Gully Rehabilitation with Native Trees [Tadjikistan]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Selina Studer
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateurs : David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_1543 - Tadjikistan
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
exploitant des terres:
Mirsoiv Iskandar
Tadjikistan
exploitant des terres:
Mirsoiv Avaz
Tadjikistan
Spécialiste GDT:
Spécialiste GDT:
Boev Jahonbek
NCCR
Tadjikistan
Spécialiste GDT:
Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
NCCR North-South (NCCR North-South) - KirghizistanNom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Tajik Soil Insitute (Tajik Soil Institute) - TadjikistanNom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - Suisse1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
Vegetative and structural technology for the rehabilitation of an expanded gully
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
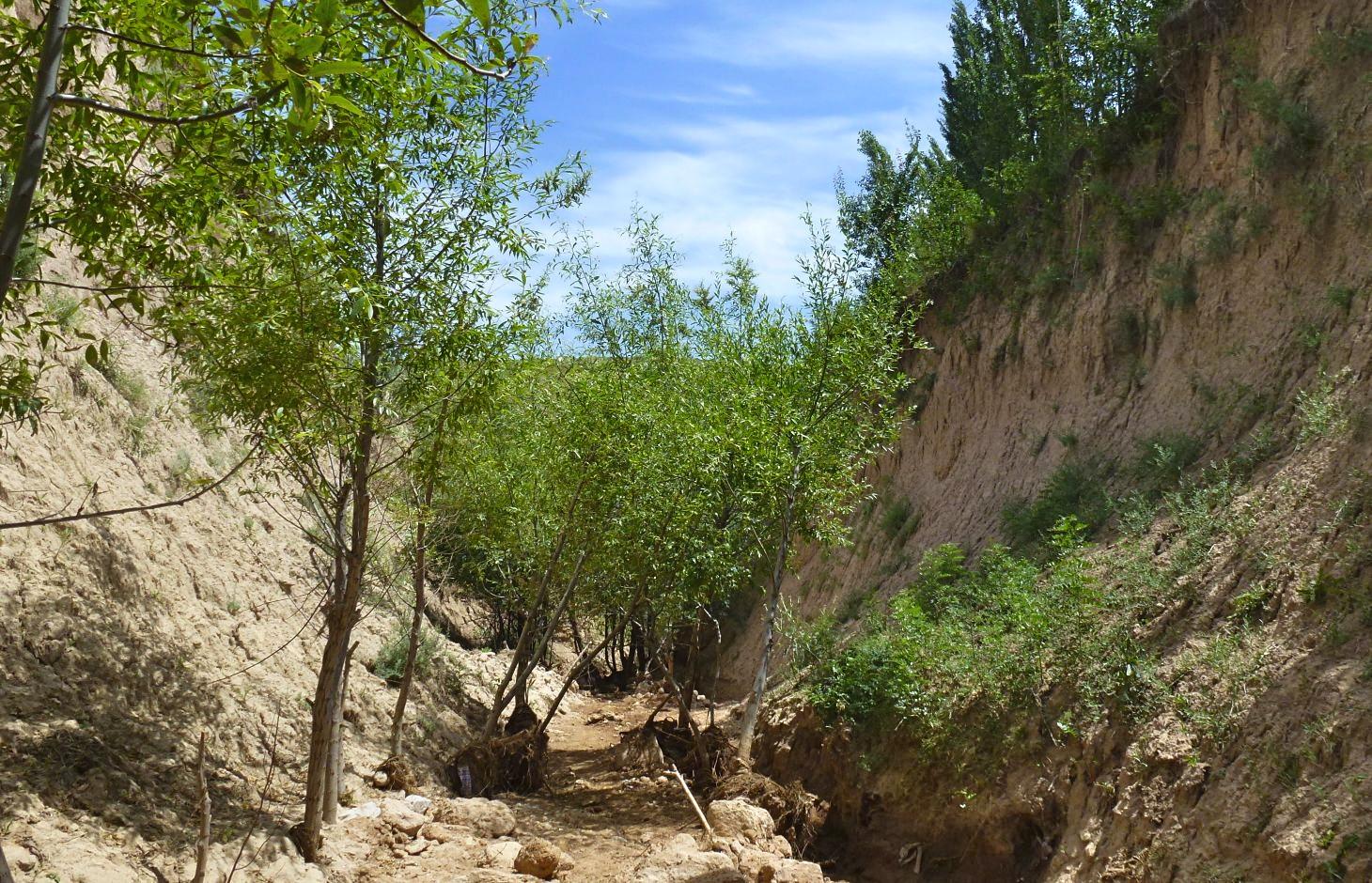
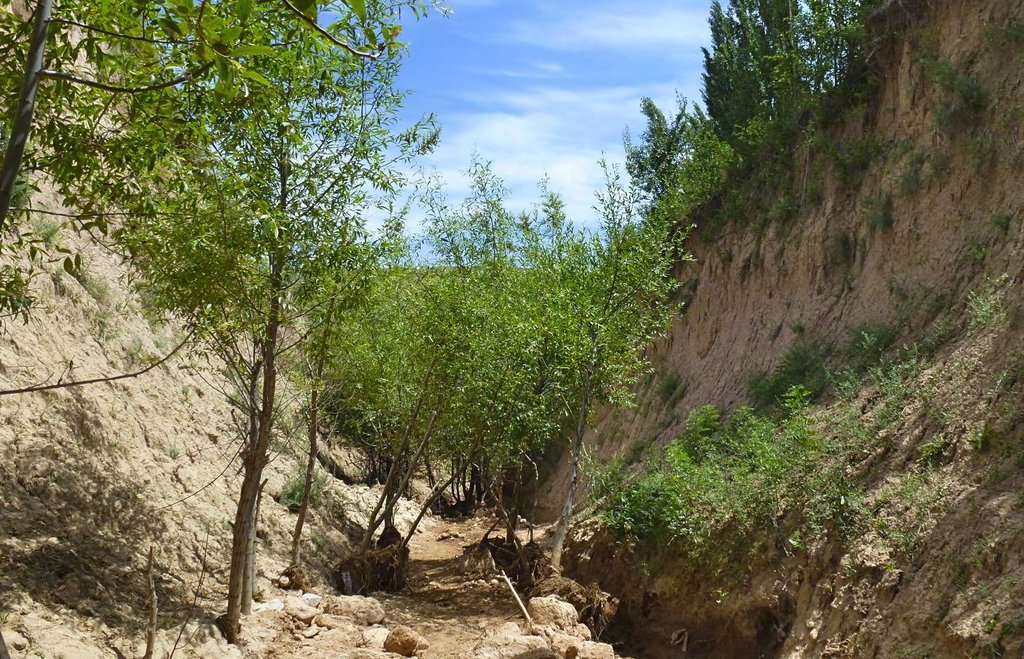
Description:
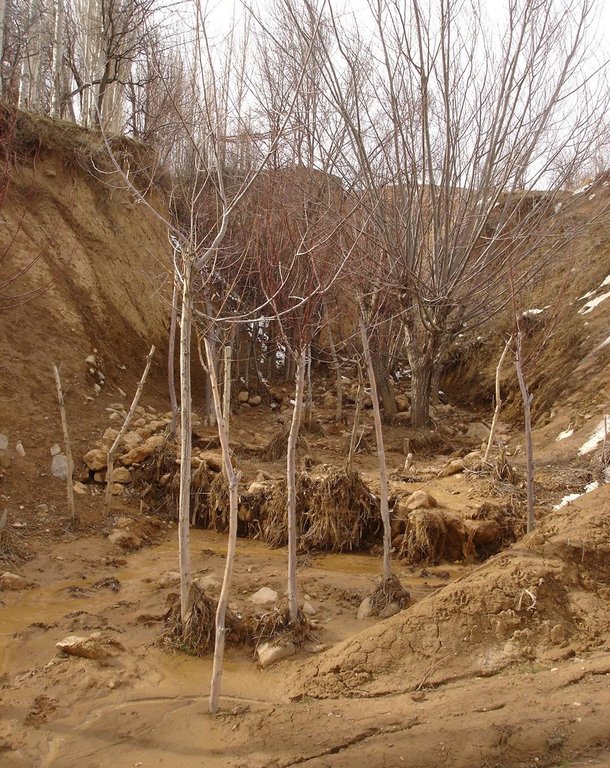
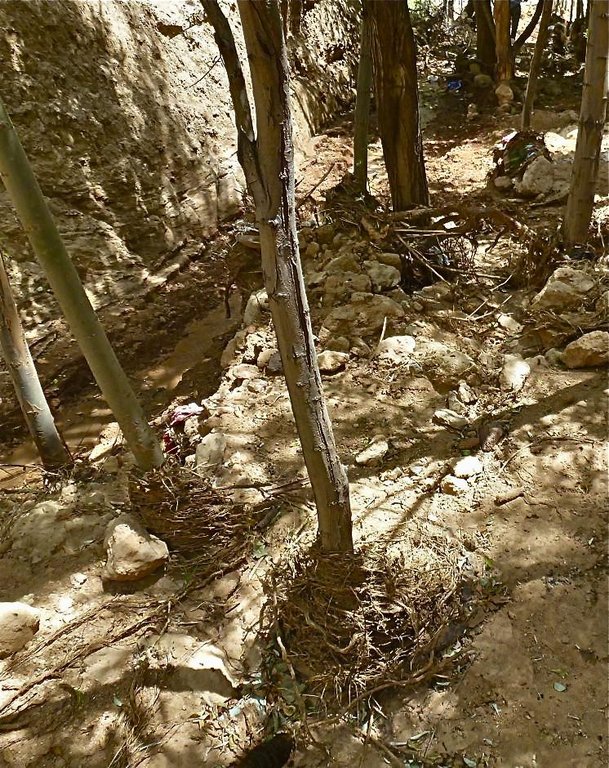
The extension of a deep incised gully, which borders a fertile orchard, is stopped and sediments are trapped by the help of vegetative and structural measures. The gully floor is vegetated with different trees inter alia willow, poplar, cherry, blackberry and walnut which are arranged in random groups. At the bottom of the gully where it intersects the road there is a stonewall, which collects the sediments that are washed down during heavy rainfalls mostly in spring. A dense bush line with Russian olives, apricots, cherries, walnuts, plums and buxus has been planted on the top of the side slopes of the gully, and roots of those bushes keep the soil stable and at the same time they prevent landslides and expansion of the gully. These tree lines are cut from time to time, otherwise they grow and become heavy and due to their weight the trees would possibly fall into the gully.
Purpose of the Technology: (1) The deep roots of willow trees on the bottom of the gully protect the soil and prevent it from being eroded during the heavy spring floods. Trees also help to collect sediment and to accumulate it in the gully. (2) The dense bush lines with its deep roots, on the top of the gully slope, stop the horizontal erosion, which endangers the fertile orchard close to the gully. (3) A stonewall at the lower end of the gully collects sediments which have been washed down. Once in a while a heightening of the stonewall has to be done. The technology with its three measures prevents from further gully expansion and supports its rehabilitation.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: These three measures, the tree line, the bottom vegetation and the stonewall were developed and implemented by the farmer's own initiative. The farmer implemented the technology on his own and expands it every year. The entire technology doesn’t have to be established at once, which allows investing money and time whenever it is available. For maintenance new trees are planted both in the gully and in the tree line, which has to be cut and pruned from time to time. The technology is relatively affordable and facile to implement. At the beginning the farmer bought some seedlings. Meanwhile, the plants reproduce themselves and the farmer doesn't have to buy seedlings for further maintenance. The stones can be collected for free in the nearby riverbed. The work is done manually; no special tools are needed for the technology.
Natural / human environment: The farmer is proud of the outcome of his initiative. However he wishes that his neighbours would follow his lead, as for them it would be beneficial to implement the technology as well. He stated that usually people do not listen to a common farmer, but if the technology would be introduced by an official person it would spread out quickly.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Tadjikistan
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Tajikistan
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Faizabad, Javonon, Chinoro
Commentaires:
Boundary points of the Technology area: northernmost: 38°36'00.09"/69°23'58.93"
southernmost: 38°35'54.77"/69°24'03.18"
Comments:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.002138 m2.
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a entre 10-50 ans
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- grâce à l'innovation d'exploitants des terres
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
The farmer implemented the technology during the civil war and teached other farmers to do it. But it is not so easy for the farmer to convince other people to follow his example.
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- réduire, prévenir, restaurer les terres dégradées
- protéger un bassin versant/ des zones situées en aval - en combinaison avec d'autres technologies
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

Terres improductives
Précisez:
gully
Remarques:
The gully floor is vegetated with different trees inter alia willow, poplar, cherry, blackberry and walnut which are arranged in random groups.
A dense bush line with Russian olives, apricots, cherries, walnuts, plums and buxus has been planted on the top of the side slopes of the gully.
Commentaires:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Highly erodible loess soil, and heavy rainfalls which causes a lot of surface runoff and erosion.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Lack of water for irrigation, too few rain, steep slopes, infertile soils which make the use of fertilizers essential.
Constraints of wastelands / deserts / glaciers / swamps
Number of growing seasons per year:
1
Specify:
Longest growing period in days: 210Longest growing period from month to month: March to August
3.5 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- mesures en travers de la pente
- gestion des eaux de surface (sources, rivières, lacs, mers)
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

pratiques végétales
- V1: Couverture d’arbres et d’arbustes

structures physiques
- S6: Murs, barrières, palissades, clôtures
Commentaires:
Main measures: vegetative measures
Secondary measures: structural measures
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -along boundary, scattered / dispersed
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

érosion hydrique des sols
- Wg: ravinement/ érosion en ravines
- Wm: mouvements de masse/ glissements de terrain
- Wr: érosion des berges
Commentaires:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wm: mass movements / landslides, Wr: riverbank erosion
Main causes of degradation: soil management (lack of knowledge for soil treatement, e.g. people dig hollows which support gully formation, agronoms from soviet times are missing), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (Trees were cut for domestic use), overgrazing, disturbance of water cycle (infiltration / runoff), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts), land tenure (land is not private property), poverty / wealth (no money for tractors, fertilizers, education, etc.,), education, access to knowledge and support services, war and conflicts (during the civil war the land was not cultivated sustainably), governance / institutional (land use rights)
Secondary causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires), change in temperature (too hot and too cold temperatures dry out the soil, plants cannot survive), change of seasonal rainfall, population pressure, inputs and infrastructure: (roads, markets, distribution of water points, other, …) (lack of machinery to treat the field properly)
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- prévenir la dégradation des terres
- restaurer/ réhabiliter des terres sévèrement dégradées
Commentaires:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation, rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
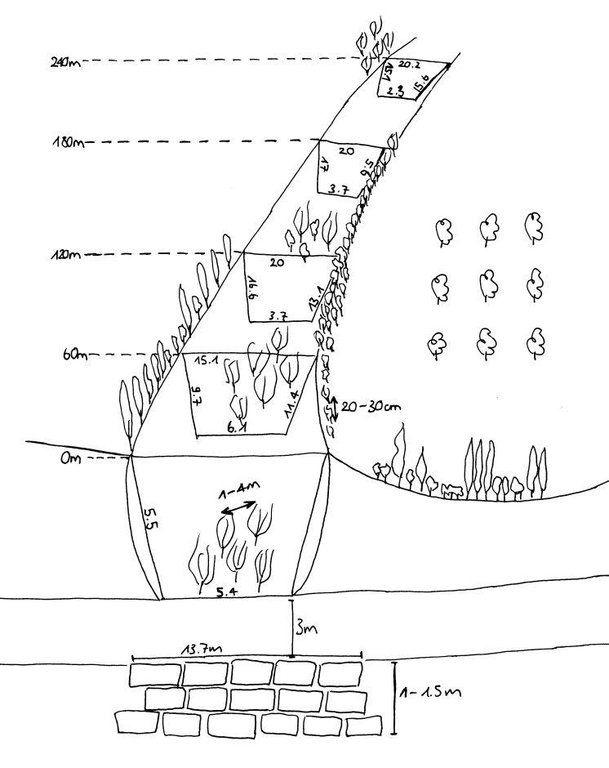
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
Spécifications techniques (associées au dessin technique):
The technology includes three different sketch information; 1) dense tree lines on the top of the side slopes, 2) stonewall at the end of the gully and 3) willow trees at the bottom of the gully.
Location: Chinoro. Faizabad/Javonon/Tajikistan
Date: 03.09.2012
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high (People do not accept a suggestion if it is not from a good educated, accepted person.)
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, increase of surface roughness, stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides)
Secondary technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, improvement of ground cover, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting, reduction in wind speed, increase of biomass (quantity), promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Aligned: -along boundary
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.2-0.4
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 2m (1-2 Row(s))
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 1-4
Trees/ shrubs species: russian olive, willow tree, acacia, poplar, box
Fruit trees / shrubs species: walnut, apple, apricot, plum, cherries
Wall/ barrier
Vertical interval between structures (m): 0
Spacing between structures (m): 0
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1.5
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 3
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 13.7
Construction material (stone): Are taken from a nearby riverbed.
Auteur:
Selina Studer
4.2 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
autre/ monnaie nationale (précisez):
Tajik Somoni
Indiquez le taux de change des USD en devise locale, le cas échéant (p.ex. 1 USD = 79.9 réal brésilien): 1 USD = :
4,7
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
12.00
4.3 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Calendrier des activités (saisonnier) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | plant trees in the gully | whole year |
| 2. | plant tree line | whole year |
| 3. | build wall |
4.4 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % du coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Build wall | wall | 1,0 | 125,0 | 125,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Planting trees | Persons/day | 3,0 | 12,0 | 36,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériel végétal | Tree seedlings | 1,0 | 166,0 | 166,0 | ||
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 327,0 | |||||
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 69,57 | |||||
4.5 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | add trees in the gully | spring |
| 2. | add trees in the tree line | spring |
| 3. | increase the height of the stonewall | once a while |
4.6 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % du coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Add trees | Persons/day | 1,0 | 12,0 | 12,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Increase the hight of the wall | - | ||||
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 12,0 | |||||
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 2,55 | |||||
Commentaires:
The fact that the inputs for the technology are not evenly distributed throughout the area, the costs were calculated for the whole technology area.
4.7 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
The material is relatively affordable. Money intensive factor are the seedlings during establishment phase. Following years the trees reproduce themselves. The establishment of the technology, the planting of the trees and the building of the stonewall require a lot of labour input in the initial phase. As the whole technology does not have to be implemented at once, the work can be split-up over years.
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Zone agro-climatique
- semi-aride
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- grossier/ léger (sablonneux)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- moyen (1-3%)
- faible (<1%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Soil depth on average: No soil in the gully
Soil fertility is medium for the treeline on top of the slopes of the gully (close to the orchard). but in the gully its very low because the soil was washed away.
Topsoil organic matter is medium at the treeline on top of the gully slope.
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium and in the orchard, gully works as drainage
Soil water storage capacity is very low
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Profondeur estimée de l’eau dans le sol:
> 50 m
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
faible/ absente
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
eau potable
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- faible
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Revenus hors exploitation:
- moins de 10% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- pauvre
- moyen
Individus ou groupes:
- individu/ ménage
Genre:
- hommes
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: The technology was directed by the farmer and implemented by the farmer's son. Only men were involved in the technology. In Tajikistan usually work for men and women is strictly divided. Women work in the household, take care for children and work on the field. The gully rehabilitation project was men's work.
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
10% of the land users are rich (trader which buy and sell products from the farmers).
60% of the land users are average wealthy and own 80% of the land.
30% of the land users are poor and own 20% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: beneath the technology the farmer has an orchard with intercropping, a flax and a wheat plot.
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres utilisées par les exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- petite dimension
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- état
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- accès libre (non organisé)
Droits d’utilisation de l’eau:
- communautaire (organisé)
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
énergie:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production de bois
surface de production
Revenus et coûts
dépenses pour les intrants agricoles
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Especially at the time of establishment.
Impacts socioculturels
connaissances sur la GDT/ dégradation des terres
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Land users acquired new knowledge.
security to have fertile land
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
ruissellement de surface
Sols
couverture du sol
perte en sol
Biodiversité: végétale, animale
biomasse/ au dessus du sol C
diversité végétale
diversité animale
espèces bénéfiques
diversité des habitats
Réduction des risques de catastrophe et des risques climatiques
vitesse du vent
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Treeline
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
inondations en aval
envasement en aval
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Changements climatiques progressifs
Changements climatiques progressifs
| Saison | Augmentation ou diminution | Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| températures annuelles | augmente | pas connu |
Extrêmes climatiques (catastrophes)
Catastrophes météorologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| pluie torrentielle locale | pas bien |
| tempête de vent locale | bien |
Catastrophes climatiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| sécheresse | pas bien |
Autres conséquences liées au climat
Autres conséquences liées au climat
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| réduction de la période de croissance | pas bien |
Commentaires:
On the bottom of the gully willow trees should be planted which have strong roots to resist floods, especially if the gully is already deep. At the slopes Russian olives and wild cherries can be planted. The higher amount of trees makes gully even more stable.
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
neutre / équilibrée
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
Commentaires:
Much more extra work comes up for the establishment, but for the farmer work is not a disadvantage.
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
Commentaires:
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
|
Stopping the expansion (prevention) of the gully and filling up the gully (rehabilitation). How can they be sustained / enhanced? Maintain the vegetative measures, plant more seedlings and let them reproduce themselves. |
|
Firewood and construction material production. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Increase the vegetation with wood of good quality and use it in a sustainable manner (cut only as much as will be reproduced). |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
|
Extensive use of the area and a relatively rich diversity of local vegetation. The maintained gully provides new habitat for natural flora and fauna. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Keep and promote the diversity of plants in the gully. |
|
Cheap and relatively less labor intensive work. Relatively little knowledge and no special tools are required. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Make the technology public. |
| The entire technology doesn’t have to be established at once, which allows investing money and time whenever it is available. |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| The trees stop the water, sediments, branches etc. too effectively and this creates problems with too much water in the gully, which is washing out the sides of the gully. |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| A disadvantage is the extra work the farmer have to spend on a little productive area. | In the land users view work is not a disadvantage, it is his job. Considering the fact that it is not that much extra work, it is not a big disadvantage. |
| For the establishment a first investment for the seedlings is required. | An establishment of the technology during a longer period allows to grow own seedlings from the plants which do not cost anything. |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
7.2 Références des publications disponibles
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Integrated spatial assessment for Sustainable Land Management „SLM-planning“ in the loess hill of central Tajikistan using WOCAT mapping tools (working title), Selina Studer, 2013, Master Thesis, University of Bern, Bern.
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
University of Bern
7.3 Liens vers les informations pertinentes en ligne
Titre/ description:
WOCAT technology movie: Orchard-Based Agroforestry
URL:
wocat@cde.ch
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens
Aucun lien
Modules
Aucun module trouvé