Increased efficiency of irrigation water use to address climate change related water shortage [Tadjikistan]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Stefan Michel
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateur : Umed Vahobov
Повышение эффективности использования ирригационной воды для решения проблемы нехватки воды, связанной с изменением климата
approaches_4318 - Tadjikistan
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de l'Approche
Personne(s) ressource(s) clé(s)
Spécialiste GDT:
Negmatov Negmatjon
negmatdzhon.negmatov@giz.de
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ)
Tadjikistan
Muhidinov Nodir
+992 92 777 0134
nodir.sfl@gmail.com
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ)
Tadjikistan
Nom du projet qui a facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de l'Approche (si pertinent)
Strengthening of Livelihoods through Climate Change Adaptation in Kyrgyzstan and TajikistanNom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de l'Approche (si pertinent)
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit - Tajikistan (GIZ Tajikistan) - Tadjikistan1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Quand les données ont-elles été compilées (sur le terrain)?
27/11/2018
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.4 Références au(x) questionnaire(s) sur les Technologies de GDT
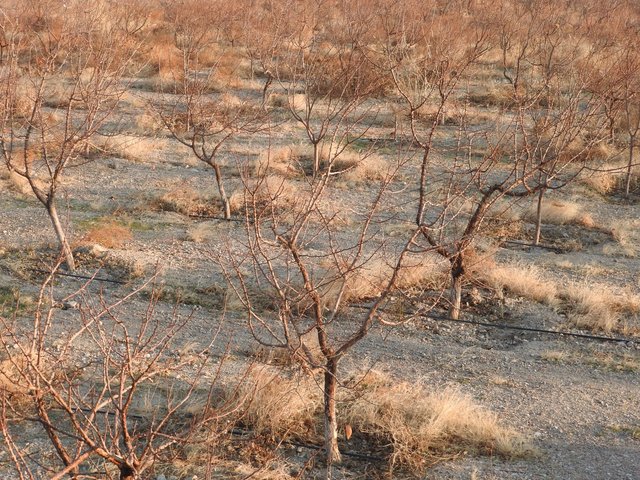

Applying drip irrigation for efficient irrigation water use … [Tadjikistan]
Drip irrigation substantially saves water compared to conventional furrow irrigation. Here the technology is applied for different perennial and annual crops and with use of different sources of water.
- Compilateur : Stefan Michel
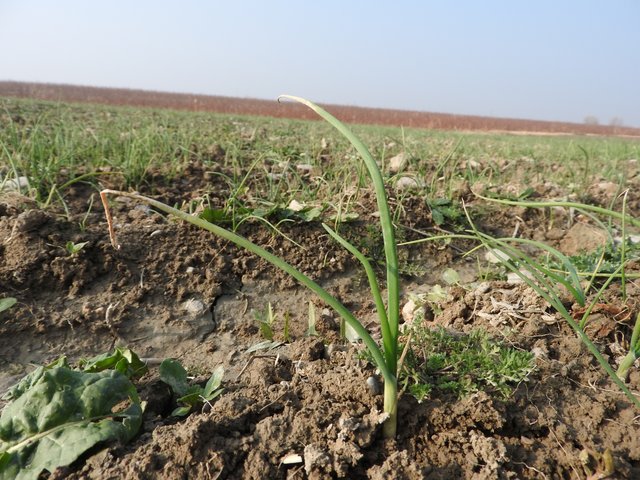

Onion production by greenhouse propagation and transplantation [Tadjikistan]
Onion seeds are sown in sheeting greenhouses, where the onion seedlings are propagated. The seedlings are then replanted in the open field. This makes them less prone to extreme weather events and provides higher yield of better quality.
- Compilateur : Stefan Michel
2. Description de l'Approche de GDT
2.1 Courte description de l'Approche
Climate change impact contributes to irrigation water shortage. The approach of improving irrigation water delivery, distribution and use prevents irrigation water losses and increases the productivity per amount of irrigation water available.
2.2 Description détaillée de l'Approche
Description détaillée de l'Approche:
Irrigated agriculture is in many areas limited by the availability of irrigation water. In many irrigated areas the canals delivering water to villages, distributing it between farms and the on-farm irrigation systems are in poor shape, which causes substantial water losses. The human population growth further contributes to shortages of irrigation water.
These problems are increasingly exacerbated by the impact of climate change. The already visible trends and predictions show higher levels of aridity, higher temperatures during the vegetation season, reduced overall precipitation in catchment areas, more irregular rainfall patterns, reduced snow packs and accelerated snow melt as well as the loss of glaciers as buffers of water flow. These factors all cause a reduction of available irrigation water, while higher temperatures and expansion of irrigated agriculture – partly also caused by increasing aridity and reduced feasibility of rain-fed farming – lead to higher irrigation water demand.
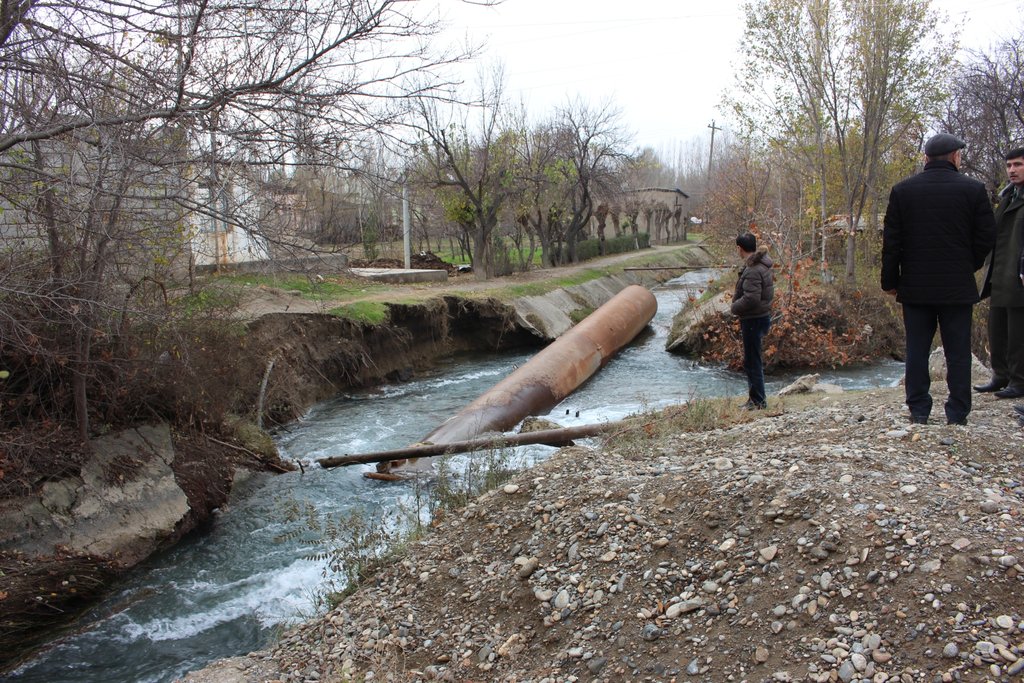
Additionally the increasing frequency and intensity of flashfloods, debris flows and landslides poses substantial risks to the stability and functioning of irrigation canals and thus to the livelihoods of farmers and food security.
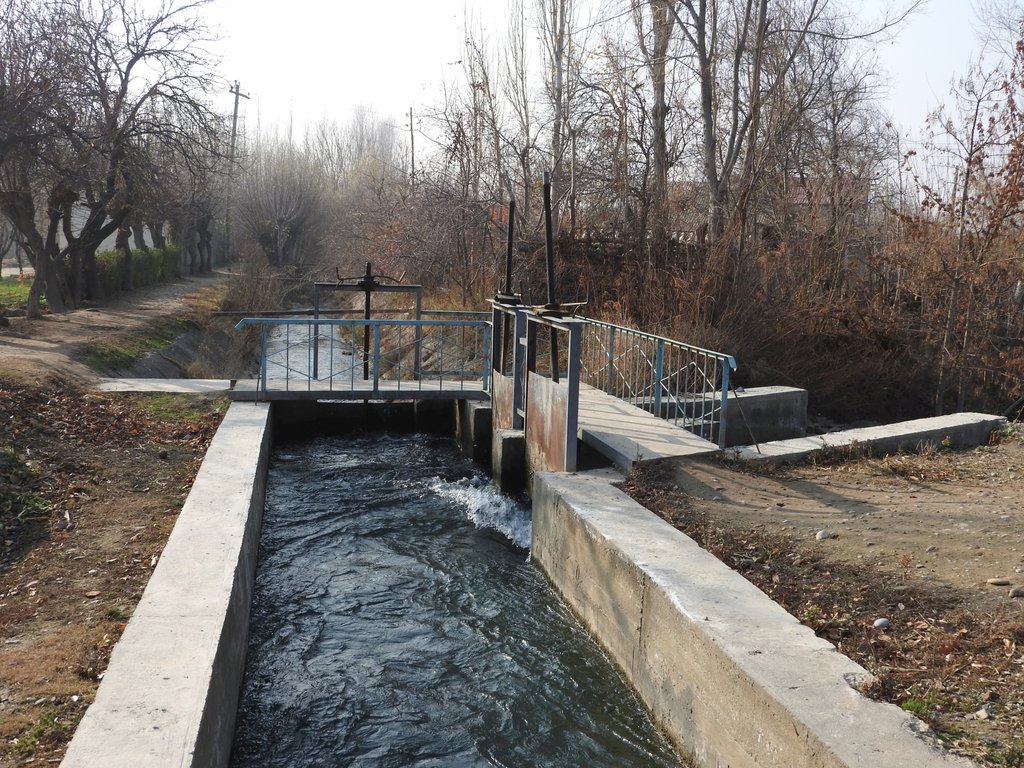
The approach therefore aims at reducing the substantial losses of irrigation water caused be seepage from delivery and distribution canals, structural problems in irrigation systems (diversion weirs) and on-farm irrigation. It also addresses risks caused by flashfloods, debris flows and landslides. The structures between major canals, which are managed by the Water Management Departments, and the individual farms are managed by the administrative communities, the mahalla committees, which represent the inhabitants of one village or a section of a larger village. These institutions are called communal self-governance structures, but are subordinated to the government as they are reporting to te sub-district or jamoat.
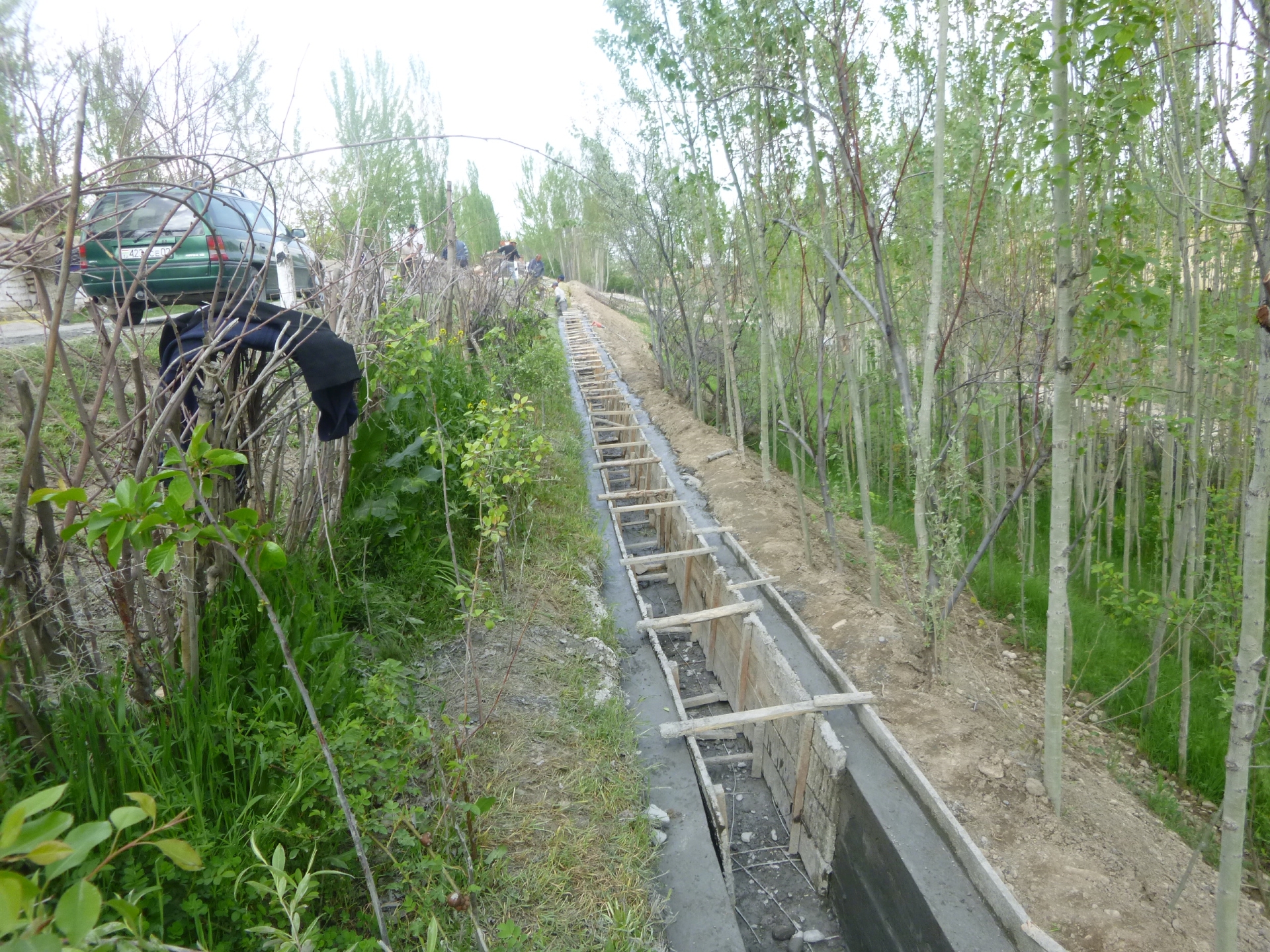
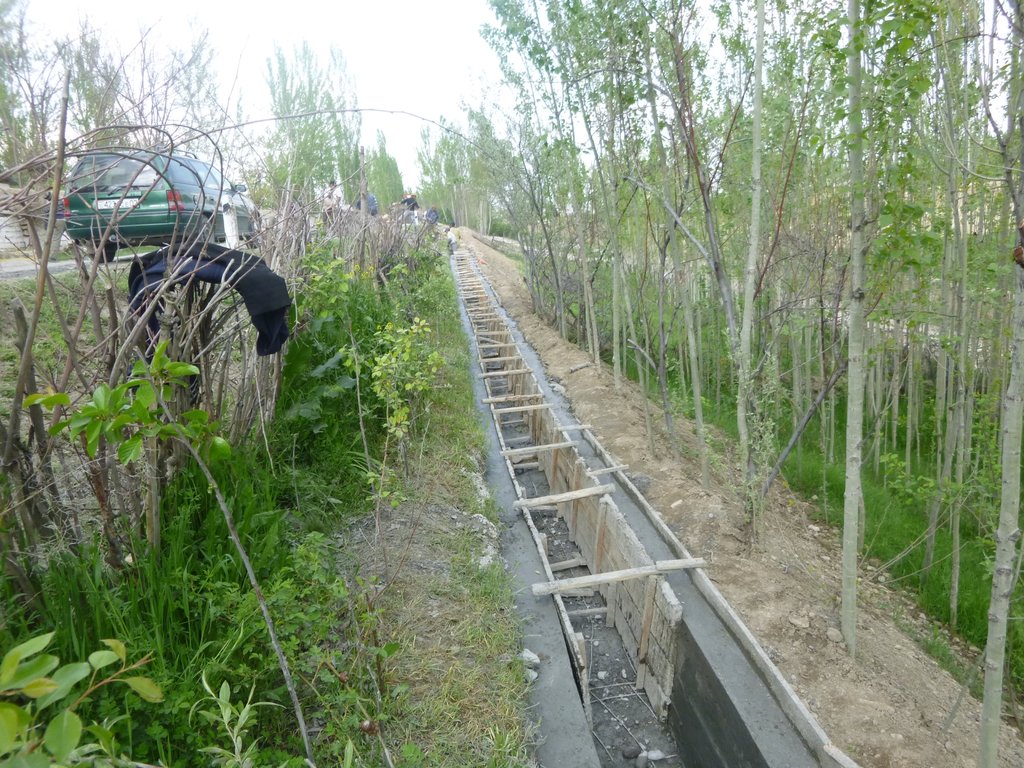
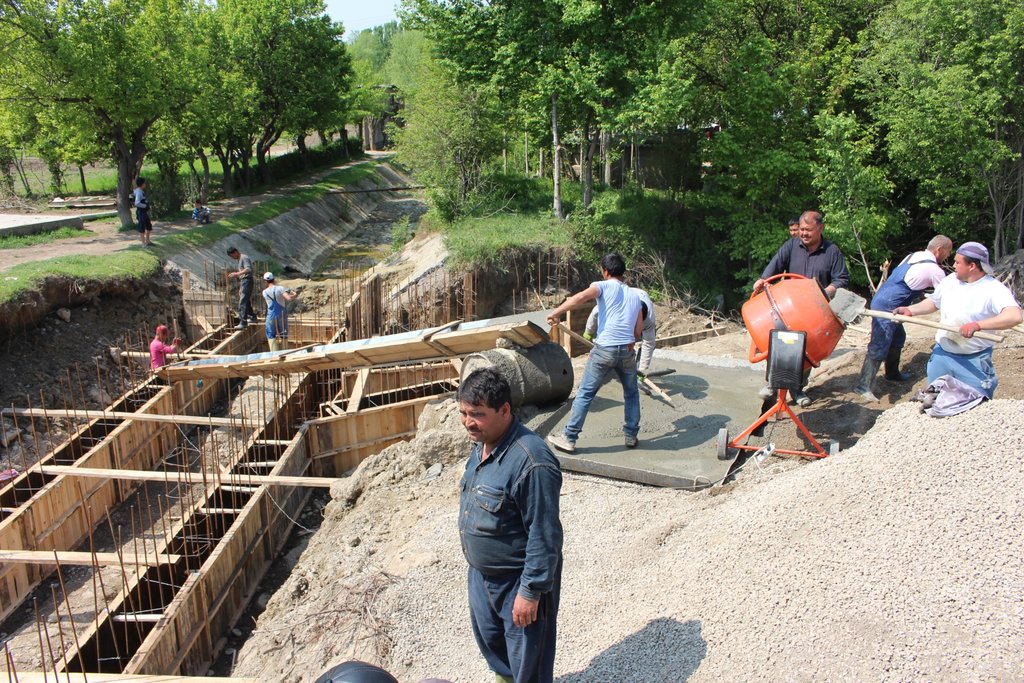
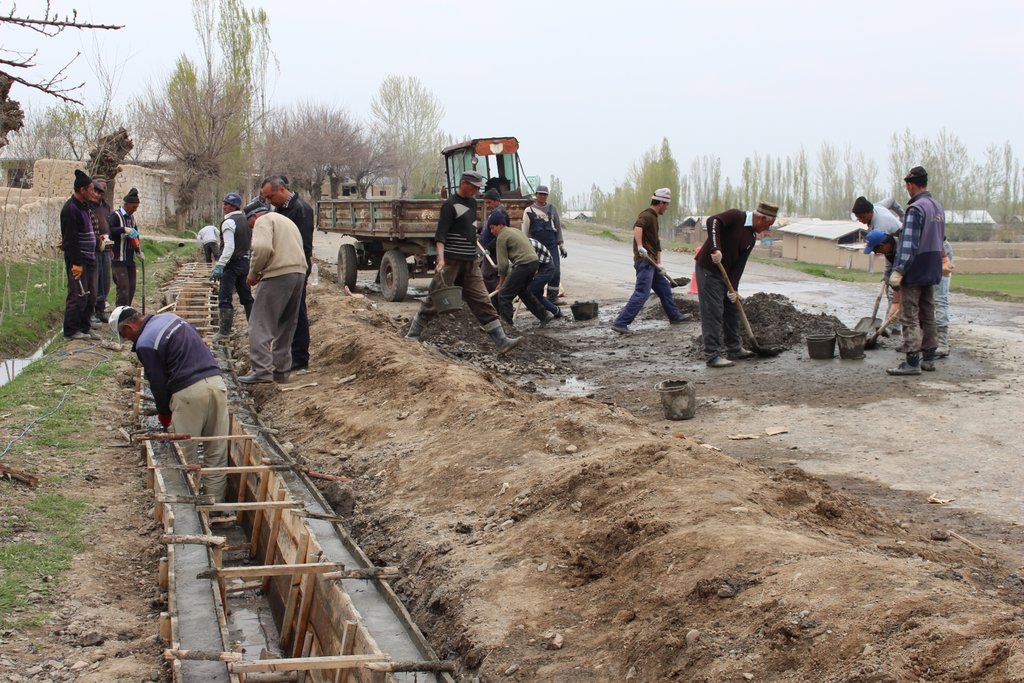
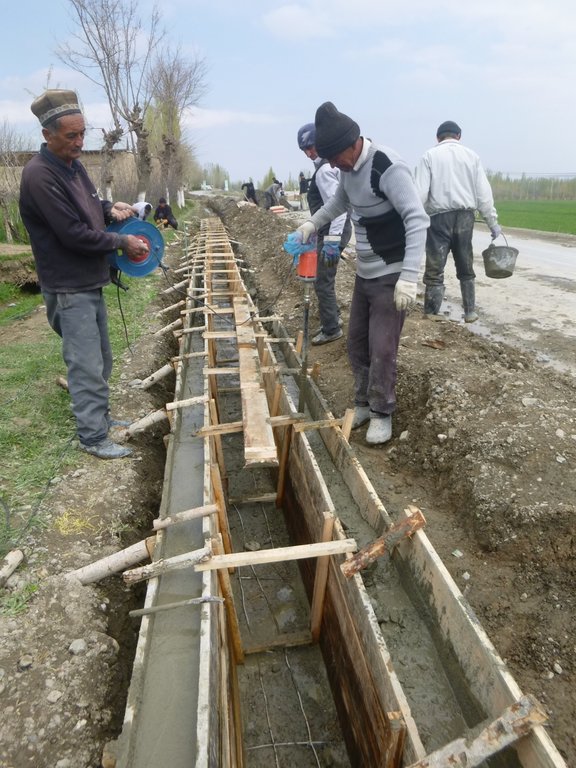
For the lining of water delivery and distribution canals, the rehabilitation of associated structures and the proofing against disaster events the project conducted a participatory assessment and planning process in the local communities, but with involvement of the district water and irrigation management authorities. In the result of this process key sections for lining and repair were selected and the project further assisted with technical planning and assistance in form of purchase of materials. The communities would contribute about 28% to 39% of the overall costs, mainly in form of voluntary communal work, the so called hashar as well as in form of construction materials.
The community is also in charge of future operation and maintenance of the rehabilitated and disaster and climate proofed irrigation structures.
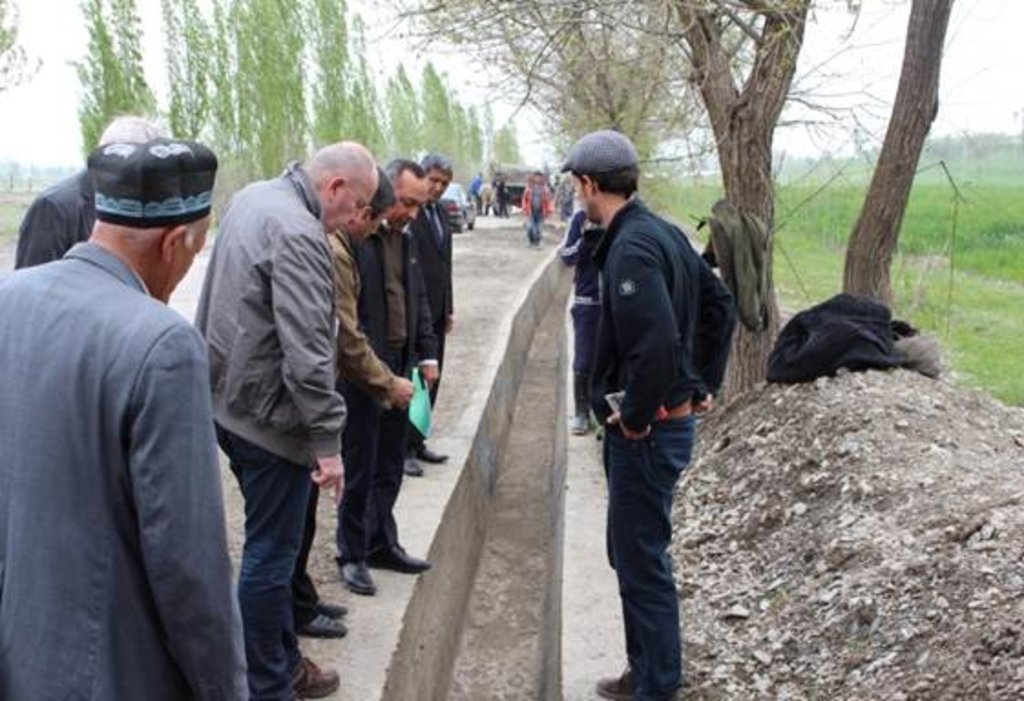
2.3 Photos de l'approche
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où l'Approche a été appliquée
Pays:
Tadjikistan
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Sughd region
Autres spécifications du lieu :
Shahriston district, Sughdiyon village and J. Rasulov district, Dehmoi village
Map
×2.6 Dates de début et de fin de l'Approche
Indiquez l'année de démarrage:
2015
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez approximativement quand l'Approche a démarré:
il y a moins de 10 ans (récemment)
2.7 Type d'Approche
- fondé sur un projet/ programme
2.8 Principaux objectifs de l'Approche
Reduction of water losses from irrigation systems, improvement of irrigation water availability under conditions of climate change.
2.9 Conditions favorisant ou entravant la mise en œuvre de la(des) Technologie(s) appliquée(s) sous l'Approche
disponibilité/ accès aux ressources et services financiers
- entrave
Without external support insufficient financial resources
cadre institutionnel
- favorise
Existence of community level management of irrigation networks
collaboration/ coordination des acteurs
- favorise
Collaboration between water management authorities and community leaders.
connaissances sur la GDT, accès aux supports techniques
- entrave
Project assistance required to provide engineering knowledge and skills to community
charge de travail, disponibilité de la main-d'œuvre
- favorise
Tradition of voluntary joint work for community needs "hashar"
3. Participation et rôles des parties prenantes impliquées dans l'Approche
3.1 Parties prenantes impliquées dans l'Approche et rôles
- exploitants locaux des terres / communautés locales
Local community members
Participation in identification of sections for rehabilitation/improvement;
Carrying out construction works.
- gouvernement local
Water management department at district level
Mahalla committee
Identification of sections for rehabilitation/improvement
Participation in planning
Organization of community work
- organisation internationale
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ)
Overall project implementation;
Technical planning and oversight;
Procurement of construction materials via competitive bidding process
Si plusieurs parties prenantes sont impliquées, indiquez l'organisme chef de file ou l'institution responsable:
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ)
3.2 Participation des exploitants locaux des terres/ communautés locales aux différentes phases de l'Approche
| Participation des exploitants locaux des terres/ communautés locales | Spécifiez qui était impliqué et décrivez les activités | |
|---|---|---|
| initiation/ motivation | interactive | Local community members, indicating problem issues to community leadership, water management department and GIZ staff |
| planification | interactive | Involvement of community members in planning |
| mise en œuvre | auto-mobilisation | Local community members carrying out works through traditional voluntary community work ("hashar"). |
| suivi/ évaluation | interactive | Local farmers involved in monitoring of water supply. |
3.4 Prises de décision pour la sélection de la Technologie/ des Technologies
Indiquez qui a décidé de la sélection de la Technologie/ des Technologies à mettre en œuvre:
- principalement les spécialistes de la GDT, après consultation des exploitants des terres
Expliquez:
Technical aspects decided by specialized engineers taking into consideration the needs and observations of community members.
Spécifiez sur quelle base ont été prises les décisions:
- l'évaluation de connaissances bien documentées en matière de GDT (prises de décision fondées sur des preuves tangibles)?
- expériences et opinions personnelles (non documentées)
4. Soutien technique, renforcement des capacités et gestion des connaissances
4.1 Renforcement des capacités/ formation
Une formation a-t-elle été dispensée aux exploitants des terres/ autres parties prenantes?
Non
4.2 Service de conseils
Les exploitants des terres ont-ils accès à un service de conseils?
Oui
Spécifiez si le service de conseils est fourni:
- dans les champs des exploitants?
4.3 Renforcement des institutions (développement organisationnel)
Des institutions ont elles été mises en place ou renforcées par le biais de l'Approche?
- oui, modérément
Spécifiez à quel(s) niveau(x), ces institutions ont été renforcées ou mises en place:
- local
Décrivez l'institution, ses rôles et responsabilités, ses membres, etc.
Existing community institutions have been strengthened through joint successful implementation of the works and the need for further maintenance of irrigation system elements as common property.
Précisez le type de soutien:
- financier
- équipement
4.4 Suivi et évaluation
Le suivi et l'évaluation font ils partie de l'Approche? :
Oui
Si oui, ce document est-il destiné à être utilisé pour le suivi et l'évaluation?
Non
4.5 Recherche
La recherche a-t-elle fait partie intégrante de l’Approche?
Non
5. Financement et soutien matériel externe
5.1 Budget annuel de la composante GDT de l'Approche
Indiquez le budget annuel de la composante GDT de l'Approche en $ US:
60000,00
Si le budget annuel précis n'est pas connu, indiquez une fourchette:
- 10 000-100 000
Commentez (par ex. principales sources de financement/ principaux bailleurs de fonds):
The number indicates the immediate construction costs of three sites, where the approach was implemented, without costs for facilitation, planning, technical supervision, monitoring and evaluation. The main source of funding was the Government of Germany via GIZ. Communities contributed 28% to 39% in form of labour and locally available construction material.
5.2 Soutiens financiers/ matériels fournis aux exploitants des terres
Les exploitants des terres ont-ils reçu un soutien financier/ matériel pour la mise en œuvre de la Technologie/ des Technologies?
Oui
Si oui, spécifiez le(s) type(s) de soutien, les conditions et les fournisseurs:
Technical planning and supervision, procurement of materials and transportation funded by GIZ.
5.3 Subventions pour des intrants spécifiques (incluant la main d'œuvre)
- aucun
Si la main d'œuvre fournie par les exploitants des terres était un intrant substantiel, elle était:
- volontaire
5.4 Crédits
Des crédits ont-ils été alloués à travers l'Approche pour les activités de GDT?
Non
5.5 Autres incitations ou instruments
D'autres incitations ou instruments ont-ils été utilisés pour promouvoir la mise en œuvre des Technologies de GDT?
Non
6. Analyses d'impact et conclusions
6.1 Impacts de l'Approche
Est-ce que l'Approche a autonomisé les exploitants locaux des terres, amélioré la participation des parties prenantes?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
Mobilization for joint work ti address problems affecting all farmers/community members
Est-ce que l'Approche a aidé les exploitants des terres à mettre en œuvre et entretenir les Technologies de GDT?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
Construction and maintenance of irrigation systems of higher efficiency with reduced water losses and risk of disaster impact.
Est-ce que l'Approche a amélioré la coordination et la mise en œuvre de la GDT selon un bon rapport coût-efficacité?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
Coordination between donor, district level water management department, community leadership and community members
Est-ce que l'Approche a mobilisé/ amélioré l'accès aux ressources financières pour la mise en œuvre de la GDT?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
Mobilization of own resources in the community and of donor funding.
Est-ce que l'Approche a amélioré les connaissances et les capacités des exploitants des terres pour mettre en œuvre la GDT?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
Improved technical knowledge on construction of irrigation systems minimizing water losses and reducing disaster risk.
Est-ce que l'Approche a amélioré les connaissances et les capacités des autres parties prenantes?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
Community leadership and district level water management department - improved technical knowledge on construction of irrigation systems minimizing water losses and reducing disaster risk.
Est-ce que l'Approche a construit/ renforcé les institutions, la collaboration entre parties prenantes?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
Coordination between donor, district level water management department, community leadership and community members
Est-ce que l'Approche a atténué les conflits?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
More efficient water delivery and distribution reduces conflict about access to irrigation water within the community and between villages.
Est-ce que l'Approche a autonomisé les groupes socialement et économiquement défavorisés?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
Mobilization of all community members to contribute to activities with common benefits.
Est-ce que l'Approche a encouragé les jeunes/ la prochaine génération d'exploitants des terres à s'engager dans la GDT?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
Mobilization of all community members to contribute to activities with common benefits.
Est-ce que l'Approche a conduit à améliorer la sécurité alimentaire et/ou la nutrition?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
Reduced shortage of irrigation water and reduced risk of failure of irrigation systems due to disasters led to secure yields in irrigated agriculture and improved food security.
Est-ce que l'Approche a conduit à améliorer l'accès à l'eau et l'assainissement?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
Water from irrigation canals is partly also used for household needs.
Est-ce que l'Approche a amélioré la capacité des exploitants des terres à s'adapter aux changements/ extrêmes climatiques et a atténué les catastrophes liées au climat?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
Increased resilience to climate change related irrigation water shortage by improved efficiency of water delivery and distribution; Reduced proneness of irrigation system to natural disaster, the frequency and intensity of which is increasing due to climate change.
Est-ce que l'Approche a conduit à des emplois, des opportunités de revenus?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
Indirectly by providing secure access to sufficient irrigation water for farming.
6.2 Principale motivation des exploitants des terres pour mettre en œuvre la GDT
- augmenter la production
Sufficient water available for irrigated agriculture
- réduire les risques de catastrophe
Proneness of irrigation system to flashfloods, debris flows and similar events.
- atténuer les conflits
Reduced conflict over access to irrigation water.
6.3 Durabilité des activités de l'Approche
Les exploitants des terres peuvent-ils poursuivre ce qui a été mis en œuvre par le biais de l'Approche (sans soutien extérieur)?
- oui
Si oui, décrivez de quelle manière:
Maintenance of irrigation systems through contributions of all water users and join voluntary work ("hashar").
6.4 Points forts/ avantages de l'Approche
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
| Access to technology and materials, which would not affordably without external support. |
| Secure and sufficient supply of irrigation water. |
| Reduced risk of failure of irrigation system caused by natural disaster during critical times (irrigation period). |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
| Same as land users' perspective. |
| Mobilization of resources of the land users and their community. |
| Strengthening of collaboration between district level water management departments, community leadership and community members. |
6.5 Faiblesses/ inconvénients de l'Approche et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| None |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| None |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
- visites de terrain, enquêtes sur le terrain
- interviews/ entretiens avec les spécialistes/ experts de GDT
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens

Applying drip irrigation for efficient irrigation water use … [Tadjikistan]
Drip irrigation substantially saves water compared to conventional furrow irrigation. Here the technology is applied for different perennial and annual crops and with use of different sources of water.
- Compilateur : Stefan Michel

Onion production by greenhouse propagation and transplantation [Tadjikistan]
Onion seeds are sown in sheeting greenhouses, where the onion seedlings are propagated. The seedlings are then replanted in the open field. This makes them less prone to extreme weather events and provides higher yield of better quality.
- Compilateur : Stefan Michel
Modules
Aucun module trouvé