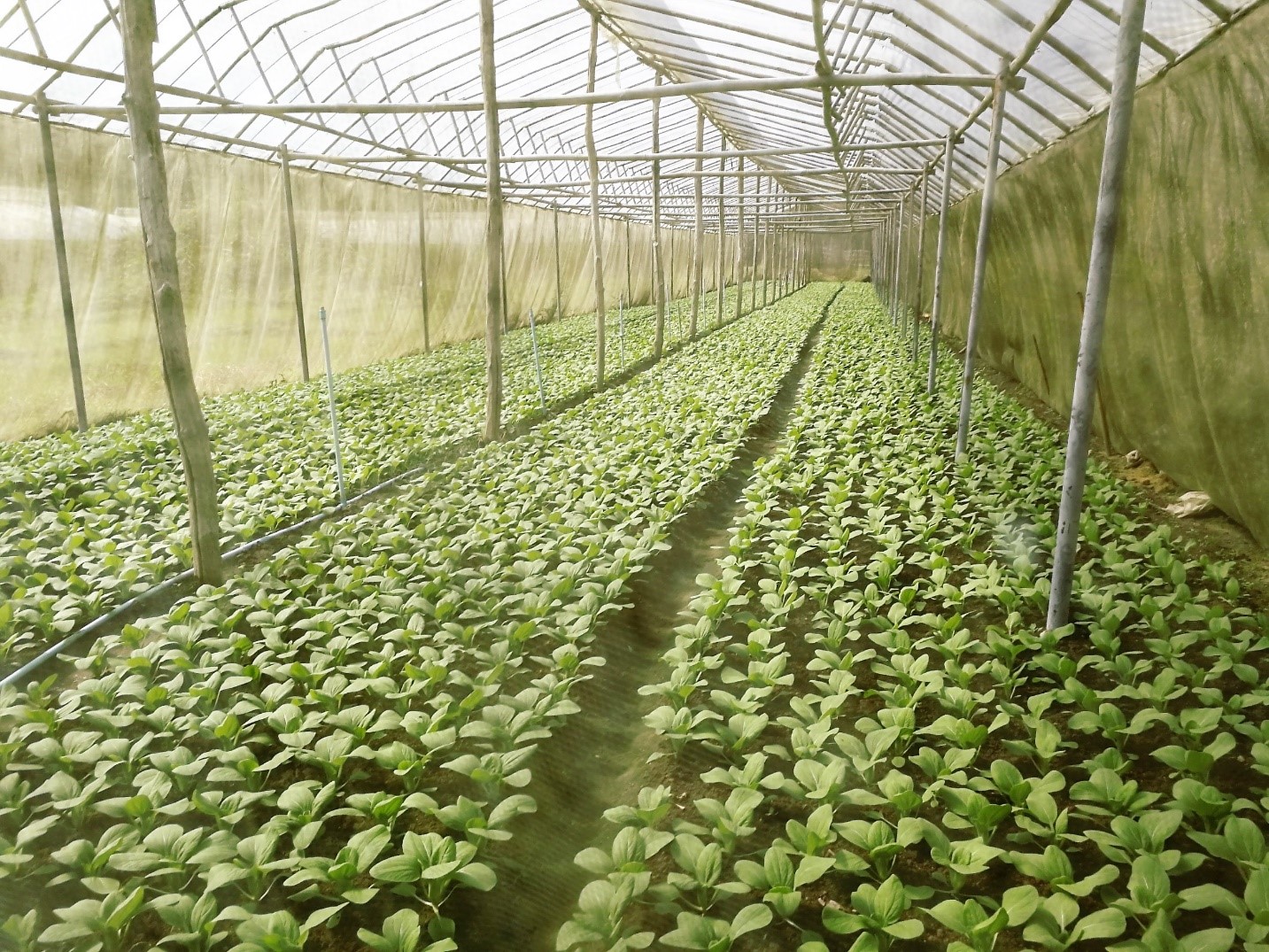
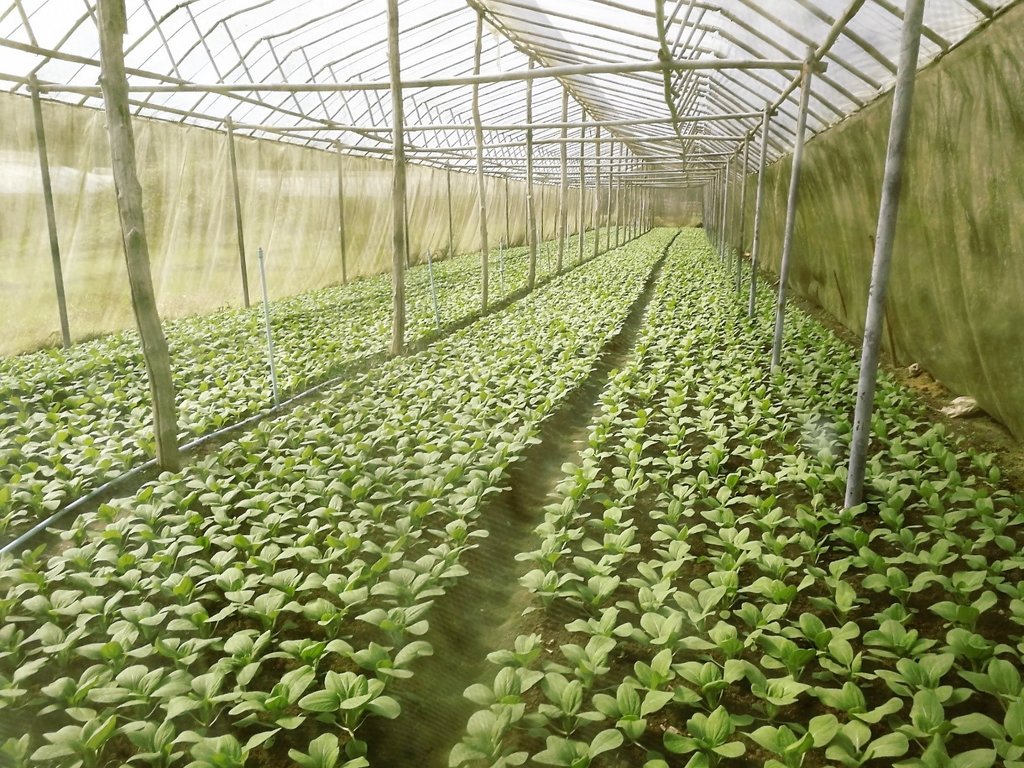
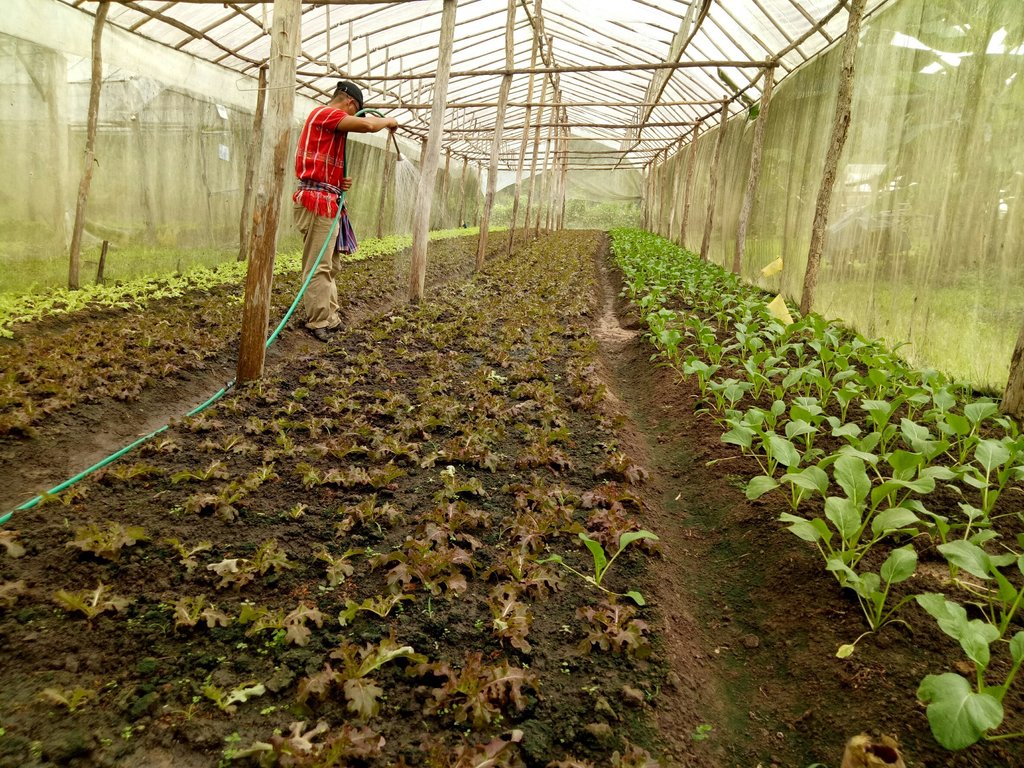
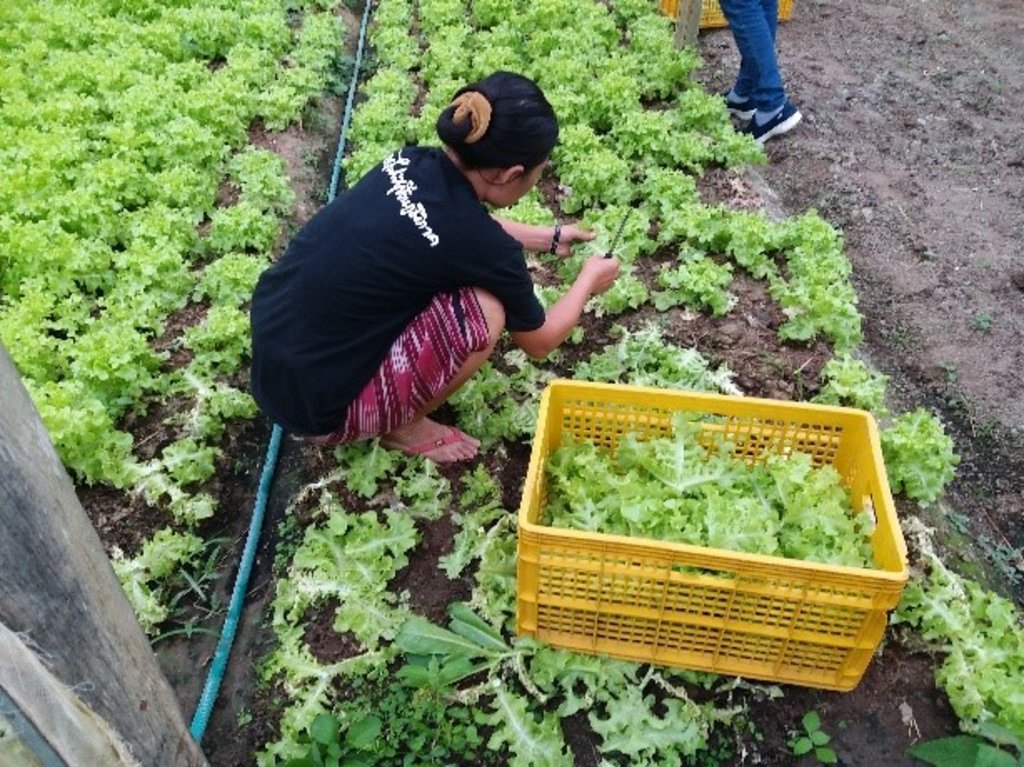
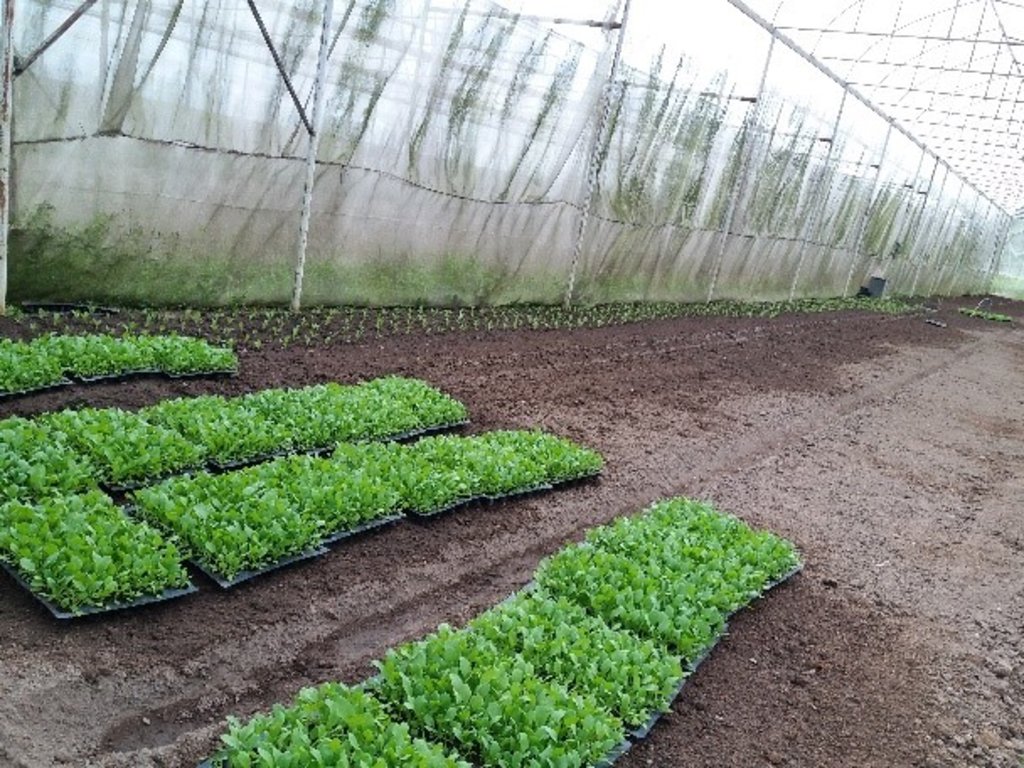
2.3 Fotografías de la Tecnología
Comentarios generales sobre las fotos:
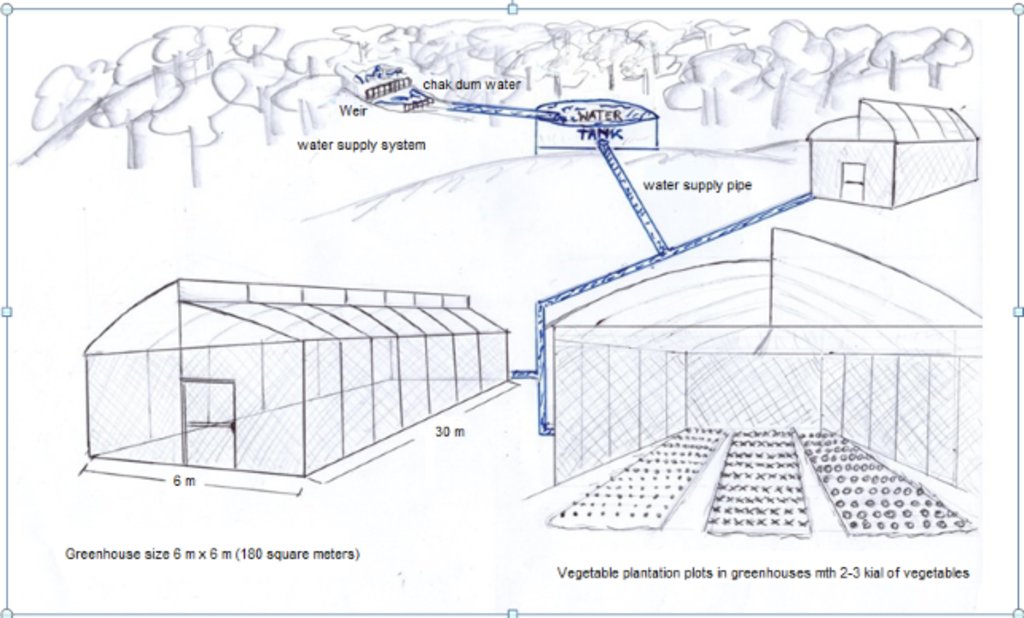
The simple nursery is 6 meters wide, 30 meters long, and 5 meters high. Organic vegetable seed is supported from the Royal Project with ready to planting into the plot.
2.4 Videos de la Tecnología
Fecha:
13/09/2018
Lugar:
Moo 9, Ban Mung Aung Village, Ban Luang Sub-district, Chom Thong District, Chiang Mai Province
Nombre del videógrafo:
Ms. Kamalapa Wattanaprapat
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde la Tecnología fue aplicada y que se hallan comprendidos por esta evaluación
País:
Tailandia
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
Ban Luang Sub-district, Chom Thong District, Chiang Mai Province
Especifique más el lugar :
Inthanon Royal Agricultural Station
Especifique la difusión de la Tecnología:
- aplicada en puntos específicos/ concentrada en un área pequeña
Comentarios:
This activity is the integrated implementation project of the Royal Project in collaboration with other government agencies.
Map
×2.6 Fecha de la implementación
Indique año de implementación:
2002
Si no se conoce el año preciso, indique la fecha aproximada:
- 10-50 años atrás
2.7 Introducción de la Tecnología
Especifique cómo se introdujo la Tecnología:
- mediante proyectos/ intervenciones externas
Comentarios (tipo de proyecto, etc.):
All knowledge and technology is supported by the Royal Project collaboration with Land Development Department and other government and private agencies.
3. Clasificación de la Tecnología MST
3.1 Propósito(s) principal(es) de la Tecnología MST
- conservar el ecosistema
- preservar/ mejorar biodiversidad
- crear impacto económico benéfico
3.2 Tipo(s) actuales de uso de la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología

Tierras cultivadas
- Cosecha anual
Especifique:
Vegetables: Cantonese, Baby Emperor, CosSalad, Oak leaf Green, Oak leaf Red, Guest Bean, Filler Iceberg, Kale Hong Kong and Baby Carrot.

vías fluviales, masas de agua, humedales
Principales productos/ servicios:
Irrigation water from a storage tank at the upper part, through PVC pipes to the area cultivated to the organic vegetables.
Comentarios:
In the past, villagers had encroached on forest areas and deforestation in highland for shifting cultivation, and also expand cultivation area into steep slope. Resulting in the destruction of forest areas and accelerated soil degradation. Villagers have low incomes: not enough to survive. But due to the grace of His Majesty King Bhumibol Adulyadej, King Rama 9 set up the Royal Project to distribute knowledge and education to all farmers in this area, and assist them to have better occupation and living standards.
3.3 ¿Cambió el uso de tierras debido a la implementación de la Tecnología?
Comentarios:
The Royal Project has promoted the production of organic vegetables. Farmers therefore have changed from shifting cultivation to organic agriculture with sustainable soil management. As well as returning from forest areas and conserving soil, water and forest resources, maintaining ecological balance, this all makes villagers lives better. According to the cultivation schedule provided by the Royal Project, this area can cultivated throughout the year due to the development of irrigation systems from the storage tank in the upper part and supply to each plot of this targeted area.
3.4 Provisión de agua
otra (ej. post-inundación):
- water from watershed area
Comentarios:
Water resources are obtained from watercourses in the watershed, with a small dam which collects water in a reservoir. A PVC pipe is connected from the reservoir to individual plots and this irrigation system allows allocation to every farmer by the water management group.
3.5 Grupo MST al que pertenece la Tecnología
- sistemas de rotación (rotación de cosecha, cosecha rotatoria con descanso, agricultura migratoria)
- manejo integrado de pestes y enfermedades (incl. agricultura orgánica)
- Manejo de irrigación: (incl. provisión de agua, invernaderos)
3.6 Medidas MST que componen la Tecnología

medidas agronómicas
- A2: materia orgánica/ fertilidad del suelo

medidas de manejo
- M2: Cambio de gestión/ nivel de intensidad
Comentarios:
-
3.7 Principales tipos de degradación de la tierra encarados con la Tecnología

erosión de suelos por agua
- Wt: pérdida de capa arable/ erosión de la superficie

deterioro químico del suelo
- Cp: contaminación del suelo

degradación biológica
- Bl: pérdida de la vida del suelo
- Bp: incremento de pestes/ enfermedades, pérdida de depredadores
Comentarios:
Organic vegetable production in greenhouses can solve the problem of soil erosion with utilization of compost, animal and green manure to increase fertility and organic matter.
3.8 Prevención, reducción o restauración de la degradación de la tierra
Especifique la meta de la Tecnología con relación a la degradación de la tierra:
- prevenir la degradación de la tierra
- reducir la degradación de la tierra
Comentarios:
This organic vegetable production on very steep land can prevent and reduce soil erosion. Moreover, organic material and fertilizers can restore and improve soil fertility and productivity.
4. Especificaciones técnicas, actividades de implementación, insumos y costos
4.1 Dibujo técnico de la Tecnología
Especificaciones técnicas (relacionadas al dibujo técnico):
Operating procedures
1. Establishment of networks: All land users set up networks of organic vegetable producers and register the members properly; all members must act strictly according to the regulations.
2. Integrated cooperation: The Inthanon Royal Agricultural Station and the Inthanon Highland Agricultural Extension Center organize training on organic farming at least once a year, including study trip/s to visit other successful organic farmers.
3. Selection of the area: Leaders and members select the area for members, each member occupying not more than three greenhouses, 6m wide, 30m long and 3-5m high (180 sq m).
4. Production planning: land users discuss with the staff of the Inthanon Royal Agricultural Station, and plan the production schedule and types of vegetables to meet the market demand.
5. Procurement of production inputs: Both of local officers with inspectors and farmers can buy production inputs by themselves. All materials must be organic and are from reliable sources. Farmers must be very careful in this matter.
6. Organic vegetables cultivation: All land users must strictly comply with the schedule of cultivation, practices in soil improvement, control of pests and diseases, plus recording every step of their activities.
7. Production monitoring: Staffs of the Inthanon Royal Agricultural Station and Department of Agricultural Extension (DOAE) monitor and observe land users’ practices in using soil improvement methods and using bioproducts for controlling insects, predators, parasites and diseases. Department of Agriculture (DOA) and the Organic Agriculture Certification Thailand (ACT Organic) monitor the production process.
8. Harvesting of Products: All land users must harvest according to the harvesting schedule and the preservation methods. DOA and ACT Organic serve as certification agencies by analyzing the contamination of substances in the products.
9. Screening and packing: All land users must clean their products with non-contaminated equipment, and also screen the quality and specified size/s of products for delivery to the Inthanon Royal Agricultural Station.
Autor:
Ms.Kamalapa Watanaprapat
Fecha:
25/10/2018
4.2 Información general sobre el cálculo de insumos y costos
Especifique cómo se calcularon los costos e insumos:
- por área de Tecnología
Indique tamaño y unidad de área:
70 rai
Si usa una unidad de área local, indique el factor de conversión a una hectárea (ej. 1 ha = 2.47 acres): 1 ha =:
1 ha = 6.25 rai
otra / moneda nacional (especifique):
Baht (THB)
Si fuera relevante, indique la tasa de cambio de dólares americanos a la moneda local (ej. 1 U$ = 79.9 Reales Brasileros): 1 U$ =:
32,0
Indique el costo promedio del salario de trabajo contratado por día:
300
4.3 Actividades de establecimiento
| Actividad | Momento (estación) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Establish organic vegetables group | The first year of cultivation |
| 2. | Site selection | Before cultivation |
| 3. | Construct greenhouse or nursery | Before cultivation |
| 4. | Production work plan | Before cultivation |
| 5. | Procurement of production factors | Before cultivation |
| 6. | Soil preparation and improvement | During soil preparation |
| 7. | Vegetables seedling preparation | During soil preparation |
| 8. | Plantation | During vegetables planting |
| 9. | Disease and pest control | During vegetables planting |
| 10. | Vegetable harvesting | During harvesting |
| 11. | Screening and packing | After harvesting |
| 12. | Technology maintenance | After harvesting |
Comentarios:
-
4.4 Costos e insumos necesarios para el establecimiento
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Construct greenhouse | man | 10,0 | 300,0 | 3000,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | During cultivation | man | 6,0 | 300,0 | 1800,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | During maintenance | man | 45,0 | 300,0 | 13500,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | During harvesting | man | 10,0 | 300,0 | 3000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | Rubber pipe | piece | 1,0 | 1000,0 | 1000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | Tractor for soil preparation | Rai | 1,0 | 300,0 | 300,0 | 100,0 |
| Material para plantas | Vegetables seed | site | 1,0 | 700,0 | 700,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | Animal manure (cow manure) | bag | 20,0 | 30,0 | 600,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | BT bio-product | litre | 100,0 | |||
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | Predators and parasites | - | ||||
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | Insect glue trap | liter | 0,5 | 290,0 | 145,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | Yellow plastic plate | piece | 60,0 | 5,0 | 300,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | Yellow plastic bag | litre | 0,5 | 120,0 | 60,0 | 100,0 |
| Material de construcción | Wood frame / mesh net / plastic cloth | site | 1,0 | 14700,0 | 14700,0 | 40,0 |
| Material de construcción | PVC pipe | piece | 40,0 | 40,0 | 1600,0 | 100,0 |
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 40705,0 | |||||
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología en USD | 1272,03 | |||||
Si el usuario de la tierra no cubrió el 100% de los costos, indique quién financió el resto del costo:
Construction greenhouse cost, land users support 40%, and Organic Vegetable Production Fund support 60% of this cost.
Comentarios:
Labor cost in greenhouse construction, greenhouse materials, which land users would only pay for the first year, but they do not pay for the second year and do not much towards repair cost.
4.5 Actividades de establecimiento/ recurrentes
| Actividad | Momento/ frequencia | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Changing the plastic sheet of the roof of greenhouse | 3,000 baht per greenhouse every 3 years |
| 2. | Washing the plastic sheet of the greenhouse roof | Once a year |
Comentarios:
-
4.6 Costos e insumos necesarios para actividades de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (por año)
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Changing plastic sheets | man | 3,0 | 300,0 | 900,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Wash plastic sheets | man | 3,0 | 300,0 | 900,0 | 100,0 |
| Material de construcción | Plastic sheet (change every 3 years) | roll | 1,0 | 3700,0 | 3700,0 | 100,0 |
| Indique los costos totales para mantenecer la Tecnología | 5500,0 | |||||
| Costos totales para mantener la Tecnología en USD | 171,88 | |||||
Si el usuario de la tierra no cubrió el 100% de los costos, indique quién financió el resto del costo:
Land users purchase 100%
Comentarios:
Land users purchase 100%
4.7 Factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Describa los factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
The most important factor that affects other costs is seed. Manure must be purchased from standard organic source. The Royal Project provides standard seed, and animal manure must be purchased from other provinces that require natural cultivation farming. The source of the materials used can be traced back to the original provider. Labor factors are not impacted because they can help each other, and land users work together in each greenhouse.
5. Entorno natural y humano
5.1 Clima
Lluvia anual
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Especifique el promedio anual de lluvia (si lo conoce), en mm:
1500,00
Especificaciones/ comentarios sobre la cantidad de lluvia:
Rainy season is from June - October
Indique el nombre de la estación metereológica de referencia considerada:
Inthanon Royal Project Meteorological Station
Zona agroclimática
- Sub-húmeda
-
5.2 Topografía
Pendientes en promedio:
- plana (0-2 %)
- ligera (3-5%)
- moderada (6-10%)
- ondulada (11-15%)
- accidentada (16-30%)
- empinada (31-60%)
- muy empinada (>60%)
Formaciones telúricas:
- meseta/ planicies
- cordilleras
- laderas montañosas
- laderas de cerro
- pies de monte
- fondo del valle
Zona altitudinal:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1,000 m s.n.m
- 1,001-1,500 m s.n.m
- 1,501-2,000 m s.n.m
- 2,001-2,500 m s.n.m
- 2,501-3,000 m s.n.m
- 3,001-4,000 m s.n.m
- > 4,000 m s.n.m
Indique si la Tecnología se aplica específicamente en:
- situaciones convexas
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre topografía :
Most of the area is mountainous slope complex, with a steep slope and attitude is 1,200-1,400 meters above sea level. The forest condition is good, and some areas of the Doi Inthanon is national park and some is in national forest reserve.
5.3 Suelos
Profundidad promedio del suelo:
- muy superficial (0-20 cm)
- superficial (21-50 cm)
- moderadamente profunda (51-80 cm)
- profunda (81-120 cm)
- muy profunda (>120 cm)
Textura del suelo (capa arable):
- mediana (limosa)
Textura del suelo (> 20 cm debajo de la superficie):
- áspera/ ligera (arenosa)
Materia orgánica de capa arable:
- media (1-3%)
Si se halla disponible, adjunte una descripción completa de los suelos o especifique la información disponible, por ej., tipo de suelo, pH/ acidez de suelo, capacidad de intercambio catiónico, nitrógeno, salinidad, etc. :
Soil pH is 5.5-6.0
5.4 Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
Agua subterránea:
> 50 m
Disponibilidad de aguas superficiales:
bueno
Calidad de agua (sin tratar):
solo para uso agrícola (irrigación)
¿La salinidad del agua es un problema?
No
¿Se está llevando a cabo la inundación del área? :
No
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre calidad y cantidad de agua:
Water flows from the watershed area of the upper forest, and not flow through the conventional agricultural area.
5.5 Biodiversidad
Diversidad de especies:
- mediana
Diversidad de hábitats:
- mediana
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre biodiversidad:
Biodiversity in this area has a variety of insects. There are both pests and predators.
5.6 Las características de los usuarios de la tierra que aplican la Tecnología
Sedentario o nómada:
- Sedentario
Orientación del mercado del sistema de producción:
- mixta (subsistencia/ comercial)
Ingresos no agrarios:
- 10-50% de todo el ingreso
Nivel relativo de riqueza:
- promedio
Individuos o grupos:
- grupos/ comunal
Nivel de mecanización:
- trabajo manual
Género:
- mujeres
- hombres
Edad de los usuarios de la tierra:
- jóvenes
- personas de mediana edad
- ancianos
Indique otras características relevantes de los usuarios de las tierras:
Land users can cultivate organic vegetables and earning more income, where young generation in the village become interested and help their families to cultivate organic vegetables. Moreover these young generation who have graduated from university like to become farmers and do not leave to other occupations.
5.7 Área promedio de la tierra usada por usuarios de tierra que aplican la Tecnología
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
¿Esto se considera de pequeña, mediana o gran escala (refiriéndose al contexto local)?
- escala mediana
Comentarios:
Most land users have an average land of 20 rai, consisting of 3-5 rai for rice fields, and 10-15 rai of rotation cultivation. They do not have right in landownership because all of these land are in the reserved forest area and national park. But they have right in utilize their land under the Royal Project.
5.8 Tenencia de tierra, uso de tierra y derechos de uso de agua
Tenencia de tierra:
- individual, sin título
Derechos de uso de tierra:
- comunitarios (organizado)
Derechos de uso de agua:
- comunitarios (organizado)
Especifique:
-
Comentarios:
Land users in this area are Lawa hill tribe who migrated from different places to settle here. The main occupation is agriculture under crop rotation, some harvesting of forest products, and some animals. They have not right in landownership but they have right to utilize their land and water for agricultural activities under the Royal Project.
5.9 Acceso a servicios e infraestructura
salud:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
educación:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
asistencia técnica:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
empleo (ej. fuera de la granja):
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
mercados:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
energía:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
caminos y transporte:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
agua potable y saneamiento:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
servicios financieros:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
Average debt 20,000 baht per person:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
Comentarios:
-
6. Impactos y comentarios para concluir
6.1 Impactos in situ demostrados por la Tecnología
Impactos socioeconómicos
Producción
producción de cultivo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Land users can cultivate 11 times per year.
calidad de cultivo
Comentarios/ especifique:
GAP and organic products
calidad de bosques
Comentarios/ especifique:
Reforestation in this area, around 1,700 rai
riesgo de fracaso de producción
Comentarios/ especifique:
Land users can cultivate continuously and local officers visit and advise them for good practices under GAP and organic agriculture.
diversidad de producto
área de producción
Comentarios/ especifique:
Area for agriculture decreased and forest area increased. That corresponds to the policy of the Royal Project to produce strictly organic vegetables.
Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
demanda de agua para irrigar
Comentarios/ especifique:
Membership in this network increased by 3-4 persons a year.
Ingreso y costos
gastos en insumos agrícolas
Comentarios/ especifique:
Cost of fertilizers, bioproduct and pesticides
ingreso agrario
Comentarios/ especifique:
GAP and organic vegetable products
carga de trabajo
Comentarios/ especifique:
They usually work in their land almost everyday because organic vegetables need more intensive practices.
Impactos socioculturales
seguridad alimentaria/ autosuficiencia
Comentarios/ especifique:
That is the main concept of the organic vegetable activities.
situación de salud
oportunidades recreativas
instituciones comunitarias
Comentarios/ especifique:
The Royal Project officers supported knowledge and suggestion to community network.
instituciones nacionales
MST/ conocimiento de la degradación de la tierra
Comentarios/ especifique:
Local officers and training in implementation
mitigación de conflicto
situación de grupos en desventaja social y económica
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo de agua/ escurrimiento de sedimento
cantidad de agua
Comentarios/ especifique:
Rainwater from the upstream of this watershed
Suelo
humedad del suelo
cubierta del suelo
pérdida de suelo
encostramiento/ sellado de suelo
compactación de suelo
materia orgánica debajo del suelo C
Comentarios/ especifique:
They usually use organic fertilizers.
Biodiversidad: vegetación, animales
Cubierta vegetal
diversidad vegetal
Comentarios/ especifique:
Several kinds of vegetables are used in this organic farming.
especies invasoras extrañas
diversidad animal
especies benéficas
control de pestes/ enfermedades
Comentarios/ especifique:
They used bioproducts for disease and pest control.
Reducción de riesgos de desastres y riesgos climáticos
impactos de ciclones, tormentas de lluvia
Especifique la evaluación de los impactos en el sitio (mediciones):
The main objective of organic vegetables cultivation is to increase their income and produce green vegetable products, they can work throughout the year with higher income with the less of area.
6.2 Impactos fuera del sitio demostrados por la Tecnología
disponibilidad de agua
corriente confiable y estable fluye en estación seca
contaminación de aguas subterráneas/ de ríos
daño a campos de vecinos
impacto de gases de invernadero
Especifique la evaluación de los impactos fuera del emplazamiento (medidas):
Moreover, land users in the upstream area would cultivate in organic vegetables with bioproducts of disease and pest control, where it would safe to the downstream area.
6.3 Exposición y sensibilidad de la Tecnología al cambio climático gradual y a extremos relacionados al clima/ desastres (desde la percepción de los usuarios de tierras)
Cambio climático gradual
Cambio climático gradual
| Estación | Incremento o reducción | ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| temperatura anual | moderadamente | ||
| temperatura estacional | verano | no muy bien | |
| temperatura estacional | estación húmeda/ de lluvias | bien | |
| temperatura estacional | invierno | bien | |
| lluvia anual | bien |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados al clima
Desastres climatológicos:
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| tormenta de lluvia local | moderadamente |
| tormenta local | moderadamente |
Desastres biológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| enfermedades epidémicas | nada bien |
| insectos/ infestación de gusanos | nada bien |
Comentarios:
-
6.4 Análisis costo-beneficio
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de establecimiento (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a largo plazo:
muy positivo
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a largo plazo:
muy positivo
6.5 Adopción de la Tecnología
- > 50%
Si tiene la información disponible, cuantifique (número de hogares y/o área cubierta):
Land users are 153 members, with 270 greenhouses
De todos quienes adoptaron la Tecnología, ¿cuántos lo hicieron espontáneamente, por ej. sin recibir nada de incentivos/ materiales:
- 0-10%
Comentarios:
In the first stage some of land user cultivated organic vegetables without greenhouses, then they lost their grain. After they had train and study trip, they improve their implement and construct greenhouse.
6.6 Adaptación
¿La tecnología fue modificada recientemente para adaptarse a las condiciones cambiantes?
No
6.7 Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades de la Tecnología
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra |
|---|
| Promoting occupation and income earning of land users in this area. |
| All land users have been well trained; they receive consistent knowledge and suggestions from local officers and several agencies. |
| All land users produce certified organic vegetables that are green and are sold as organic food in the market. |
| They established the community enterprises of organic vegetables producer group. |
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
| Encouraging organic vegetable production is the activity of the government and the Royal Project in order to conserve this highland area with the intensive management. |
| Members of the land users community trust and assist each other with willingness to share the knowledge and experience in organic farming practices. |
| As a model of self-sufficient agriculture, they should have more income from the sustainable use of their land. |
| Establish and strengthen the community network to carry out and extend to others in this area. |
6.8 Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos de la Tecnología y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| They are allowed to use the land for cultivating organic vegetables. | The government policy needs to have stability and consistency in using this land for a long time. |
| They need educational opportunity for their children. | The government needs to set up more schools in this area, and also to provide more chance to study in the higher level. |
| They need to have opportunity to access energy resources, especially in electricity. | Provincial Electricity Authority (PEA) has allocated budget for installing small electrical systems. |
| Transportation and road conditions are not convenient to access this area. | Local administrative organizations should be allocated more budget to develop such infrastructure. |
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| They do not have land ownership but they are allowed to use their land. | The government has a policy to "Issue a community land title deed" to solve this problem. |
| Almost of them cannot produce such as manure, compost, insect repellents by themselves. | Local officers have supported the knowledge and financial advice. |
| Almost of them cannot find organic product market by themselves. | establishment their cooperatives or network to promote in marketing. |
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.1 Métodos/ fuentes de información
- visitas de campo, encuestas de campo
4
- entrevistas con usuarios de tierras
1
- compilación de informes y otra documentación existente
2
Comentarios:
-
7.2 Vínculos a las publicaciones disponibles
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
-
¿Dónde se halla disponible? ¿Costo?
-
7.3 Vínculos a la información relevante disponible en línea
Título/ descripción:
The North attitude: Ang village cultivate vegetables to the forest
URL:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dKLG2ImGwDE
Título/ descripción:
Organic vegetables at Ang village, Joam Tong Sub-district
URL:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ALL9jJYzVyI
Título/ descripción:
Regional 4.0: ภูมิภาค 3.0: Ang village cultivate vegetables to the forest
URL:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6u02SB_53IM
7.4 Comentarios generales
-
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos
No hay vínculos
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos