Water run-off control plan on cultivated land [Afrique du Sud]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Carin Pretorius
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateur : Alexandra Gavilano
Watercourses and contours
technologies_956 - Afrique du Sud
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Quand les données ont-elles été compilées (sur le terrain)?
01/06/1999
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
Artificially built watercourses with contour banks with a specific gradient
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
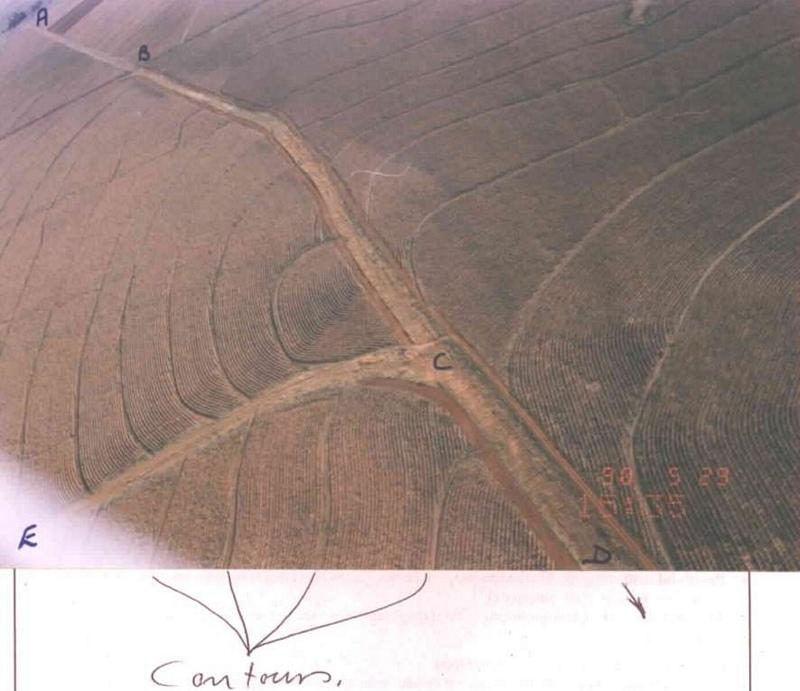
Watercourse: According to the topography, one or two watercourses are needed to drain any excess run-off water during high rainfall intensities. A watercourse is built directly downhill. A perennial grass adapted to the specific environment is established in the watercourses. Maintenance requires that the grass must be fertilised according to the climate of the area. Regular (once or twice a year) cutting of the grass is very important to maintain a good grass cover, through which soil erosion in the watercourse can be prevented.
Contour banks: These are built with a gradient to spill the excess water into the watercourse. The purpose of contour banks is to shorten the slope so as to reduce the speed of the water and prevent soil erosion. The maintenance requires keeping the canal in good shape and maintaining the height of the banks.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Afrique du Sud
Région/ Etat/ Province:
North West Province
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Lichtenburg
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a entre 10-50 ans
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- par le biais de projets/ d'interventions extérieures
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
The contour part came mainly form the USA.
The watercourse part was developed in South Africa.
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

Terres cultivées
- Cultures annuelles
Commentaires:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Cultivating lands without the necessary soil conservation works to prevent soil erosion.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Cultivating the lands preventing soil erosion through plant directions
3.3 Informations complémentaires sur l'utilisation des terres
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- pluvial
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 1
Précisez:
Longest growing period in days: 180
Longest growing period from month to month: Oct - Mar
3.5 Diffusion de la Technologie
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- répartie uniformément sur une zone
Si la Technologie est uniformément répartie sur une zone, indiquez la superficie couverte approximative:
- 1-10 km2
Commentaires:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 3 m2.
Although the total extent of the farm is 584 ha, only 250 ha plus 50 ha adjacent land was addressed through this technology.
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

érosion hydrique des sols
- Wg: ravinement/ érosion en ravines
- Wt: perte de la couche superficielle des sols (couche arable)/ érosion de surface

dégradation hydrique
- Ha: aridification

dégradation chimique des sols
- Cn: baisse de la fertilité des sols et réduction du niveau de matière organique (non causée par l’érosion)
Commentaires:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Ha: aridification
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
Main causes of degradation: other human induced causes (specify) (Agricultural causes - Cultivating land on a step slope without proper conservation practices.), education, access to knowledge and support services (Lack of knowledge - How to solve the problem)
Secondary causes of degradation: other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (Topography; concentrating water in valleys causing soil erosion (steep slopes).), Poor conservation ethic
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- réduire la dégradation des terres
- prévenir la dégradation des terres
Commentaires:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation, mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
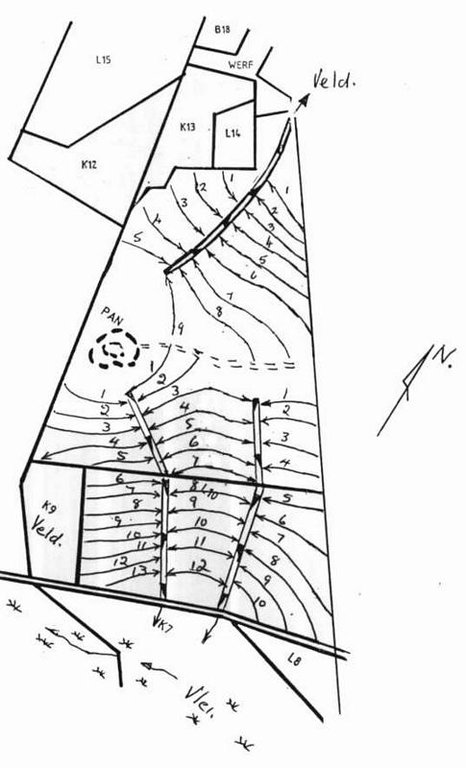
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
4.2 Spécification/ explications techniques du dessin technique
Water run-off control plan
Location: Lichtenburg. North West
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert, reduction of slope length
Secondary technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, Maintain soil fertility as less fertilizer are lost by water run-off
Vegetative measure: watercourses
Vegetative material: C : perennial crops, G : grass
Number of plants per (ha): seeds 6-8kg/ha
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: C : perennial crops, G : grass
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: C : perennial crops, G : grass
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: C : perennial crops, G : grass
Grass species: Digitaria Smuts, Eragrostis curvula, Cynodom dactylon
Structural measure: bunds/banks: contour
Vertical interval between structures (m): 1.3-1.75
Spacing between structures (m): 72-33
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.4
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 2
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.3
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 4
Construction material (earth): Construction contour banks with soil form the ditches
Lateral gradient along the structure: 0.3%
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
4.3 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
autre/ monnaie nationale (précisez):
rand
Indiquer le taux de change du dollars en monnaie locale (si pertinent): 1 USD= :
6.00
4.4 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Established grass in the watercourses | Végétale | After construction according to design specifications |
| 2. | Surveying | Structurel | Dry season |
| 3. | Construction of contours | Structurel | Any time depending on soil moisture |
| 4. | Construction of watercourse | Structurel | Before growing season |
4.5 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
Commentaires:
Duration of establishment phase: 24 month(s)
4.6 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Building contours and watercourses | Agronomique | Any time / Before planting of crops |
| 2. | Building contours and watercourses | Agronomique | Depending on soil moisture / |
| 3. | Maintenance | Agronomique | Before planting of crops / Annually |
| 4. | Cultivation between contours | Agronomique | Depending on the crop / Annually |
| 5. | Maintaining a good grass cover | Végétale | Rainy season /Once or more times a year depending on the grass |
| 6. | Fertilisation of the grass in the watercourse | Végétale | Rainy season /Once or twice in the rainy season |
| 7. | Watercourse, cutting the grass | Structurel | Beginning of rainy season/Annual |
| 8. | Contours repairing flood damage | Structurel | Dry season/After heavy rains |
| 9. | Contour opening ditches | Structurel | Before planting of cops/Annual |
4.7 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
Commentaires:
Machinery/ tools: Tractor & plough or a grader
Contours per kilometre. NB currant tariff for subsidy. Watercourse construction per volume soil moved and grass establishing per ha above the current tariff for subsidy from April 1998
4.8 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
Soil moisture and clay contents
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Zone agro-climatique
- semi-aride
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- moyen (limoneux)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- faible (<1%)
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Orientation du système de production:
- commercial/ de marché
Revenus hors exploitation:
- moins de 10% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- moyen
Niveau de mécanisation:
- mécanisé/ motorisé
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
10% of the land users are very rich and own 100% of the land.
90% of the land users are average wealthy and own 100% of the land (If management is good).
Off-farm income specification: Farmers are dedicated to make a living out of farming, although there are some farmers with an off-farm income such as transport.
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres détenues ou louées par les exploitants appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- individu, avec titre de propriété
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- individuel
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
surface de production
gestion des terres
Impacts socioculturels
apaisement des conflits
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
ruissellement de surface
Quantité avant la GDT:
60
Quantité après la GDT:
20
drainage de l'excès d'eau
Sols
humidité du sol
perte en sol
Quantité avant la GDT:
25
Quantité après la GDT:
4
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
envasement en aval
pollution des rivières/ nappes phréatiques
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
neutre / équilibrée
Rentabilité à long terme:
neutre / équilibrée
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
neutre / équilibrée
Rentabilité à long terme:
neutre / équilibrée
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
Commentaires:
15% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: estimates
1% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: So little, almost none. The lack in technicians from government promoting this technology and to deliver technical services are the main reasons expect for the poor conservation ethic of the farmers.
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
|
Prevent soil erosion How can they be sustained / enhanced? Good regular maintenance |
| Building up a good layer of topsoil |
| Effective run-off control of excess rainwater |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
|
Effective erosion control How can they be sustained / enhanced? Regular maintenance |
|
Improve water infiltration How can they be sustained / enhanced? Good cultivation practices and maintenance of contours |
|
Increase crop yield How can they be sustained / enhanced? Good cultivation practices and maintenance of contours |
|
Prevent off-site siltation How can they be sustained / enhanced? Good maintenance |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Hampers cultivation | Adapt change in cultivation practises |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Cannot think of any |
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens
Aucun lien
Modules
Aucun module trouvé