Gully rehabilitation [Tadjikistan]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Qobiljon Shokirov
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateurs : David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_1541 - Tadjikistan
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Spécialiste GDT:
Boev Jahonbek
Tajik Soil Institute
Tadjikistan
Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Tajik Soil Insitute (Tajik Soil Institute) - TadjikistanNom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
NCCR North-South (NCCR North-South) - Kirghizistan1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.5 Référence au(x) Questionnaires sur les Approches de GDT (documentées au moyen de WOCAT)

Field research station for analysing soil conservation measures [Tadjikistan]
Research Station of the Tajik Academy of Agrarian Science, Soil Institute conducting research on soil conservation and productivity in the rainfed hill zones of central Tajikistan.
- Compilateur : Gulniso Nekushoeva
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
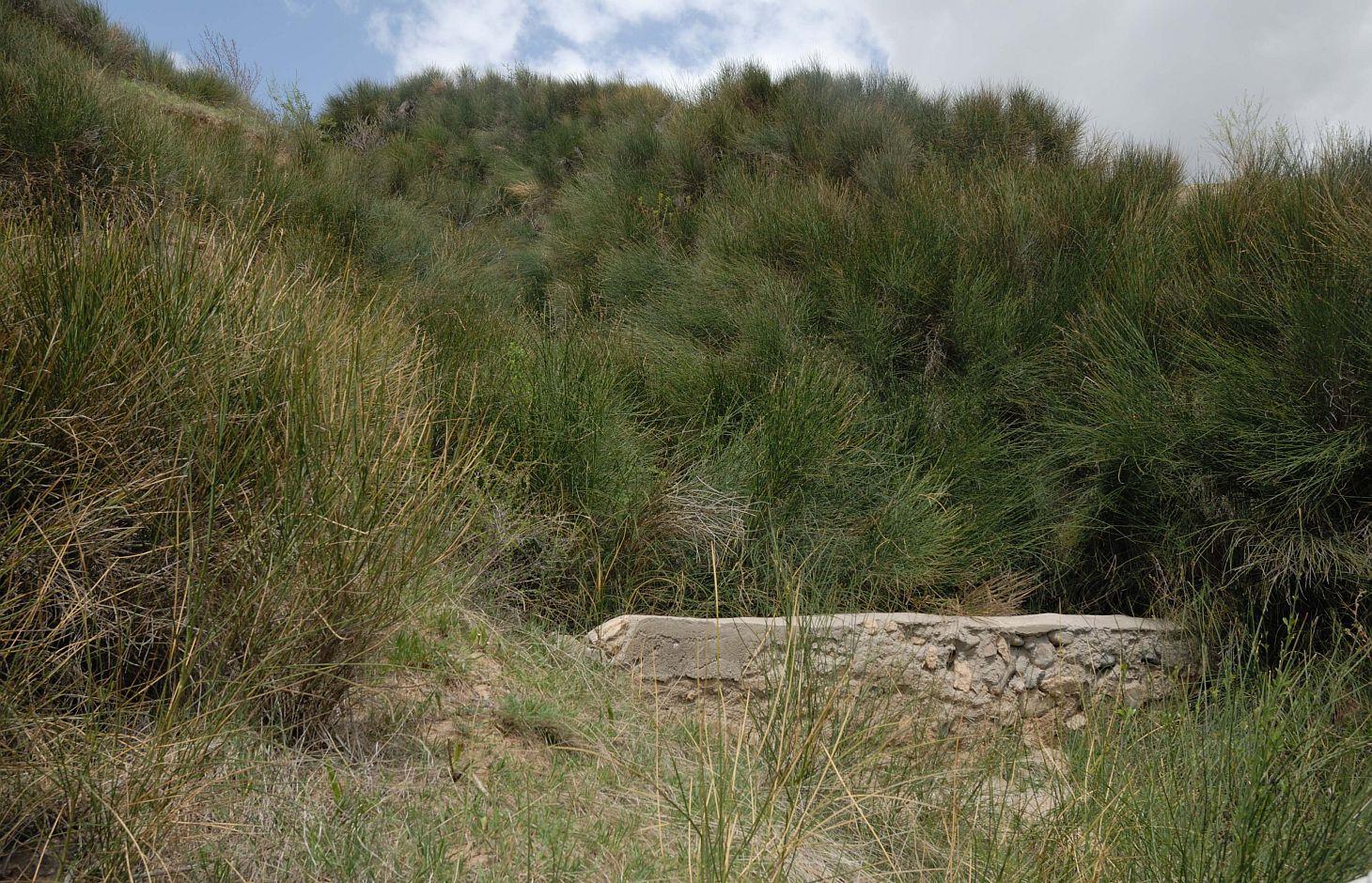
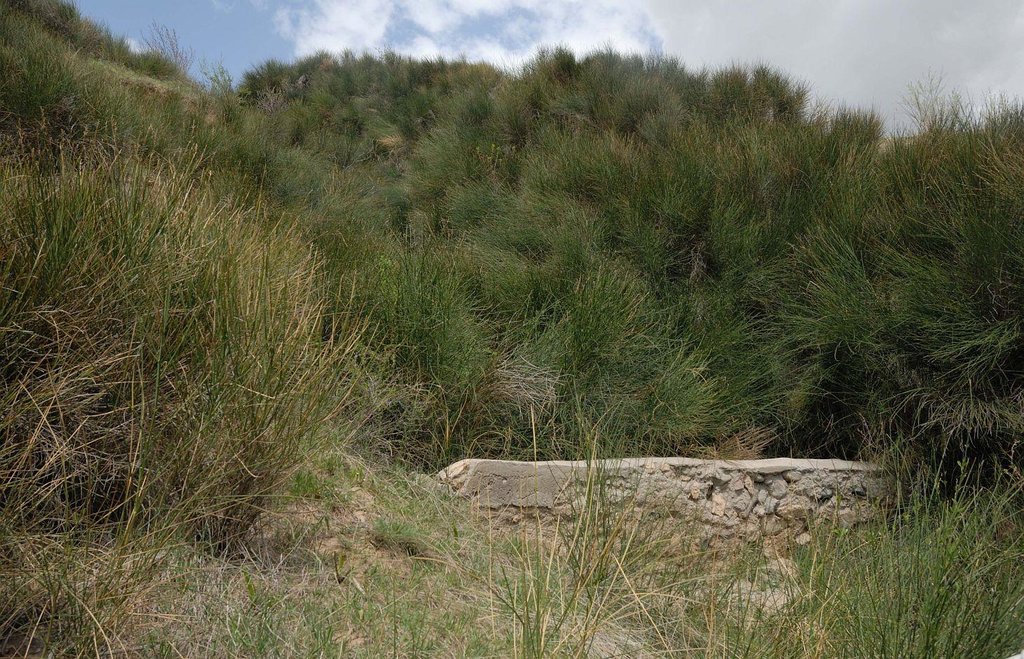
Gullies are stabilized through the establishment of a gabion and the plantation of spanish drok (Spartium junceum L).
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
The research station of the Soil Science Institute tested the stabilisation of large gullies created by water erosion through the plantation of Spanish drok (Spartium junceum L). The plantation of Spanish drok was introduced in 1972 for the first time in the research field station. Spanish drok is a perennial plant and has the ability of spreading fast through its roots and also via seeds. Most of the gullies are covered with Spanish drok by now. In total 150,000 seedlings were planted at the research station.
Purpose of the Technology: Water erosion is highly threatening croplands by washing away the fertile topsoil. Severe gullies have formed on the hilly slopes. The research station of the soil institute therefore selected a number of gullies to test different techniques of rehabilitation.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: In a first step a survey of gullies in the vicinity of the research station was conducted in order to determine an appropriate place for testing the stabilization. Spanish drok was planted and spread very fast through vegetative underground reproduction until the whole gully was covered. A gabion made out of stone and concrete was constructed at the foot of the gully. It contains a pipe to allow for outflow of excess water. Maintenance of the technology is less cost efficient and doesn't involve much cost associated activities.
Natural / human environment: The positive results of the implementation of this technology are very important as there is a great need for spreading it to other areas suffering from the same problems in Tajikistan. Spanish drok is generally not available in Tajikistan. Nowadays, the research station is providing seedlings for sale to interested farmers with a cost of roughly $ 0.40 per seedling.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Tadjikistan
Région/ Etat/ Province:
RRS
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Javanon, Karsang
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a entre 10-50 ans
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- au cours d'expérimentations / de recherches
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
through the Karsang field research station
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- réduire, prévenir, restaurer les terres dégradées
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

Terres cultivées
- Cultures annuelles
- Plantations d’arbres ou de buissons
- spanish drop
Précisez:
Longest growing period from month to month: April through November
Commentaires:
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): loss of arable land, development of gullies, water erosion
3.4 Approvisionnement en eau
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- pluvial
3.5 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- Amélioration de la couverture végétale/ du sol
- mesures en travers de la pente
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

pratiques végétales
- V1: Couverture d’arbres et d’arbustes

structures physiques
- S5: Barrages/retenues, micro-bassins, étangs
Commentaires:
Main measures: vegetative measures, structural measures
Type of vegetative measures: scattered / dispersed
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

érosion hydrique des sols
- Wg: ravinement/ érosion en ravines
- Wo: effets hors-site de la dégradation
Commentaires:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Wo: offsite degradation effects
Main causes of degradation: overgrazing, Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (It usually rains in March-April with duration of 20-45 minutes)
Secondary causes of degradation: wind storms / dust storms (Wind storms in winter), droughts (Hot summer months without rain)
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- réduire la dégradation des terres
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
Spécifications techniques (associées au dessin technique):
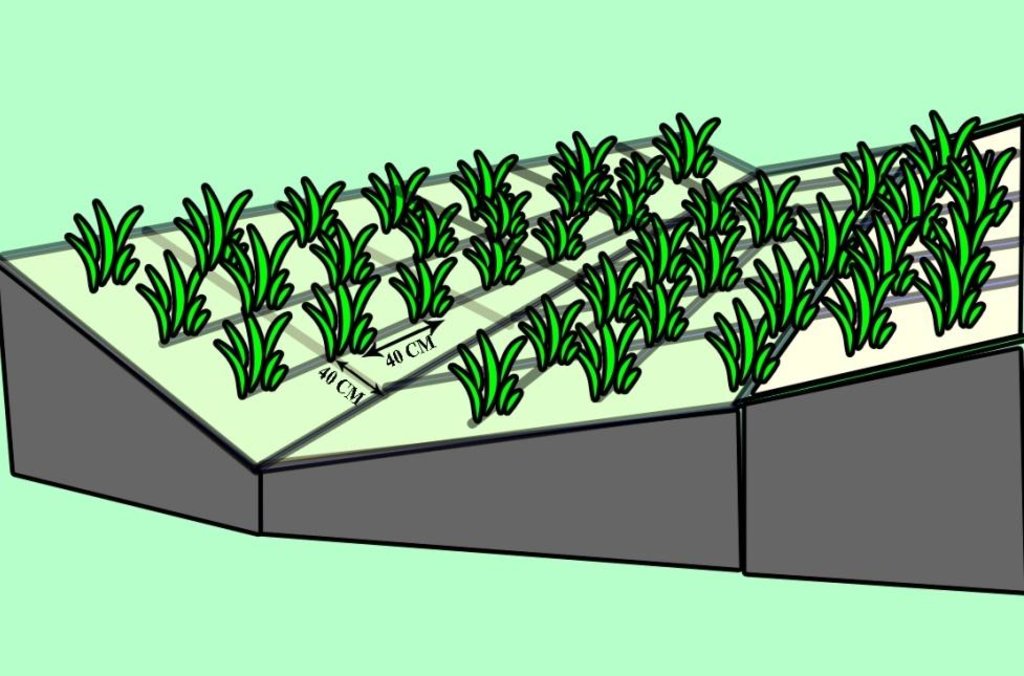
Scheme of how the Spanish Drok was planted on a eroded slopes of Karsang Research Field Station.
Location: Karsang Research Field Station. Javonon, Karsang
Date: 16-07-2012
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, improvement of ground cover, stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides)
Scattered / dispersed
Number of plants per (ha): 5000
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.3
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.2
Trees/ shrubs species: Spanish drop.
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 25%
Wall/ barrier
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1.2
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 1.2
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.2
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 3.5
Construction material (stone): stone and concrete was used for the establishment of the gabion
Construction material (concrete): stone and concrete was used for the establishment of the gabion
Auteur:
Q. Shokirov
4.2 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
autre/ monnaie nationale (précisez):
Somoni
Indiquez le taux de change des USD en devise locale, le cas échéant (p.ex. 1 USD = 79.9 réal brésilien): 1 USD = :
4,5
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
7.00
4.3 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Calendrier des activités (saisonnier) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Selection of area | early spring |
| 2. | Planting of spanish drop | early march |
| 3. | Construction of gabion |
4.4 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Selection of area | Persons/day | 30,0 | 30,0 | 900,0 | |
| Main d'œuvre | Planting of spanish drop | Persons/day | 36,0 | 30,0 | 1080,0 | |
| Main d'œuvre | Construction of gabion | Gabion | 1,0 | 700,0 | 700,0 | |
| Matériaux de construction | Stones | Gabion | 1,0 | 800,0 | 800,0 | |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 3480,0 | |||||
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 773,33 | |||||
Si le coût n'est pas pris en charge à 100% par l'exploitant des terres, indiquez qui a financé le coût restant:
Tajik Soil Institue
Commentaires:
Duration of establishment phase: 1 month(s)
4.5 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | As the plant spreads through root propagation, the dispersal has to be limited by removing some of the plants every year |
4.7 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
buying seeds, tools, additional labor cost needs to be filled out more.
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Zone agro-climatique
- semi-aride
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Indiquez si la Technologie est spécifiquement appliquée dans des:
- situations concaves
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- moyen (limoneux)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- faible (<1%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Soil fertility is low
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium
Soil water storage capacity is low
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Profondeur estimée de l’eau dans le sol:
5-50 m
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
moyenne
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
eau potable
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- moyenne
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Orientation du système de production:
- subsistance (auto-approvisionnement)
- exploitation mixte (de subsistance/ commerciale)
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- pauvre
- moyen
Individus ou groupes:
- individu/ ménage
Niveau de mécanisation:
- travail manuel
Genre:
- femmes
- hommes
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
10% of the land users are average wealthy.
90% of the land users are poor.
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres utilisées par les exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- petite dimension
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- état
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- accès libre (non organisé)
Commentaires:
Research station belongs to the State, but land is leased to the local farmers for use.
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
énergie:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production de bois
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Spanish drok is used as firewood, increased availability
surface de production
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Prevents gullies from spreading and destroying production area
Revenus et coûts
charge de travail
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
No need to take care of eroded land every year
Impacts socioculturels
connaissances sur la GDT/ dégradation des terres
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Farmers are aware of erosion problems and benefits of Spanish drok
Livelihood and human well-being
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Many farmers have now understanding of mitigating soil erosion by water with the use of Spanish Drok.
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
ruissellement de surface
nappes phréatiques/ aquifères
évaporation
Sols
humidité du sol
couverture du sol
perte en sol
Biodiversité: végétale, animale
biomasse/ au dessus du sol C
diversité des habitats
Réduction des risques de catastrophe et des risques climatiques
émissions de carbone et de gaz à effet de serre
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
inondations en aval
capacité tampon/de filtration
dommages sur les champs voisins
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Changements climatiques progressifs
Changements climatiques progressifs
| Saison | Augmentation ou diminution | Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| températures annuelles | augmente | bien |
Extrêmes climatiques (catastrophes)
Catastrophes météorologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| tempête de vent locale | bien |
Catastrophes climatiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| sécheresse | bien |
Autres conséquences liées au climat
Autres conséquences liées au climat
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| réduction de la période de croissance | bien |
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
neutre / équilibrée
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
Commentaires:
Full establishment of the Spanish drok takes about 10 years, however, through the establishment of the gabion some immediate benefits occur
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
- cas isolés/ expérimentaux
Si disponible, quantifiez (nombre de ménages et/ou superficie couverte):
NA
De tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle, ou aucune rémunération? :
- 0-10%
Commentaires:
Comments on acceptance with external material support: The technology was implemented through the research station using their employees.
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Earlier Spanish drok was not yet known among the farmers as it is an exotic species. A handful of farmers have been interested and adopted the technology in their plots. According to farmers from the station more people are interested applying such technologies as a protection for soil erosion and establishment of gabions.
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
| Affordable technology for land restoration and degraded plots. |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
| Effectively puts a halt to water erosion. |
| The bushes provide valuable firewood for the local land users. |
| A special microclimate is created through the establishment of the plants with humidity being preserved all year long and birds and bees seem to use it as a preferred habitat. |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| The planting material is generally not available in Tajikistan, only now the research station is selling it to interested farmers, however, availability is still very localised. | Farmer to farmer spreading of planting material in addition to providing planting material to the different tree nurseries in the country. |
| Spanish drok is very easily inflammable in the dry summermonths due to essential oils which can pose a potential risk. | Good care has to be taken during the dry period and maybe some warning signs put up to tell people not to drop their cigarette stumps. |
| For the coverage of a whole gully with spanish drok about 10 years are needed as it happens through natural root propagation. |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens

Field research station for analysing soil conservation measures [Tadjikistan]
Research Station of the Tajik Academy of Agrarian Science, Soil Institute conducting research on soil conservation and productivity in the rainfed hill zones of central Tajikistan.
- Compilateur : Gulniso Nekushoeva
Modules
Aucun module trouvé