Lake Revival: Towards Environmental Conservation [Butão]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Tshering Yangzom
- Editor: Tashi Wangdi
- Revisores: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Tsho Lar Chey
technologies_6857 - Butão
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Pessoa(s) capacitada(s)
usuário de terra:
La Tshultrim
NA
Butão
usuário de terra:
Thinley Kinzang
NA
Butão
usuário de terra:
Wangmo Dorji
NA
Butão
usuário de terra:
Wangdi Yeshi
NA
Butão
Nome do projeto que facilitou a documentação/avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Strengthening national-level institutional and professional capacities of country Parties towards enhanced UNCCD monitoring and reporting – GEF 7 EA Umbrella II (GEF 7 UNCCD Enabling Activities_Umbrella II)Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
National Soil Services Center, Department of Agric (National Soil Services Center, Department of Agric) - Butão1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O compilador e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através do WOCAT:
Sim
1.4 Declaração de sustentabilidade da tecnologia descrita
A tecnologia descrita aqui é problemática em relação a degradação da terra de forma que não pode ser declarada uma tecnologia de gestão sustentável de terra?
Não
Comentários:
Technology is not problematic with regard to land degradation as lake revival plays an important role in sustained water source and environmental conservation.
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
The lake conservation initiative at Tali was conceived with the vision of protecting the lake and transforming the surrounding area into a community eco-tourism hub. The initiative is a testament to how science and spirituality, and culture and the environment can coexist and benefit from one another.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
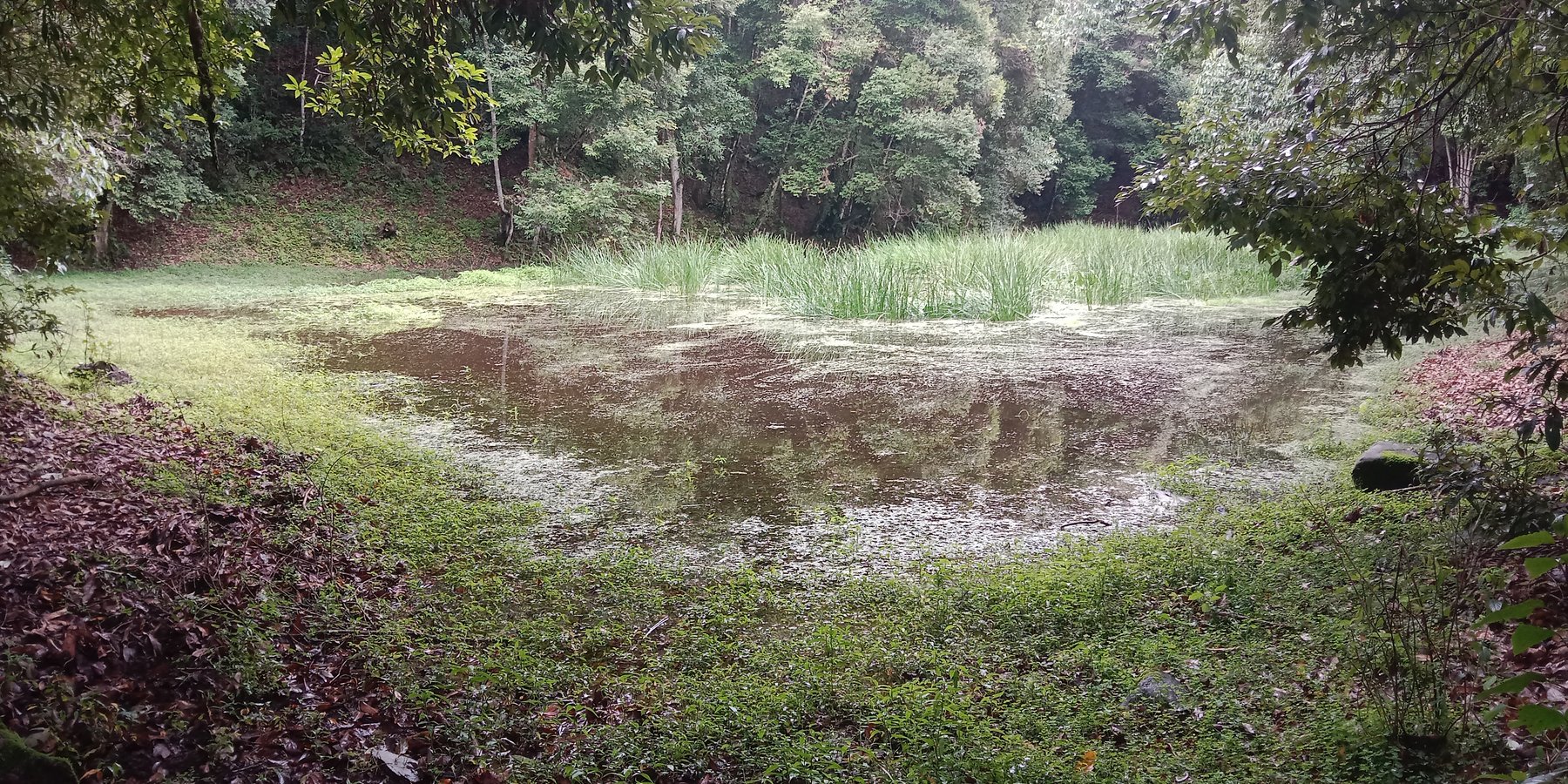
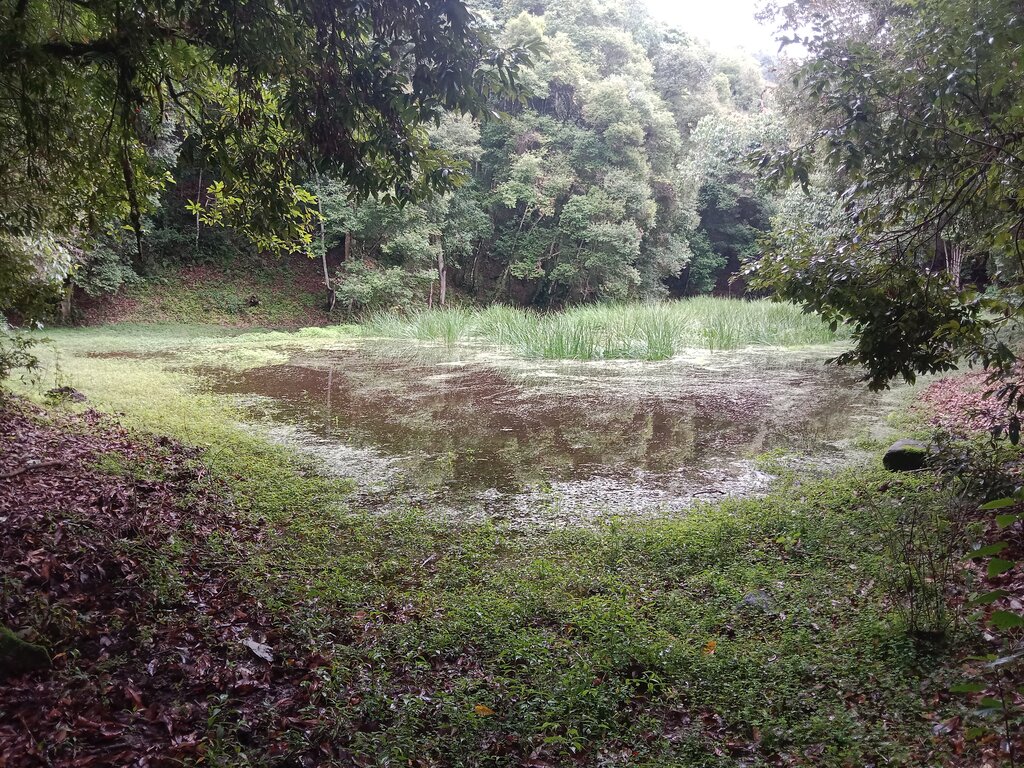
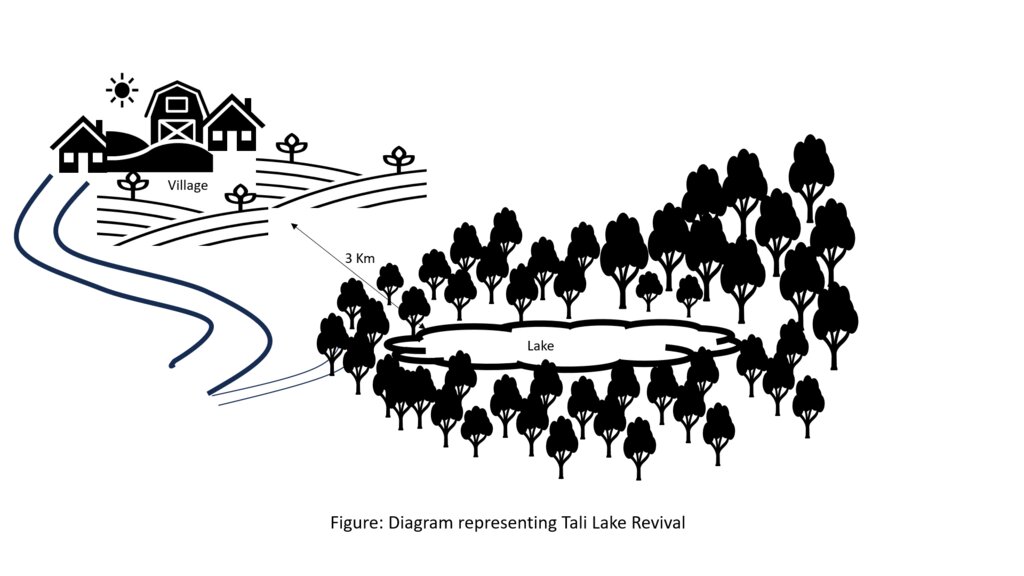
The lake conservation initiative at Tali was conceived with the vision of protecting the lake and transforming the surrounding area into a community eco-tourism hub. The initiative is a testament to how science and spirituality, and culture and the environment can coexist and benefit from one another. The Tali Lake is a major water source (both irrigation and drinking) for the community and both livestock and wild animals.
Bhutanese believe lakes to be sacred and religiously significant. Buli Lake and Tali Lake (Tangsibi Tsho) epitomise how nature and culture come together. Tali village under Nangkor gewog in Zhemgang Dzongkhag lies on the shoulder of mountains at an elevation of 1880 m.a.s.l. with broad-leaved forests. It comprises 25 households with around 280 residents. According to local legend, Tangsibi Tsho in Tali is the “Jewellery basket of Buli Tsho which was left behind when Buli Tsho moved from Tali to Buli”. Tali Lake is spread over an area of 0.40 ha. The 18.2 ha forest around the lake is dominated by species of oak. The forest around the lake harbours a very rich variety of mammals (22 species) that are ecologically important and visit the lake for water and predation. Also, 70 species of birds have been recorded in the forest around the lake.
The community, along with the Loden Foundation and the monastic body, has been engaged in reviving the lake as 90% of the surface was covered with waterweeds and grasses. The aim was to clean, beautify, and sustain the ecosystem through an integrated and holistic management project by combining scientific, social, and spiritual approaches. There was support of USD 33,550 from the United Nations Development Programme Global Environment Facility (UNDP GEF) Small Grants Programme (SGP) and USD 12,650 from the Loden Foundation and the Community.
Tangsibi Tsho in Tali has significant cultural importance which includes water for irrigation and drinking purposes both for people as well as livestock and wild animals. Thus, the initiative was aimed at conserving the lake and transforming the lake area into a community eco-tourism hub. According to the villagers and senior citizens of the community, the revival of the lake would help in mitigating water shortage problems for irrigation which they require for rice and wheat - as well as preserving the sacred location. The District Forest Division, Zhemgang under the Department of Forests and Park Services (DoFPS) conducted a survey and recorded 21 plant species (trees and shrubs) and 22 orchid species.
To commence the revival activities, meetings were held with the institutions and conservation groups, by-laws were developed, and extensive mapping and demarcation of the area around the lake were done. Then, during the site development phase of Tali Lake area management, there was development of footpaths and eco-cultural trails, identification of plants and trees and name tagging, installation of waste bins and procurement of materials, installation of signboards at the site, and access roads were completed. Research and documentation on the lake and the village were carried out, and audio-video recordings and interviews were done. Advocacy and awareness of output were also accomplished. Through community engagement and religious ceremonies, the lake was successfully cleared after consulting with the National Biodiversity Centre, advice from concerned authorities and local experts as well as recommendations contained in the biodiversity assessment report from Zhemgang Forest Division under DoFPS. Men and women from the village joined together to construct a bamboo raft to transport the weeds across the lake and over three truckloads of weeds and tree stumps were cleared to revive the lake. The National Environment Commission tested the water quality and the result showed that the pH of the water is slightly acidic (6.49), 0.95mg/L of dissolved oxygen, and chemical oxygen demand of 10.4mg/L.
The revival of Tali Tangsibi Lake has benefitted downstream water supplies for irrigation and has prevented the sacred local lake from drying up.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Butão
Região/Estado/Província:
Tali Community
Especificação adicional de localização:
Nangkhor Gewog, Zhemgang Dzongkhag
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Aplicado em pontos específicos/concentrado numa pequena área
O(s) local(is) tecnológico(s) está(ão) localizado(s) em uma área permanentemente protegida?
Sim
Caso afirmativo, especifique:
The lake falls under the protected area 'Biological Corridor'.
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Indique o ano de implementação:
2020
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- através de projetos/intervenções externas
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
The lake revival activities were funded by UNDP GEF SGP (US$33550 ) and the Loden Foundation (US$12650) and they were all completed in 2020.
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Reduz, previne, recupera a degradação do solo
- Preserva ecossistema
- Preservar/melhorar a biodiversidade
- Criar impacto econômico benéfico
- Cria impacto social benéfico
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada
Uso do solo misturado dentro da mesma unidade de terra:
Não

Floresta/bosques
- Florestas/bosques (semi)naturais
Florestas (semi)naturais/ bosques: Especificar o tipo de manejo:
- Derrubada seletiva
- Uso florestal não madeireiro
As árvores especificadas acima são decíduas ou perenes?
- decíduas mistas/perene
Produtos e serviços:
- Madeira
- Lenha
- Conservação/proteção da natureza
- Lazer/turismo

Vias navegáveis, corpo d'água, zonas úmidas
Principais produtos/serviços:
Lake
3.3 O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
- Não (Continuar com a pergunta 3.4)
3.4 Abastecimento de água
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Misto de precipitação natural-irrigado
Comentários:
The community benefits from five irrigation sources viz. Bangleng Chhu, Budigang Chhu, Khatoed Chhu, Dungmangla Chhu, and Kokaling Chhu. The latter three irrigation channels are equipped with cement and pipelines.
3.5 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Gestão de água de superfície (nascente, rio, lagos, mar)
- Redução de riscos de desastre baseada no ecossitema
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Outras medidas
Especifique:
Lake revival
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Degradação biológica
- Bh: perda dos habitats
- Bs: Qualidade e composição de espécies/declínio de diversidade

Degradação da água
- Hs: mudança na quantidade de água de superfície
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Não aplicável
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
4.2 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Especifique como custos e entradas foram calculados:
- Por unidade de tecnologia
Especifique a moeda utilizada para os cálculos de custo:
- USD
Se for relevante, indique a taxa de câmbio do USD para moeda local (por exemplo, 1 USD = 79,9 Real): 1 USD =:
80,0
4.3 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Periodicidade (estação do ano) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Project inception and area mapping. | |
| 2. | Lake management and eco-cultural trail development. | After crop harvest (November and December, 2020) |
| 3. | Research and documentation phase. | |
| 4. | Output dissemination. |
4.4 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
Se você não conseguir discriminar os custos na tabela acima, forneça uma estimativa dos custos totais para estabelecer a Tecnologia:
46200,0
Se o usuário da terra arca com menos que 100% dos custos, indique quem cobre os custos remanescentes:
The whole of expenditures were borne by UNDP GEF SGP (US$33550) and the Loden Foundation (US$12650).
Comentários:
The unit cost breakdown was impossible due to the unavailability of the expenditure statements.
4.5 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
Comentários:
Since the completion of the activity in 2020, no maintenance activities have been conducted so far. However, the physical monitoring is done by the chairman, secretary, and treasurer of the community forest management group of Tali.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especificações/comentários sobre a pluviosidade:
Average annual rainfall: 1200-1800 mm
The rain estimate has been derived based on the agro-ecological zone (AEZ) the area falls under.
Bhutan is divided into six AEZs (source: https://www.fao.org/3/ad103e/AD103E02.htm).
Bhutan has six AEZs. The wet sub-tropical zone is from 150 to 600 m, followed by the humid sub-tropical zone from 600 to 1,200 m. The dry sub-tropical zone starts at 1,200 m and extends to 1,800 m, followed by the warm temperate zone, which reaches 2,600 m. The cool temperate zone lies between 2,600 and 3,600 m and, finally, the alpine zone between 3,600 m and 4,600 m.
Zona agroclimática
The lake area falls under the Dry Subtropical Zone in Bhutan.
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Indique se a tecnologia é aplicada especificamente em:
- Posições côncavas
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a topografia:
1742 m a.s.l
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
- Fino/pesado (argila)
Textura do solo (>20 cm abaixo da superfície):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
- Fino/pesado (argila)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Alto (>3%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
Moisture content-2.95%
Organic matter-3.77%
Organic carbon-2.19%
pH-6.45
Electrical conductivity-36.27 µs/cm
Nitrogen-0.11
Phosphorus-0.95
Potassium-98.40 mg/100ml
Soil texture-Clay Loam
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
5-50 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Bom
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
Água potável boa
A qualidade da água refere-se a:
água de superfície
A salinidade da água é um problema?
Não
Ocorre inundação da área?
Não
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Alto
Diversidade de habitat:
- Alto
Comentários e outras especificações sobre biodiversidade:
Some 21 plant species (trees and shrubs) and 22 orchid species were identified and documented by Zhemgang Forest Division during the biodiversity survey conducted in and around the lake area.
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Sedentário ou nômade:
- Sedentário
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- misto (subsistência/comercial)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- 10-50% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Média
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Grupos/comunidade
Nível de mecanização:
- Mecanizado/motorizado
Gênero:
- Mulheres
- Homens
Idade dos usuários da terra:
- Jovens
- meia-idade
5.7 Área média de terrenos utilizados pelos usuários de terrenos que aplicam a Tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Grande escala
Comentários:
The average handholding of the community ranges from 7 to 8 acres, falling under the large scale based on local context. In general, the average household land holding in Bhutan is 3 acres.
In the local context:
3 acres (1.2 ha) = medium scale
> 3 acres = large-scale
<3 acres = small-scale
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
- Family land
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Indivíduo
Direitos do uso da água:
- Comunitário (organizado)
Os direitos de uso da terra são baseados em um sistema jurídico tradicional?
Sim
Especifique:
The land use rights in Bhutan is based on a traditional legal system guided by formal land act and land rules and regulations.
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Comentários/especificar:
The lake is a critical source of irrigation water. The lake revival has aided in crop production via water availability.
Produção animal
Comentários/especificar:
The lake is a critical source of drinking water for domestic animals. The lake revival has aided in animal production via water availability.
Risco de falha de produção
Comentários/especificar:
The risk of production failure has decreased as there are enhanced crop and animal productions due to water availability from the lake.
Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Disponibilidade de água potável
Comentários/especificar:
The lake is a source of drinking water for the Tali community and because the lake is cleaned and managed the water availability and quality have improved.
Qualidade da água potável
Comentários/especificar:
The lake is a source of drinking water for the Tali community and because the lake is cleaned and managed the water availability and quality have improved.
Disponibilidade de água para criação de animais
Comentários/especificar:
The lake is a source of drinking water for domestic animals so the water availability for livestock has increased.
Qualidade da água para criação de animais
Comentários/especificar:
The lake is a source of drinking water for domestic animals and because the lake is cleaned and managed the water quality for livestock has improved.
Disponibilidade de água para irrigação
Comentários/especificar:
The lake is a source of irrigation water and because the lake is cleaned, managed, and conserved the availability of irrigation has increased.
Qualidade da água para irrigação
Comentários/especificar:
The lake is a source of irrigation water and because the lake is cleaned, managed, and conserved the quality of irrigation water has improved.
Impactos socioculturais
Conhecimento de GST/ degradação da terra
Comentários/especificar:
The lake revival has created awareness among the Tali community against the irresponsible exploitation of forests. It has thrown light on the importance of water conservation.
Impactos ecológicos
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Diversidade animal
Comentários/especificar:
The quantity is not known. However, the beneficiaries believe that the lake revival along with eco-tourism area demarcation followed by enhanced area protection could have improved the animal diversity.
Diversidade de habitat
Comentários/especificar:
The dedicated area (lake and the nearby forest) identified and protected is assumed to have diversified the habitats.
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Disponibilidade de água
Comentários/especificar:
Increased water availability for drinking and irrigation.
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | aumento ou diminuição | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | muito bem |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres meteorológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Temporal local | muito bem |
| Trovoada local | muito bem |
| Tempestade de granizo local | muito bem |
| Tempestade de vento local | muito bem |
Comentários:
About the annual rainfall, the land users shared that the quantity over the years has remained the same. But the rainfall pattern has changed. In the earlier years (past 10 - 15 years) there used to be gentle and steady rainfall. However, in recent years, some sudden heavy rain has been following some prolonged dry spells.
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
levemente negativo
Retornos a longo prazo:
negativo
Comentários:
No maintenance was carried out until now.
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- > 50%
Se disponível, determine a quantidade (número de unidades familiares e/ou área abordada):
25 households of Tali
De todos aqueles que adotaram a Tecnologia, quantos o fizeram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo/ pagamento material?
- 0-10%
6.6 Adaptação
A tecnologia foi recentemente modificada para adaptar-se as condições variáveis?
Não
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
| Enhance the understanding of scientific, cultural, and spiritual ecology for environmental conservation. |
| Enhance livelihood through the promotion of community-based ecotourism activities. |
| Retaine or increase water volume of the lake. |
| Continued transmission of local cultural knowledge and spiritual and scientific practices beneficial for environmental conservation. |
| Promote community stewardship of the lake and the environment. |
| Revive and conserve lake and the surrounding ecosystem. |
| Create awareness against the irresponsible exploitation of forests. |
| Increased awareness to sustain watersheds and sources for irrigation. |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Internal conflicts and misunderstandings are common during group labor contribution. | Regular group meetings, guidance from District Forest Division |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do compilador ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Weeds cover the lake periodically. | Cleaning the lake surface by identifying certain routine time. |
| The trails and monuments near the lake are kept unmanaged. | Regular clearing of these trails and management of monuments. |
| Unmanaged water hole present above the lake. | A small water hole present above the lake can be improved and maintained, so that the pressure on the lake will be reduced and can serve as a water reservoir for the lake. |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
- visitas de campo, pesquisas de campo
Four
- entrevistas com usuários de terras
Four
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
15/07/2023
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
REVIVAL: LEVERAGING CULTURAL & SCIENTIFIC KNOWLEDGE AND PRACTICES FOR ENVIRONMENTAL CONSERVATION IN TALI, The Loden Foundation, 2022
Disponível de onde? Custos?
https://www.undp.org/bhutan/publications/revival-leveraging-cultural-scientific-knowledge-and-practices-environmental-conservation-tali
7.3 Links para informações on-line relevantes
Título/ descrição:
The Loden Foundation
URL:
https://loden.org/
Título/ descrição:
Revival: Leveraging cultural, scientific knowledge and practices for environmental conservation in Tali
URL:
https://www.undp.org/bhutan
Título/ descrição:
Leveraging Cultural and Scientific Knowledge and Practices for Environmental Conservation in Tali
URL:
http://3.14.34.174/spacial-itemid-projects-landing-page/spacial-itemid-project-search-results/spacial-itemid-project-detailpage.html?view=projectdetail&id=28078
Título/ descrição:
Jewel basket of Tali
URL:
https://kuenselonline.com/jewel-basket-of-tali/
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos