Contour Trench cum Bund [Inde]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Niranjan Sahu
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateurs : Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
Samapatana nali o huda ( Oriya)
technologies_1480 - Inde
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Spécialiste GDT:
Spécialiste GDT:
Patel Anita
1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.5 Référence au(x) Questionnaires sur les Approches de GDT (documentées au moyen de WOCAT)

Participatory Sustainable Rural Livelihood Approach [Inde]
Participatory Sustainable Rural Livelihood Approach adopts participatory tools for livelihood situational analysis of the five capitals(Physical, Financila,Social, Human and Natural) and prepare livelihood focussed micro plan with the commuity for sustai
- Compilateur : Niranjan Sahu
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
Contour trench cum bund is a bund laid out on contour along with trench either staggered or continuous to check the velocity of run off, conserve in situ moisture, increse ground water recharge and there by establish a sustainable land use system.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
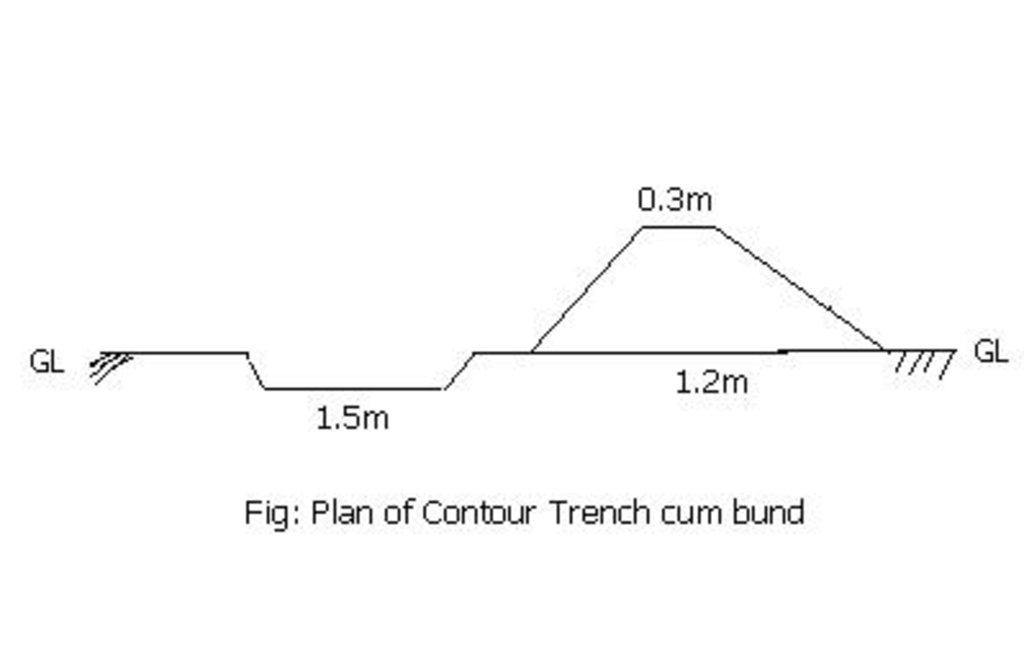
It is a structural measure. The bund is constructed taking the excavated earth from a trench of 1.5m X 0.3m cross section and leaving a berm of 0.3m and put along the contour. Loose boulder water way are constructed on the bund for safe disposal of excess run off.
Purpose: To break the slope of land. To reduce the velocity of runoff. To increase the in situ soil moisture and increase ground water table. To reduce down stream sand casting.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The process adopted for implementation of the intervention followed participatory planning through resource mapping, transect, well being ranking, problem identification, prioritisation and negotiation; thus benefit sharing, contribution and future maintenance of the stucture is ensured before establishment of the structure. The poor land and poor people get the opportunity first.
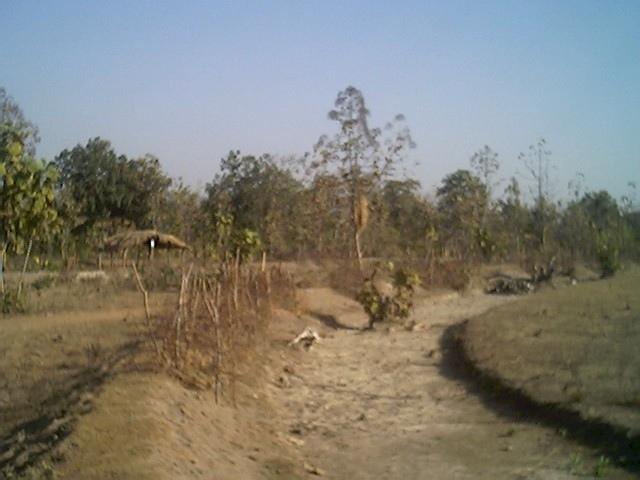
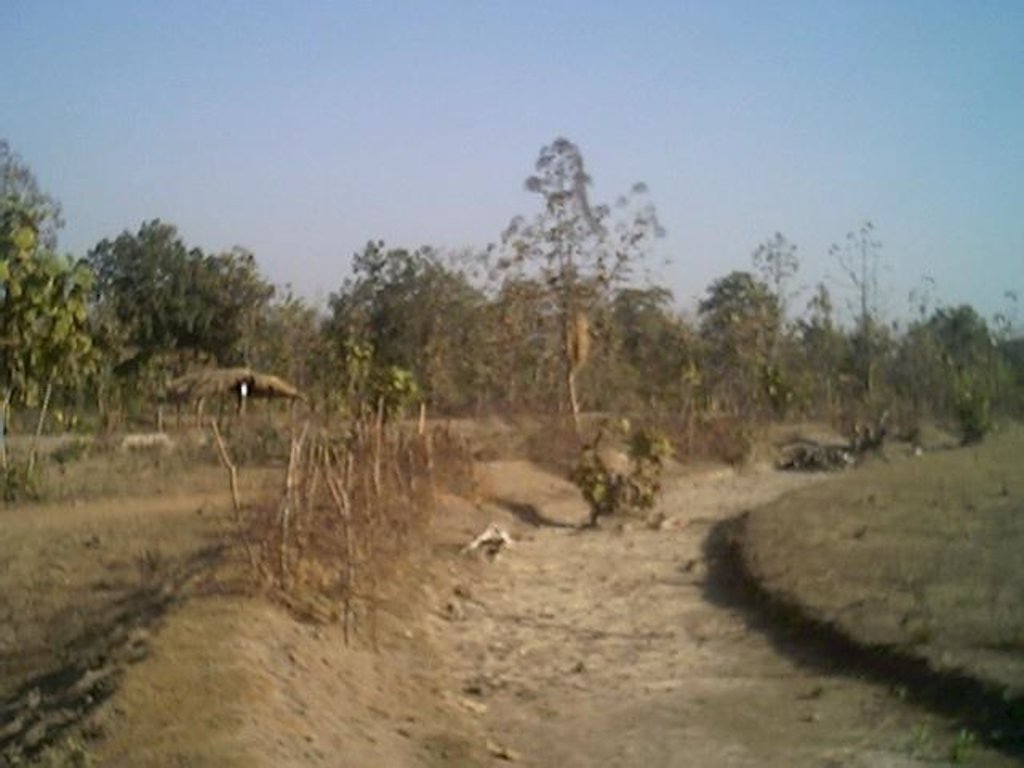
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Inde
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Orissa
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Nangalbod-Tankamal Watershed,Mahanadi Basin
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- répartie uniformément sur une zone
Si la Technologie est uniformément répartie sur une zone, précisez la superficie couverte (en km2):
0,32
S'il n'existe pas d'informations exactes sur la superficie, indiquez les limites approximatives de la zone couverte:
- 0,1-1 km2
Commentaires:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.32 km2.
The technology area comprises of 0.3 2km2 within the watershed of 6 km2. The technology is an improvement of the age old practice of field bunding by the farmers.This has been promoted by the Soil Conservation department and watershed mission through watershed development programme.
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a plus de 50 ans (technologie traditionnelle)
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- par le biais de projets/ d'interventions extérieures
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
Indegeneous but improved by Soil Conservation department, Watershed Mission, UNDP.
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- réduire, prévenir, restaurer les terres dégradées
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée
Les divers types d'utilisation des terres au sein du même unité de terrain: :
Oui
Précisez l'utilisation mixte des terres (cultures/ pâturages/ arbres):
- Agro-sylvo-pastoralisme

Terres cultivées
- Cultures annuelles
Cultures annuelles - Précisez les cultures:
- céréales - mil
- rice
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 1
Précisez:
Longest growing period in days: 150 Longest growing period from month to month: Jun - Oct

Pâturages
Pâturage extensif:
- Nomadisme
- cattle

Forêts/ bois
- Forêts (semi-)naturelles/ bois
Forêts (semi-)naturelles/ terres boisées: précisez le mode de gestion:
- Coupes sélectives
Produits et services:
- Bois de chauffage
- Fruits et noix
- Pâturage/ broutage
Commentaires:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): The fertile top soil is gradually washed away.Productivity of the soil is also reduced. Thus, farmer is only taking minor millet in kharif.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Loss of production. Soil is unable to retain moisture, so we suffer crop loss during long dry spell.Due to sand casting crop is also partially damaged in the down stream.
Nomadism: People allow the cattle to graze freely in the field after the crop is harvested
Selective felling of (semi-) natural forests: Yes
Problems / comments regarding forest use: People have started managing forest through VSS and Forest protection committee.
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: minor millets and up land paddy are the major crop under rain fed condition
3.4 Approvisionnement en eau
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- pluvial
3.5 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- mesures en travers de la pente
- dérivation et drainage de l'eau
- gestion des eaux de surface (sources, rivières, lacs, mers)
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

érosion hydrique des sols
- Wt: perte de la couche superficielle des sols (couche arable)/ érosion de surface
- Wg: ravinement/ érosion en ravines
Commentaires:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires), education, access to knowledge and support services (Absence of institutional arrangements to disseminate the knowledge from lab to land and involve the users in implementation)
Secondary causes of degradation: overgrazing (Subsistence economy, dependance on forests for fuelwood and fodder, livestock were low quality, free grazing type. And these were no regulatory mechanisms to share usufruct from forests with people.), poverty / wealth (Lack of capital at the grassroot to take the initiative by the farmers themselves)
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- réduire la dégradation des terres
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
Spécifications techniques (associées au dessin technique):
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: reduction of slope length
Secondary technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard
Bund/ bank: semi-circular/V shaped trapezoidal
Vertical interval between structures (m): 1.5
Spacing between structures (m): 50
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.45
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 1.2
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 60
Construction material (earth): earth is dug from the trench in the up stream
Construction material (stone): picked up boulders available locally
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 3%
4.2 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
autre/ monnaie nationale (précisez):
Indian Rupee
Indiquez le taux de change des USD en devise locale, le cas échéant (p.ex. 1 USD = 79.9 réal brésilien): 1 USD = :
50,0
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
1.00
4.3 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Calendrier des activités (saisonnier) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Survey and alignment of trench, bund | dry season |
| 2. | Digging of trenches and construction of bunds | dry season |
| 3. | Construction of water way | dry season |
4.4 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 100,0 | 100,0 | 30,0 |
| Matériaux de construction | Stone | ha | 1,0 | 2,0 | 2,0 | |
| Matériaux de construction | Earth | ha | 1,0 | 98,0 | 98,0 | 30,0 |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 200,0 | |||||
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 4,0 | |||||
Commentaires:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.5 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Grass turfing on bunds | during rainy season/annual |
| 2. | Maintaining shape and size of bund | after rainy season/annual |
| 3. | rearranging dispersed stone in water way | after rainy season/annual |
4.6 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
Commentaires:
Cross-section and length of the structure per hectare
4.7 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
labour
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifiez la pluviométrie moyenne annuelle (si connue), en mm:
1382,00
Zone agro-climatique
- semi-aride
80-100 days of rainfall occurs in most part of the state
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la topographie:
Altitudinal zone: 101-500 m a.s.l. ( the technology area is located at 196m.a.s.l.)
Landforms: Hill slopes (ranked 1, the surrounding area is coverd with hillocks with forest) and footslopes (ranked 2, the technology area has undulating slopes with forest in betweem and mild slope)
Slopes on average: Also gentle (ranked 2) and flat (ranked 3)
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- grossier/ léger (sablonneux)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- faible (<1%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Soil depth on average: Also moderately deep (ranked 2) and deep (ranked 3)
Soil texture: Also medium (ranked 2) and fine/havey (ranked 3)
Soil fertility: Very low (ranked 1), low (ranked 2) and medium (ranked 3)
Topsoil organic matter: Also medium (ranked 2) and high (ranked 3)
Soil drainage/infiltration: Good (ranked 1) and medium (ranked 2)
Soil water storage capacity: Very low (ranked 1), low (ranked 2) and medium (ranked 3)
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Orientation du système de production:
- subsistance (auto-approvisionnement)
- exploitation mixte (de subsistance/ commerciale)
Revenus hors exploitation:
- 10-50% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- riche
- très riche
Niveau de mécanisation:
- travail manuel
- traction animale
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
Annual population growth: > 4%
30% of the land users are very rich and own 5% of the land.
20% of the land users are rich and own 15% of the land.
25% of the land users are average wealthy and own 20% of the land.
20% of the land users are poor and own 30% of the land.
5% of the land users are poor and own 25% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: The livelihoods is less diversified. They also depends on NTFP marketing, off farm activities.
Level of mechanization: Animal traction (ranked ) and manual work (ranked 2)
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres utilisées par les exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Commentaires:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology:
Cropland: 0.5-1ha (ranked 1, marginal farmers)
1-2 ha (ranked 2, small farmers)
2-5 ha (ranked 3, big farmers)
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- communauté/ village
- individu, avec titre de propriété
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- communautaire (organisé)
- individuel
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
production fourragère
qualité des fourrages
production animale
surface de production
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Due to construction of bund
Revenus et coûts
revenus agricoles
Autres impacts socio-économiques
Formal credit
Input constraints
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Timely availability of inputs
Impacts socioculturels
institutions communautaires
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
22 SHGs has been formed and strengthened
connaissances sur la GDT/ dégradation des terres
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
NRM volunteers has been developed
apaisement des conflits
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
During identification of land ownership and location of waterways
Impacts écologiques
Sols
humidité du sol
couverture du sol
Autres impacts écologiques
Soil fertility
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
inondations en aval
envasement en aval
Water table in wells
Water availability in WHS
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
Si disponible, quantifiez (nombre de ménages et/ou superficie couverte):
24
Commentaires:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
12 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: survey results
12 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: survey results
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: The farmers have realised the benefits from farmers' group meeting and visiting to the technology area.The farmers have started maintaining the bunds. They have also started taking crops both on bunds and field.
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
|
Our crop can with stand dry spell How can they be sustained / enhanced? Planting of glaricidia and use of compost |
|
Value of land will increase How can they be sustained / enhanced? By maintaining bunds |
|
We can take crop in bunds How can they be sustained / enhanced? planting of bengal grams, tils, cow pea and sima |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
|
Reduce runoff and velocity How can they be sustained / enhanced? Desilting from the trenches |
|
Reduce sand casting in the down stream How can they be sustained / enhanced? Desilting from the trenches |
|
Crop diversification and promotion of improved agricultural practices How can they be sustained / enhanced? Through capacity building of volunteers and land users |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| loss of land | Productive use of trench and bunds |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Regular maintenance of the stone surplus | promote and strengthen user group |
| Open grazing | Promote community farming for collective actions |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
7.2 Références des publications disponibles
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Micro plan of Nangalbod-tankamal watershed. 12/30/2004.
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
Project Direcotr watershed, Nuapada
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
district Statistical hand book. 12/30/2004.
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
Project Direcotr watershed, Nuapada
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens

Participatory Sustainable Rural Livelihood Approach [Inde]
Participatory Sustainable Rural Livelihood Approach adopts participatory tools for livelihood situational analysis of the five capitals(Physical, Financila,Social, Human and Natural) and prepare livelihood focussed micro plan with the commuity for sustai
- Compilateur : Niranjan Sahu
Modules
Aucun module trouvé