Agro-forestry [Inde]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Unknown User
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateurs : Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
Kaadu, Vilai, Thottam (Tamil)
technologies_1083 - Inde
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
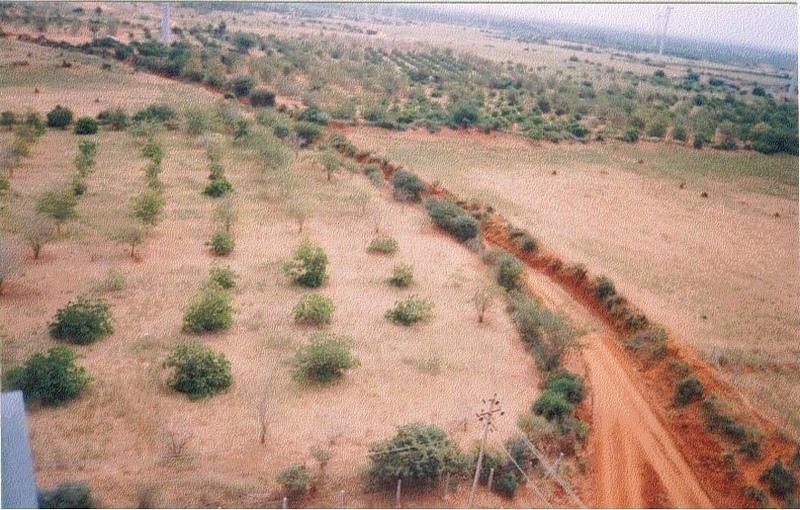
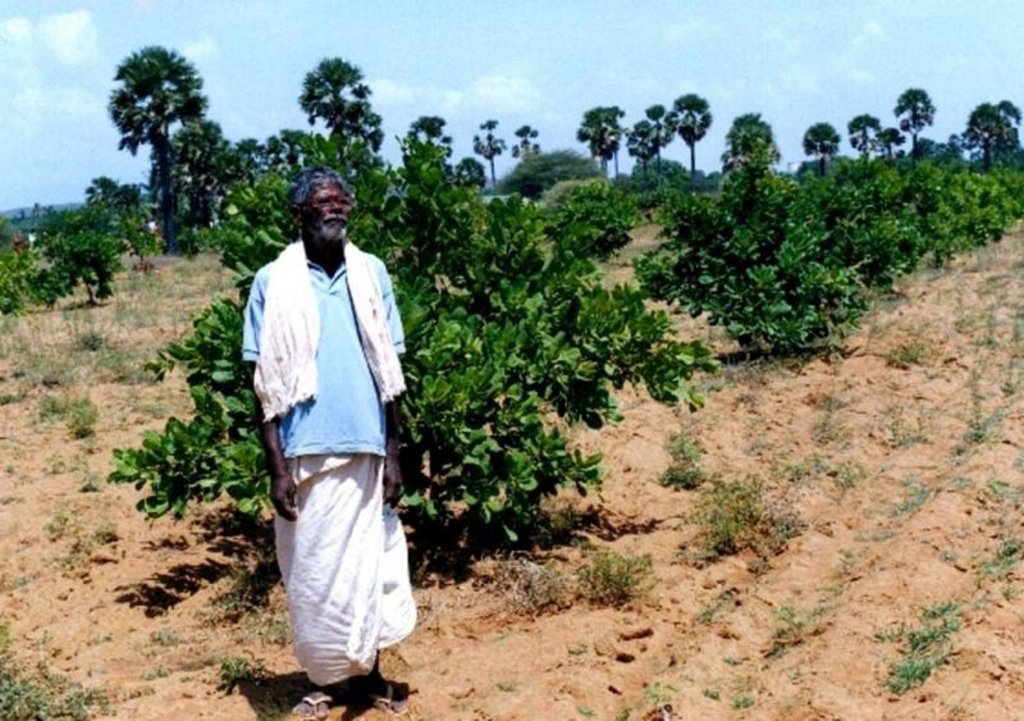
Development of degraded lands through plantation of productive tree species for long term benefit (conservation and economic) and cultivation of intercrop for short term benefit.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
The technology can be described as a combination of tree cultivation ( mainly horticulture species) along with intercrop of pulse crops on degraded private lands, supported by in-situ measures for soil and water conservation. The supportive technology required is provision of water for protective irrigation during establishment phase.
Purpose of the Technology: the technology serves the folowing purposes 1. Short and long term economic benefits to land owners 2. Employment generation leading to reduced migration 3. Conservation of soil and water through vegetative and mechanical measures.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: 1. Community organisation, formation of Village Development Association, Identification and training of beneficiaries 2. Delineation of micro-watersheds and plantation blocks. 3. Establishment of farmers's nurseries 4. Land preparation, sinking bore-well, plantation and inter-cropping 5. Watch and ward.
Natural / human environment: The environment is semi-arid, drought prone and subject to wind erosion. Soil depth is good.
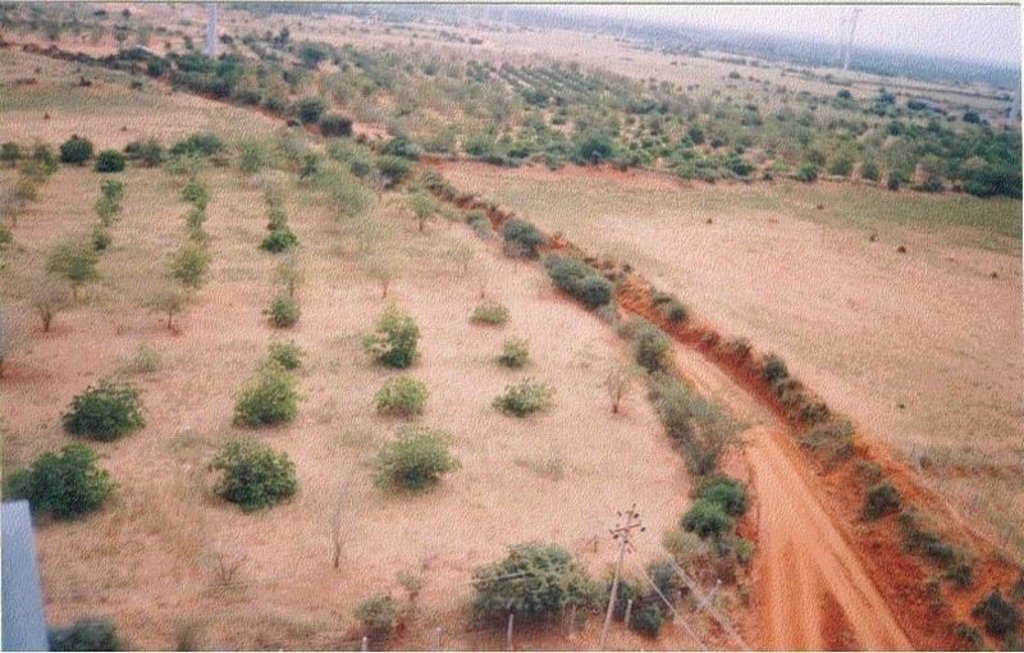
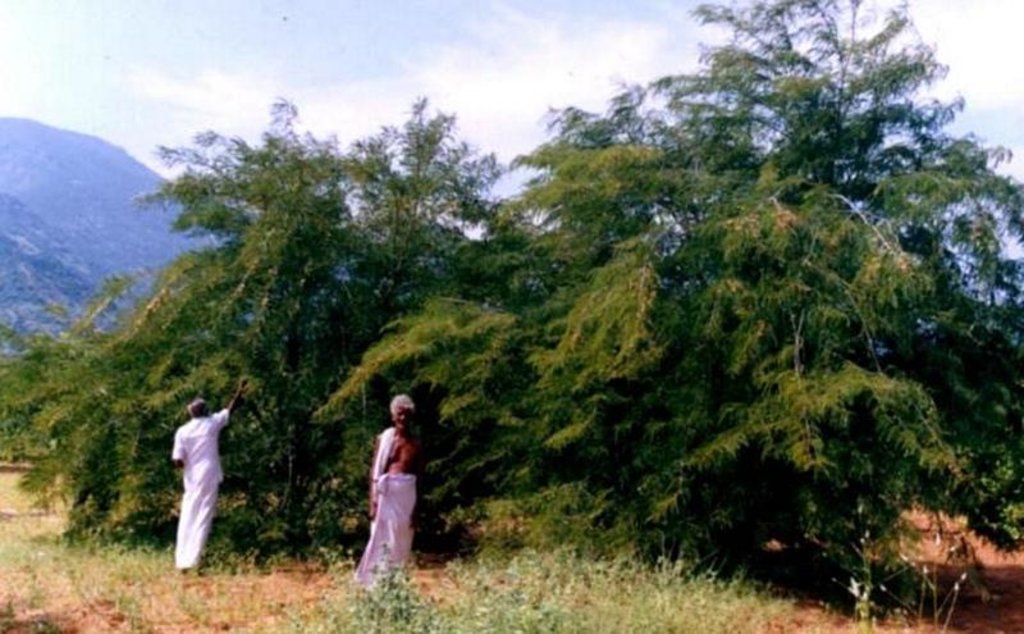
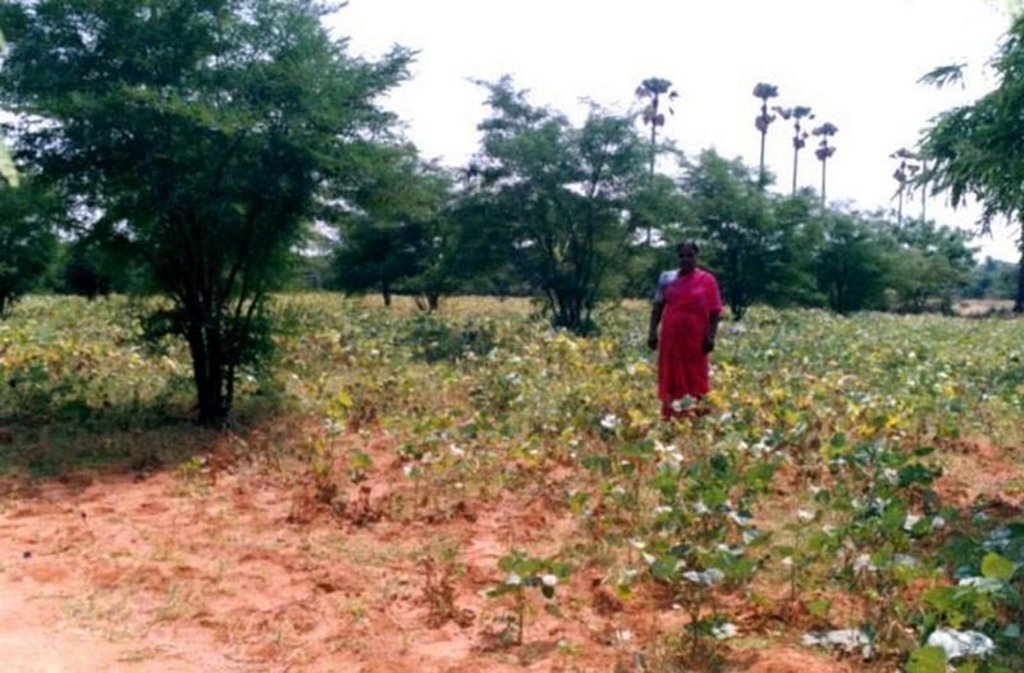
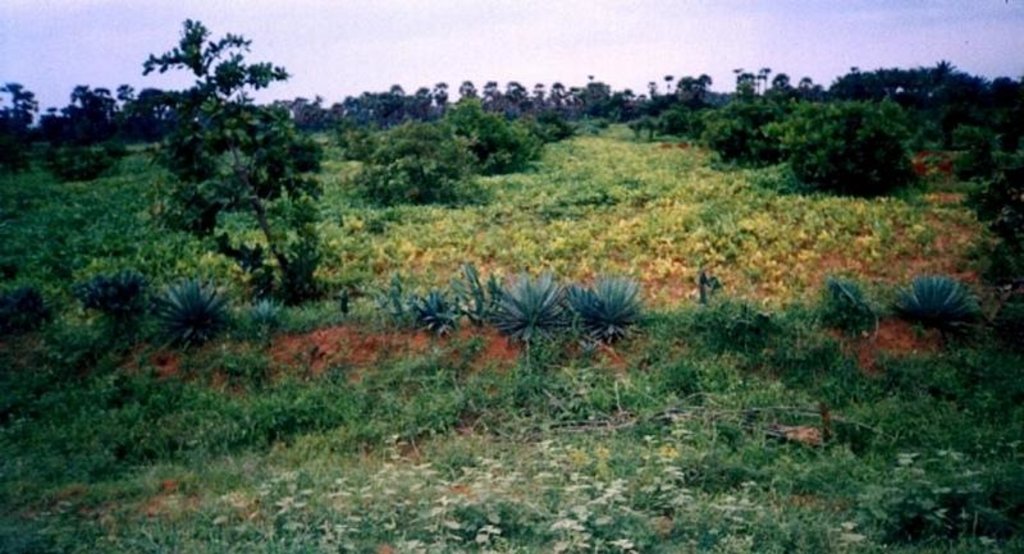
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Inde
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Tamilnadu
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- répartie uniformément sur une zone
Si la Technologie est uniformément répartie sur une zone, précisez la superficie couverte (en km2):
3,83
Commentaires:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 3.83 km2.
The area is predominantly degraded land affected by wind erosion. The annual rainfall is <600 mm, however distribution is erratic resulting in drought conditions. People are mostly small farmers engaged in rainfed agriculture, however large areas have been abandoned due to frequent crop failure. The technology has been applied in a gross area of over 300 sq.km.
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a plus de 50 ans (technologie traditionnelle)
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- par le biais de projets/ d'interventions extérieures
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
The technology evolved out farmers suggestions and project experiences while implementing the shelter programme to combat wind erosion.
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- améliorer la production
- réduire, prévenir, restaurer les terres dégradées
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée
Les divers types d'utilisation des terres au sein du même unité de terrain: :
Oui
Précisez l'utilisation mixte des terres (cultures/ pâturages/ arbres):
- Agroforesterie

Terres cultivées
- Cultures annuelles
- Plantations d’arbres ou de buissons
Cultures annuelles - Précisez les cultures:
- légumineuses et légumes secs - fèves
- légumineuses et légumes secs - autres
- cultures oléagineuses - arachide
- euphorbia sp.
Plantations d'arbres et d'arbustes - Précisez les cultures:
- noix de cajou
- fruits, autres
- manguier, mangostane, goyave
- Tamarandus indicus, Emblica officianalis
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 1
Précisez:
Longest growing period in days: 100 Longest growing period from month to month: Oct - Jan

Forêts/ bois
Type d’arbres:
- Azadirachta indica (azadira d'Inde)
- Albizia lebeck
Commentaires:
Crop: agace, euphorbia sp.
Trees/ shrubs species: Azadirachta indica, Albizia lebeck
Fruit trees / shrubs species: Anacardium occidentale, Tamarandus indicus, Emblica officianalis, Mangifera incica
Other species: Phaseolus mungo, Arachis hypogea
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Uncontrolled grazing on un-cultivated lands, abandonment of fields by poor farmers due to recurrent crop failure as a result of drought.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Crop lands are not economocal to cultivate due to recurrent crop failure as a result of drought. This has lead to abandonment of fields and increase in numbers of small livestock which are left free to graze.
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: The area is single cropped and hence only one food crop is taken per year.
3.4 Approvisionnement en eau
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- mixte: pluvial-irrigué
3.5 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- agroforesterie
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

pratiques agronomiques
Commentaires:
Type of agronomic measures: better crop cover, mixed cropping / intercropping, mulching, pits, deep tillage / double digging
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

érosion hydrique des sols
- Wt: perte de la couche superficielle des sols (couche arable)/ érosion de surface
- Wg: ravinement/ érosion en ravines

érosion éolienne des sols
- Et: perte de la couche superficielle des sols (couche arable)
Commentaires:
Main type of degradation addressed: Et: loss of topsoil
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Wg: gully erosion / gullying
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
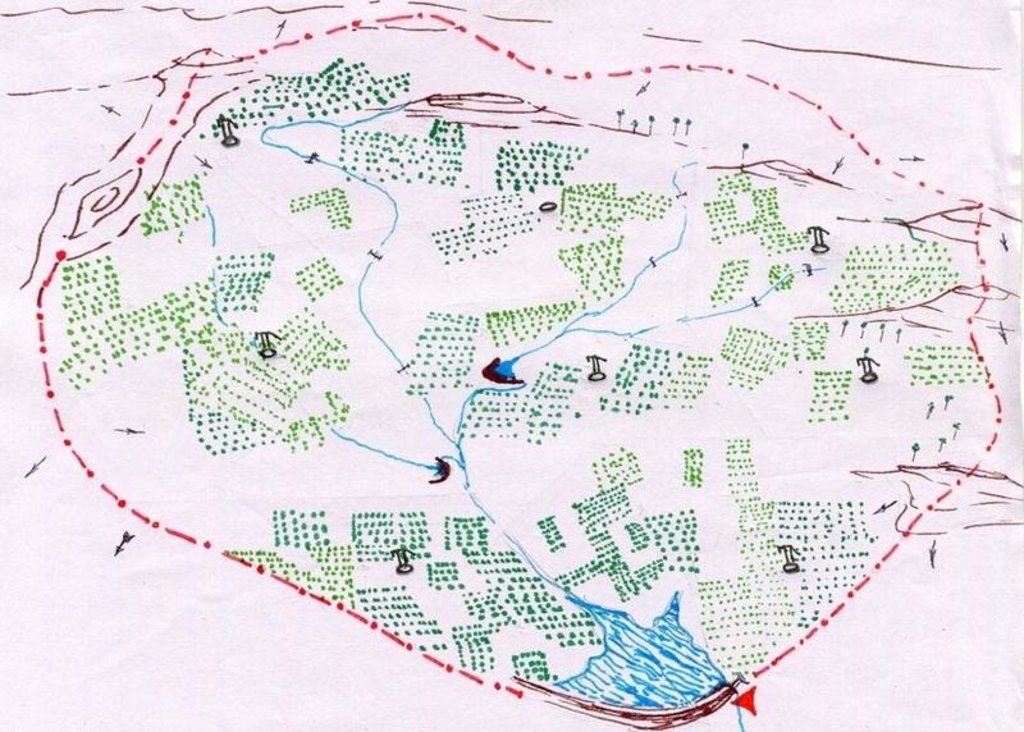
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
Spécifications techniques (associées au dessin technique):
Technical Drawing Agro-forestry
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover
Secondary technical functions: control of raindrop splash, reduction in wind speed
Better crop cover
Material/ species: trees + legume crops
Quantity/ density: 125 trees/
Remarks: Block plantation/ intercorp
Mixed cropping / intercropping
Material/ species: trees + legume crops
Quantity/ density: 125 trees/
Remarks: Block plantation/ intercorp
Mulching
Material/ species: soil mulch
Quantity/ density: 125 basins
Remarks: 1 m. diameter basin per tree
Agronomic measure: vegetative hedges
Material/ species: agace, euphorbia sp.
Quantity/ density: 15 cm. Spa
Remarks: Along field boundries
Pits
Remarks: 125 pits/ha., 9 m. spacing. 45*45*45 cm for local species & 60*60*60 cm for grafts.
Deep tillage / double digging
Remarks: disc ploughing before pitting in first year, tiller ploughing annually at sowing of intercorp..
Trees/ shrubs species: Azadirachta indica, Albizia lebeck
Fruit trees / shrubs species: Anacardium occidentale, Tamarandus indicus, Emblica officianalis, Mangifera incica
Other species: Phaseolus mungo, Arachis hypogea
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 3.00%
Change of land use type: open grazing, cropping to agro-forestry
Change of land use practices / intensity level: open access to protected
Layout change according to natural and human environment: borewell blocks formed as per human environment but within watershed boundary.
Control / change of species composition: scrub clearance followed by plantation of agro-horticulture species.
Other type of management: VDA established - to manage all activities at village level
Auteur:
D. Samraj, Tiruneveli, Tamilna
4.2 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
autre/ monnaie nationale (précisez):
Indian Rupee
Indiquez le taux de change des USD en devise locale, le cas échéant (p.ex. 1 USD = 79.9 réal brésilien): 1 USD = :
48,85
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
1.00
4.3 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Calendrier des activités (saisonnier) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Nursery raising | May - Nov |
| 2. | Planting in pits | Oct -Dec, onset of monsoon |
| 3. | Life watering | immediately after plantation |
| 4. | Planting of vegetative hedges | Oct - Dec |
| 5. | Sowing of intercrop (broadcasting, dibbling) | Premonsoon-groundnut, monsoon-legumes |
| 6. | Application of FYM to intercrop | September during tiller ploughing |
| 7. | Selection of village as per criteria | Mar/Apr, dry season |
| 8. | Rapport building, awareness generation | |
| 9. | VDA formation | April / May |
| 10. | Development of watershed plan including agroforestry | May / June |
| 11. | Trainings for VDA, farmers, nursery etc. | Jun - Aug |
4.4 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
Commentaires:
Duration of establishment phase: 24 month(s)
4.5 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | scrub clearance | Sept/Oct,dry season / once before planting |
| 2. | deep ploughing | Oct/Nov,onset of monsoon / once before planting |
| 3. | pitting | Oct/Nov / once before planting |
| 4. | manuring | Oct/Nov / once before planting |
| 5. | filling pits, planting, forming basins | Nov / once before planting |
| 6. | life watering | Nov / after planting |
| 7. | tiller ploughing & sowing | Oct/Nov / annually after onset of monsoon |
| 8. | maintenance of tree basins | Oct / after annual tiller ploughing |
| 9. | Periodical watering | dry months 1st year /weekly |
| 10. | Weed removal | Nov / Dec /once during annual crop |
| 11. | Application of pesticides | Dec - Feb /as necessary |
| 12. | Pruning | Nov /annually |
| 13. | Casualty replacement | Nov /One year after plantation |
| 14. | Monitoring by VDA | - / monthly |
| 15. | Hand pump maintenance | / as required |
| 16. | Protection against animals | Year one / full time |
4.6 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
Commentaires:
- The costs were calculated for establishment of one block (average area 12.5 ha.) of horticulture plantation with project support. The agriculture component was implemented by farmer with project support for seeds during first monsoon and tiller ploughing during second monsoon.
4.7 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
- Establishment of the technology requires high labor input, specially for watering and watch & ward, which adds significantly to the cost. - Presence of hard pan necessiates deep ploughing with machinery. - Horticulture tree species were selected over forest species.
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifications/ commentaires sur les précipitations:
680 mm, however the rainfall over the past few years has been < 500 mm.
Zone agro-climatique
- semi-aride
Since past few years arid conditions prevail in the area
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la topographie:
Landforms: Plateau/plains (level lands lying between hill slopes of Western mountain range & East coast of south India.)
Slopes on average: Flat (level land with some gullies passing through (originating in upper hilly area))
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- moyen (limoneux)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- moyen (1-3%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Soil depth on average: Moderately deep (ranked 1) and deep (ranked 2, patches of deep soil)
Soil texture: Medium (sandy loam)
Soil fertility: Medium (loss of top soil due to erosion)
Topsoil organic matter: Medium (originally low before agro-forestry)
Soil drainage/infiltration level: Medium (presence of hardpan below six inch depth. However, no waterlogging is observed due to runoff.)
Soil water storage capacity: Medium (has improved due to deep ploughing post treatment)
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Revenus hors exploitation:
- 10-50% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- pauvre
- moyen
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
11% of the land users are rich and own 18% of the land (large holdings > 2 ha.).
50% of the land users are average wealthy and own 56% of the land (holdings of 1 to 2 ha.).
39% of the land users are poor and own 26% of the land (holdings < 1 ha.).
Off-farm income specification: Off farm sources are; poor - rolling beedis (locally made cigarettes), daily wage labor in fields and brick kilns. Average / rich; Business, livestock.
Level of mechanization: Manual labour (ranked 1, pitting, planting, watering, cultivating, watch and ward), mechanised (ranked 2, deep ploughing, tiller ploughing, drilling borewell) and animal traction (ranked 3, ploughing)
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- individu, avec titre de propriété
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- individuel
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
légèrement négative
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
légèrement négative
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
Commentaires:
99% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
284 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: estimates
1% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
2 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Farmers are purchasing seedlings for plantation on their fields in small patches around existing water sources - Farmers who did not participate initially are now expressing a desire to treat their lands under the project.
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
7.2 Références des publications disponibles
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Review reports.
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
Chief Engineer, Agriculture Engineering Department, Anna Salai-439, Nandanam, Chennai-600035
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Project Implementation Plan. 2001.
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
Programme Coordinator, WDCU, 11/1 Sarvapriya Vihar, New Delhi-110016.
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Participatory Impact Evaluation. 2001.
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens
Aucun lien
Modules
Aucun module trouvé