MANGO AND CITRUS TRESS GROWN AS CASHCROPS AND FOR SOIL FERTILITY IMPROVEMENT [Ouganda]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : betty adoch
- Rédacteurs : JOY TUKAHIRWA, Kamugisha Rick Nelson
- Examinateurs : Drake Mubiru, Nicole Harari, Stephanie Jaquet, Udo Höggel
Gwoko nyig yen igang
technologies_2319 - Ouganda
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Personne(s)-ressource(s) clé(s)
exploitant des terres:
Okello Vincent
0782954875
okellovincent7@gmail.com
Pagwari Fruit Farmers Association
Pader district, Acoro Sub-County , Acoro parish, Pagwari East village
Ouganda
Nom du projet qui a facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Scaling-up SLM practices by smallholder farmers (IFAD)Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - Suisse1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Quand les données ont-elles été compilées (sur le terrain)?
09/05/2017
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.4 Déclaration sur la durabilité de la Technologie décrite
Est-ce que la Technologie décrite ici pose problème par rapport à la dégradation des terres, de telle sorte qu'elle ne peut pas être déclarée comme étant une technologie de gestion durable des terres?
Non
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
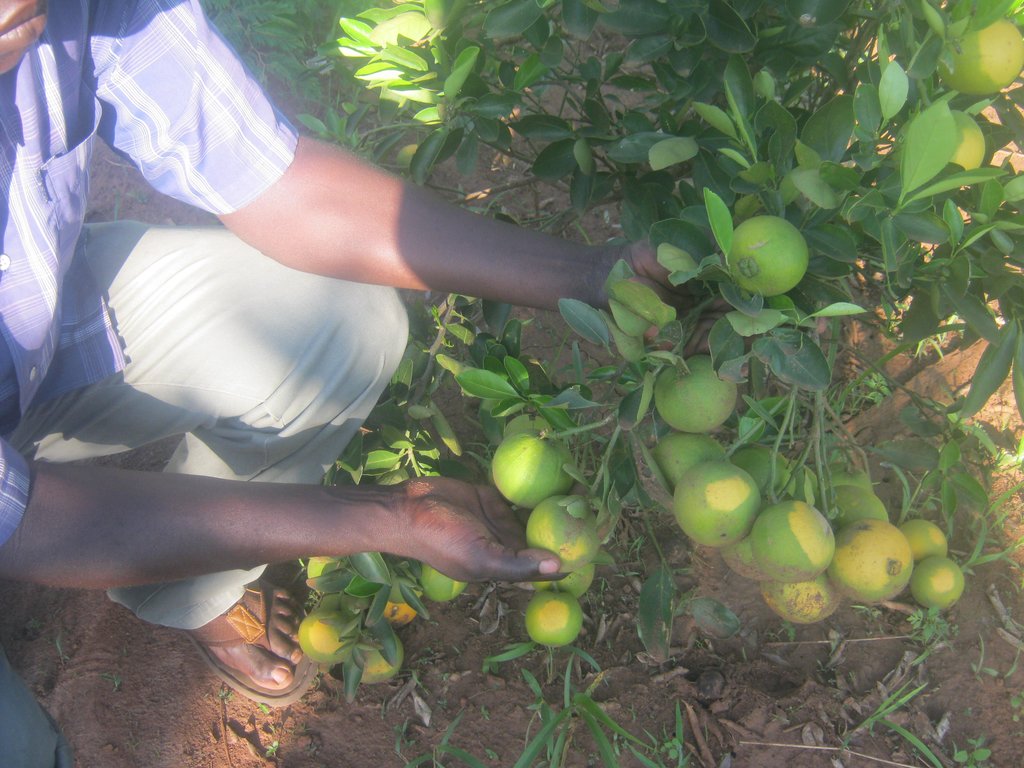
Different varieties of mangoes such as Banganapalle, Alphonso, Kesar, Haden, Bombay, Kent, Keitt, oranges such as Washington Navel, Valencies, Tangarine, jack fruits and avacados are grown for purposes of household income and soil fertility improvement.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
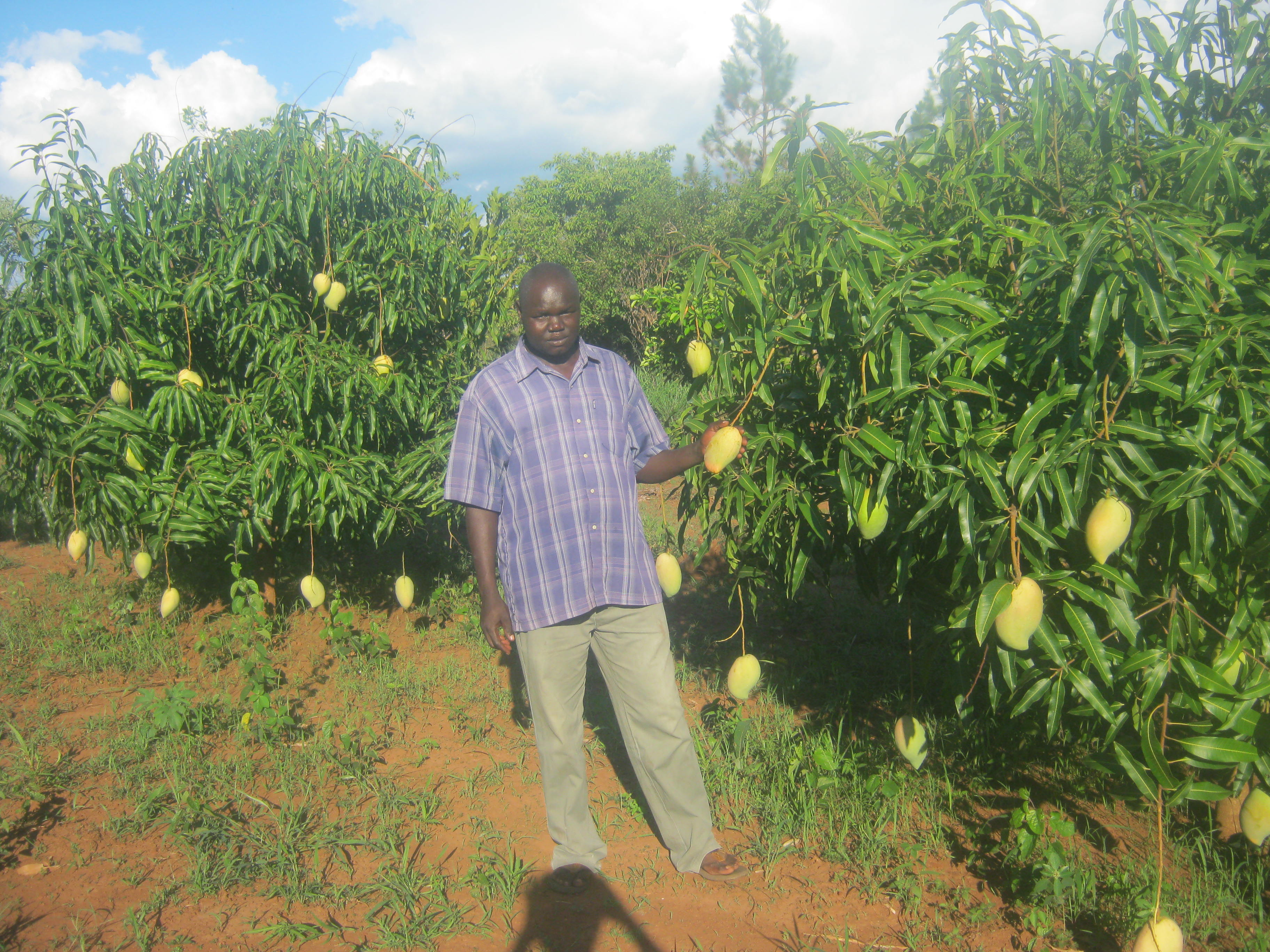
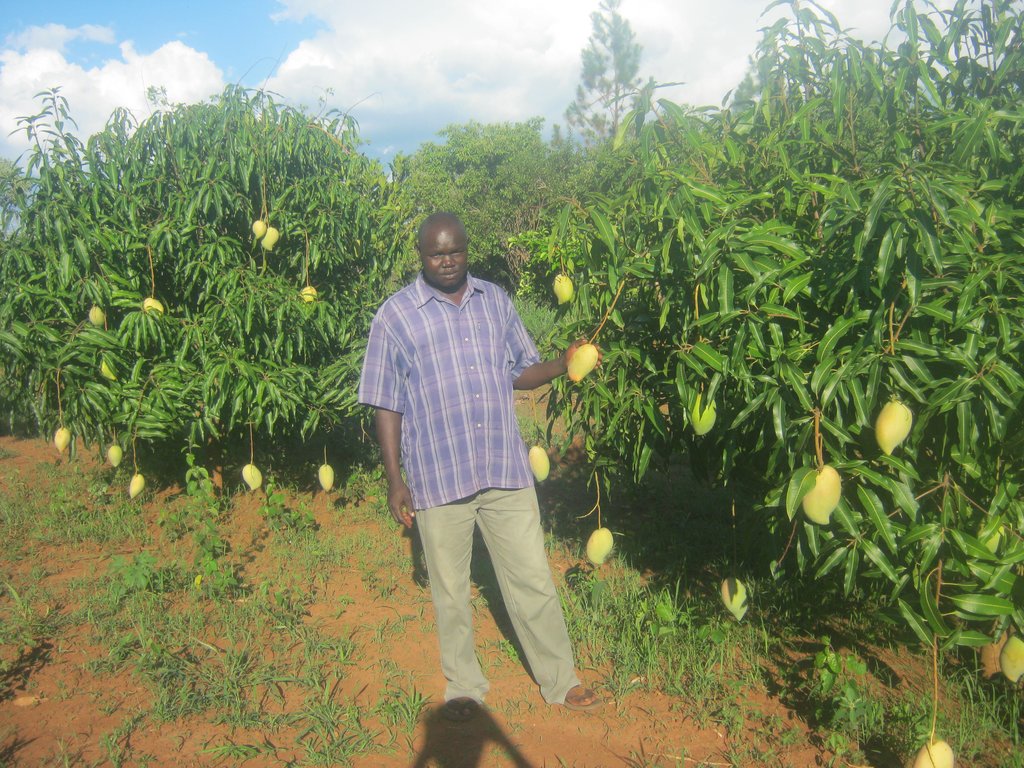
Home fruit tree groves of grafted mango (mangifera indica) and citrus (citrus aurantium) is a farming practice that farmers practice in Northern Uganda to diversify their economic activity, for soil fertility improvement and household income.
Northern Uganda has tropical savanna climate which receives moderate amount of rainfall ranging from 750-1000mm per annum. The soils are moderately fertile with less organic matters coupled with soil erosion, which leads to low crop productions hence low incomes. The moderate rainfall is also unreliable which makes the region to experience drought. Farmers grow fruits as an alternative source of income.
This land user generates over 90% of his household income from fruit growing. The planted fruit trees increase the organic matter content in the soil when dry leaves decompose, rooting prevents soil erosion, pruned brunches are a source of fuel wood and trees acts as wind breaks. Major fruits grown include jack fruits, grafted mangoes, oranges and avocados.
For all these fruits, seeds are first planted in a nursery bed for a period for about two months with the following required inputs: hoes, pangas, spades, wheelbarrows, and shovels. Afterwards, transplanting into the gardens is done. Selection and clearing of the field is done and the planting holes are marked. Excavation is done in accordance to the slope direction: the top soil is put on the hillward side of the planting hole then the sub-soil is put on the downward side of the planting hole. The planting holes are dug in a square shape at 60*60 cm. Composite manure is mixed with top soil and applied into the hole to speed up the seedling establishment and to enhance growth. When planting, the hole is not fully filled but ends 5 cm below the surface so to enable water harvesting, moisture retentions and infiltration. This ensures ample soil moisture and water supply to plants.
The spacing for avocados is 8 × 8 m (65 seedlings/acre), jack fruits is 10 × 10 m (44 seedlings/acre), mangoes 10 × 10 m (44 seedlings/acre) and oranges 4 × 5 m (200 seedlings/acre). After planting, mulching is done by saw dust, kitchen waste like groundnut husks, vegetables and so on. 75 mangoes, 150 oranges, 20 avocados, 20 jack fruits and 4 grapes trees are spread evenly over the planting area. To realize maximum production, the land user needs to have constant water for irrigation.
On the other side, fruit tree growing has brought negative feelings from neighbors who don't promote this practice. Fruit farmers' lifestyle has changed due to revenues realised from growing fruit trees. To maintain this technology, weeding, pruning and creating fire lines during dry seasons to protect the farm is very critical . The technology is highly susceptible to pests and diseases that may require support from the local extension worker from time to time to be able to obtain high yields.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
Remarques générales concernant les photos:
Fruit trees protect the soil from environmental degradation and its effects such as soil erosion and landslides.
2.4 Vidéos de la Technologie
Date:
19/05/2017
Lieu:
Pader District, Acoro parish, Pagwari East village.
Nom du vidéaste:
Betty Adoch
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Ouganda
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Northern Uganda.
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Pader District, Acoro parish,Pagwari East village.
Commentaires:
GPS point indicating the land user fruits garden
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Indiquez l'année de mise en œuvre:
2013
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- grâce à l'innovation d'exploitants des terres
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
Land user needs to generate income.
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- améliorer la production
- s'adapter au changement et aux extrêmes climatiques et à leurs impacts
- créer un impact économique positif
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

Terres cultivées
- Cultures annuelles
- Plantations d’arbres ou de buissons

Forêts/ bois
Plantations d'arbres, boisements:
- Variétés mixtes
Produits et services:
- Fruits et noix
Si l'utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie, indiquez l'utilisation des terres avant la mise en œuvre de la Technologie:
The land was use for brick making
3.3 Informations complémentaires sur l'utilisation des terres
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- pluvial
Commentaires:
Drip irrigation is done during dry seasons
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 1
Densité d'élevage/ chargement (si pertinent):
Cows: 5, Goats:7. Improved breeds of goat and cattle which are high yielding
3.4 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- amélioration des variétés végétales, des races animales
- Jardins/ potagers familiaux
3.5 Diffusion de la Technologie
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- répartie uniformément sur une zone
Si la Technologie est uniformément répartie sur une zone, indiquez la superficie couverte approximative:
- < 0,1 km2 (10 ha)
Commentaires:
The fruits gardens covers 2 acres of land.
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

pratiques végétales
- V1: Couverture d’arbres et d’arbustes

modes de gestion
- M1: Changement du type d’utilisation des terres
Commentaires:
Fruit growing promotes soil conversation.
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

érosion hydrique des sols
- Wt: perte de la couche superficielle des sols (couche arable)/ érosion de surface

érosion éolienne des sols
- Et: perte de la couche superficielle des sols (couche arable)

dégradation chimique des sols
- Cn: baisse de la fertilité des sols et réduction du niveau de matière organique (non causée par l’érosion)
Commentaires:
Fruit growing conserves the environment by preventing tree cutting.
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- réduire la dégradation des terres
Commentaires:
The area initially was severly degraded by brick making work but after putting it under fruit growing, it became very fertile.
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
Auteur:
Betty Adoch
Date:
19/05/2017
4.2 Spécification/ explications techniques du dessin technique
The fruit trees are planted on a generally flat average land size of 2 acres of land with following spacing: mangoes 10X10msq, jack fruits 10X10msq because it forms a big canopy, oranges 5X5 msq.
4.3 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
Spécifiez la manière dont les coûts et les intrants ont été calculés:
- par superficie de la Technologie
Indiquez la taille et l'unité de surface:
2 acres
autre/ monnaie nationale (précisez):
UGX
Indiquer le taux de change du dollars en monnaie locale (si pertinent): 1 USD= :
3500,0
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
3000 UGX
4.4 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Site clearing for nursery bed | Agronomique | dry season |
| 2. | Raising the nursery | Agronomique | dry season |
| 3. | Digging planting holes | Agronomique | dry season |
| 4. | Applying composite manure | Agronomique | dry season |
| 5. | Transplanting at 15 to 30cm seedling high | Agronomique | onset of rain |
Commentaires:
Different fruit species have different nursery beds
4.5 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Site clearing for nursery bed | Meters | 2,0 | 10000,0 | 20000,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Raising the nursery | Meters | 2,0 | 10000,0 | 20000,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Transplanting | Acres | 2,0 | 50000,0 | 100000,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Pitting for fruit tree planting | Acres | 2,0 | 50000,0 | 100000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Pangas | Pieces | 10,0 | 5000,0 | 50000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Hoes | Pieces | 15,0 | 10000,0 | 150000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Axes | Pieces | 5,0 | 10000,0 | 50000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Wheelbarrows | Pieces | 4,0 | 95000,0 | 380000,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériel végétal | String | Pieces | 4,0 | 5000,0 | 20000,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériel végétal | Dipper | Pieces | 4,0 | 45000,0 | 180000,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériel végétal | Watering can | Pieces | 2,0 | 25000,0 | 50000,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériel végétal | Spray pump | Pieces | 4,0 | 75000,0 | 300000,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériaux de construction | Bamboo | Pieces | 10,0 | 10000,0 | 100000,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériaux de construction | Dry grass | Bundles | 5,0 | 3000,0 | 15000,0 | 100,0 |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 1535000,0 | |||||
Commentaires:
The technology is technically easy to maintain once established and can be replicated by other land users.
4.6 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Weeding | Agronomique | after every 3 months |
| 2. | Pest control | Agronomique | dry season use cow dung and driny use season pesticide |
| 3. | Stray animal control | Agronomique | dry season |
| 4. | Thieves control | Agronomique | rainy season |
| 5. | Prunning branches | Agronomique | rainy season |
| 6. | Buying pesticides | Agronomique | rainy season |
| 7. | Transportation to market | Agronomique | season of harvest |
| 8. | Buying mulching materials | Agronomique | onset of rain |
4.7 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Hired labour | Man day | 4,0 | 3000,0 | 12000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Spray pump | Piece | 4,0 | 75000,0 | 300000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Irrigation during dry season | Litres | 10000,0 | 200,0 | 2000000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Syringe pipe | Piece | 1,0 | 2500,0 | 2500,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériel végétal | Seedings | Pieces | 269,0 | 3500,0 | 941500,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériel végétal | Composite manures | Wheelbarrows | 1,0 | 5000,0 | 5000,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériel végétal | Stringes for making holes in a stright line | Rolls | 4,0 | 5000,0 | 20000,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériel végétal | Peg for setting holes | Boundle | 1,0 | 10000,0 | 10000,0 | 100,0 |
| Engrais et biocides | Pesticides (dythen m45) | kg | 1,0 | 40000,0 | 40000,0 | |
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 3331000,0 | |||||
Commentaires:
The land user has knowledge on agronomic practices.
4.8 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
High costs of labor
High transportation cost
Purchase of pesticides
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifiez la pluviométrie moyenne annuelle (si connue), en mm:
950,00
Spécifications/ commentaires sur les précipitations:
Heavy rains in April, May, August and September
Indiquez le nom de la station météorologique de référence considérée:
Pader weather station
Zone agro-climatique
- subhumide
Savanna climate
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Indiquez si la Technologie est spécifiquement appliquée dans des:
- non pertinent
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- moyen (limoneux)
Texture du sol (> 20 cm sous la surface):
- moyen (limoneux)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- moyen (1-3%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Loamy, silty soil at the top and deep down there is gravel. Soil pH is neutral and less saline.
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Profondeur estimée de l’eau dans le sol:
5-50 m
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
moyenne
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
eau potable
La salinité de l'eau est-elle un problème? :
Non
La zone est-elle inondée?
Non
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la qualité et la quantité d'eau:
Very low water table
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- élevé
Diversité des habitats:
- moyenne
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Sédentaire ou nomade:
- Sédentaire
Orientation du système de production:
- mixte (de subsistance/ commercial)
Revenus hors exploitation:
- moins de 10% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- moyen
Individus ou groupes:
- individu/ ménage
Niveau de mécanisation:
- traction animale
Genre:
- femmes
- hommes
Age des exploitants des terres:
- personnes d'âge moyen
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
The land user is a typical farmer who is contented with his lifestyle as a fruit grower due to the income derived from sale of fruits.
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres détenues ou louées par les exploitants appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- petite dimension
Commentaires:
The land user bought the land from the community members.
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- individu, avec titre de propriété
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- individuel
Droits d’utilisation de l’eau:
- communautaire (organisé)
Commentaires:
The land user has fenced his land and put marked stones.
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
énergie:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Due to the litter from the leaves, increased soil fertility leading to increased production.
qualité des cultures
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Due to the nutrients from the soil.
production fourragère
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Especially from the jack fruits wastes
risque d'échec de la production
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Increased level of nutrients in the soil.
diversité des produits
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Because of the different fruit trees species planted.
surface de production
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The land user recently acquired additional plot of land (0.5 acres) from the sale of fruit trees.
gestion des terres
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Fruit trees reduce soil erosion and increase soil fertility due to leaves litter.
Revenus et coûts
dépenses pour les intrants agricoles
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Fruit trees dont require alot of inputs once established; minimal costs for reducing pests and diseases; minimized by the role of extension workers during trainings.
revenus agricoles
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
From the sale of fruits and reduced expenses on farm in puts
diversité des sources de revenus
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
From the sale of diverse fruit types (mangoes, oranges, jack fruits and others)
charge de travail
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Only labour for maintenance and monitoring against thieves
Impacts socioculturels
sécurité alimentaire/ autosuffisance
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Income from sale of fruits is used to buy other household income.
situation sanitaire
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Daily portion of fruits within diet.
droits d'utilisation des terres/ de l'eau
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Community bye-laws on controlled grazing and encroachment were put in place.
institutions communautaires
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Local bye-law committee (LBC) was put in place and supported by the Sub-County and District Council.
Bye-law on controlled grazing and encroachment passed at Sub-County Level.
connaissances sur la GDT/ dégradation des terres
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Trainings conducted by extension workers and fellow champion farmers, also integrating exposure learning events.
apaisement des conflits
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The presence of the local bye-law committee and bye-laws reduced conflicts: no encroachment, no grazing on fruit gardens and no thieves.
situation des groupes socialement et économiquement désavantagés
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Integrating people with disabilities (PWDs) in fruit tree growing trainings and exposure learning events.
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
ruissellement de surface
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Planted fruit trees control soil run off/soil erosion.
Sols
couverture du sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Due to vegetation litter, plant growth and reduced cutting of trees.
perte en sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Due to vegetation litter, plant growth and reduced cutting of trees.
accumulation de sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Due to vegetation litter, plant growth and reduced cutting of trees
compaction du sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Due to vegetation litter, plant growth and reduced cutting of trees
matière organique du sol/ au dessous du sol C
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Due to vegetation litter, plant growth and reduced cutting of trees
Réduction des risques de catastrophe et des risques climatiques
glissements de terrains/coulées de débris
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Due to planted fruit trees and soil&water conservation bye-law on tree planting.
impacts de la sécheresse
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Planted trees reduce drought.
risques d'incendies
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Due to firelines to control bush burning during dry season.
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
dommages sur les champs voisins
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Due to presence of strict community bye-laws.
Commentaires concernant l'évaluation des impacts:
The technology is rewarding in the short, medium and long term and can be replicated by any farmer in any climatic region especially tropical regions.
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Changements climatiques progressifs
Changements climatiques progressifs
| Saison | Type de changements/ extrêmes climatiques | Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| températures annuelles | décroît | très bien | |
| températures saisonnières | saison des pluies/ humide | décroît | très bien |
| précipitations annuelles | augmente | bien | |
| précipitations saisonnières | saison des pluies/ humide | augmente | très bien |
Extrêmes climatiques (catastrophes)
Catastrophes climatiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| sécheresse | très bien |
| feu de forêt | très bien |
| feu de végétation | modérément |
Catastrophes hydrologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| glissement de terrain | très bien |
Commentaires:
This technology is drought resistant and manageable by any farmer who has the interest to practice it.
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
légèrement positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
Commentaires:
The fruits are locally sold expensively at 1000 UGX@ and raise much income to the farmer.
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
- 10-50%
Si disponible, quantifiez (nombre de ménages et/ou superficie couverte):
20 household
Parmi tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle ou aucun paiement?
- 90-100%
Commentaires:
The land user uses the little resources he has to establish the technology.
6.6 Adaptation
La Technologie a-t-elle été récemment modifiée pour s'adapter à l'évolution des conditions?
Non
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
| Constant supply of fruits provides high income to the land user. To realize maximum production, there is need for irrigation to have a constant fruit supply with support from extension workers who are readily available with the extension workers for technical advice. |
| The fruit trees modify the micro-environment making it conducive. |
| The technology is very rewarding, cost effective once established and can easily be replicated by other land users. |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
| The technology is good for small , medium and large scale farmers due to its ability to improve soil fertility, increase production and household income. |
| Can easily be replicated by other land users. |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Before establishment the technology requires some knowledge and skills on fruit growing which can be extended by the extension worker who are located far from the land user. Associated with high costs in terms of transport and allowances to the land user. |
Training and capacity building of local land users / experts. Training champion farmers. Establishment of learning sites / demonstrations. |
| Prone to climate change | Irrigation during the dry season |
| Requires water supply | Irrigation during dry seasons |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| High establishment costs associated with reduced maintenance costs both in the short, medium and long term. | Adapt low cost practices for those starting and integrate with time and for those with low incomes. |
| Associated with high prevalence of pests and diseases. Risky to spray during flowering season. |
Close monitoring of the field all the time. Seek technical advice from the extension worker. |
| Labour intensive at the time of establishment. | Supplement with family labour. |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
- visites de terrain, enquêtes sur le terrain
1
- interviews/entretiens avec les exploitants des terres
1
- interviews/ entretiens avec les spécialistes/ experts de GDT
1
7.2 Références des publications disponibles
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Do Trees on Farms Improve Household Well-Being? Evidence From National Panel Data in Uganda, Daniel, C.Miller,September 2020.2020.0010
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
On-line. Free of cost.
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens
Aucun lien
Modules
Aucun module trouvé