Lake Revival: Towards Environmental Conservation [Bután]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: Tshering Yangzom
- Editor: Tashi Wangdi
- Revisores: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Tsho Lar Chey
technologies_6857 - Bután
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación de la Tecnología
Persona(s) de referencia clave
usuario de la tierra:
La Tshultrim
NA
Bután
usuario de la tierra:
Thinley Kinzang
NA
Bután
usuario de la tierra:
Wangmo Dorji
NA
Bután
usuario de la tierra:
Wangdi Yeshi
NA
Bután
Nombre del proyecto que financió la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Strengthening national-level institutional and professional capacities of country Parties towards enhanced UNCCD monitoring and reporting – GEF 7 EA Umbrella II (GEF 7 UNCCD Enabling Activities_Umbrella II)Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
National Soil Services Center, Department of Agric (National Soil Services Center, Department of Agric) - Bután1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT:
Sí
1.4 Declaración de la sostenibilidad de la Tecnología descrita
¿La Tecnología aquí descrita resulta problemática en relación a la degradación de la tierra, de tal forma que no puede considerársela una tecnología sostenible para el manejo de la tierra?
No
Comentarios:
Technology is not problematic with regard to land degradation as lake revival plays an important role in sustained water source and environmental conservation.
2. Descripción de la Tecnología MST
2.1 Breve descripción de la Tecnología
Definición de la Tecnología:
The lake conservation initiative at Tali was conceived with the vision of protecting the lake and transforming the surrounding area into a community eco-tourism hub. The initiative is a testament to how science and spirituality, and culture and the environment can coexist and benefit from one another.
2.2 Descripción detallada de la Tecnología
Descripción:
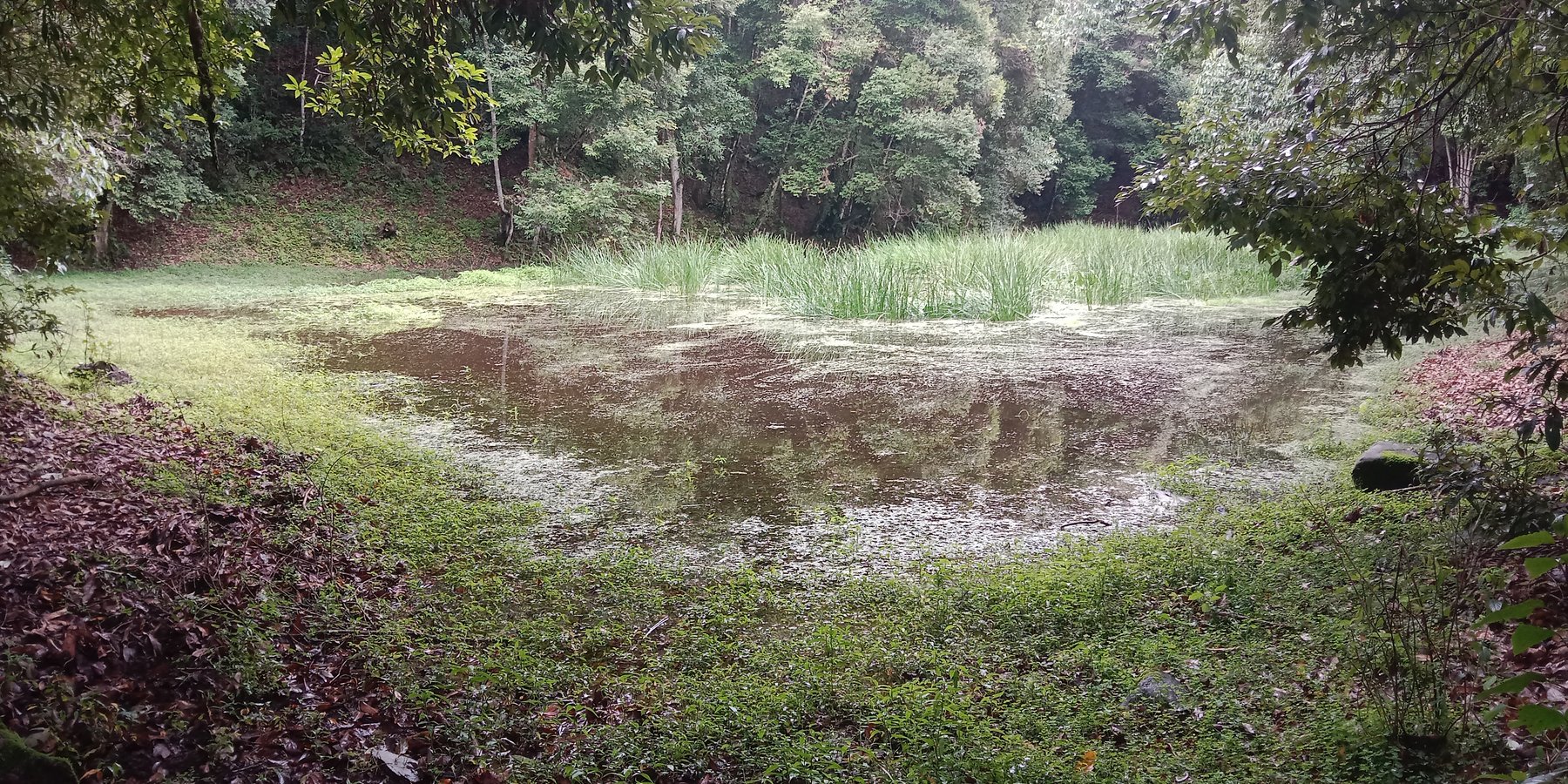
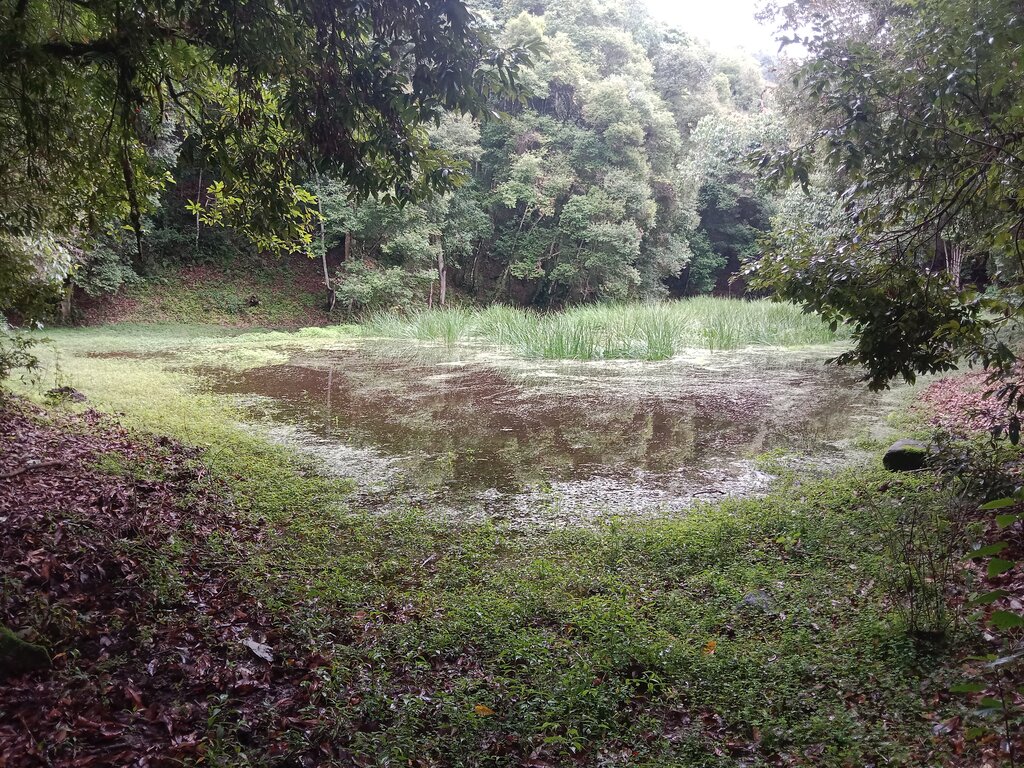
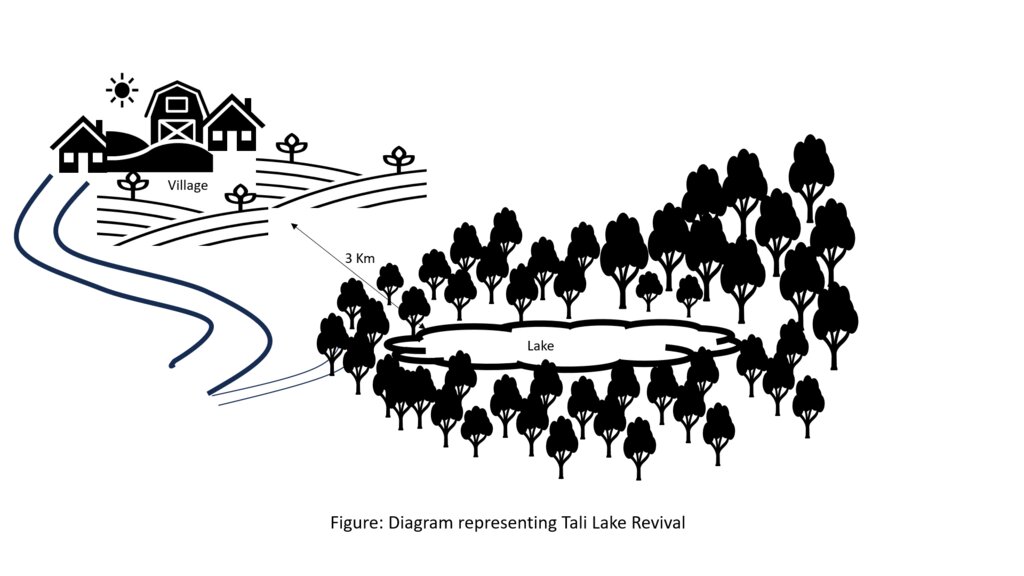
The lake conservation initiative at Tali was conceived with the vision of protecting the lake and transforming the surrounding area into a community eco-tourism hub. The initiative is a testament to how science and spirituality, and culture and the environment can coexist and benefit from one another. The Tali Lake is a major water source (both irrigation and drinking) for the community and both livestock and wild animals.
Bhutanese believe lakes to be sacred and religiously significant. Buli Lake and Tali Lake (Tangsibi Tsho) epitomise how nature and culture come together. Tali village under Nangkor gewog in Zhemgang Dzongkhag lies on the shoulder of mountains at an elevation of 1880 m.a.s.l. with broad-leaved forests. It comprises 25 households with around 280 residents. According to local legend, Tangsibi Tsho in Tali is the “Jewellery basket of Buli Tsho which was left behind when Buli Tsho moved from Tali to Buli”. Tali Lake is spread over an area of 0.40 ha. The 18.2 ha forest around the lake is dominated by species of oak. The forest around the lake harbours a very rich variety of mammals (22 species) that are ecologically important and visit the lake for water and predation. Also, 70 species of birds have been recorded in the forest around the lake.
The community, along with the Loden Foundation and the monastic body, has been engaged in reviving the lake as 90% of the surface was covered with waterweeds and grasses. The aim was to clean, beautify, and sustain the ecosystem through an integrated and holistic management project by combining scientific, social, and spiritual approaches. There was support of USD 33,550 from the United Nations Development Programme Global Environment Facility (UNDP GEF) Small Grants Programme (SGP) and USD 12,650 from the Loden Foundation and the Community.
Tangsibi Tsho in Tali has significant cultural importance which includes water for irrigation and drinking purposes both for people as well as livestock and wild animals. Thus, the initiative was aimed at conserving the lake and transforming the lake area into a community eco-tourism hub. According to the villagers and senior citizens of the community, the revival of the lake would help in mitigating water shortage problems for irrigation which they require for rice and wheat - as well as preserving the sacred location. The District Forest Division, Zhemgang under the Department of Forests and Park Services (DoFPS) conducted a survey and recorded 21 plant species (trees and shrubs) and 22 orchid species.
To commence the revival activities, meetings were held with the institutions and conservation groups, by-laws were developed, and extensive mapping and demarcation of the area around the lake were done. Then, during the site development phase of Tali Lake area management, there was development of footpaths and eco-cultural trails, identification of plants and trees and name tagging, installation of waste bins and procurement of materials, installation of signboards at the site, and access roads were completed. Research and documentation on the lake and the village were carried out, and audio-video recordings and interviews were done. Advocacy and awareness of output were also accomplished. Through community engagement and religious ceremonies, the lake was successfully cleared after consulting with the National Biodiversity Centre, advice from concerned authorities and local experts as well as recommendations contained in the biodiversity assessment report from Zhemgang Forest Division under DoFPS. Men and women from the village joined together to construct a bamboo raft to transport the weeds across the lake and over three truckloads of weeds and tree stumps were cleared to revive the lake. The National Environment Commission tested the water quality and the result showed that the pH of the water is slightly acidic (6.49), 0.95mg/L of dissolved oxygen, and chemical oxygen demand of 10.4mg/L.
The revival of Tali Tangsibi Lake has benefitted downstream water supplies for irrigation and has prevented the sacred local lake from drying up.
2.3 Fotografías de la Tecnología
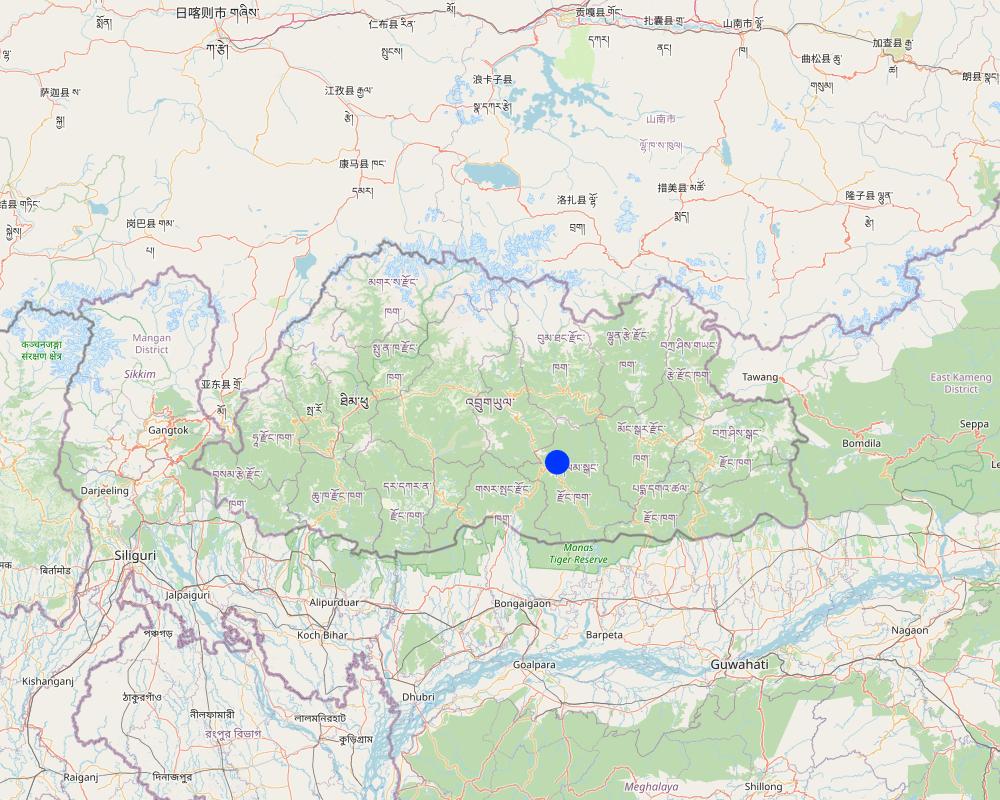
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde la Tecnología fue aplicada y que se hallan comprendidos por esta evaluación
País:
Bután
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
Tali Community
Especifique más el lugar :
Nangkhor Gewog, Zhemgang Dzongkhag
Especifique la difusión de la Tecnología:
- aplicada en puntos específicos/ concentrada en un área pequeña
¿El/los sitio(s) de la Tecnología se ubica(n) en un área de protección permanente?
Sí
Si fuera el caso, especifique :
The lake falls under the protected area 'Biological Corridor'.
Map
×2.6 Fecha de la implementación
Indique año de implementación:
2020
2.7 Introducción de la Tecnología
Especifique cómo se introdujo la Tecnología:
- mediante proyectos/ intervenciones externas
Comentarios (tipo de proyecto, etc.):
The lake revival activities were funded by UNDP GEF SGP (US$33550 ) and the Loden Foundation (US$12650) and they were all completed in 2020.
3. Clasificación de la Tecnología MST
3.1 Propósito(s) principal(es) de la Tecnología MST
- reducir, prevenir, restaurar la degradación del suelo
- conservar el ecosistema
- preservar/ mejorar biodiversidad
- crear impacto económico benéfico
- crear impacto social benéfico
3.2 Tipo(s) actuales de uso de la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología
Mezcla de tipos de uso de tierras dentro de la misma unidad de tierras: :
No

Bosques
- Bosques/ zonas boscosas (semi) naturales
Bosques/ zonas boscosas (semi-) naturales: Especifique tipo de manejo:
- Tala selectiva
- Uso de productos forestales no madereros
¿Los árboles especificados son deciduos o imperecederos?
- mixto deciduo/ imperecedero
Productos y servicios:
- Madera
- Leña
- Conservación/ Protección de la naturaleza
- Recreación/ turismo

vías fluviales, masas de agua, humedales
Principales productos/ servicios:
Lake
3.3 ¿Cambió el uso de tierras debido a la implementación de la Tecnología?
¿Cambió el uso de tierras debido a la implementación de la Tecnología?
- No (Continúe con la pregunta 3.4)
3.4 Provisión de agua
Provisión de agua para la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología:
- mixta de secano – irrigada
Comentarios:
The community benefits from five irrigation sources viz. Bangleng Chhu, Budigang Chhu, Khatoed Chhu, Dungmangla Chhu, and Kokaling Chhu. The latter three irrigation channels are equipped with cement and pipelines.
3.5 Grupo MST al que pertenece la Tecnología
- manejo de agua superficial (manantial, río, lagos, mar):
- reducción de riesgos de desastres basados en el ecosistema
3.6 Medidas MST que componen la Tecnología

otras medidas
Especifique:
Lake revival
3.7 Principales tipos de degradación del suelo encarados con la Tecnología

degradación biológica
- Bh: pérdida de hábitats
- Bs: reducción en la calidad y composición/ diversidad de las especies

degradación del agua
- Hs: cambio en la cantidad de aguas superficiales
3.8 Prevención, reducción o restauración de la degradación del suelo
Especifique la meta de la Tecnología con relación a la degradación de la tierra:
- no aplica
4. Especificaciones técnicas, actividades de implementación, insumos y costos
4.1 Dibujo técnico de la Tecnología
4.2 Información general sobre el cálculo de insumos y costos
Especifique cómo se calcularon los costos e insumos:
- por unidad de Tecnología
Especifique la moneda usada para calcular costos:
- USD
Si fuera relevante, indique la tasa de cambio de dólares americanos a la moneda local (ej. 1 U$ = 79.9 Reales Brasileros): 1 U$ =:
80,0
4.3 Actividades de establecimiento
| Actividad | Momento (estación) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Project inception and area mapping. | |
| 2. | Lake management and eco-cultural trail development. | After crop harvest (November and December, 2020) |
| 3. | Research and documentation phase. | |
| 4. | Output dissemination. |
4.4 Costos e insumos necesarios para el establecimiento
Si no puede desglosar los costos especificados en la tabla anterior, proporcione un estimado de los cálculos totales en los que se incurrió para establecer la Tecnología:
46200,0
Si el usuario de la tierra no cubrió el 100% de los costos, indique quién financió el resto del costo:
The whole of expenditures were borne by UNDP GEF SGP (US$33550) and the Loden Foundation (US$12650).
Comentarios:
The unit cost breakdown was impossible due to the unavailability of the expenditure statements.
4.5 Actividades de establecimiento/ recurrentes
Comentarios:
Since the completion of the activity in 2020, no maintenance activities have been conducted so far. However, the physical monitoring is done by the chairman, secretary, and treasurer of the community forest management group of Tali.
5. Entorno natural y humano
5.1 Clima
Lluvia anual
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Especificaciones/ comentarios sobre la cantidad de lluvia:
Average annual rainfall: 1200-1800 mm
The rain estimate has been derived based on the agro-ecological zone (AEZ) the area falls under.
Bhutan is divided into six AEZs (source: https://www.fao.org/3/ad103e/AD103E02.htm).
Bhutan has six AEZs. The wet sub-tropical zone is from 150 to 600 m, followed by the humid sub-tropical zone from 600 to 1,200 m. The dry sub-tropical zone starts at 1,200 m and extends to 1,800 m, followed by the warm temperate zone, which reaches 2,600 m. The cool temperate zone lies between 2,600 and 3,600 m and, finally, the alpine zone between 3,600 m and 4,600 m.
Zona agroclimática
The lake area falls under the Dry Subtropical Zone in Bhutan.
5.2 Topografía
Pendientes en promedio:
- plana (0-2 %)
- ligera (3-5%)
- moderada (6-10%)
- ondulada (11-15%)
- accidentada (16-30%)
- empinada (31-60%)
- muy empinada (>60%)
Formaciones telúricas:
- meseta/ planicies
- cordilleras
- laderas montañosas
- laderas de cerro
- pies de monte
- fondo del valle
Zona altitudinal:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1,000 m s.n.m
- 1,001-1,500 m s.n.m
- 1,501-2,000 m s.n.m
- 2,001-2,500 m s.n.m
- 2,501-3,000 m s.n.m
- 3,001-4,000 m s.n.m
- > 4,000 m s.n.m
Indique si la Tecnología se aplica específicamente en:
- situaciones cóncavas
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre topografía :
1742 m a.s.l
5.3 Suelos
Profundidad promedio del suelo:
- muy superficial (0-20 cm)
- superficial (21-50 cm)
- moderadamente profunda (51-80 cm)
- profunda (81-120 cm)
- muy profunda (>120 cm)
Textura del suelo (capa arable):
- mediana (limosa)
- fina/ pesada (arcilla)
Textura del suelo (> 20 cm debajo de la superficie):
- mediana (limosa)
- fina/ pesada (arcilla)
Materia orgánica de capa arable:
- elevada (>3%)
Si se halla disponible, adjunte una descripción completa de los suelos o especifique la información disponible, por ej., tipo de suelo, pH/ acidez de suelo, capacidad de intercambio catiónico, nitrógeno, salinidad, etc. :
Moisture content-2.95%
Organic matter-3.77%
Organic carbon-2.19%
pH-6.45
Electrical conductivity-36.27 µs/cm
Nitrogen-0.11
Phosphorus-0.95
Potassium-98.40 mg/100ml
Soil texture-Clay Loam
5.4 Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
Agua subterránea:
5-50 m
Disponibilidad de aguas superficiales:
bueno
Calidad de agua (sin tratar):
agua potable de buena calidad
La calidad de agua se refiere a:
agua superficial
¿La salinidad del agua es un problema?
No
¿Se está llevando a cabo la inundación del área? :
No
5.5 Biodiversidad
Diversidad de especies:
- elevada
Diversidad de hábitats:
- elevada
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre biodiversidad:
Some 21 plant species (trees and shrubs) and 22 orchid species were identified and documented by Zhemgang Forest Division during the biodiversity survey conducted in and around the lake area.
5.6 Las características de los usuarios de la tierra que aplican la Tecnología
Sedentario o nómada:
- Sedentario
Orientación del mercado del sistema de producción:
- mixta (subsistencia/ comercial)
Ingresos no agrarios:
- 10-50% de todo el ingreso
Nivel relativo de riqueza:
- promedio
Individuos o grupos:
- grupos/ comunal
Nivel de mecanización:
- mecanizado/motorizado
Género:
- mujeres
- hombres
Edad de los usuarios de la tierra:
- jóvenes
- personas de mediana edad
5.7 Área promedio de la tierra usada por usuarios de tierra que aplican la Tecnología
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
¿Esto se considera de pequeña, mediana o gran escala (refiriéndose al contexto local)?
- gran escala
Comentarios:
The average handholding of the community ranges from 7 to 8 acres, falling under the large scale based on local context. In general, the average household land holding in Bhutan is 3 acres.
In the local context:
3 acres (1.2 ha) = medium scale
> 3 acres = large-scale
<3 acres = small-scale
5.8 Tenencia de tierra, uso de tierra y derechos de uso de agua
- Family land
Derechos de uso de tierra:
- individual
Derechos de uso de agua:
- comunitarios (organizado)
¿Los derechos del uso de la tierra se basan en un sistema legal tradicional?
Sí
Especifique:
The land use rights in Bhutan is based on a traditional legal system guided by formal land act and land rules and regulations.
5.9 Acceso a servicios e infraestructura
salud:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
educación:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
asistencia técnica:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
empleo (ej. fuera de la granja):
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
mercados:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
energía:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
caminos y transporte:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
agua potable y saneamiento:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
servicios financieros:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
6. Impactos y comentarios para concluir
6.1 Impactos in situ demostrados por la Tecnología
Impactos socioeconómicos
Producción
producción de cultivo
Comentarios/ especifique:
The lake is a critical source of irrigation water. The lake revival has aided in crop production via water availability.
producción animal
Comentarios/ especifique:
The lake is a critical source of drinking water for domestic animals. The lake revival has aided in animal production via water availability.
riesgo de fracaso de producción
Comentarios/ especifique:
The risk of production failure has decreased as there are enhanced crop and animal productions due to water availability from the lake.
Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
disponibilidad de agua potable
Comentarios/ especifique:
The lake is a source of drinking water for the Tali community and because the lake is cleaned and managed the water availability and quality have improved.
calidad de agua potable
Comentarios/ especifique:
The lake is a source of drinking water for the Tali community and because the lake is cleaned and managed the water availability and quality have improved.
disponibilidad de agua para ganado
Comentarios/ especifique:
The lake is a source of drinking water for domestic animals so the water availability for livestock has increased.
calidad de agua para ganado
Comentarios/ especifique:
The lake is a source of drinking water for domestic animals and because the lake is cleaned and managed the water quality for livestock has improved.
disponibilidad de agua para irrigar
Comentarios/ especifique:
The lake is a source of irrigation water and because the lake is cleaned, managed, and conserved the availability of irrigation has increased.
calidad de agua para irrigar
Comentarios/ especifique:
The lake is a source of irrigation water and because the lake is cleaned, managed, and conserved the quality of irrigation water has improved.
Impactos socioculturales
MST/ conocimiento de la degradación del suelo
Comentarios/ especifique:
The lake revival has created awareness among the Tali community against the irresponsible exploitation of forests. It has thrown light on the importance of water conservation.
Impactos ecológicos
Biodiversidad: vegetación, animales
diversidad animal
Comentarios/ especifique:
The quantity is not known. However, the beneficiaries believe that the lake revival along with eco-tourism area demarcation followed by enhanced area protection could have improved the animal diversity.
diversidad de hábitats
Comentarios/ especifique:
The dedicated area (lake and the nearby forest) identified and protected is assumed to have diversified the habitats.
6.2 Impactos fuera del sitio demostrados por la Tecnología
disponibilidad de agua
Comentarios/ especifique:
Increased water availability for drinking and irrigation.
6.3 Exposición y sensibilidad de la Tecnología al cambio climático gradual y a extremos relacionados al clima/ desastres (desde la percepción de los usuarios de tierras)
Cambio climático gradual
Cambio climático gradual
| Estación | Incremento o reducción | ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| temperatura anual | incrementó | muy bien |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados al clima
Desastres climatológicos:
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| tormenta de lluvia local | muy bien |
| tormenta local | muy bien |
| granizada local | muy bien |
| tormenta de viento | muy bien |
Comentarios:
About the annual rainfall, the land users shared that the quantity over the years has remained the same. But the rainfall pattern has changed. In the earlier years (past 10 - 15 years) there used to be gentle and steady rainfall. However, in recent years, some sudden heavy rain has been following some prolonged dry spells.
6.4 Análisis costo-beneficio
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de establecimiento (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
ligeramente negativo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
negativo
Comentarios:
No maintenance was carried out until now.
6.5 Adopción de la Tecnología
- > 50%
Si tiene la información disponible, cuantifique (número de hogares y/o área cubierta):
25 households of Tali
De todos quienes adoptaron la Tecnología, ¿cuántos lo hicieron espontáneamente, por ej. sin recibir nada de incentivos/ materiales:
- 0-10%
6.6 Adaptación
¿La tecnología fue modificada recientemente para adaptarse a las condiciones cambiantes?
No
6.7 Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades de la Tecnología
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra |
|---|
| Enhance the understanding of scientific, cultural, and spiritual ecology for environmental conservation. |
| Enhance livelihood through the promotion of community-based ecotourism activities. |
| Retaine or increase water volume of the lake. |
| Continued transmission of local cultural knowledge and spiritual and scientific practices beneficial for environmental conservation. |
| Promote community stewardship of the lake and the environment. |
| Revive and conserve lake and the surrounding ecosystem. |
| Create awareness against the irresponsible exploitation of forests. |
| Increased awareness to sustain watersheds and sources for irrigation. |
6.8 Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos de la Tecnología y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| Internal conflicts and misunderstandings are common during group labor contribution. | Regular group meetings, guidance from District Forest Division |
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| Weeds cover the lake periodically. | Cleaning the lake surface by identifying certain routine time. |
| The trails and monuments near the lake are kept unmanaged. | Regular clearing of these trails and management of monuments. |
| Unmanaged water hole present above the lake. | A small water hole present above the lake can be improved and maintained, so that the pressure on the lake will be reduced and can serve as a water reservoir for the lake. |
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.1 Métodos/ fuentes de información
- visitas de campo, encuestas de campo
Four
- entrevistas con usuarios de tierras
Four
¿Cuándo se compilaron los datos (en el campo)?
15/07/2023
7.2 Vínculos a las publicaciones disponibles
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
REVIVAL: LEVERAGING CULTURAL & SCIENTIFIC KNOWLEDGE AND PRACTICES FOR ENVIRONMENTAL CONSERVATION IN TALI, The Loden Foundation, 2022
¿Dónde se halla disponible? ¿Costo?
https://www.undp.org/bhutan/publications/revival-leveraging-cultural-scientific-knowledge-and-practices-environmental-conservation-tali
7.3 Vínculos a la información relevante disponible en línea
Título/ descripción:
The Loden Foundation
URL:
https://loden.org/
Título/ descripción:
Revival: Leveraging cultural, scientific knowledge and practices for environmental conservation in Tali
URL:
https://www.undp.org/bhutan
Título/ descripción:
Leveraging Cultural and Scientific Knowledge and Practices for Environmental Conservation in Tali
URL:
http://3.14.34.174/spacial-itemid-projects-landing-page/spacial-itemid-project-search-results/spacial-itemid-project-detailpage.html?view=projectdetail&id=28078
Título/ descripción:
Jewel basket of Tali
URL:
https://kuenselonline.com/jewel-basket-of-tali/
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos
No hay vínculos
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos