Usage of Gher boundary for cropping [Bangladesh]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Jalal Uddin Md. Shoaib
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateur : David Streiff
Gherer bunder upar nana prokar shakshabjee uthpadon
technologies_1171 - Bangladesh
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Spécialiste GDT:
Shaha Tapan Kuma
SRDI
Bangladesh
Spécialiste GDT:
Bhander Bidhan Kumar
SRDI
Bangladesh
Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Soil Resource Development Institute (SRDI) (Soil Resource Development Institute (SRDI)) - Bangladesh1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
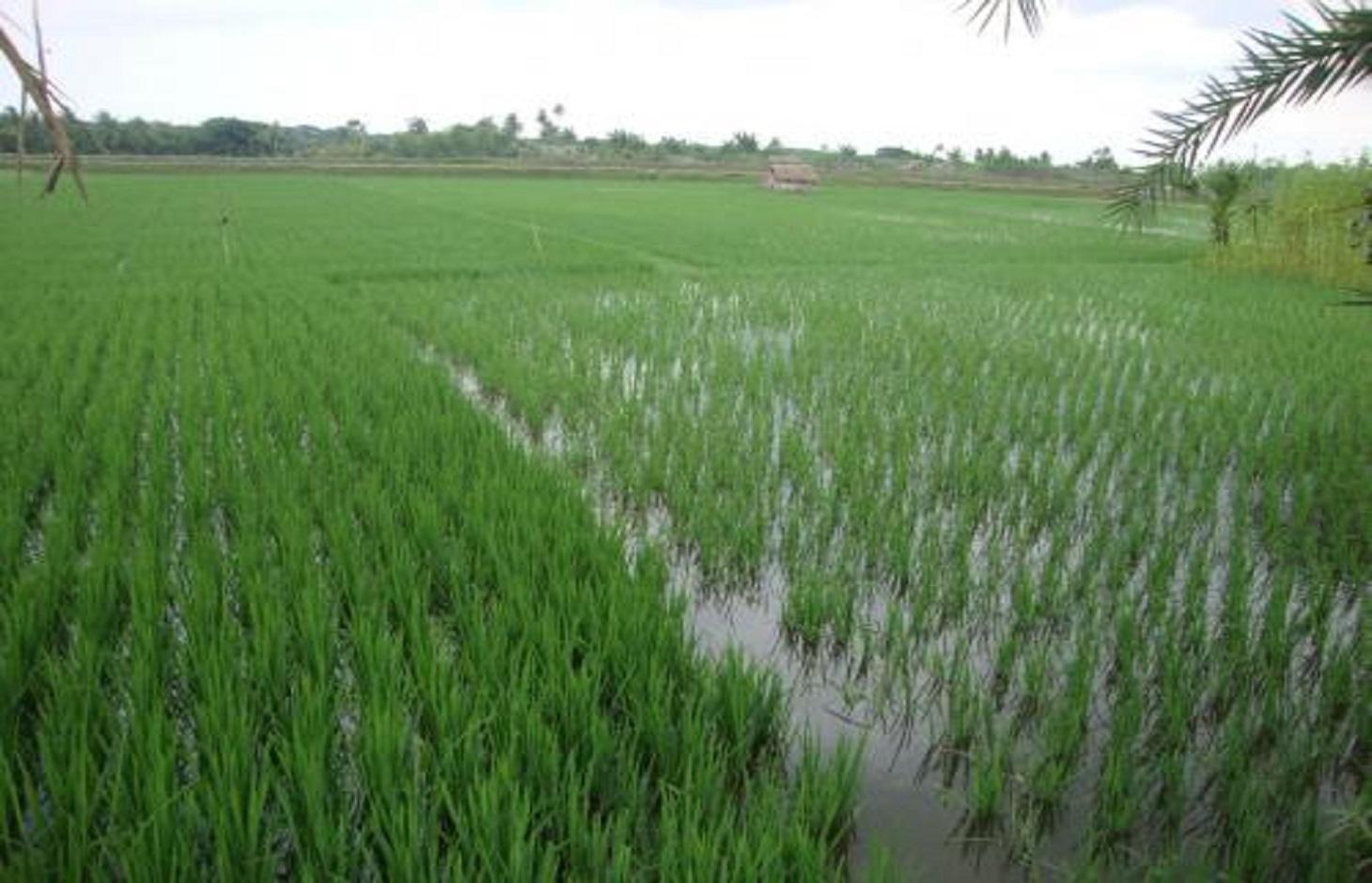
Gher (shrimp cultivation) boundary usage for multiple cropping.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
Gher is a local word used for shrimp cultivation plot. The boundaries of these ghers are nowadays raised and maintained to grow vegetables, fruits and also some tree species. In this case the boundary of the plot is raised at least 3 feet with grest width 1 feet plus depending on the height of the boundary (Bund/dyke). Within the gher the land is used for both sweet water prawn (Golda) or saline water prawn (Bagda) with other different types of fishes (locally called Sada Mach) if suitable depending on the salinity of water. Some of the gher lands are used for transplanted Aman with shrimp/fishes.
Farmers dug a ditch along the boundary or in any corner of the field or at the center of the plot to preserve water and fishes during the dry season. In some of the cases the farmers used shallow tube well water to sustain the fishes. In non-to slightly saline areas they used it even for boro (winter rice).
Purpose of the Technology: The purpose of this technology is a boundary which is used for various types of crops, including year round vegetables and land for rice and fishes including shrimps.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The boundary is constructed above flood level (2-3 feet), the width is approx. 2-3 feet, the ditches are 2-3 feet deep along the boundary or at the corner or at the center.
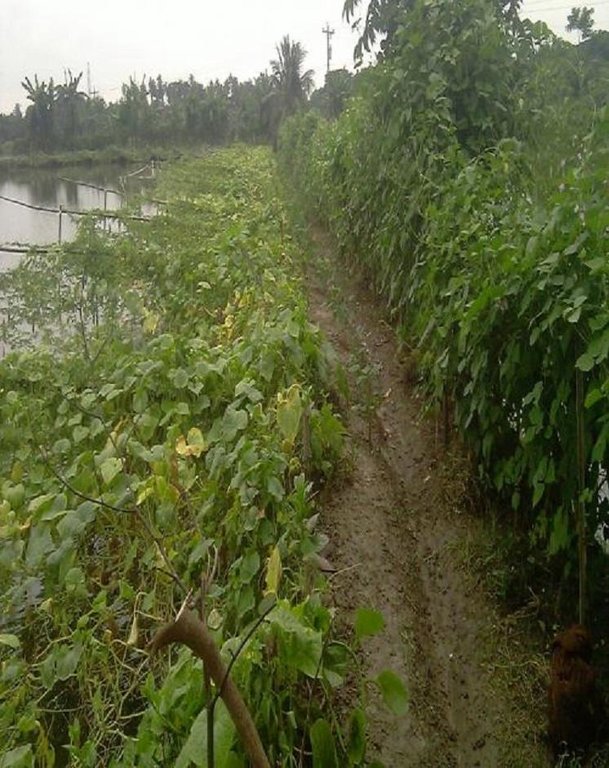
To grow vegetables farmers used nylon nets for creeping supported by the bamboo or Dhaincha or strings.
Top soils kept on top of the bunds to avoid relatively less fertile soil on the bunds.
Main inputs are seeds of vegetables, nets, bamboo, strings, fingerlings of fish etc.
Natural / human environment: The salinity of the soils from the bunds is washed away by rainwater, which facilitates vegetable production: Rain water desolves salt and moves to the bottom of the bund, and soil becomes non-saline or slightly saline where vegetable could be grown.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Bangladesh
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Bangladesh Southern region
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Khulna
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a moins de 10 ans (récemment)
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- grâce à l'innovation d'exploitants des terres
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- améliorer la production
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

Terres cultivées
- Cultures annuelles

Mixte (cultures/ pâturages/ arbres), incluant l'agroforesterie
- Cropland and aquaculture
Commentaires:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Soil and water salinity during dry season; tidal surge; cyclones
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Water salinity; tidal surge; sidre (name of a cyclone)
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Mixed: Mo: Other
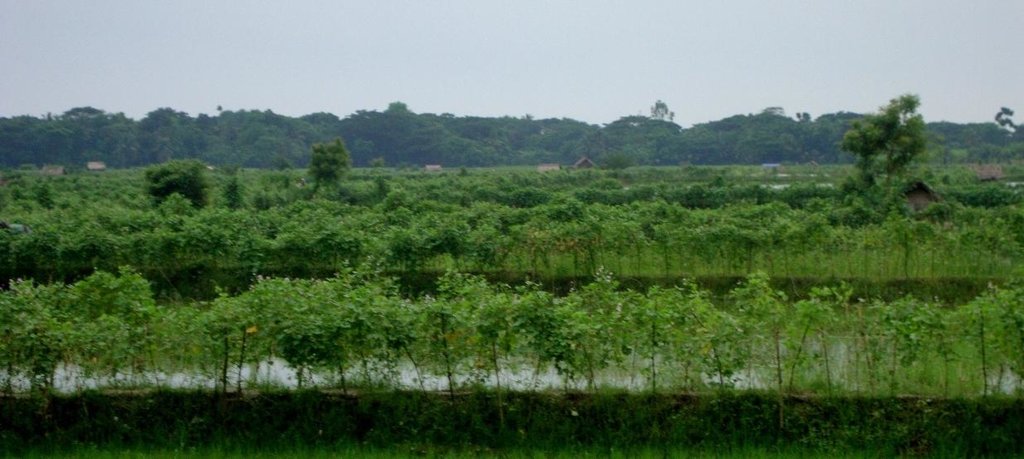
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: Gher use is very much variable. The main issue of using land is to adapt soil and water salinity. Some ghers are used for only shrimp, some are mixed with other fishes, some are mixed with transplanted Aman. But the boundary/bunds are used for year round vegetables, Banana, fruits (Kul, Guava, Mango) etc.
Si l'utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie, indiquez l'utilisation des terres avant la mise en œuvre de la Technologie:
Mixed: Mo: Other
3.3 Informations complémentaires sur l'utilisation des terres
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- pluvial
Commentaires:
Also mixed rainfed - irrigated
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 1
Précisez:
Longest growing period in days: 160; Longest growing period from month to month: July to Sept
3.4 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- apiculture, aquaculture, élevage de volailles, de lapins, du ver à soie, etc.
3.5 Diffusion de la Technologie
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- répartie uniformément sur une zone
Si la Technologie est uniformément répartie sur une zone, indiquez la superficie couverte approximative:
- 1-10 km2
Commentaires:
Gher (Shrimp cultivation) boundary used for multiple crops; vegetables, fruits, tree etc in southern coastal region of Bangladesh.
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

pratiques agronomiques
- A1: Couverture végétale/ du sol

structures physiques
- S2: Diguettes, digues

modes de gestion
- M1: Changement du type d’utilisation des terres
Commentaires:
Type of agronomic measures: better crop cover, mixed cropping / intercropping
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

dégradation chimique des sols
- Cs: salinisation/ alcalinisation
Commentaires:
Main causes of degradation: other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (Salinization: salination of top soil is due to saline ground water coming in shallow depth), Salinization (The area under this issue is in coastal zone. Conflict of land use is prominent. The lands became saline as other stakeholders keep saline water for other uses (salt production, shrimp))
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- restaurer/ réhabiliter des terres sévèrement dégradées
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
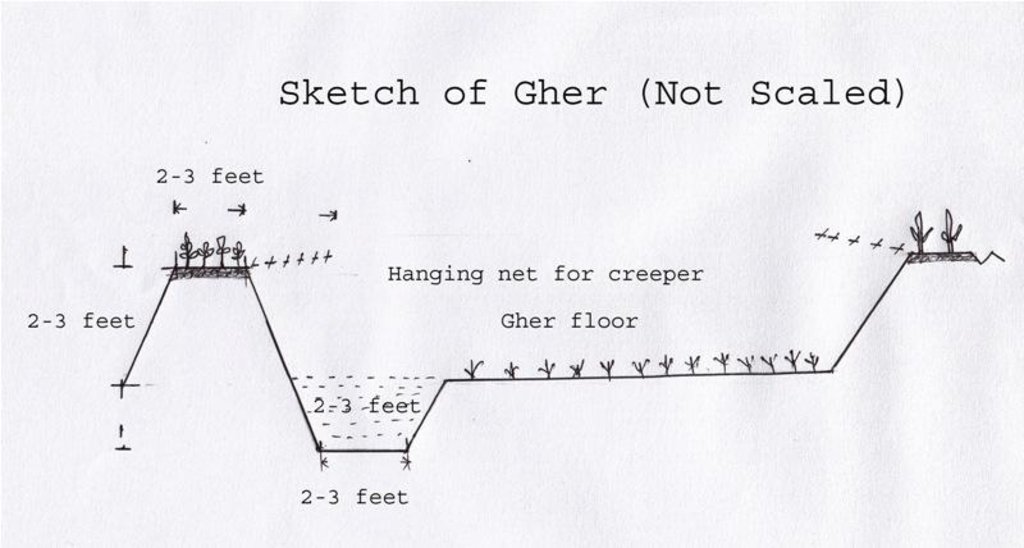
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
4.2 Spécification/ explications techniques du dessin technique
The gher boundary is raised approximately 2-3 feet with a crest of 2-3 feet. A ditch also dug to store water and fish during dry season.
Location: Dumuria. Khulna
Date: 03-09-13
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (It is only land manipulation.)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (Previously farmer did not put the top soil on the top of the bunds. That impedes crop production on bunds.)
Main technical functions: increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), water harvesting / increase water supply, improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water, promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder), spatial arrangement and diversification of land use, Decrease of soil salinity, Increase of options for growing more crops
Agronomic measure: Top soil kept on top
Structural measure: Bunds
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 1
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.5-1
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 10-50
Construction material (earth): Bunds are raised by piling earth
Change of land use practices / intensity level: Bunds are used for year round cropping
4.3 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
autre/ monnaie nationale (précisez):
Taka
Indiquer le taux de change du dollars en monnaie locale (si pertinent): 1 USD= :
79,0
4.4 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Farmers cut the earth from adjacent lands | Structurel | Nov-Dec |
4.5 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Farmers cut the earth from adjacent lands | ha | 10,0 | 65,0 | 650,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Labour | ha | 2,0 | 300,0 | 600,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Watch and ward | ha | 1,0 | 300,0 | 300,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Seeds, nets etc | ha | 1,0 | 50,0 | 50,0 | 100,0 |
| Engrais et biocides | Fertilizer | ha | 1,0 | 5,0 | 5,0 | 100,0 |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 1605,0 | |||||
Commentaires:
Duration of establishment phase: 1 month(s)
4.6 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Transplanting seedlings/seeds | Agronomique | July/Nov |
| 2. | Cultural practices | Agronomique | Aug-Oct/Dec-March |
4.7 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Transplanting seedlings/seeds | persons/day/ha | 2,0 | 10,0 | 20,0 | 100,0 |
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 20,0 | |||||
Commentaires:
Piling earth to construct gher bunds
4.8 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
Availability of labour
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifications/ commentaires sur les précipitations:
Most of the rainfall experienced in rainy season
Zone agro-climatique
- humide
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la topographie:
Landforms: Coastal plain, narrow ridge with broad flat basin
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- moyen (limoneux)
- fin/ lourd (argile)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- faible (<1%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Soil fertility is low
Soil drainage / infiltration is poor
Soil water storage capacity is very low - low
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Profondeur estimée de l’eau dans le sol:
< 5 m
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
faible/ absente
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
uniquement pour usage agricole (irrigation)
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- faible
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Orientation du système de production:
- mixte (de subsistance/ commercial)
- commercial/ de marché
Revenus hors exploitation:
- 10-50% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- pauvre
Individus ou groupes:
- individu/ ménage
Niveau de mécanisation:
- mécanisé/ motorisé
Genre:
- hommes
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Women casually worked during harvesting vegetables
Population density: > 500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
70% of the land users are poor.
Level of mechanization: Power triller on hire.
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres détenues ou louées par les exploitants appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- petite dimension
Commentaires:
15-50 ha: Mainly owner of lands of this area
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- individu, avec titre de propriété
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- loué
- individuel
Droits d’utilisation de l’eau:
- loué
- individuel
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
énergie:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Desalinized soil of the bund
Impacts socioculturels
sécurité alimentaire/ autosuffisance
situation sanitaire
opportunités culturelles
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Cash from vegetables
apaisement des conflits
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Conflicts to use water resource
situation des groupes socialement et économiquement désavantagés
livelihood and human well-being
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Growing and marketing of year round vegetables help the farmer to get cash money throughout the year. That improves their livelihood and access to health care, education etc.
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
drainage de l'excès d'eau
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Ghers are ponded and no water can be drained
Sols
salinité
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
+ Soil salinity reduced as washed by rainwater -> found in soils of Gher bunds
- Due to ground water abstraction -> found in coastal regions, increasing trend
Biodiversité: végétale, animale
diversité végétale
Réduction des risques de catastrophe et des risques climatiques
émissions de carbone et de gaz à effet de serre
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Changements climatiques progressifs
Changements climatiques progressifs
| Saison | Type de changements/ extrêmes climatiques | Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| températures annuelles | augmente | pas bien |
Extrêmes climatiques (catastrophes)
Catastrophes météorologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| pluie torrentielle locale | pas bien |
| tempête de vent locale | pas bien |
Commentaires:
Salinity is washed out from the bund by rainwater. Consequently year round vegetable can be grown on bunds of the gher besides fish in the main land or transplanted rice (depending on the salinity of soil and water and choice of farmers).
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
très positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
légèrement positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
très positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
légèrement positive
Commentaires:
Long term benefit is yet to be observed
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
Commentaires:
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Leased land users are not capable to adopt the technology.
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
|
Growing more crops will benefit the farmer with more return. As of now marketing of the goods are facilitated by local small entrepreneurs. Most of them have poor linkage with broader markets. How can they be sustained / enhanced? These entrepreneurs could be appropriately linked with bigger one at regional levels (Upazila/ Districts). At the same time road net works are to be alleviated to facilitate access of transport to carry farmers good with all securities. |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
|
Land could be used as farmers are managing themselves How can they be sustained / enhanced? To sustain production and produce such as vegetables and fishes deserve uninterrupted marketing linkage essential. |
|
Changes in land management by the farmer to grow multiple crops indeed scale up their economy than before. How can they be sustained / enhanced? To sustain the farming system good variety and quality seeds supply will enhance the scenario. |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Water management of the areas became critical, specially sweet water | Good water management system is to be introduced through local and regional planning. |
| Conflicts of land uses are prominent. | Social awareness and concept of land zoning seems to be essentials at all levels. |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Due to construction or rearrangement of field bunds (Dykes) almost all drainages ways blocked. Consequently the whole area became water logged. This situation will definitely aggravate soil quality, environment and ultimate ecosystem | Community approach to manage the landscape will be effective. In this regard local administration and community leaders can play a vital role. |
| Soils of Gher boundaries (Dykes) are subject to erosion when exposed to rain water. | Good cover crops and management are necessary to protect soils from erosion. At same time farmers may be trained on this issue. |
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens
Aucun lien
Modules
Aucun module trouvé