Lake Revival: Towards Environmental Conservation [Bhoutan]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Tshering Yangzom
- Rédacteur : Tashi Wangdi
- Examinateurs : William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Tsho Lar Chey
technologies_6857 - Bhoutan
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Personne(s)-ressource(s) clé(s)
exploitant des terres:
La Tshultrim
NA
Bhoutan
exploitant des terres:
Thinley Kinzang
NA
Bhoutan
exploitant des terres:
Wangmo Dorji
NA
Bhoutan
exploitant des terres:
Wangdi Yeshi
NA
Bhoutan
Nom du projet qui a facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Strengthening national-level institutional and professional capacities of country Parties towards enhanced UNCCD monitoring and reporting – GEF 7 EA Umbrella II (GEF 7 UNCCD Enabling Activities_Umbrella II)Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
National Soil Services Center, Department of Agric (National Soil Services Center, Department of Agric) - Bhoutan1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.4 Déclaration sur la durabilité de la Technologie décrite
Est-ce que la Technologie décrite ici pose problème par rapport à la dégradation des terres, de telle sorte qu'elle ne peut pas être déclarée comme étant une technologie de gestion durable des terres?
Non
Commentaires:
Technology is not problematic with regard to land degradation as lake revival plays an important role in sustained water source and environmental conservation.
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
The lake conservation initiative at Tali was conceived with the vision of protecting the lake and transforming the surrounding area into a community eco-tourism hub. The initiative is a testament to how science and spirituality, and culture and the environment can coexist and benefit from one another.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
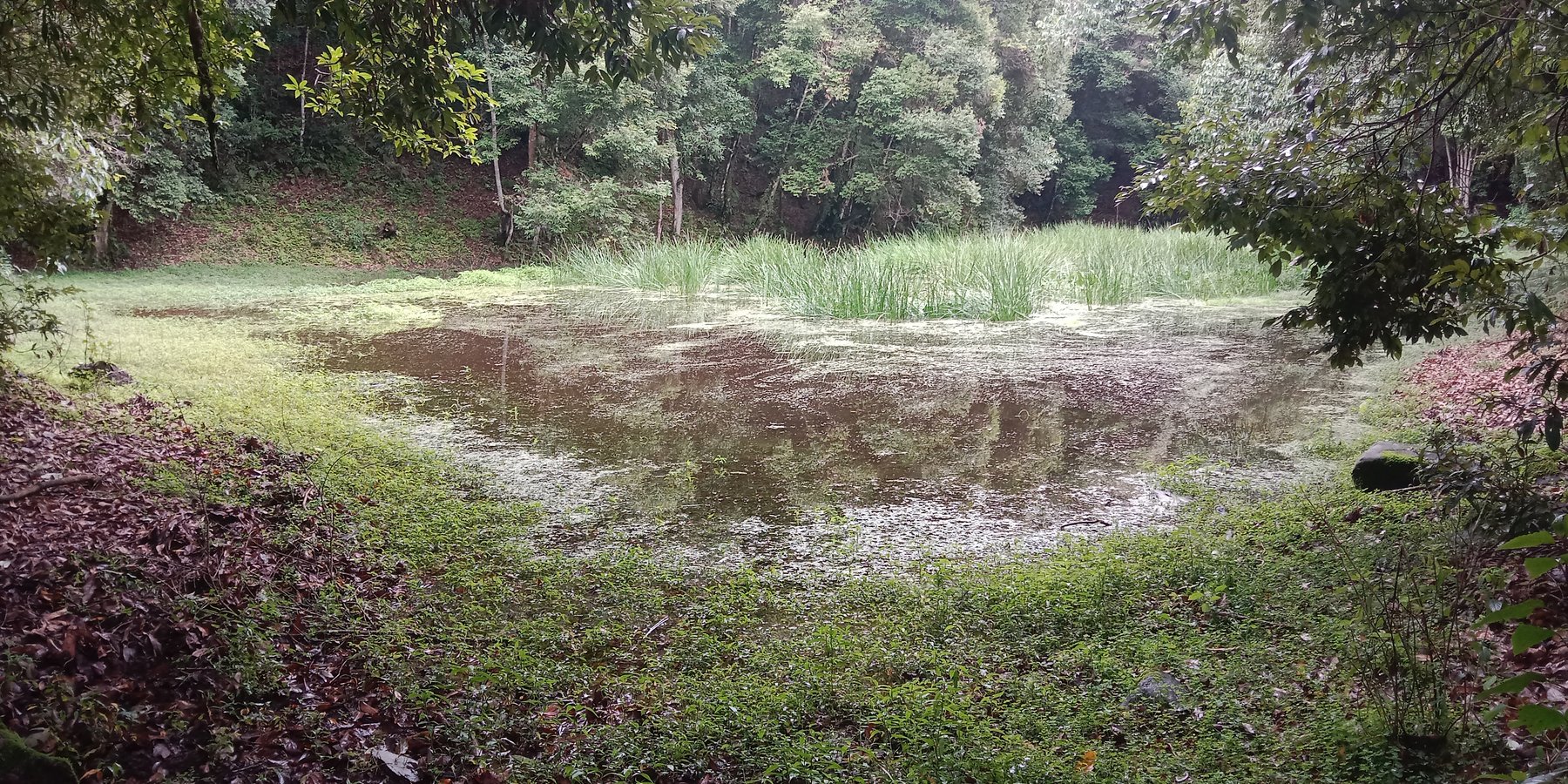
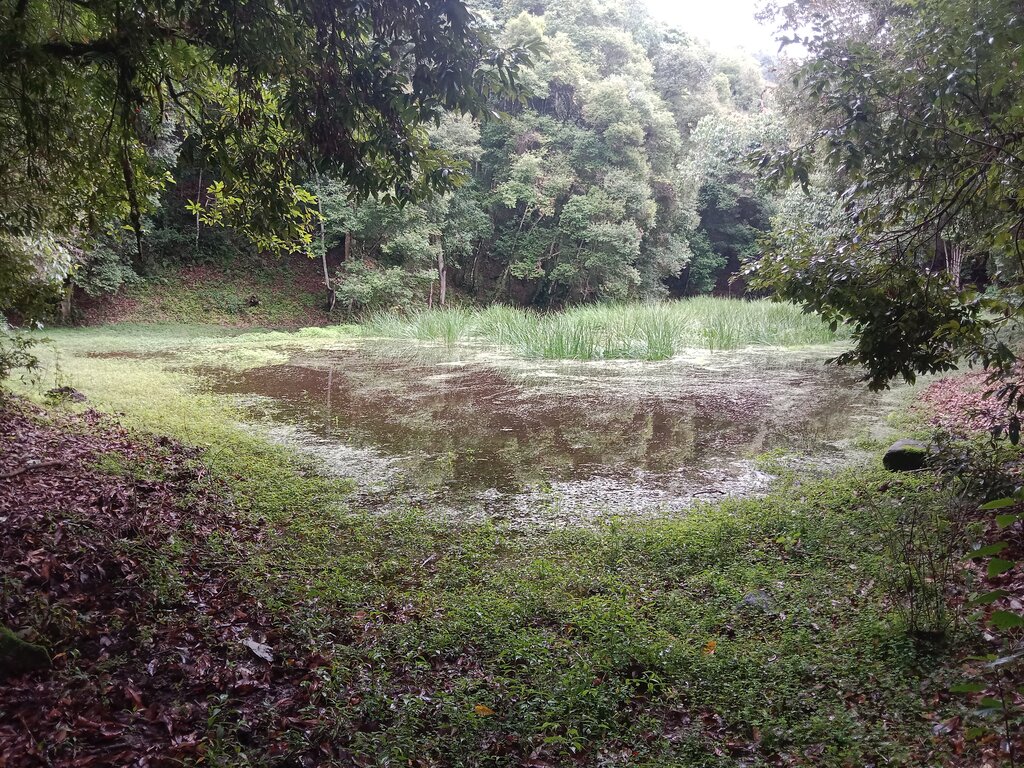
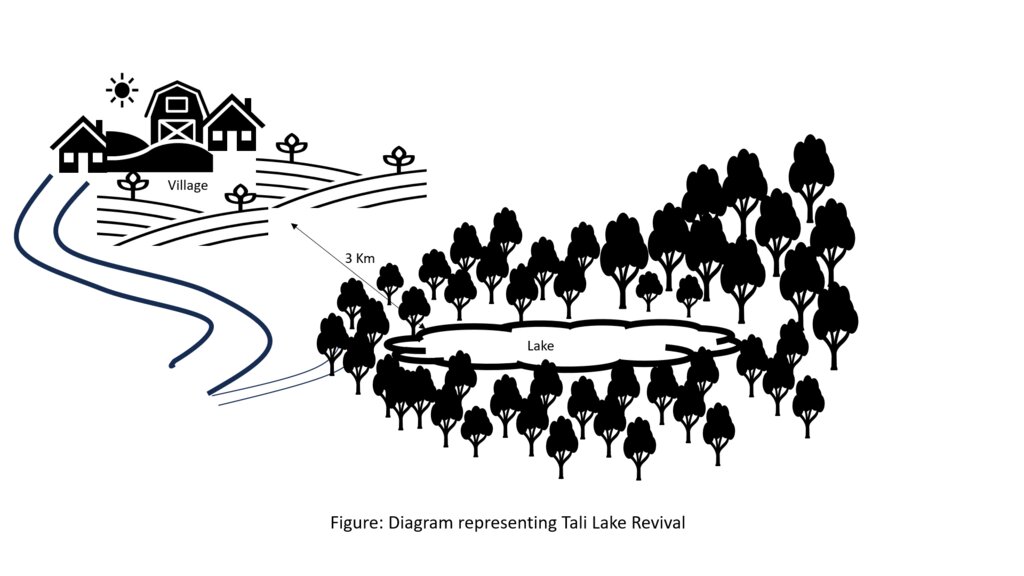
The lake conservation initiative at Tali was conceived with the vision of protecting the lake and transforming the surrounding area into a community eco-tourism hub. The initiative is a testament to how science and spirituality, and culture and the environment can coexist and benefit from one another. The Tali Lake is a major water source (both irrigation and drinking) for the community and both livestock and wild animals.
Bhutanese believe lakes to be sacred and religiously significant. Buli Lake and Tali Lake (Tangsibi Tsho) epitomise how nature and culture come together. Tali village under Nangkor gewog in Zhemgang Dzongkhag lies on the shoulder of mountains at an elevation of 1880 m.a.s.l. with broad-leaved forests. It comprises 25 households with around 280 residents. According to local legend, Tangsibi Tsho in Tali is the “Jewellery basket of Buli Tsho which was left behind when Buli Tsho moved from Tali to Buli”. Tali Lake is spread over an area of 0.40 ha. The 18.2 ha forest around the lake is dominated by species of oak. The forest around the lake harbours a very rich variety of mammals (22 species) that are ecologically important and visit the lake for water and predation. Also, 70 species of birds have been recorded in the forest around the lake.
The community, along with the Loden Foundation and the monastic body, has been engaged in reviving the lake as 90% of the surface was covered with waterweeds and grasses. The aim was to clean, beautify, and sustain the ecosystem through an integrated and holistic management project by combining scientific, social, and spiritual approaches. There was support of USD 33,550 from the United Nations Development Programme Global Environment Facility (UNDP GEF) Small Grants Programme (SGP) and USD 12,650 from the Loden Foundation and the Community.
Tangsibi Tsho in Tali has significant cultural importance which includes water for irrigation and drinking purposes both for people as well as livestock and wild animals. Thus, the initiative was aimed at conserving the lake and transforming the lake area into a community eco-tourism hub. According to the villagers and senior citizens of the community, the revival of the lake would help in mitigating water shortage problems for irrigation which they require for rice and wheat - as well as preserving the sacred location. The District Forest Division, Zhemgang under the Department of Forests and Park Services (DoFPS) conducted a survey and recorded 21 plant species (trees and shrubs) and 22 orchid species.
To commence the revival activities, meetings were held with the institutions and conservation groups, by-laws were developed, and extensive mapping and demarcation of the area around the lake were done. Then, during the site development phase of Tali Lake area management, there was development of footpaths and eco-cultural trails, identification of plants and trees and name tagging, installation of waste bins and procurement of materials, installation of signboards at the site, and access roads were completed. Research and documentation on the lake and the village were carried out, and audio-video recordings and interviews were done. Advocacy and awareness of output were also accomplished. Through community engagement and religious ceremonies, the lake was successfully cleared after consulting with the National Biodiversity Centre, advice from concerned authorities and local experts as well as recommendations contained in the biodiversity assessment report from Zhemgang Forest Division under DoFPS. Men and women from the village joined together to construct a bamboo raft to transport the weeds across the lake and over three truckloads of weeds and tree stumps were cleared to revive the lake. The National Environment Commission tested the water quality and the result showed that the pH of the water is slightly acidic (6.49), 0.95mg/L of dissolved oxygen, and chemical oxygen demand of 10.4mg/L.
The revival of Tali Tangsibi Lake has benefitted downstream water supplies for irrigation and has prevented the sacred local lake from drying up.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Bhoutan
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Tali Community
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Nangkhor Gewog, Zhemgang Dzongkhag
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- appliquée en des points spécifiques ou concentrée sur une petite surface
Est-ce que les sites dans lesquels la Technologie est appliquée sont situés dans des zones protégées en permanence?
Oui
Si oui, veuillez préciser:
The lake falls under the protected area 'Biological Corridor'.
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Indiquez l'année de mise en œuvre:
2020
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- par le biais de projets/ d'interventions extérieures
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
The lake revival activities were funded by UNDP GEF SGP (US$33550 ) and the Loden Foundation (US$12650) and they were all completed in 2020.
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- réduire, prévenir, restaurer les terres dégradées
- préserver l'écosystème
- conserver/ améliorer la biodiversité
- créer un impact économique positif
- créer un impact social positif
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée
Les divers types d'utilisation des terres au sein du même unité de terrain: :
Non

Forêts/ bois
- Forêts (semi-)naturelles/ bois
Forêts (semi-)naturelles/ terres boisées: précisez le mode de gestion:
- Coupes sélectives
- Utilisation de la forêt non liée au bois
Est-ce que les espèces d’arbres précisées ci-dessus sont des espèces d'arbre arbres à feuilles caduques ou à feuilles persistantes ?
- forêt mixte décidue/ à feuillage persistant
Produits et services:
- Bois d'œuvre (de construction)
- Bois de chauffage
- Conservation/ protection de la nature
- Loisirs/ tourisme

Voies d'eau, plans d'eau, zones humides
Principaux produits/ services:
Lake
3.3 Est-ce que l’utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie ?
Est-ce que l’utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie ?
- Non (Passez à la question 3.4)
3.4 Approvisionnement en eau
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- mixte: pluvial-irrigué
Commentaires:
The community benefits from five irrigation sources viz. Bangleng Chhu, Budigang Chhu, Khatoed Chhu, Dungmangla Chhu, and Kokaling Chhu. The latter three irrigation channels are equipped with cement and pipelines.
3.5 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- gestion des eaux de surface (sources, rivières, lacs, mers)
- réduction des risques de catastrophe fondée sur les écosystèmes
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

autres mesures
Précisez:
Lake revival
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

dégradation biologique
- Bh: perte d’habitats
- Bs: baisse de la qualité et de la composition/ diversité des espèces

dégradation hydrique
- Hs: changement de la quantité d’eau de surface
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- non applicable
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
4.2 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
Spécifiez la manière dont les coûts et les intrants ont été calculés:
- par entité de la Technologie
Indiquez la monnaie utilisée pour le calcul des coûts:
- dollars américains
Indiquez le taux de change des USD en devise locale, le cas échéant (p.ex. 1 USD = 79.9 réal brésilien): 1 USD = :
80,0
4.3 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Calendrier des activités (saisonnier) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Project inception and area mapping. | |
| 2. | Lake management and eco-cultural trail development. | After crop harvest (November and December, 2020) |
| 3. | Research and documentation phase. | |
| 4. | Output dissemination. |
4.4 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
Si vous n'êtes pas en mesure de décomposer les coûts dans le tableau précédent, donnez une estimation du coût total de la mise en place de la Technologie:
46200,0
Si le coût n'est pas pris en charge à 100% par l'exploitant des terres, indiquez qui a financé le coût restant:
The whole of expenditures were borne by UNDP GEF SGP (US$33550) and the Loden Foundation (US$12650).
Commentaires:
The unit cost breakdown was impossible due to the unavailability of the expenditure statements.
4.5 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
Commentaires:
Since the completion of the activity in 2020, no maintenance activities have been conducted so far. However, the physical monitoring is done by the chairman, secretary, and treasurer of the community forest management group of Tali.
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifications/ commentaires sur les précipitations:
Average annual rainfall: 1200-1800 mm
The rain estimate has been derived based on the agro-ecological zone (AEZ) the area falls under.
Bhutan is divided into six AEZs (source: https://www.fao.org/3/ad103e/AD103E02.htm).
Bhutan has six AEZs. The wet sub-tropical zone is from 150 to 600 m, followed by the humid sub-tropical zone from 600 to 1,200 m. The dry sub-tropical zone starts at 1,200 m and extends to 1,800 m, followed by the warm temperate zone, which reaches 2,600 m. The cool temperate zone lies between 2,600 and 3,600 m and, finally, the alpine zone between 3,600 m and 4,600 m.
Zone agro-climatique
The lake area falls under the Dry Subtropical Zone in Bhutan.
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Indiquez si la Technologie est spécifiquement appliquée dans des:
- situations concaves
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la topographie:
1742 m a.s.l
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- moyen (limoneux)
- fin/ lourd (argile)
Texture du sol (> 20 cm sous la surface):
- moyen (limoneux)
- fin/ lourd (argile)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- abondant (>3%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Moisture content-2.95%
Organic matter-3.77%
Organic carbon-2.19%
pH-6.45
Electrical conductivity-36.27 µs/cm
Nitrogen-0.11
Phosphorus-0.95
Potassium-98.40 mg/100ml
Soil texture-Clay Loam
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Profondeur estimée de l’eau dans le sol:
5-50 m
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
bonne
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
eau potable
La qualité de l'eau fait référence à:
eaux de surface
La salinité de l'eau est-elle un problème? :
Non
La zone est-elle inondée?
Non
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- élevé
Diversité des habitats:
- élevé
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la biodiversité:
Some 21 plant species (trees and shrubs) and 22 orchid species were identified and documented by Zhemgang Forest Division during the biodiversity survey conducted in and around the lake area.
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Sédentaire ou nomade:
- Sédentaire
Orientation du système de production:
- exploitation mixte (de subsistance/ commerciale)
Revenus hors exploitation:
- 10-50% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- moyen
Individus ou groupes:
- groupe/ communauté
Niveau de mécanisation:
- mécanisé/ motorisé
Genre:
- femmes
- hommes
Age des exploitants des terres:
- jeunes
- personnes d'âge moyen
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres utilisées par les exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- grande dimension
Commentaires:
The average handholding of the community ranges from 7 to 8 acres, falling under the large scale based on local context. In general, the average household land holding in Bhutan is 3 acres.
In the local context:
3 acres (1.2 ha) = medium scale
> 3 acres = large-scale
<3 acres = small-scale
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
- Family land
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- individuel
Droits d’utilisation de l’eau:
- communautaire (organisé)
Est-ce que les droits d'utilisation des terres sont fondés sur un système juridique traditionnel?
Oui
Précisez:
The land use rights in Bhutan is based on a traditional legal system guided by formal land act and land rules and regulations.
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
énergie:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The lake is a critical source of irrigation water. The lake revival has aided in crop production via water availability.
production animale
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The lake is a critical source of drinking water for domestic animals. The lake revival has aided in animal production via water availability.
risque d'échec de la production
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The risk of production failure has decreased as there are enhanced crop and animal productions due to water availability from the lake.
Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
disponibilité de l'eau potable
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The lake is a source of drinking water for the Tali community and because the lake is cleaned and managed the water availability and quality have improved.
qualité de l'eau potable
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The lake is a source of drinking water for the Tali community and because the lake is cleaned and managed the water availability and quality have improved.
disponibilité de l'eau pour l'élevage
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The lake is a source of drinking water for domestic animals so the water availability for livestock has increased.
qualité de l'eau pour l'élevage
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The lake is a source of drinking water for domestic animals and because the lake is cleaned and managed the water quality for livestock has improved.
disponibilité de l'eau d'irrigation
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The lake is a source of irrigation water and because the lake is cleaned, managed, and conserved the availability of irrigation has increased.
qualité de l'eau d'irrigation
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The lake is a source of irrigation water and because the lake is cleaned, managed, and conserved the quality of irrigation water has improved.
Impacts socioculturels
connaissances sur la GDT/ dégradation des terres
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The lake revival has created awareness among the Tali community against the irresponsible exploitation of forests. It has thrown light on the importance of water conservation.
Impacts écologiques
Biodiversité: végétale, animale
diversité animale
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The quantity is not known. However, the beneficiaries believe that the lake revival along with eco-tourism area demarcation followed by enhanced area protection could have improved the animal diversity.
diversité des habitats
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The dedicated area (lake and the nearby forest) identified and protected is assumed to have diversified the habitats.
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
disponibilité de l'eau
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Increased water availability for drinking and irrigation.
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Changements climatiques progressifs
Changements climatiques progressifs
| Saison | Augmentation ou diminution | Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| températures annuelles | augmente | très bien |
Extrêmes climatiques (catastrophes)
Catastrophes météorologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| pluie torrentielle locale | très bien |
| orage local | très bien |
| averse de grêle locale | très bien |
| tempête de vent locale | très bien |
Commentaires:
About the annual rainfall, the land users shared that the quantity over the years has remained the same. But the rainfall pattern has changed. In the earlier years (past 10 - 15 years) there used to be gentle and steady rainfall. However, in recent years, some sudden heavy rain has been following some prolonged dry spells.
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
légèrement négative
Rentabilité à long terme:
négative
Commentaires:
No maintenance was carried out until now.
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
- > 50%
Si disponible, quantifiez (nombre de ménages et/ou superficie couverte):
25 households of Tali
De tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle, ou aucune rémunération? :
- 0-10%
6.6 Adaptation
La Technologie a-t-elle été récemment modifiée pour s'adapter à l'évolution des conditions?
Non
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
| Enhance the understanding of scientific, cultural, and spiritual ecology for environmental conservation. |
| Enhance livelihood through the promotion of community-based ecotourism activities. |
| Retaine or increase water volume of the lake. |
| Continued transmission of local cultural knowledge and spiritual and scientific practices beneficial for environmental conservation. |
| Promote community stewardship of the lake and the environment. |
| Revive and conserve lake and the surrounding ecosystem. |
| Create awareness against the irresponsible exploitation of forests. |
| Increased awareness to sustain watersheds and sources for irrigation. |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Internal conflicts and misunderstandings are common during group labor contribution. | Regular group meetings, guidance from District Forest Division |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Weeds cover the lake periodically. | Cleaning the lake surface by identifying certain routine time. |
| The trails and monuments near the lake are kept unmanaged. | Regular clearing of these trails and management of monuments. |
| Unmanaged water hole present above the lake. | A small water hole present above the lake can be improved and maintained, so that the pressure on the lake will be reduced and can serve as a water reservoir for the lake. |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
- visites de terrain, enquêtes sur le terrain
Four
- interviews/entretiens avec les exploitants des terres
Four
Quand les données ont-elles été compilées (sur le terrain)?
15/07/2023
7.2 Références des publications disponibles
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
REVIVAL: LEVERAGING CULTURAL & SCIENTIFIC KNOWLEDGE AND PRACTICES FOR ENVIRONMENTAL CONSERVATION IN TALI, The Loden Foundation, 2022
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
https://www.undp.org/bhutan/publications/revival-leveraging-cultural-scientific-knowledge-and-practices-environmental-conservation-tali
7.3 Liens vers les informations pertinentes en ligne
Titre/ description:
The Loden Foundation
URL:
https://loden.org/
Titre/ description:
Revival: Leveraging cultural, scientific knowledge and practices for environmental conservation in Tali
URL:
https://www.undp.org/bhutan
Titre/ description:
Leveraging Cultural and Scientific Knowledge and Practices for Environmental Conservation in Tali
URL:
http://3.14.34.174/spacial-itemid-projects-landing-page/spacial-itemid-project-search-results/spacial-itemid-project-detailpage.html?view=projectdetail&id=28078
Titre/ description:
Jewel basket of Tali
URL:
https://kuenselonline.com/jewel-basket-of-tali/
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens
Aucun lien
Modules
Aucun module trouvé